High school chemistry unit one (copy)
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
What is made out of atoms?
Everything in our word
What are atoms?
The basic unit of mater
What are atoms made out of?
Smaller subatomic particles called neutrons, protons and electrons
What is the center of an atom called and what is it composed of?
The center on an atom is called the nucleus and composed of protons and neutrons
What is out side of the nucleus?
Out side of the nucleus there is an electron cloud which is where electrons are likely to be found
How much larger can an electron cloud be than a nucleus?
An electron cloud can be 100 thousand times bigger than the nucleus
What makes up most of the atoms volume?
Electrons make up most of the atoms volume
What does (u) stand for?
Unified atomic unit
What does (u) measure?
A subatomic particles mass
What’s the charge and mass of a proton?
A protons charge is 1+ and its mass in 1u (1.007)
What’s the charge and mass of an electron?
An electrons charge is 1- and its mass in 0.0005u
What’s the charge and mass of a Neutron?
A neutrons charge is 0 which means it’s neutral and its mass is 1u (1.008)
Which subatomic particles have a charge that’s equal and opposite?
Protons and electrons have a charge that’s equal and opposite
What happens to the charge of protons and electrons when they are paired in an atom if the amount of protons and electrons are equal?
Their charge cancel each other out
Which subatomic particles have about the same mass (u)?
protons and neutrons have about the same mass (u) of about 1u
How much times smaller is an electron than protons and neutrons?
About 2000 times smaller
What takes most of the atoms mass?
The nucleus takes most of the atoms mass which is composed of protons and neutrons
What’s the difference between mass and volume?
Mass - the amount of mater an object contains
Volume - the amount of space it takes up
What’s different about each element?
Each one has a unique set of physical and chemical properties
How is an element identified?
An element is identified by the number of protons inside the nucleus of an atom
What is an atoms atomic number?
An atoms atomic number is determined based on the amount of protons in the nucleus of an atom
What letter represents the atomic number of an element in the periodic table?
The letter (z)
What can an element’s atomic (z) number also determine other than the amount of protons in an atom and why?
An element’s atomic Number (z) can also determine how much electrons is in an atom
an atom’s charge has to be equal and for that to happen the protons with the charge of 1+ and the electrons with the charge of 1- have to cancel each other out hence the amount of protons and electrons in an atom have to be equal
How are all the known elements organized in the periodic table?
The elements are organized based on their atomic number from left to right and from top to bottom
What do the elements that are put in the same columns in the periodic table have in common?
The elements that are put into the same columns have similar physical and chemical properties
What is a chemical symbol of an element in the periodic table?
A chemical symbol of an element is a one or two letter abbreviation that’s unique to each element
If the chemical symbol has two letters. The first will always be an uppercase letter, and the second will always be a lowercase letter.
What information does each elements box include?
-Atomic number
-Chemical symbol
-name
-mass (sometimes)
What’s an element with a different amount of neutrons called?
An isotope
what is an atomic mass number?
It’s the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an element
What’s the equation of an elements mass number?
Protons + neutrons =mass number
How do we represent isotopes in writing?
We represent it with an isotope notation
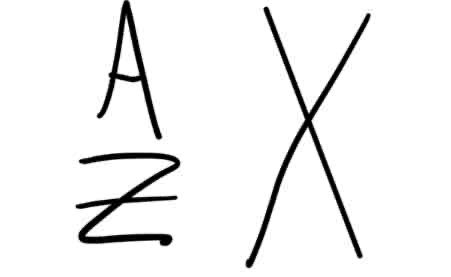
What does each letter mean in this isotope notation?
X- Chemical symbol
A- mass number
Z- atomic number

What does each letter in this isotope notation mean?
X- chemical symbol or element name
A- mass number
What does the average atomic mass mean on the periodic table?
It’s the combination of the mass number of all the different types of isotopes of an element depending on how much percent each isotope takes
What information do we need to know to calculate the average mass number of an element?
-How many different isotopes of that element exist
-How much percent each Isotope takes in our world
-What’s the individual atomic mass of each isotope?
Give an example of a calculation of the average atomic number of an element
Give on or make one
An example is in the picture
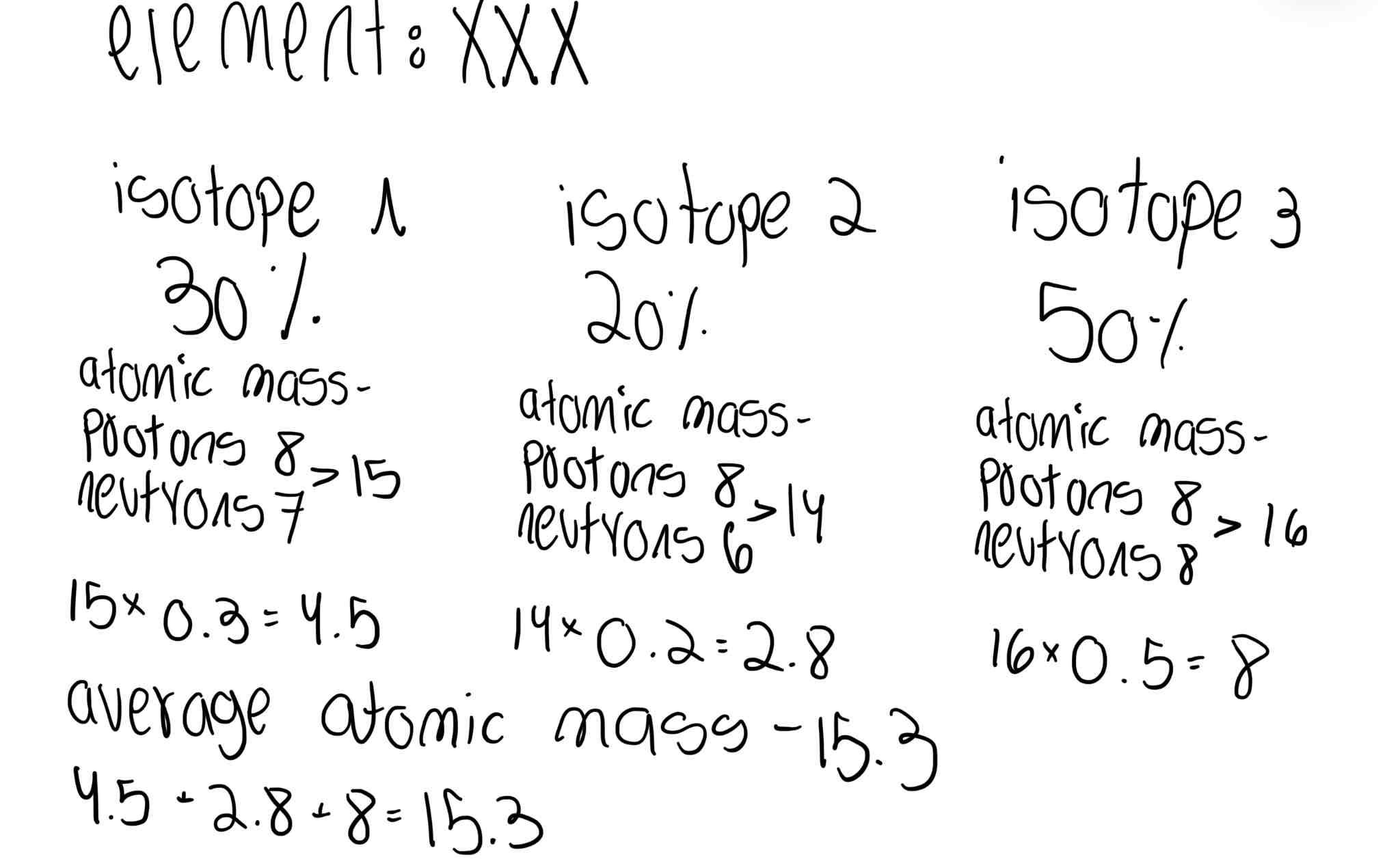
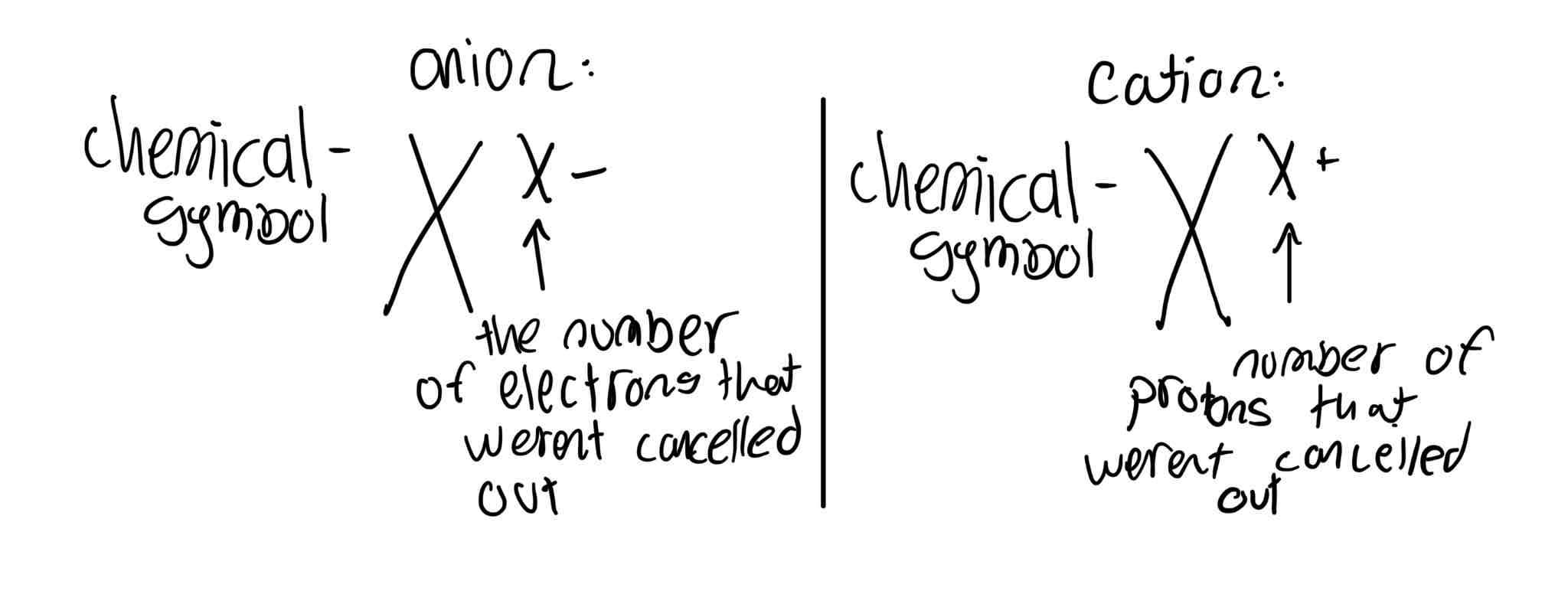
What’s an ion?
An ion is an element / atom with less or more electrons than protons
What is an atom / element with less and more electrons than protons called and what charge does each one leave?
less electrons than protons - cation -leaves a positive charge
More electrons than protons - anion -leaves a negative charge
How do you write down an ion with a negative or positive charge?
Answer is in the image
In what unit to we calculate the mass amount of an atom?
(U) - 1.660540×10^-27kg

This is a Bohr model of a helium atom.
The electrons in Bohr models are shown as black dots on rings.
How many electrons does this helium Bohr model have?
Two electrons

Where is the nucleus is this Bohr model of a helium atom?
In the center of the ring in the color green
What are the strengths of Bohr Models?
Shows how many electrons a neutral model has
We can tell that electrons that are on the same ring/shell/n have the same energy level
What are the limitations of Bohr models?
The nucleus is show as on green circle which if false because the nucleus is made out of protons and neutrons
Doesn’t reflect the wave properties of electrons, the electrons appear to be in specific locations which is not entirely true
What is the maximum amount of electrons that the first and second ring in Bohr models can hold?
N1 = 2
N2 = 8
How many electrons can one orbital hold in Bohr models?
Two electrons
Why are unpaired electrons always in the outmost ring/energy level in Bohr models?
The lower levels have to fill in completely for the next ones to start filing.
In Bohr models where can the electron exit and where can it not?
Electrons can only exit of the energy levels and not in between them
What do the rings/levels in Bohr models represent?
Energy levels that electrons can occupy
What are the shells in Bohr models labeled as?
n
Which level in a Bohr model has the most energy?
The outermost level
What is the valence shell and valence electrons?
The outermost shell and the electrons on that shell
What is the core shell and core electrons?
Every shell but the outermost shell and all the electrons on those inner shells
What do electrons NOT do around the nucleus?
They don’t orbit the nucleus nor do they move in circular path around it
What is radiation?
Energy that travels through space
What is electromagnetic radiation?
Energy transferred by electromagnetic fileds oscillating through space
What two things does electromagnetic radiation have?
An electric field and magnetic field
Which two things in electromagnetic radiation are perpendicular to each other?
The electric filed and magnetic field
How does an EM wave propagate itself through space?
A changing electric filed creates a magnetic filed and a magnetic filed creates an electric field hence it moves
What does an EM wave always have?
Wavelength, frequency and speed
What are photons and what do they contain?
Particles of EM radiation and they contain specific amounts energy

What does this symbol represent?
Photons
At what speed does all EM radiation travel and in what way but is the only exception ?
The speed of light in a vacuum but travels at a lower speed in matter such as water or glass
What letter represents the speed of light?
C = speed of light
C = 3×10^8m/s = 300,000,000 m/s
What’s the abbreviation for electromagnetic?
EM
The wavelength, frequency and energy of EM radiation can fall within a wide range. What is that range called?
Electromagnetic (EM) spectrum
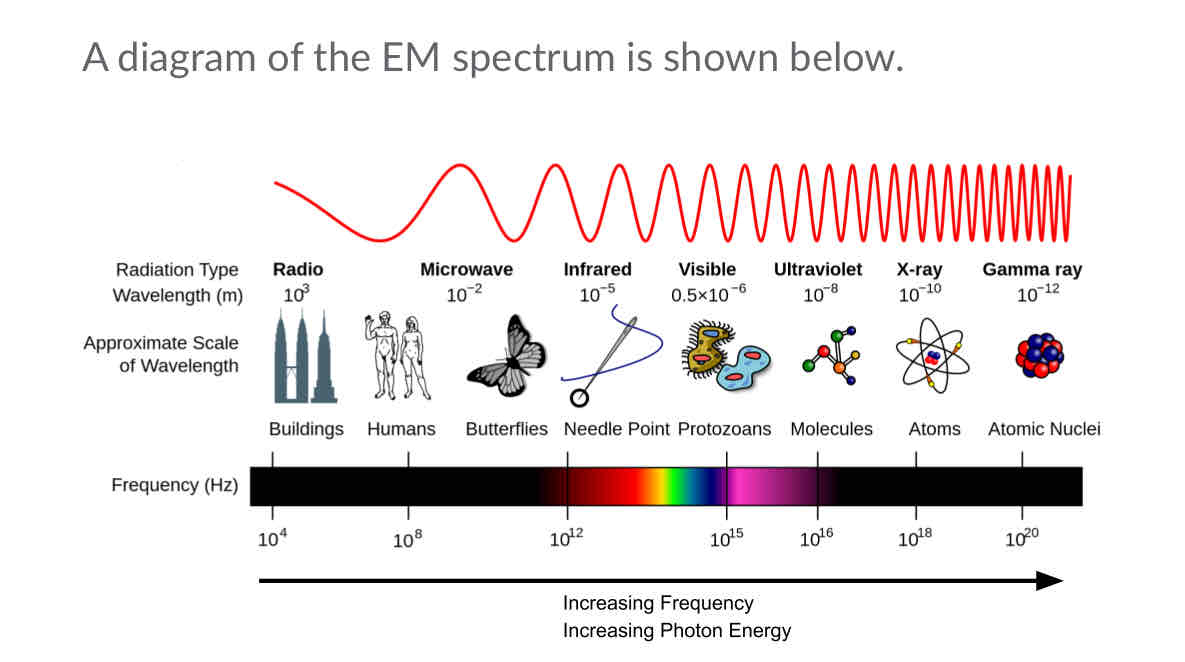
What is the wavelength in the EM speqctrum?
It’s the distance from one peak of a wave to the next peak
What’s the range of the EM wavelength?
From 10³ (1000) meters to 10^-12 (0.00000000001) meters
What is EM frequency?
The number of wave cycles in a period of time or how often the wave cycles happen in certain amount of time
What’s the range for EM frequency?
10^4 (10,00) hertz (Hz) to 10^20 (100,000,000,000,000,000,000) hertz (Hz)
What happens to photons as frequency increases?
Photons increase
What is one unit of measure that is used to measure the energy of individual photons?
Electron volt (eV)
Name each region of the EM spectrum
Radio waves
Microwaves
Infrared
Visible light
Ultraviolet (UV)
X-rays
Gamma rays
What does radio wave on the EM spectrum mean?
Has the longest wavelength and lowest frequency
What does Microwaves on the EM spectrum mean?
Has a higher frequency than radio waves and shorter wavelengths
What does Infrared mean on the EM spectrum?
Has a higher frequency than microwaves and shorter wavelengths
What objects radiate infrared radiation and what is it associated with?
Everyday objects
Human bodies
Living things
Surfaces warmed by the sun
Heat and warmth are associated with this type of radiation
What does Visible light on the EM spectrum mean and why is it called this way?
It’s called this way because its what the human eye can see
Has a higher frequency than Infrared radiation and shorter wavelength
Our brains perceive different frequencies in the visible light spectrum as different colors. What color do we see that has the longest wavelength and lowest frequency in the visible light spectrum?
Red
Our brains perceive different frequencies in the visible light spectrum as different colors. What color do we see with the shortest wavelength and highest frequency on the visible light spectrum?
Violet
Where do all the other colors, other than red and violet fall under the visible light spectrum?
All other colors fall in between red with a lower frequency and a longer wavelength and violet, with a higher frequency and shorter wavelength.
Other colors might have a higher frequency than red, but A lower frequency than violet, creating a different color once the light enters our eyes.
What does ultraviolet (UV) mean on the EM spectrum?
Higher frequency than violet light and has a shorter wavelength hence we lose the power to see it
Why can UV radiation cause damage to living tissues?
As frequency increases the photons energy also increases, in UV radiation the protons energy is high enough that is can cause damage to living tissues
What does X-ray on the EM spectrum mean?
High frequency than UV radiation and shorter wavelength
What causes X-ray radiation to be ionizing and how does it effect mater?
The energy in X-ray photons is so high that its ionizing radiation so when it enters mater it knocks out the electrons out of the maters atoms
Why is ionizing radiation dangerous to the cells of organisms?
Repeated ionization can cause damage and mutations to the cells of organisms
How do medical X-rays work?
When getting an X-ray photons are sent into you.
Dense tissues like bones block more of these X-ray photons than softer tissues creating a shadow image when the X-ray reaches a detector on the other side
What are gamma rays on the EM spectrum?
They have the highest frequency, energy and shortest wavelength than any other EM radiation.
And just like X-rays it is also ionizing radiation.
Which EM radiation is the most hazardous to living thing?
Gamma rays
By what are gamma rays produced?
By High energy interactions in space
By gamma decay
What does gamma decay happen?
It happens when unstable nuclei with a very high frequency release large amounts of energy/radiation (gamma rays which is a type of EM radiation) in order to stabilize the nuclei
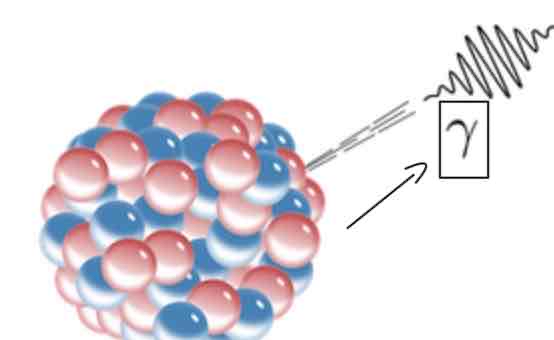
Which EM radiation on the EM spectrum is represented by this symbol?
Gamma rays
Though gamma rays are hazardous, they can also be used for good. Give one example in which gamma rays are used for good.
They can be used in radiation therapy to kill cancer cells
Which to from of EM radiation are Ionizing?
X-rays and Gamma rays
What’s the lowest energy level an electron can be on called?
The ground state
What needs to happen for an electron to move energy levels?
The electron needs more energy
How does an electron get more energy/moves to a higher energy level?
An electron needs to get hit by light , if a photon with the right energy level hits an electron, the electron can get more energy and jump to a different energy level
Let’s say we have an atom with four shell/rings.
The first shell has 0 eV with an electron on it,
The second shell needs 4 eV,
The third shell needs 6 eV,
The fourth shell needs 7 eV
What happens if a photon with 5 eV hits the electron and why?
The photon will go through the electron and will not get absorbed because the electron CANT exist between energy levels only on them, the electron needs to get hit by a photon with 4, 6 or 7 eV for it to be able to jump to one of the energy levels
What happens to a photon when it hits an electron?
If it has the right energy level it will get absorbed by the electron and the electron will jump to a different energy level
What does eV mean?
Electron volt