Vectors
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Define a scalar quantity.
A quantity completely defined by its magnitude (it has no direction).
Define a vector quantity.
A quantity completely described by its magnitude and direction.
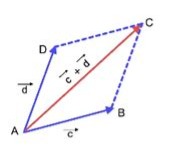
What are the two methods of adding vectors?
Tip to tail
Parallelogram method
How do we subtract vectors?
By adding the inverse of the vector, i.e the same value acting in the opposite direction.
Tip to tail method:
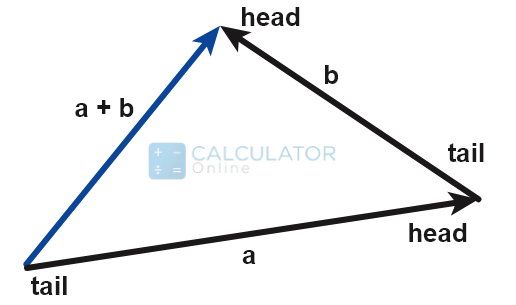
Parallelogram method:

Define distance.
The total length of a path travelled.
Define displacement.
Straight-line distance from start point to end point.
What are the two sets of vector components?
Horizontal and vertical
Parallel and perpendicular (to a slope)
How do we solve for vectors using trigonometry?
Vector B = Vector A (cos angle)
or
Vector B = Vector A (sin angle)
How do you find the vector sum of more than one vector?
Add all the horizontal components
Add all the vertical components
Use pythagoras to find the resultant magnitude
Use trigonometry to find the resultant direction
For a body to be in equilibrium, it must either have:
No resultant force
No resultant moment
What are the two types of equilibrium?
Translational Equilibrium
Rotational Equilibrium
How can you describe translational equilibrium?
The sum of all forces acting on a body is zero
There is no resultant force on a body
Net force = 0
If vectors are drawn tip-to-tail, they form a closed loop
There is zero acceleration: the object is still or moving at a constant velocity
How can you describe rotational equilibrium?
The sum of clockwise moments = the sum of anti-clockwise moments (about the same point)
The sum of moments about any given point is zero
Net moment is zero
What does it mean if the line of action of all vectors on a body cross at the same point?
The body is in rotational equilibrium.
What are co-planar forces?
Forces which all lie on the same plane.