2.7 Indirect Tax and Subsidies
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Direct Tax
Taxes are paid directly from the incomes of individual (income tax) or from the income of business (profit tax)
Indirect Tax
Tax imposed on spending to buy goods and services
Excise Taxes (or excise duties)
A Type of Indirect Tax
Tax that is imposed on particular good or services, normally (but not always), because they have significant negative externalities
Taxes on spending on all (or most) goods and services
A Type of Indirect Tax
GST (General sale Taxes) in the United States,
VAT (Value add Tax) in the United Kingdom
Good services tax in Singapore
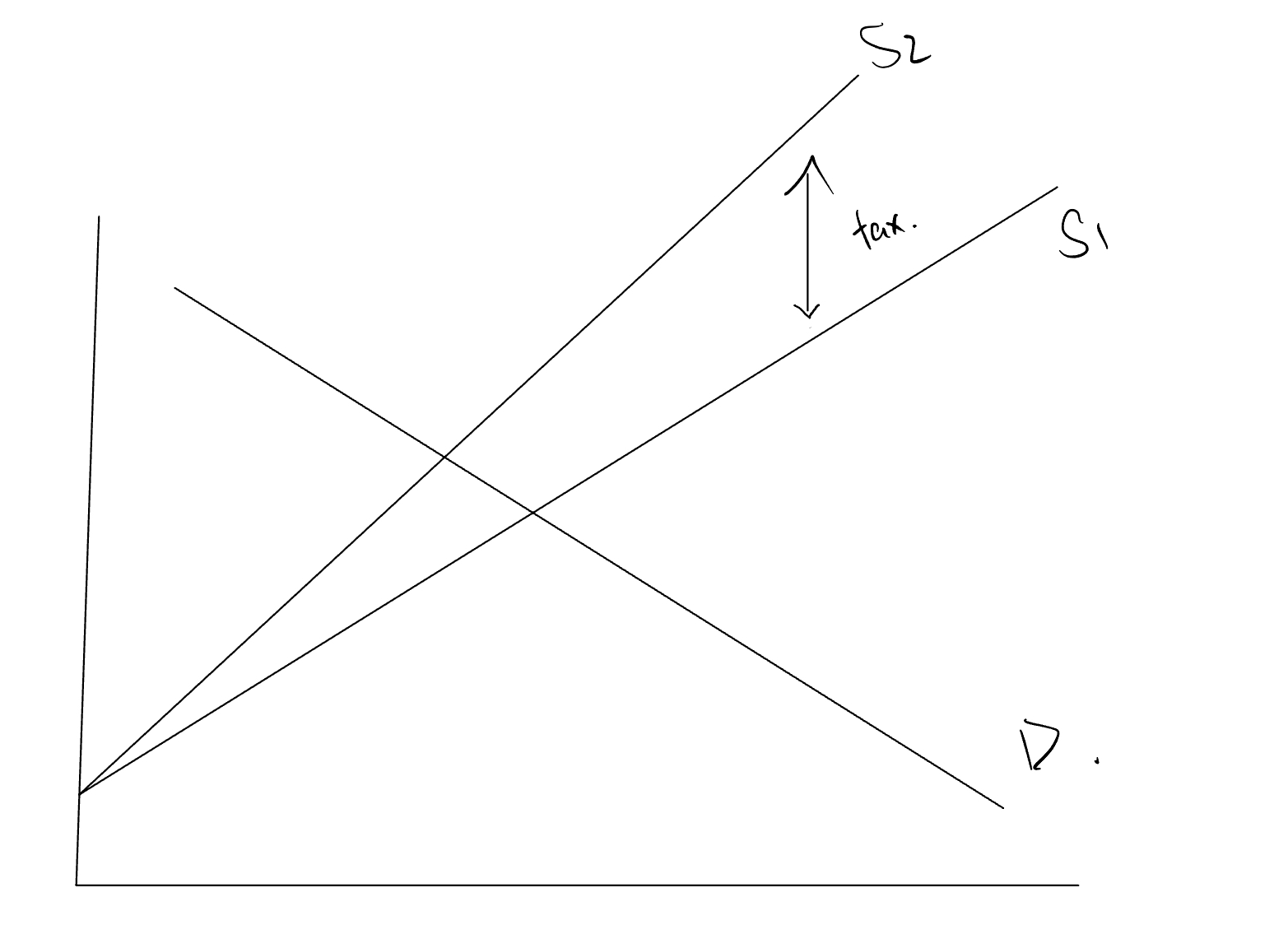
Specific Tax
A Type of Indirect Tax
A fixed dollar amount is imposed for each unit of good
Amount of tax paid is independent of price of the good
For instance;
if a milk is at $3 dollars we need to pay $6 (tax is $3)
if a milk is at $7 dollars we need to pay $10 (tax is $13)
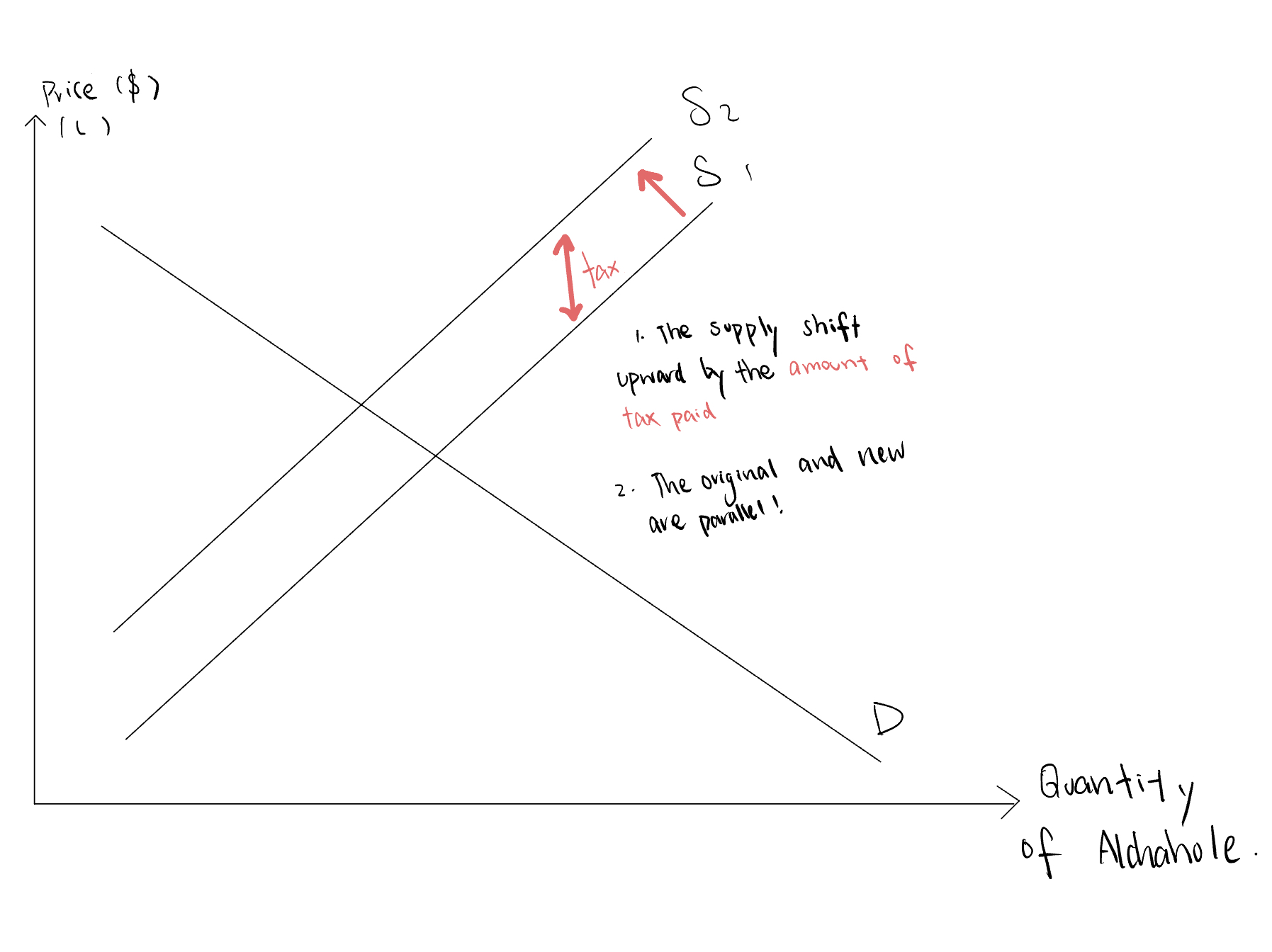
Ad-valorem Tax (supplementary information)
A fixed percentage amount is imposed on each unit of output.
As the percentage of the good increase, the amount of tax paid increase.
Real World Example
(Ad-valorem Tax)
Sugar Tax in Asean
Laos: 5%-10% in soft sugar drinks
Vietnam: 10% to 20% in sugar tax
Direct Tax
Taxes are paid directly from the incomes of individuals (for example, income tax) or from the profit earned by businesses (known as profit tax). These taxes are based on the individual's or corporation's ability to pay, and they are often considered progressive, meaning higher earners pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes.
Subsidies
Refers to per-unit fixed amount of payment that are used to lower production costs and increase the output of the market
Single unit payment, for every unit you receive a certain amount of this.
Grants
Iumpsum of money
Reasons why government gives subsidies
To support growth of industries
To encourage exports and protect national industry from foreign competition.
To support growth of particular industry
Since subsidies have the effect of increasing the output, they could help industry to grow. Governments make want particular industries to grow because they provide positive externalities related to environmental benefits or they want to protect it during its development
To encourage exports and protect national industry from foreign competition.
Subsidies reduce export crisis which helped firms sell more exports. The government may want this because it will boost the economic growth and help its domestic needs to grow their business overseas.