AQA A-Level Product Design; Manufacturing Processes
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
die cutting process
the method most often used for adding a dimensional quality to a display; the technique requires a die, a cutting tool designed to suit the material being cut, and is similar to cutting out cookies from rolled dough.
creasing process
whilst the net is being cut by the die cutter it can also be creased - which creates lines that can be later folded. To produce the scored lines the creasing rules are not as tall as the die cutters and are blunt.
bending process
this happens after die cutting and creasing. the net is placed onto a folding table (a specially made piece of equipment). the net is held firmly whilst the sides are bent into place along the crease lines. intricate details are done by hand.
laser cutting
for prototype construction or small-scale production. it can cut, engrave, carve, and perforate paper and boards. 2D drawings can be easily downloaded to a laser cutter.

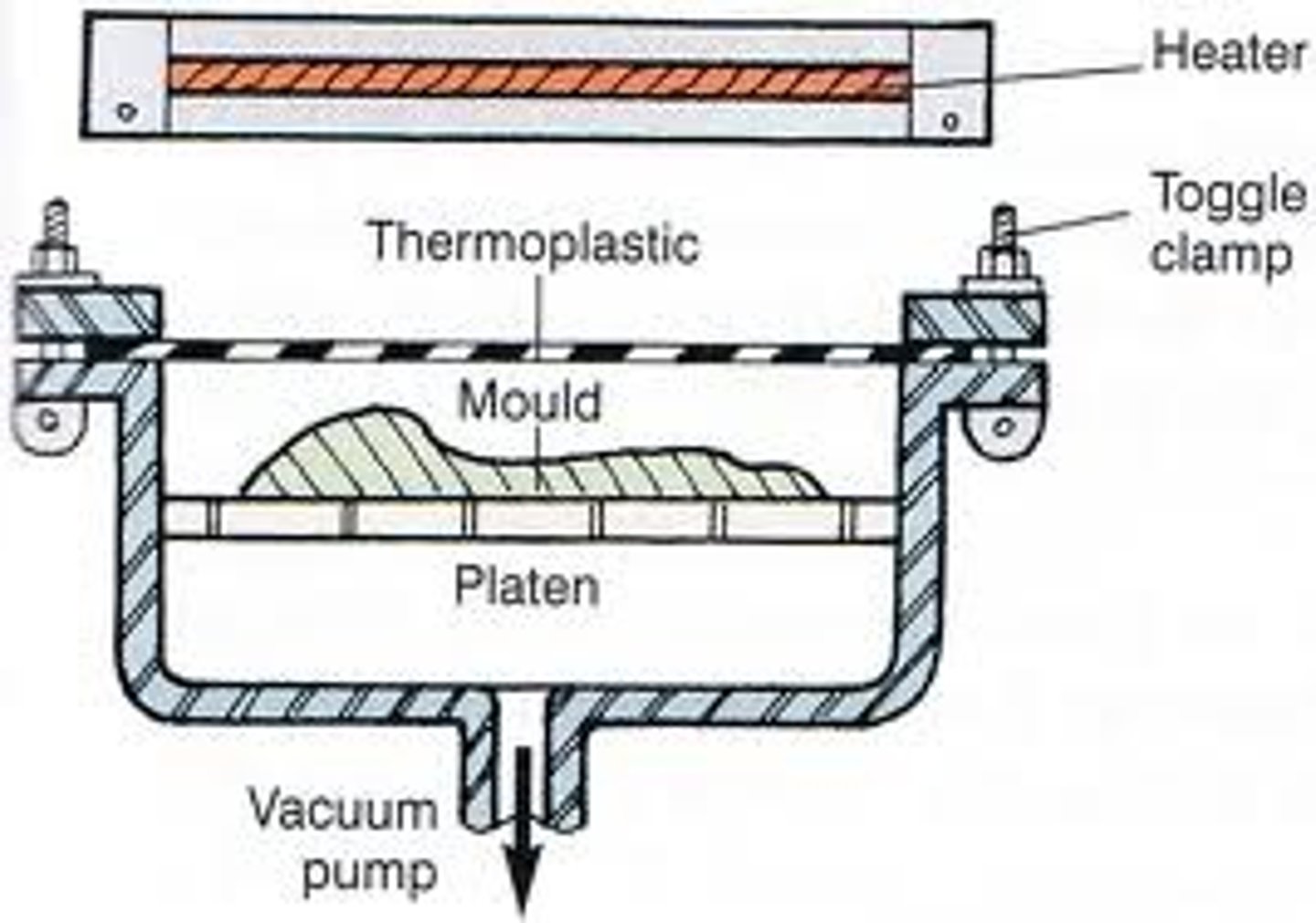
vacuum forming
mould is placed on a Platen, which is lowered to the bottom of the machine. HIPs sheet is clamped over mould, heater is pulled over sheet. heater is turned on and the HIPS sheet soften. vacuum is turned on which pulls sheet over mould. once cooled the mould is removed and excess polymer is trimmed.
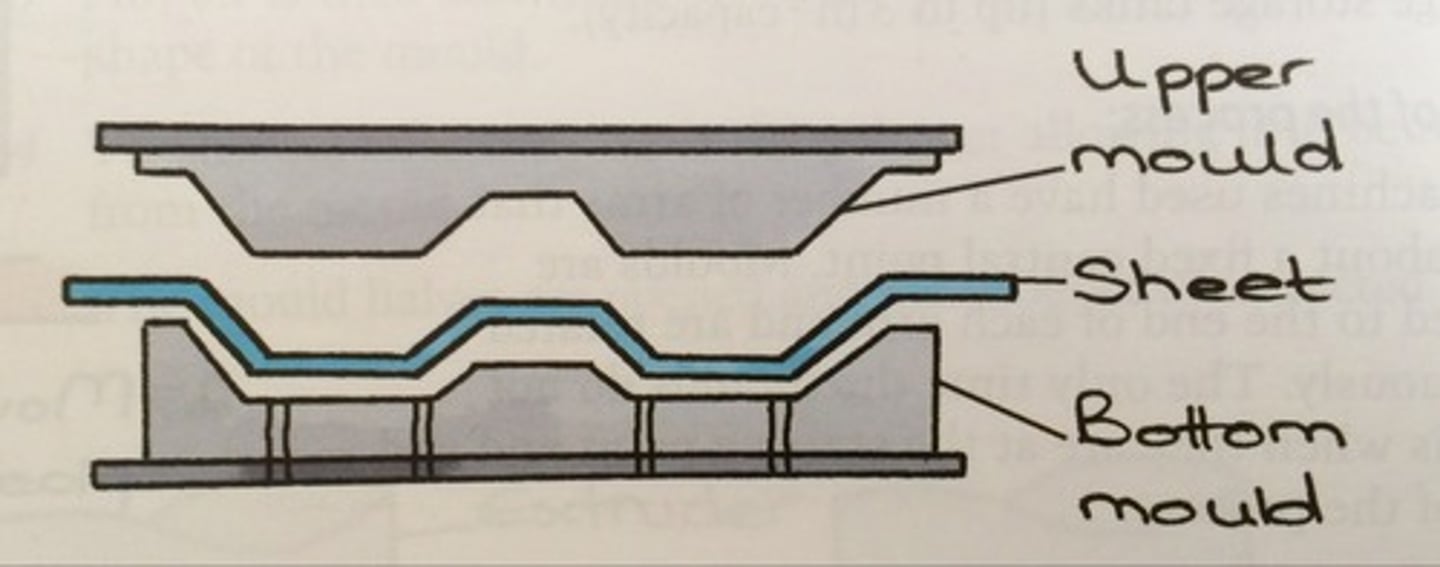
thermoforming
plastic sheets are heated over an open mould to a working temperature. once workable, a vacuum is applied to the mould, forcing the plastic sheet to take the shape of the mould whilst another mould is forced on top of the sheet.
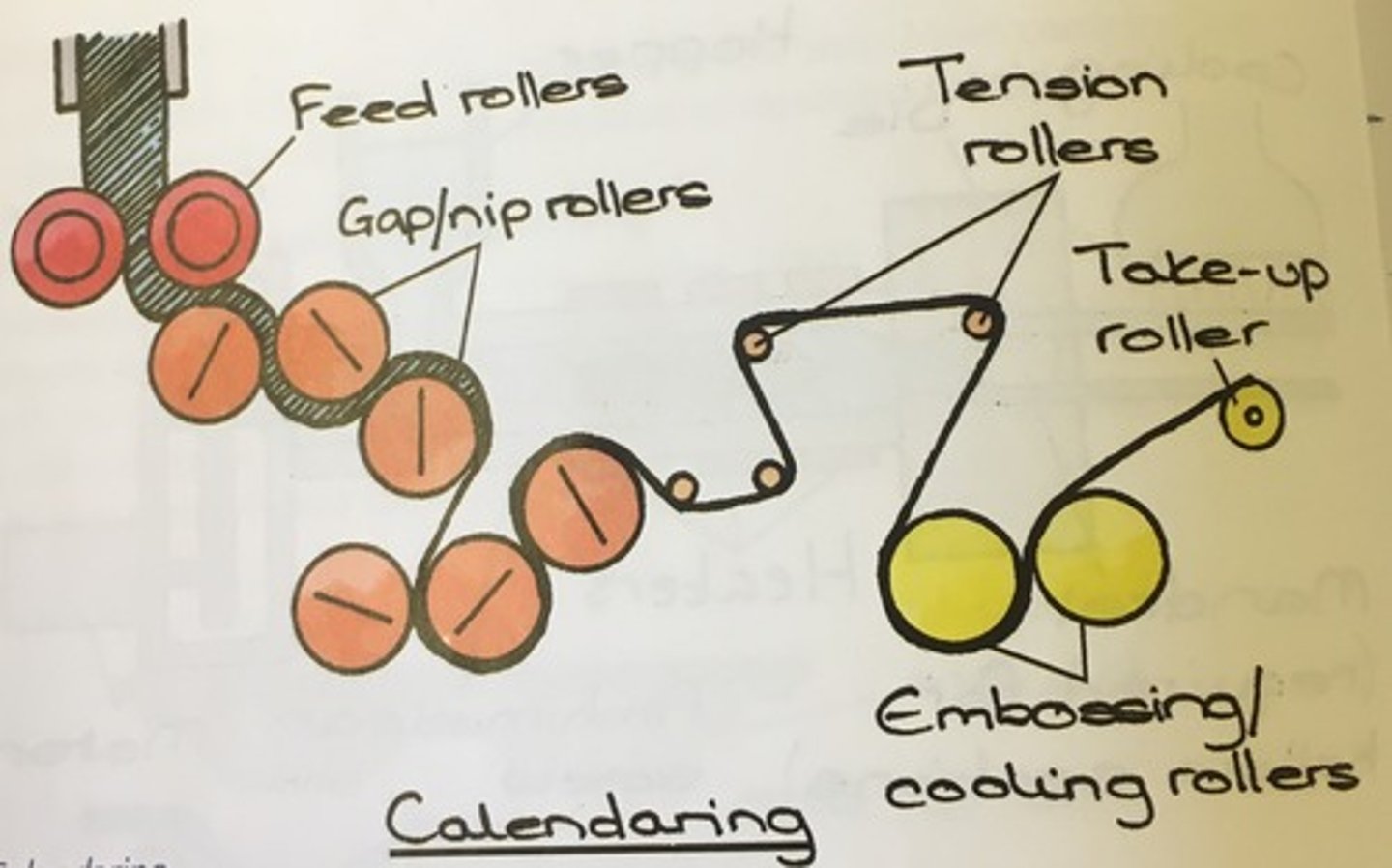
calendaring
the process of pressing polymer between rollers to give it a smooth surface. afterwards it is chopped into standard stock sizes. continuous manufacture.
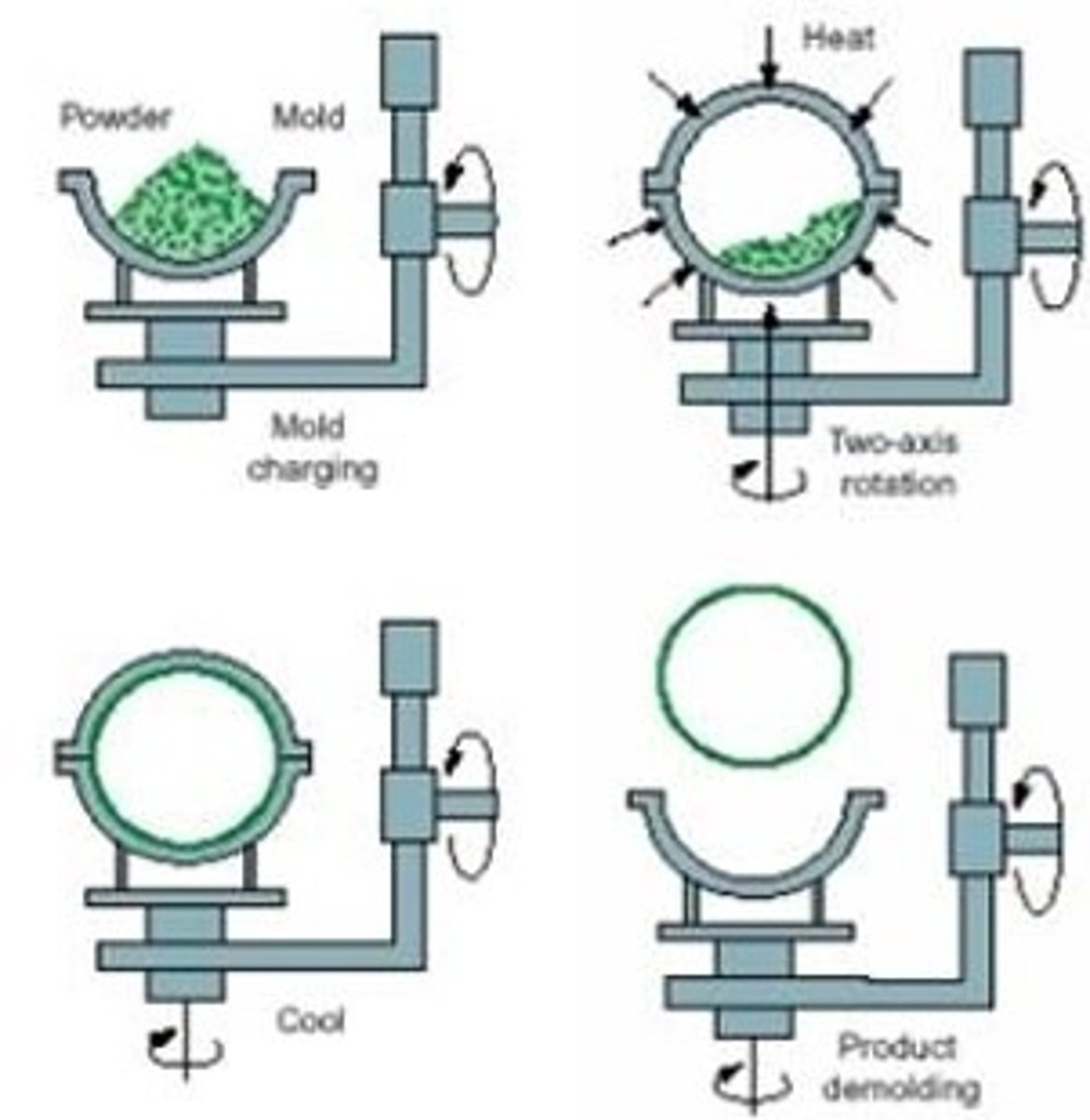
rotational moulding
polymer powder put in mould (clamped & sealed). mould put in heater (260-370 .c) mould is rotated (>20 rotations/min) around 2 axes. this cause the polymer to coat the inside of the mould. once at the correct thickness it is cooled with fan or water. it shrinks and can be removed. (high set-up costs; mass production)
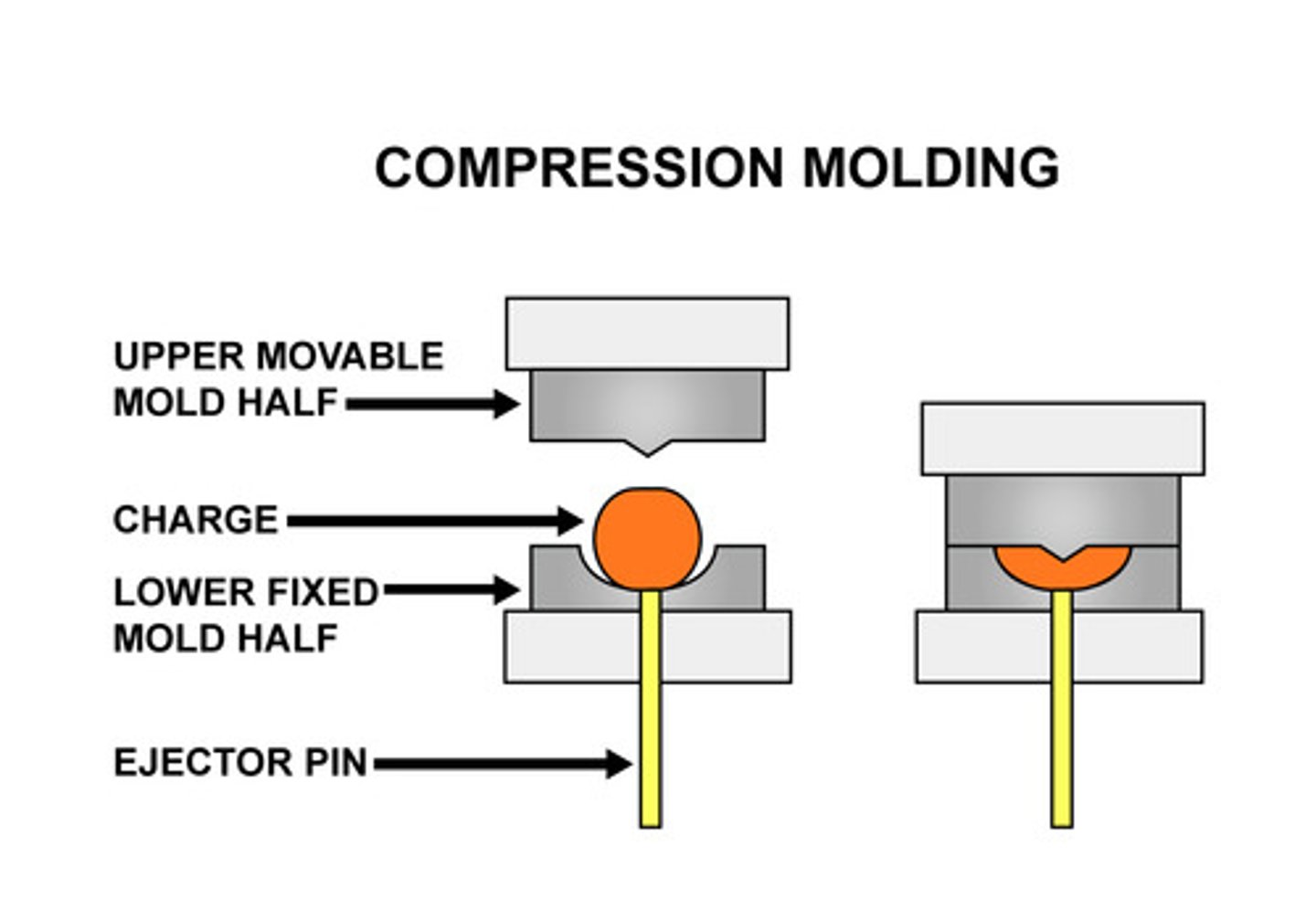
compression moulding
a slug or pre-weighed thermoset polymer is inserted into preheated moulds. moulds closed and hydraulic ram applied. it remains until it cures then removed and excess trimmed.
extrusion
polymer granules put into a hopper, an Archimedean screw moves granules past heaters. heaters soften granules until melted. hydraulic ram pushes screw and polymer through a steel die (which determines extrusion shape). extrusion may be supported by rollers as it cools by air. then cut to length.
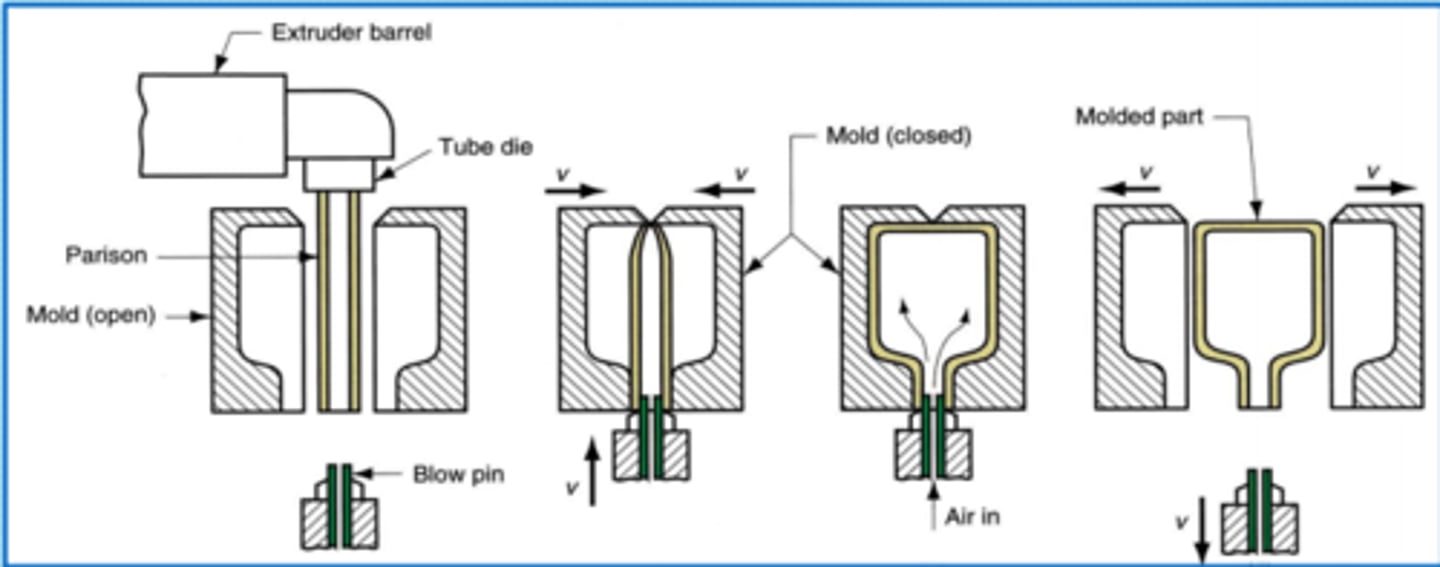
blow moulding
polymer is fed into hopper; Archimedean screw pulls polymer through heaters. melted polymer is extruded through a tube (parison). mould sides close around the parison and air is injected into mould which forces polymer to edge of the mould. cooled and then ejected.
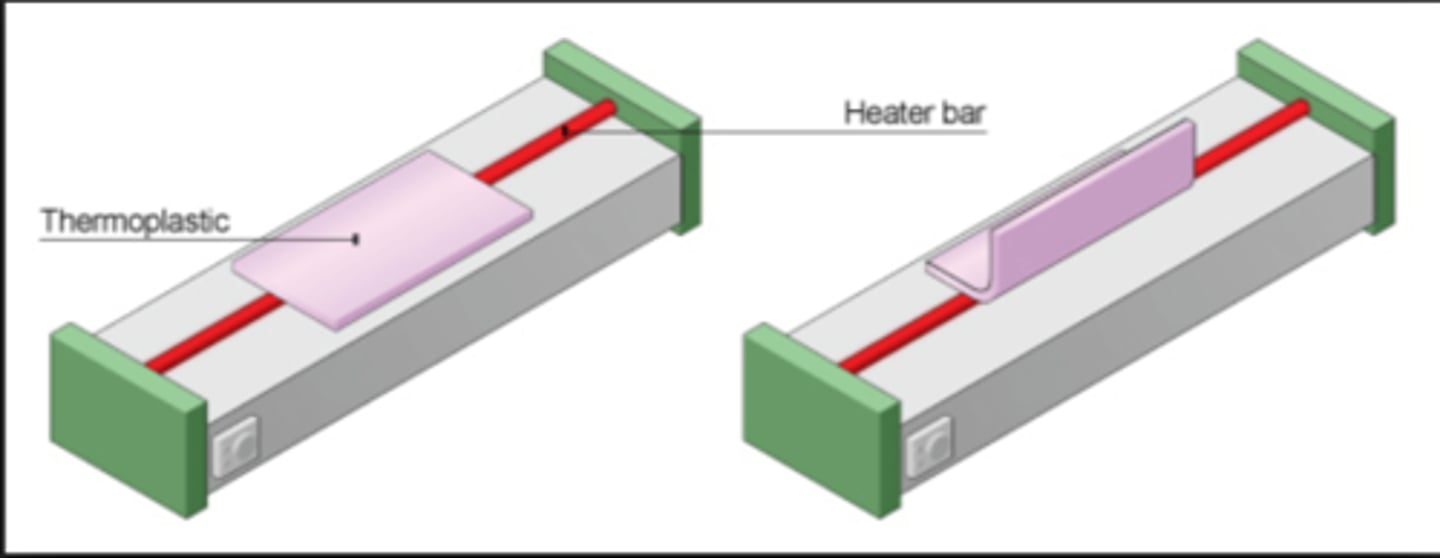
line bending
process used to bend straight lines in heated thermoplastic using a strip line of heat. very slow process- limited batch production.
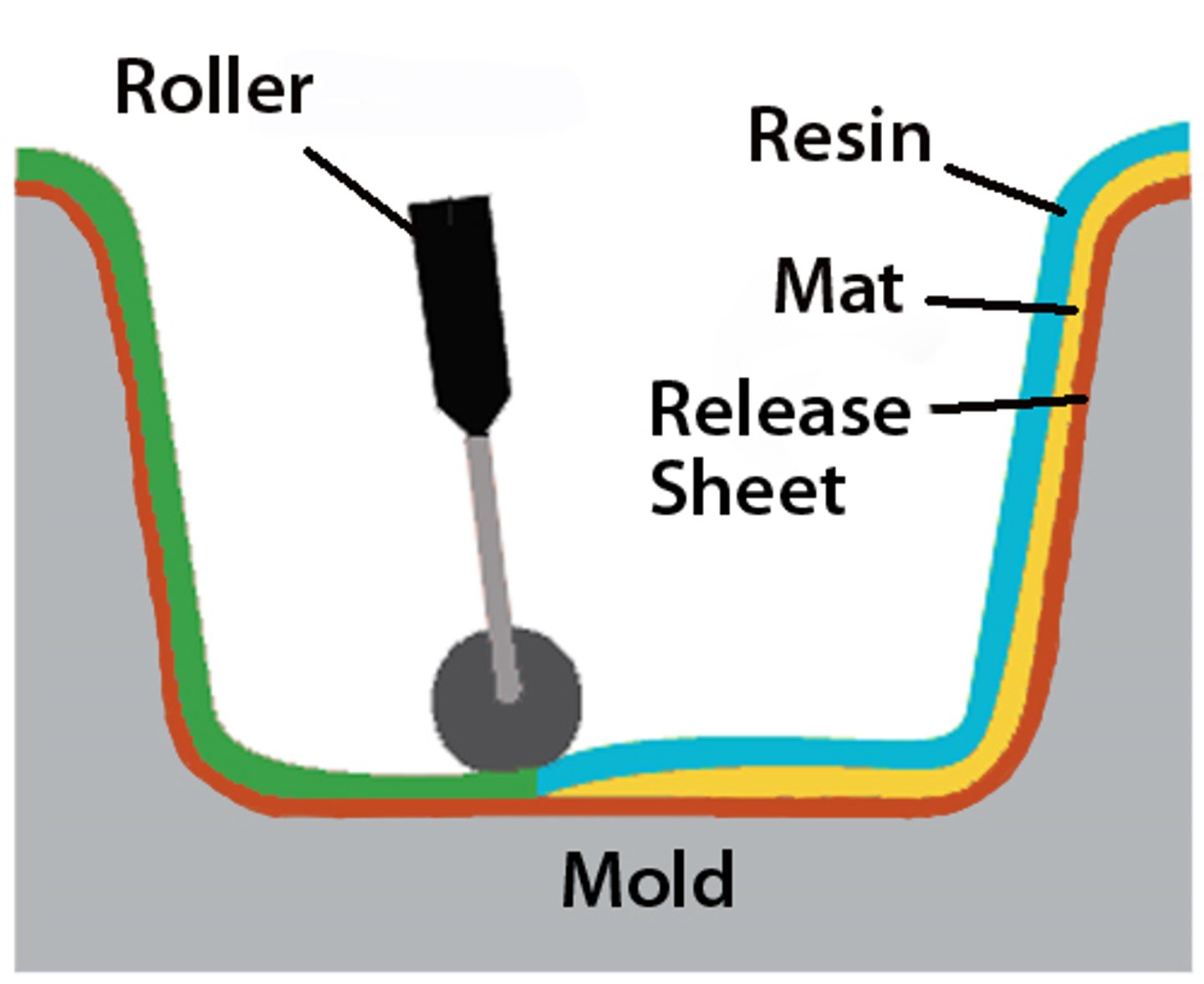
lamination (lay-up)
a mould is coated in a release agent (i.e. wax, PVA, parcel tape). a top layer gel is applied (typically polyester resin and pigment). fibreglass matting is cut to size and laid over the former; resin is brushed over the matting. this is repeated until required thickness is met. fine tissue matting is used on top layer. vacuum bag may compress layers. it is left to set.
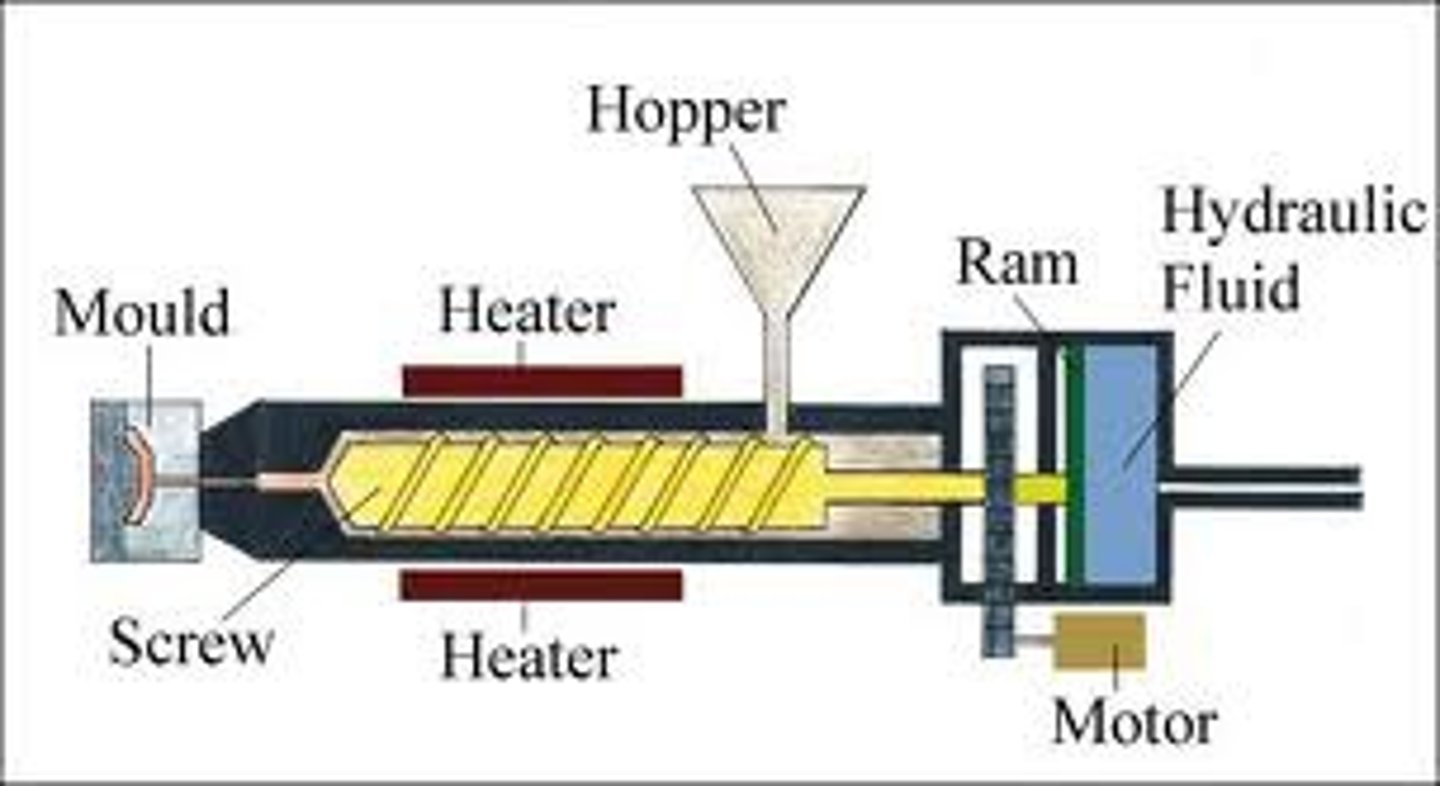
injection moulding
thermoplastic pellets/granules are poured into hopper. screw thread is rotated by motor which pulls granules into chamber past heater melting the polymer. melted polymer is injected into mould by hydraulic ram . mould is cooled in water. ejector pins push out moulded shape.
die casting
gravity; pouring molten metal into mould. pressure; hot- pneumatic or hydraulic plunger forces shot of metal through goose neck of die. cold- molten metal is ladled into shot chamber and ram forces it into mould cavity.
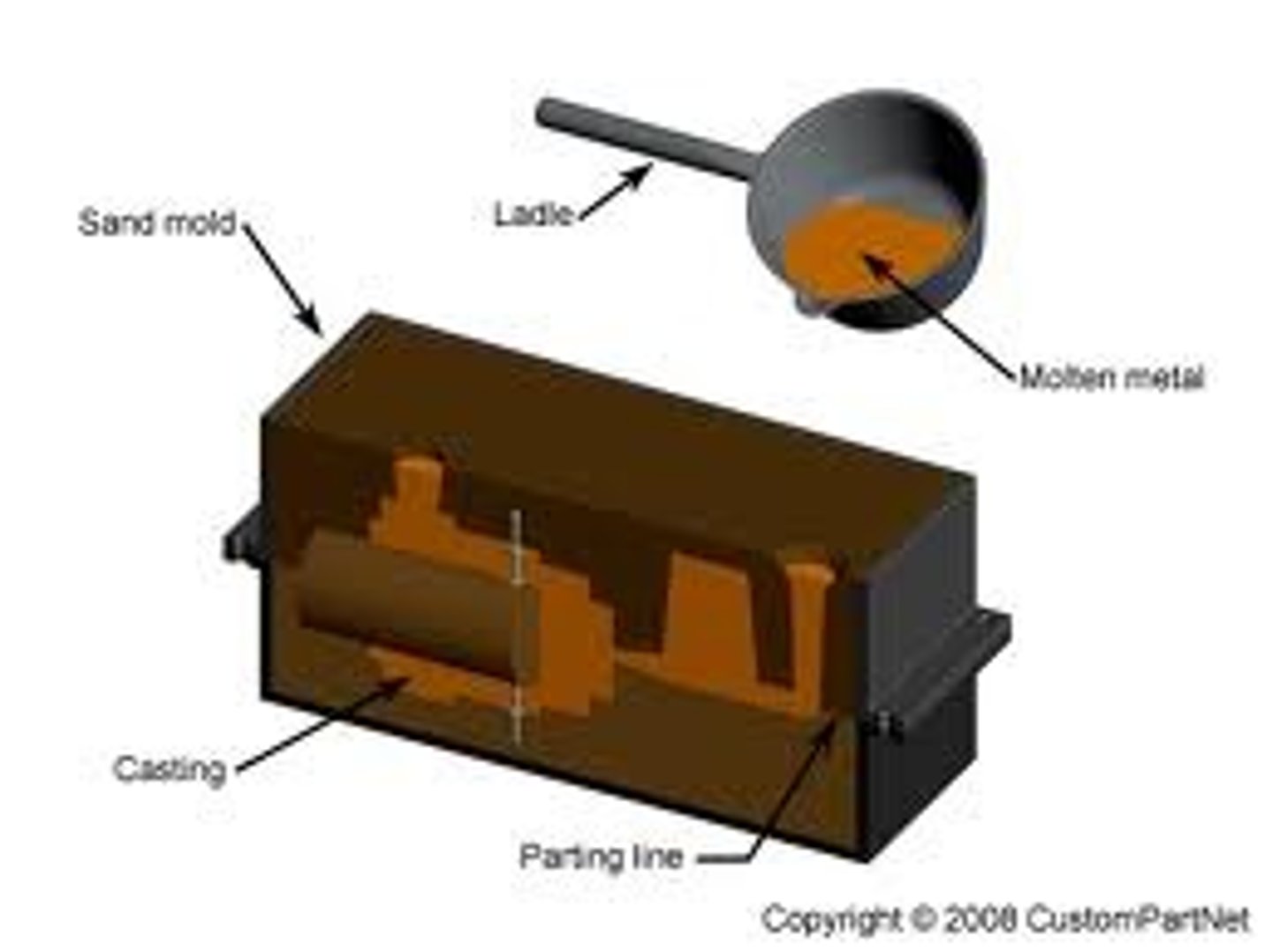
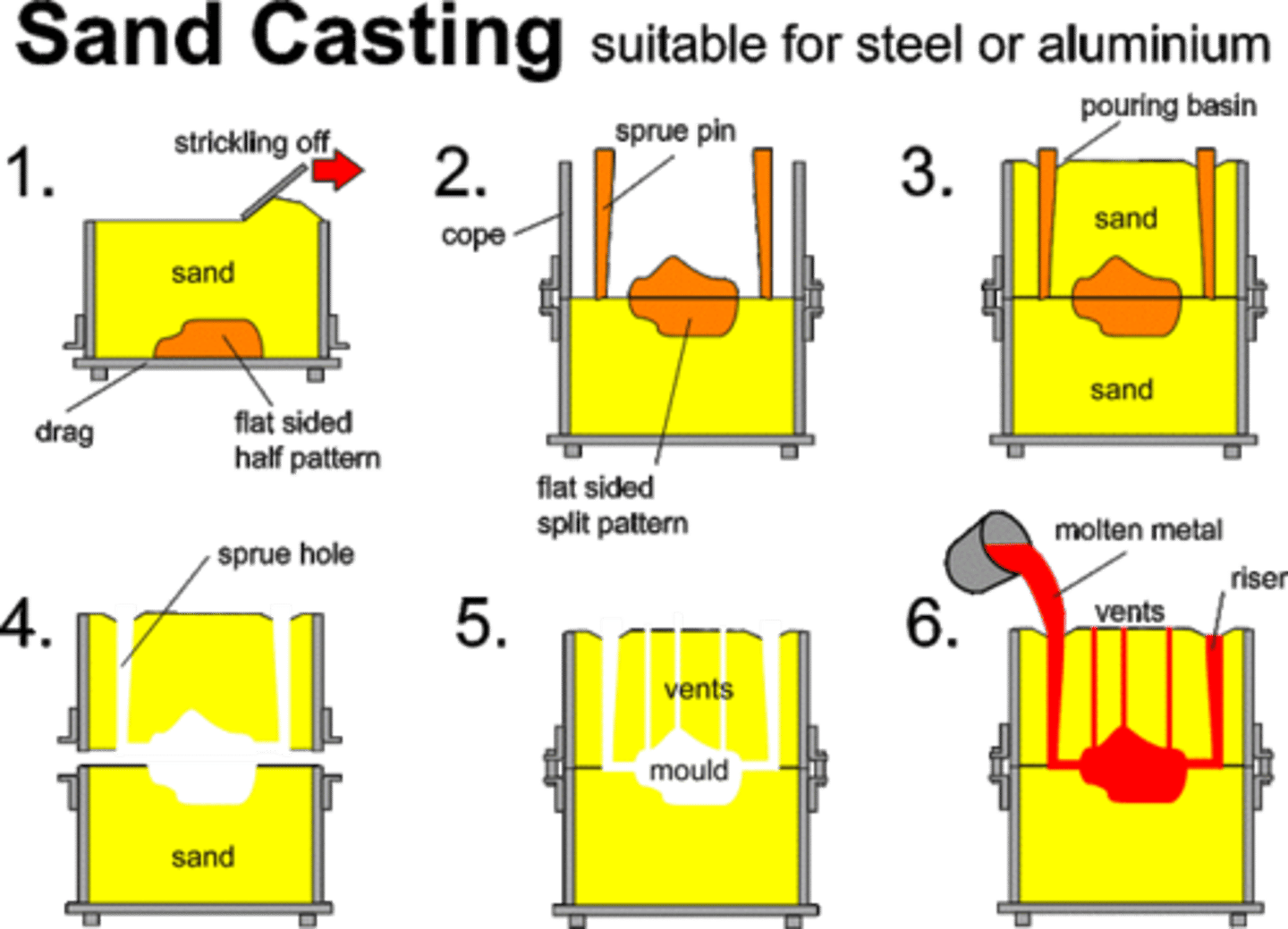
sand casting
pattern is made from wood and placed at the bottom of a steel box (drag) drag is filled with sand and tightly packed. it is flipped over and second sand filled box is clamped on top of cope wooden stakes are positioned into cope (sprue, runner, riser). sand is packed around pattern and small indent is made around sprue for pouring. cope and drag are separated and mould removed , then reassembled. small metal spikes inserted to make vents. metal is poured into basin until cavity is full. channels are cut of with hacksaw.
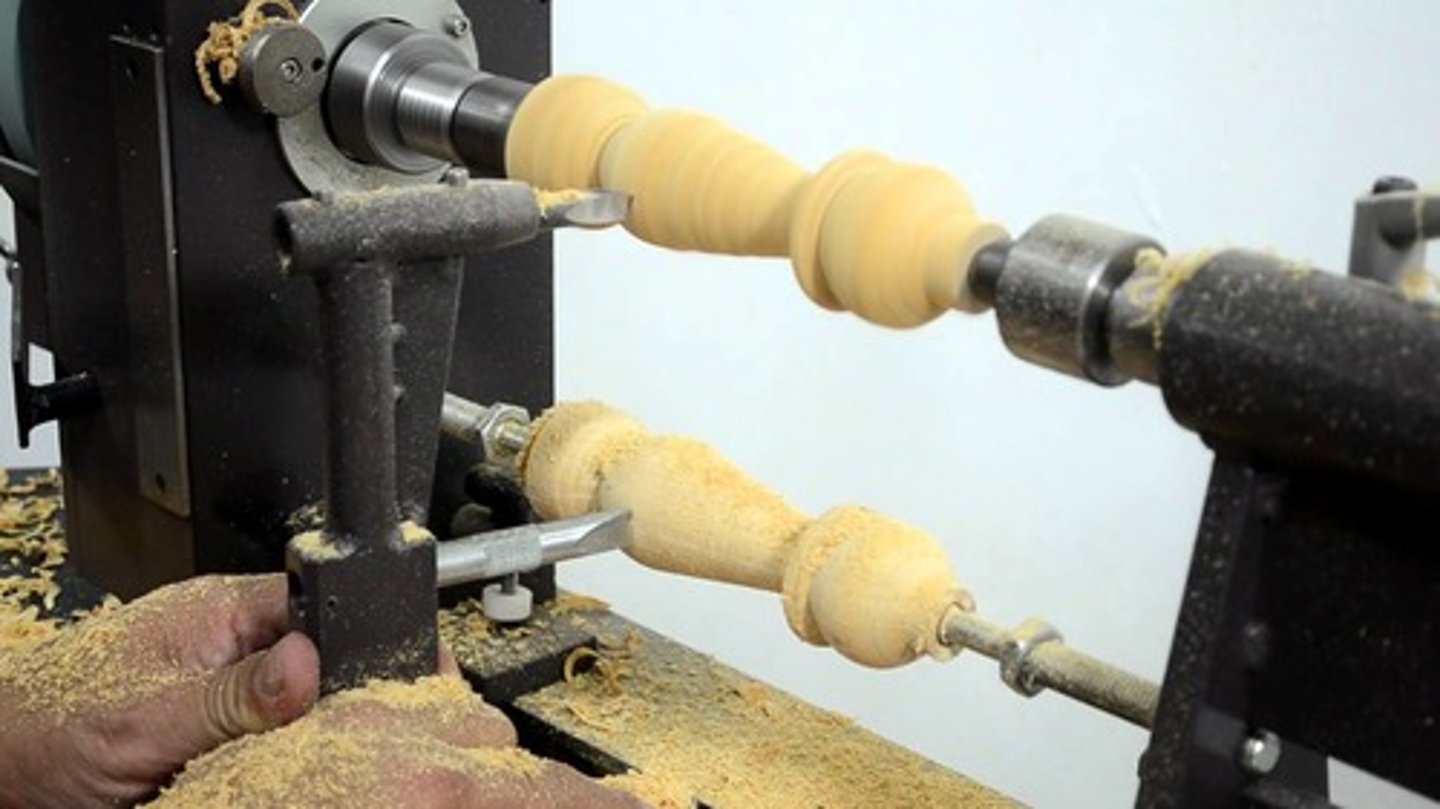
turning
using a centre lathe to rotate a metal bar to reduce its diameter, to square, or face-off, thread, or drill. turning can be done manually or with a CNC lathe. the tools are made from high speed steel or tungsten carbide. a liquid coolant is flooded over the cutting site and tool to prevent the tool from blunting and to maintain a good finish.

butt joint (traditional)
simple but effective- using an adhesive (i.e. PVA) to make a bond on 2 flat surfaces in lightweight models. lightweight wood is cut square and then clamped with adhesive of joining edge.
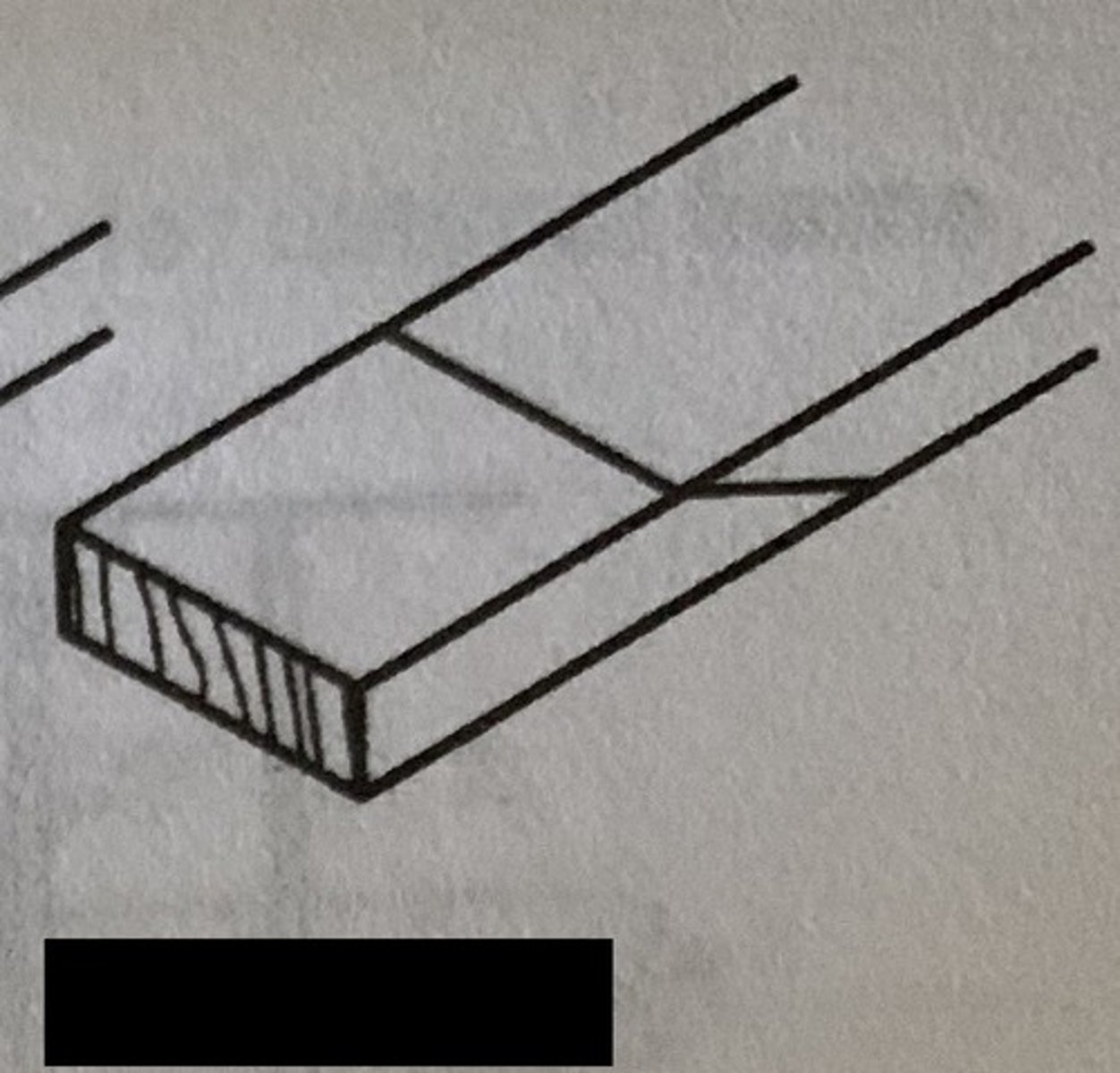
mitre joint (traditional)
pieces are glued and clamped to make a 90 angle from pieces of wood cut at 45 angle. often used to make picture frames. a mitre jig is used to keep the joint straight.
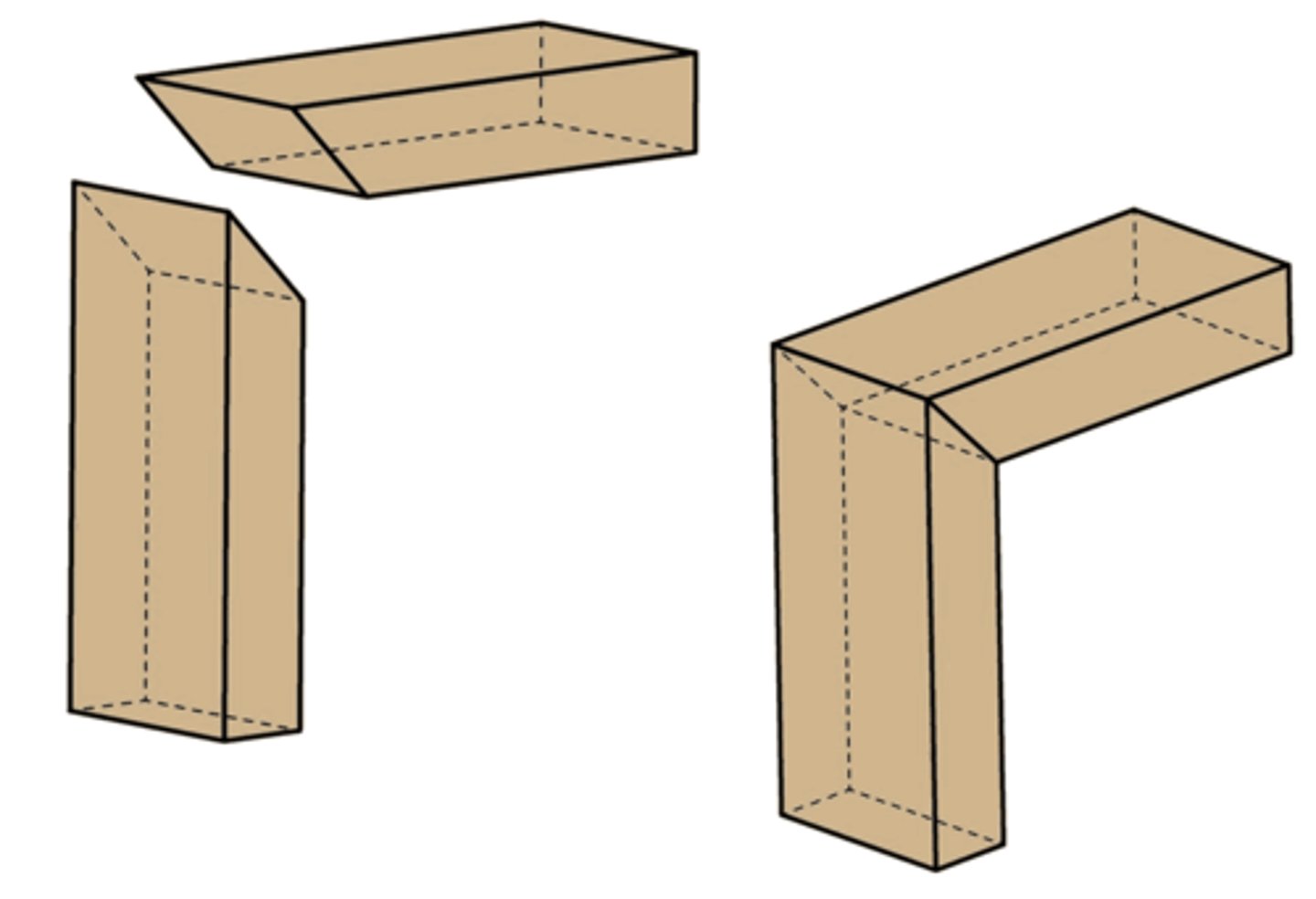
dovetail joint (traditional)
similar to comb joints but have directional strength due to the interlocking parts cut to an angle. once glued the pieces are impossible to pull apart. they can be cut by hand using a dovetail saw but typically done with a router and jig (less skill). often used to make drawers.
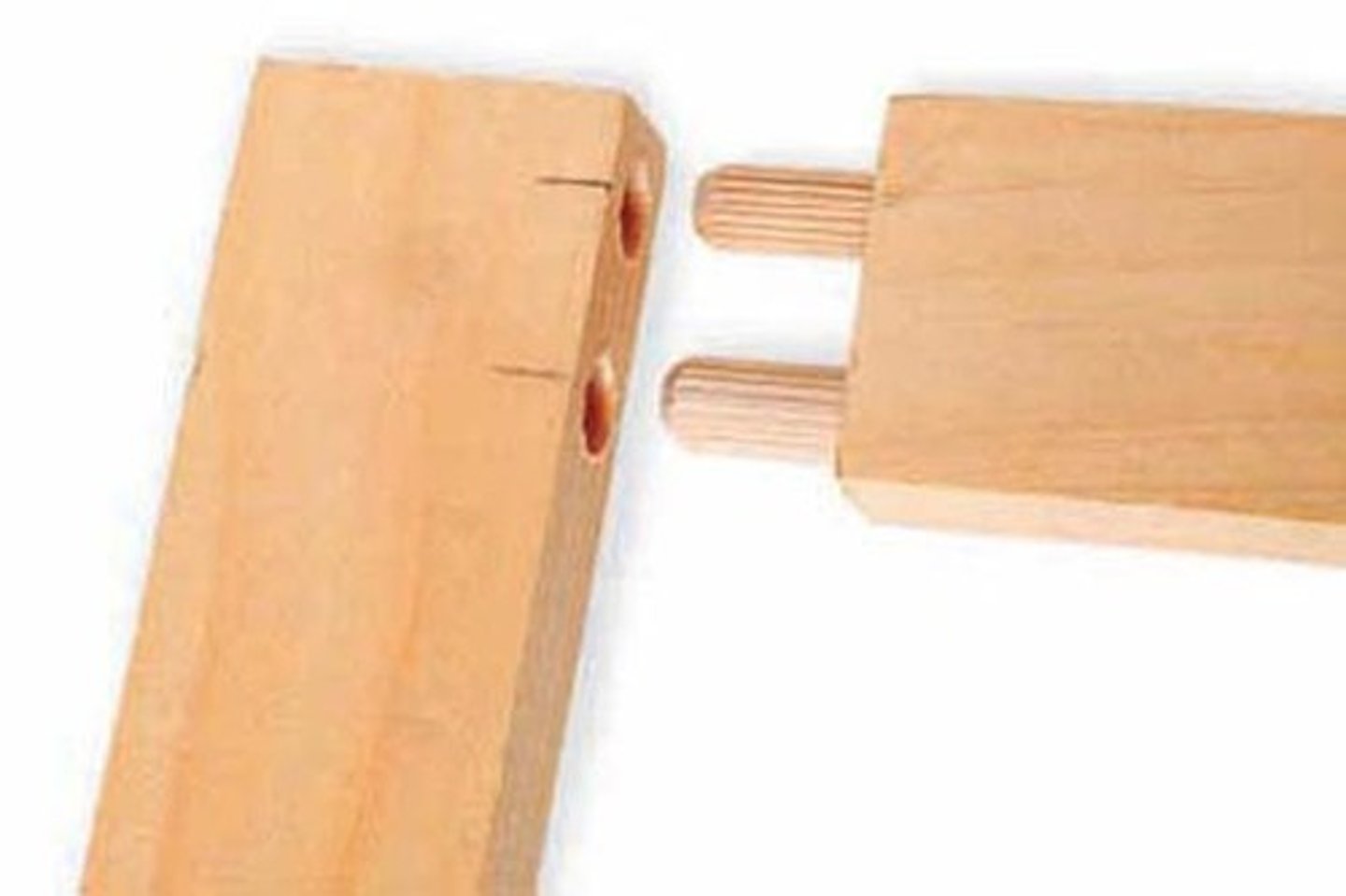
dowel joint (traditional)
uses small wooden pegs made from hardwood which are hammered into drilled holes. once hammered and glued the pieces are clamped together. stronger than butt joint, but still simplistic. often used in flat-pack furniture as they require little skill.

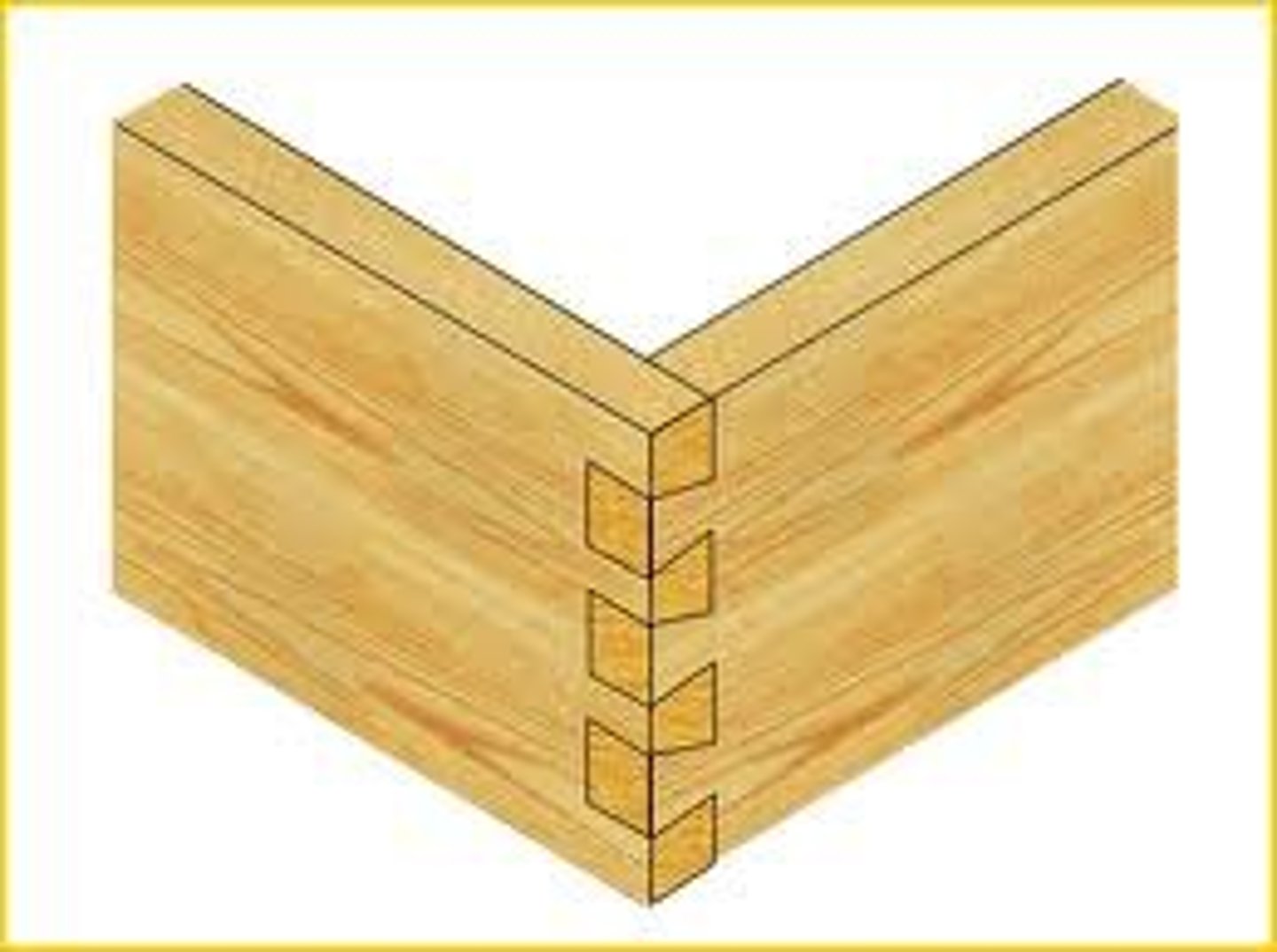
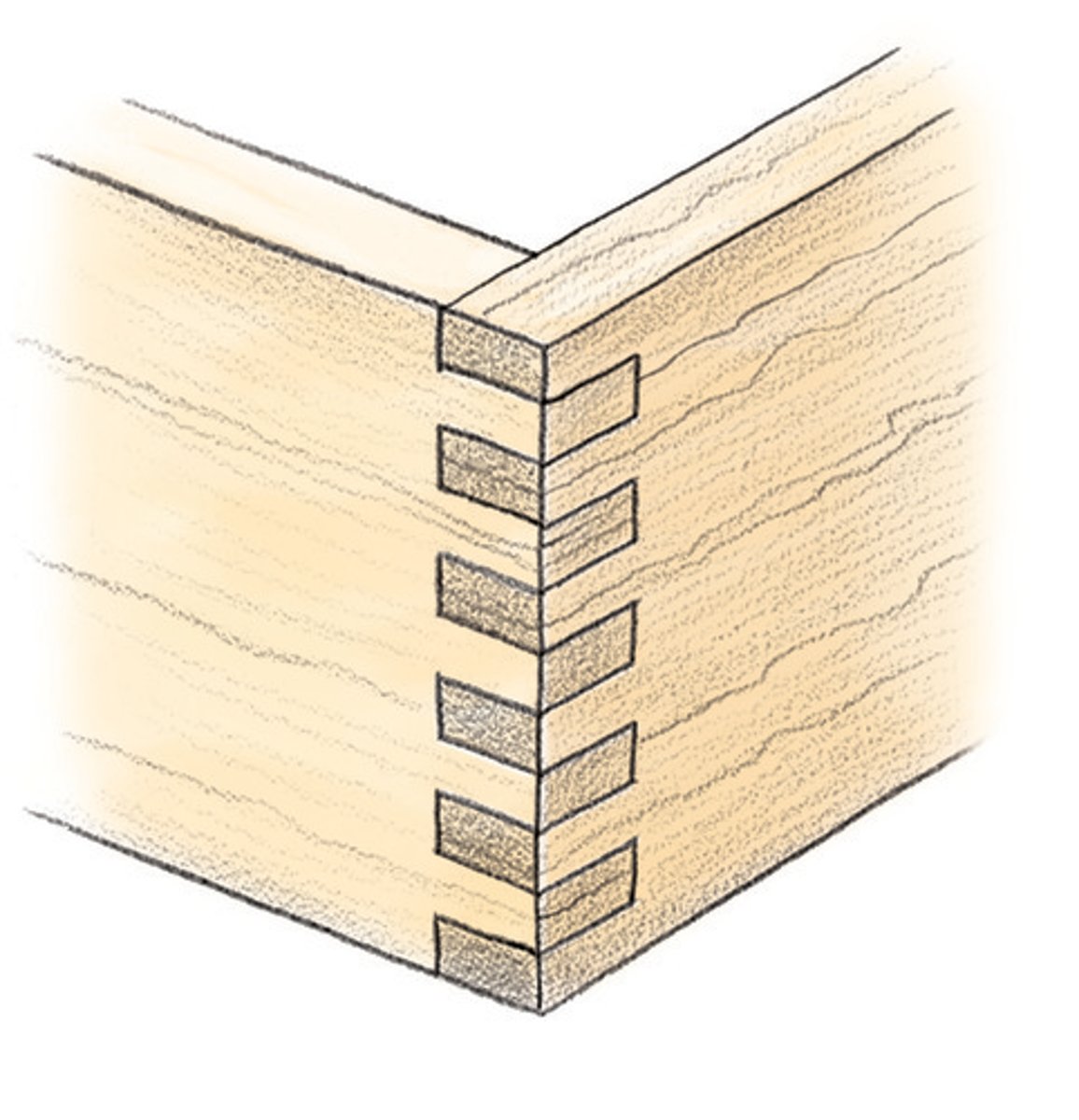
comb joint (traditional)
commonly used to make boxes as the comb makes an increased surface area to glue on, making a very strong joint. these can be cut quite easily using a band saw, tenon saw & chisel, or a laser cutter.
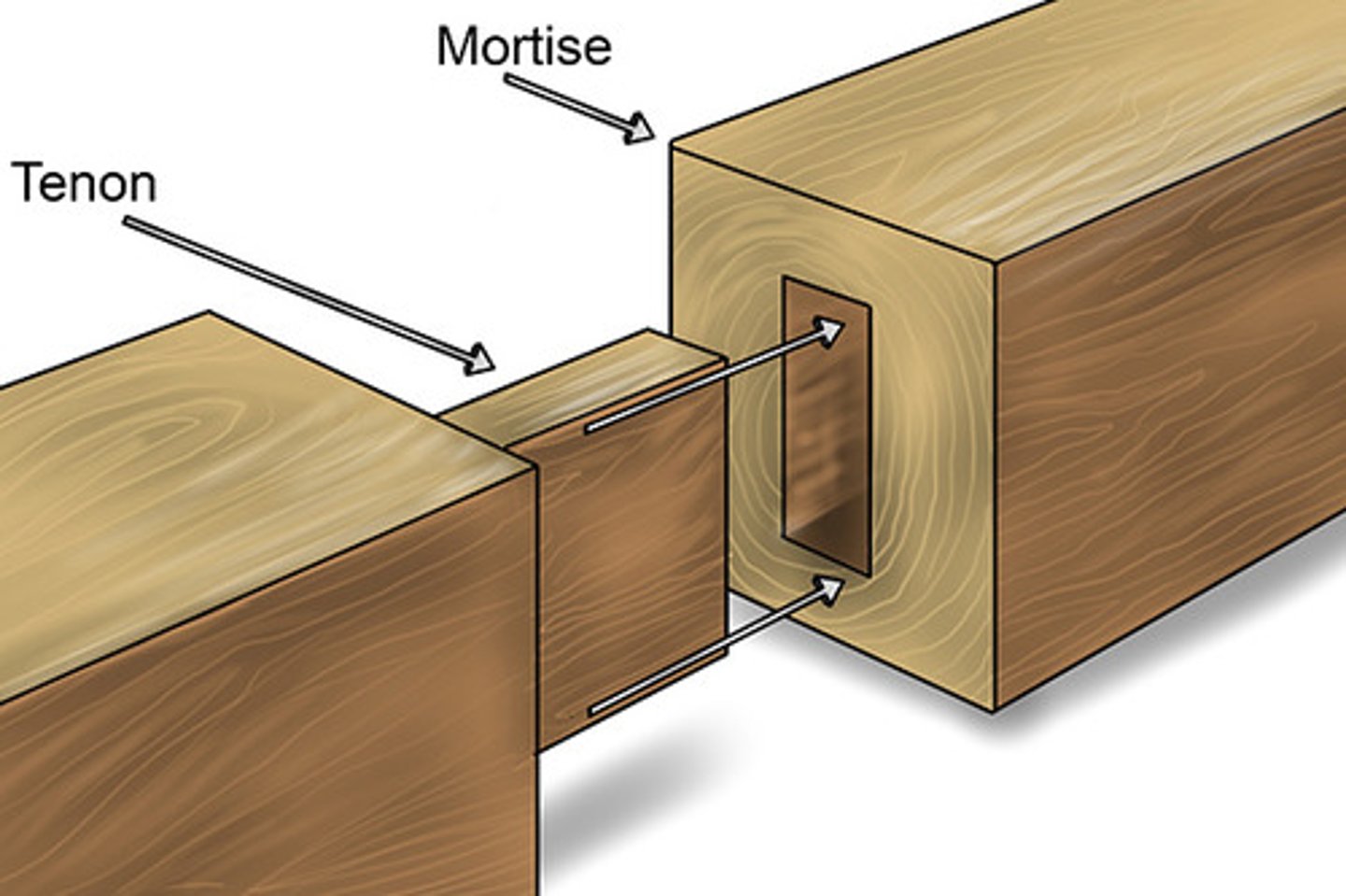
mortoise and tenon joint (traditional)
this is used in heavy-duty frame constructions for furniture. a square rectangle hole (mortoise) is drilled and cut {or made using a mortoise router} into one piece of the wood joint. in the other piece of wood a tenon or band saw is used to make a small rectangle (tenon). adhesive like PVA is spread in the mortoise and the two parts are clamped together.
housing joint (traditional)
useful in framework construction like cabinets and shelving. a groove is cut across one piece it is the same length and width of the end of the other piece. to make a permanent joint glue is applied then the second piece is inserted into the 1st. it can be a temporary joint without glue . it is structurally strong and can be made using a tenon saw and chisel or router.
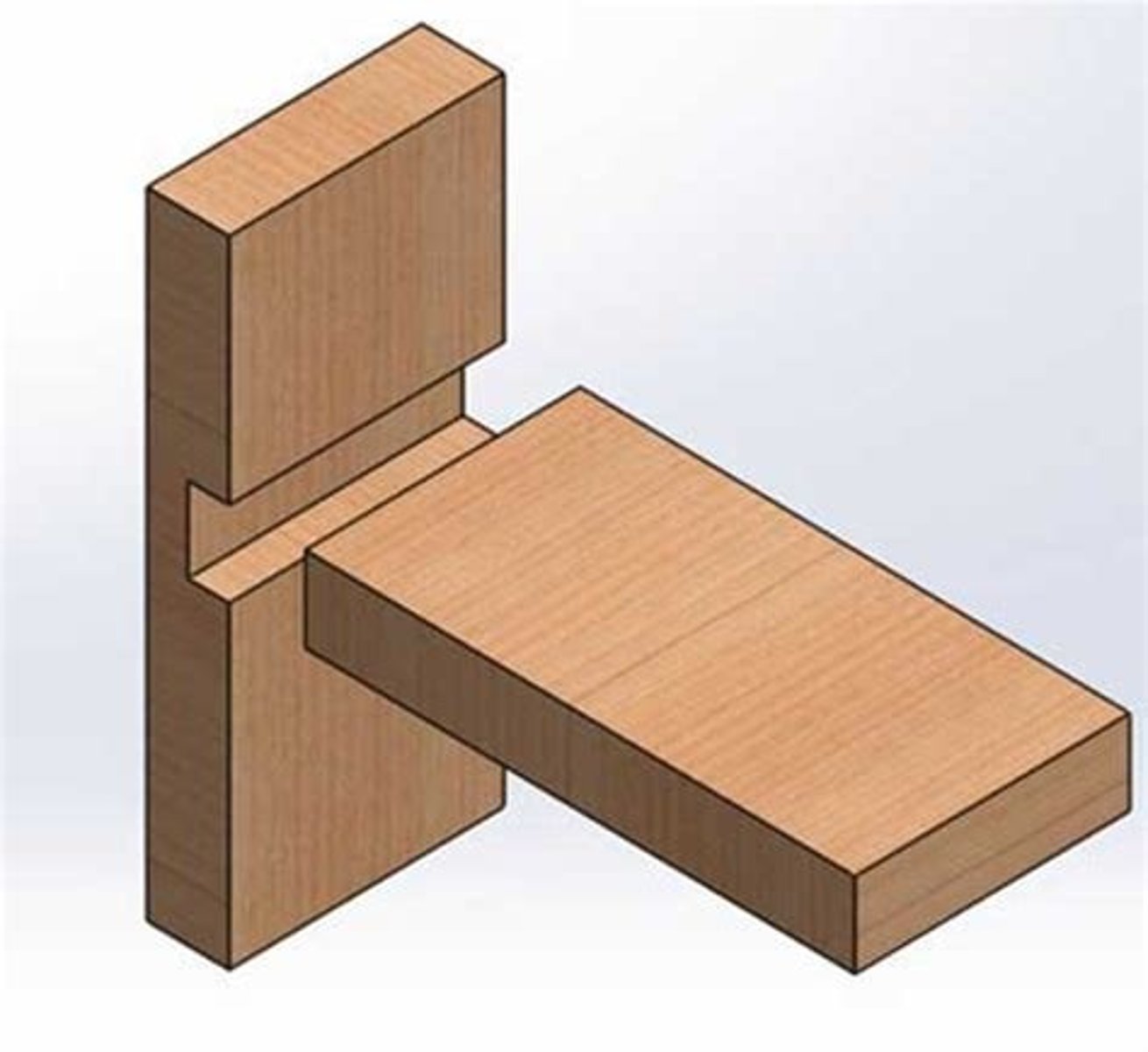
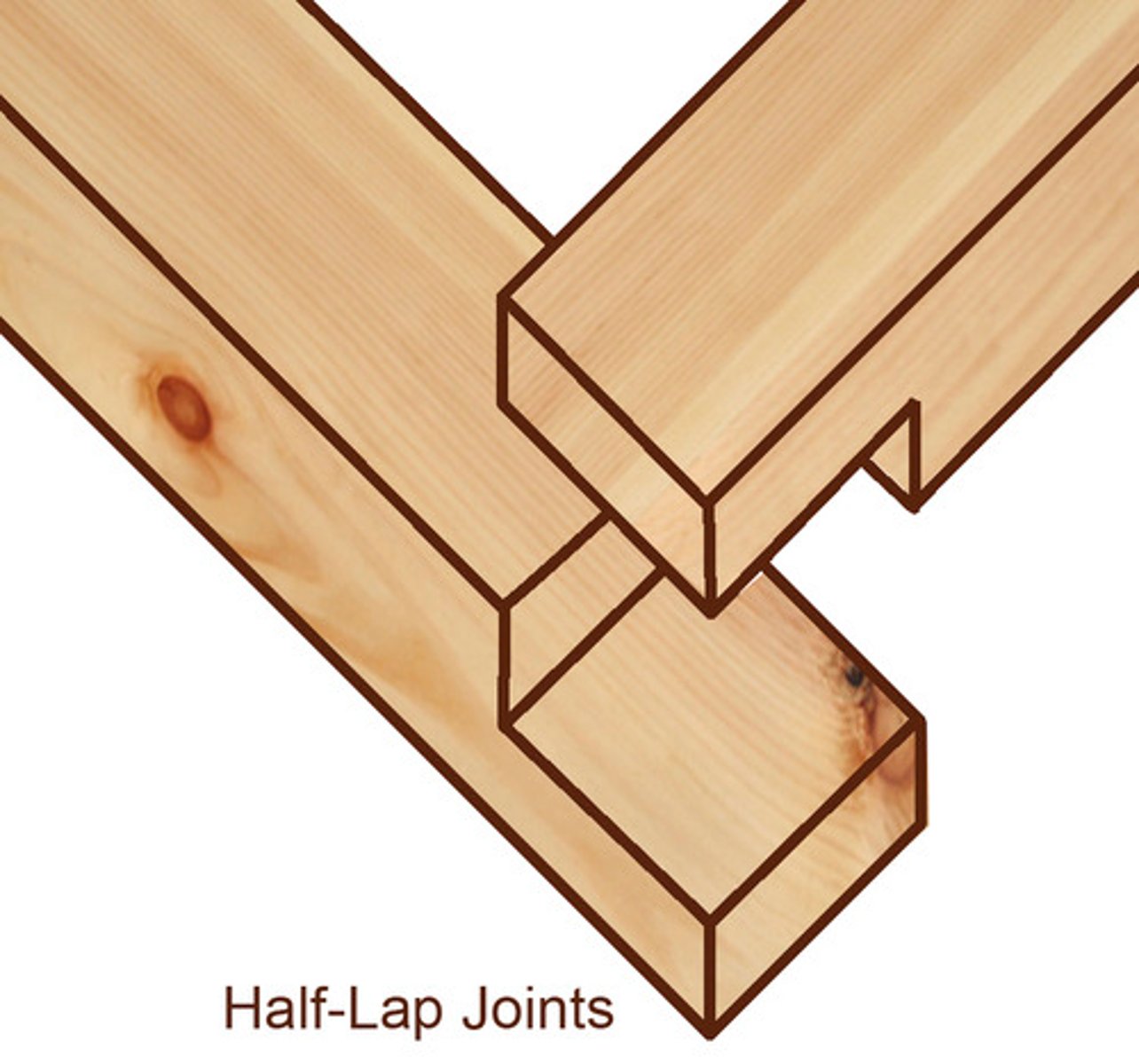
half-lap joint (traditional)
a simple joint used to make frames and boxes. a "step" is cut into each piece of wood and adhesive (PVA) is attached and the two steps are stuck together like butt joints. steps can be made with band or tenon saw. joints are quite strong (increased gluing area).
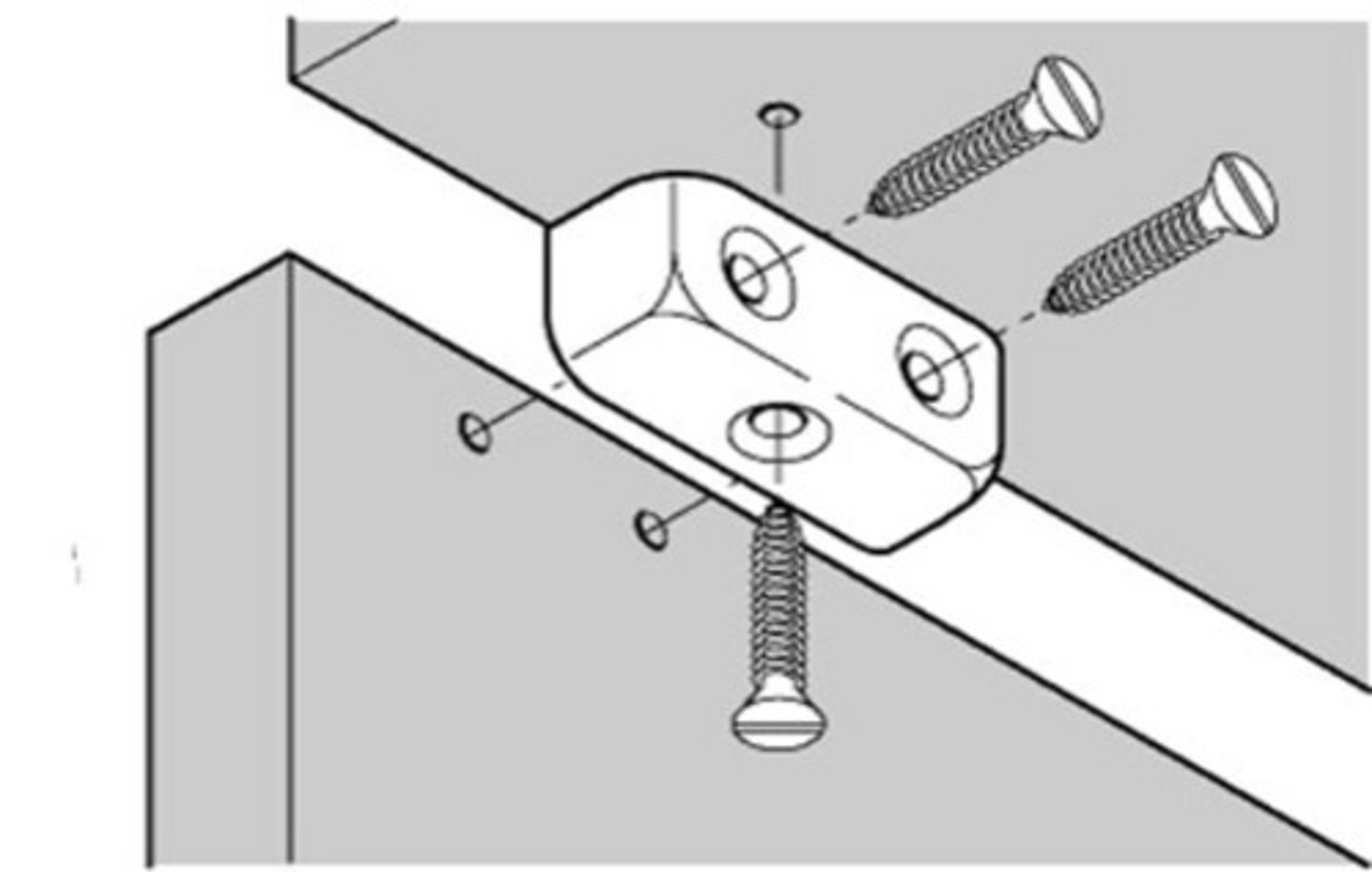
knock down fittings (KDF)
these reduce cost for both manufacturer and consumer, and reduces making time. it is easier to store and transport the products. KDF are easy to use and easy to fit with limited tools which is crucial for flatpack furniture as it has to be accessible. KDF are standardised and interchangeable (used in a variety of products)
modesty blocks (KDF)
small, rigid polymer blocks that have moulded screw holes in them. screw holes take screws that are used to join the blocks to panels. typically used in storage units (like cupboards) as they are simple and strong. it is an unattractive joint and is being phased out of mainstream furniture manufacture.
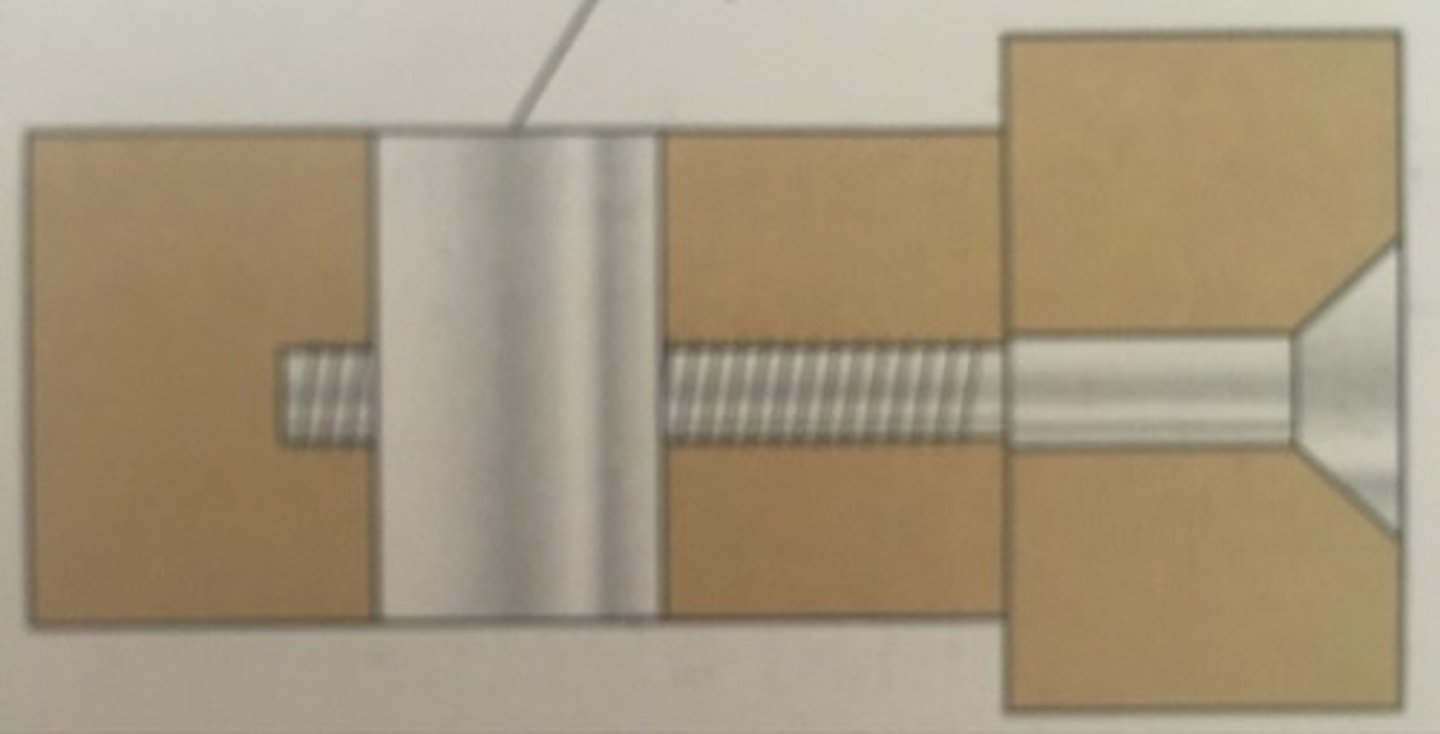
barrel nut and bolt (KDF)
very common KDF. uses a cross-dowel which is fitted to one piece of the wood and a bolt is inserted through the other piece of wood. the bolt is then tightened into the cross-dowel using an allen key.
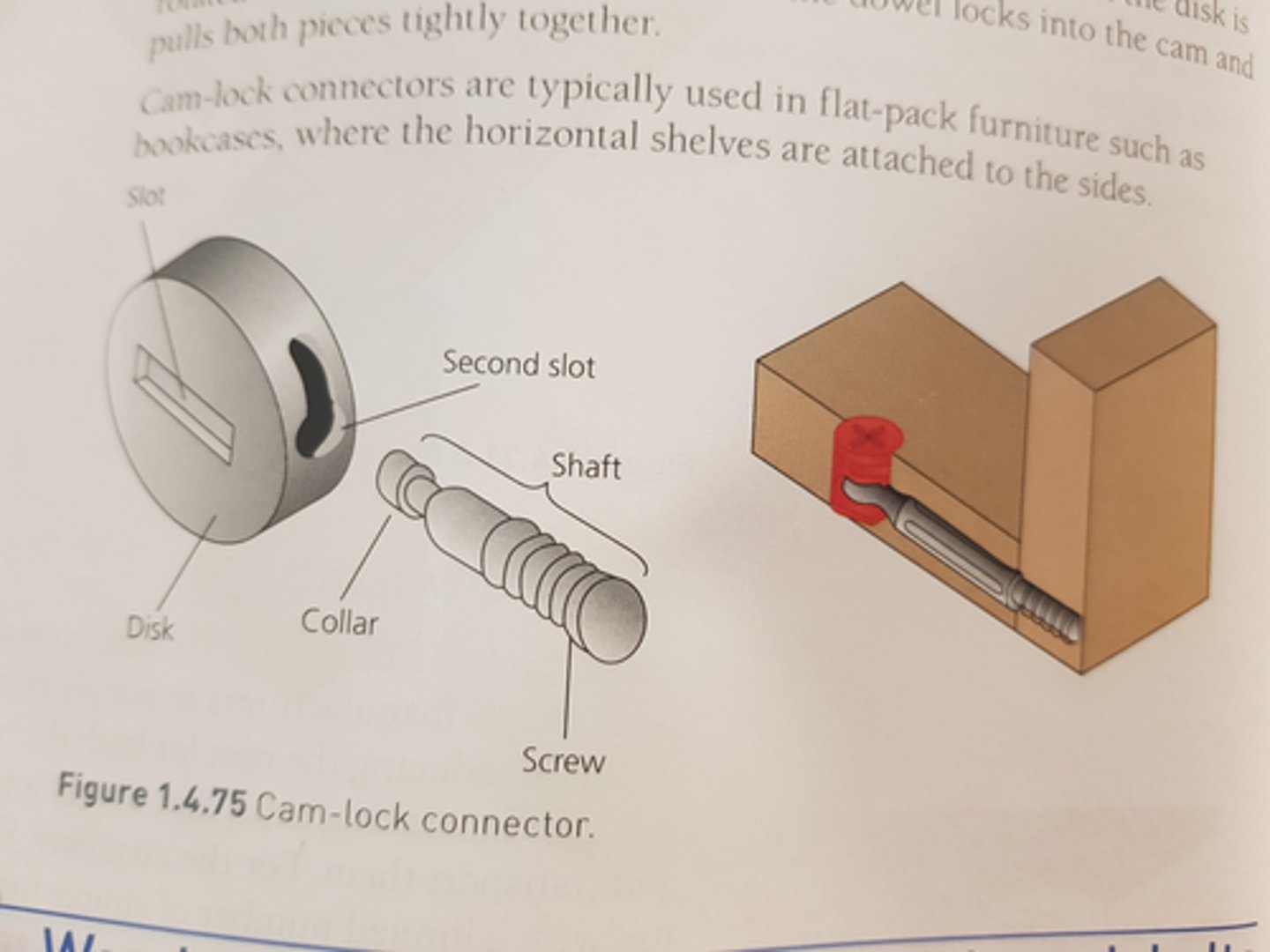
cam-lock connector (KDF)
uses a metal dowel and cam disk. the metal dowel is screwed into one piece of wood by inserting a screwdriver into the slot on the side. the cam disk is rotated with a screwdriver so that the collar of the dowel locks into the cam and pulls both pieces of wood tightly together.
turning timber
TURNIING BETWEEN CENTRES- turning to reduce diameters (used to make spindles or chair legs).
TURNING ON A FACEPLATE- a thick piece of wood is screwed into a faceplate where it is machined in a way to remove the inside and turn the outside circumference (i.e. a bowl).
TURNING IN A CHUCK-wood is turned on a lathe and uses a chuck to grip the item whilst it is machined.

routing timber
this is used to make slots, holes, or decorative mouldings on timber. the depth of the router is adjustable, and come with a range of accessories (guides/fences). can be CNC or done using a handheld router. both 2D and 3D CAD can be used. debris (like dust) must be extracted.

milling timber
the material to be shaped is clamped onto the table of the machine. the table can run in X direction (left & right/ horizontally), Y direction (forwards & backwards horizontally), and Z direction (up and down/ vertically). milling can be used to cut slots, shape edges/surfaces, drill and thread holes. however, these run too slowly to produce accurate products, but are suitable for projects. they do not have the same range of motion as routers.
