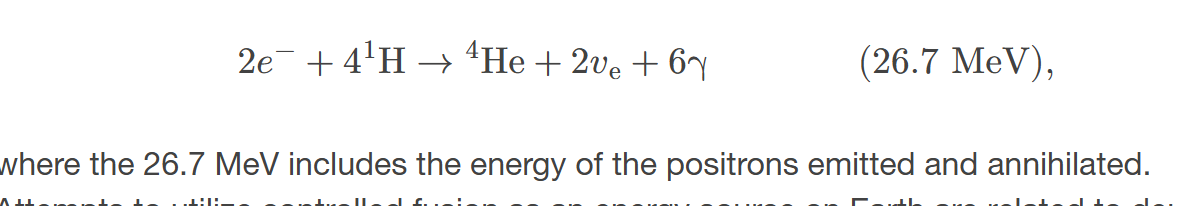Chapter 32: Medical Applications of Nuclear Physics
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Anger Camera
a common medical imaging device that uses a scintillator connected to a series of photomultipliers
break-even
when fusion power produced equals the heating power input
breeder reactors
reactors that are designed specifically to make plutonium
breeding
reaction process that produces 239Pu
critical mass
minimum amount necessary for self-sustained fission of a given nuclide
criticality
condition in which a chain reaction easily becomes self-sustaining
fission fragments
a daughter nuclei
food irradiation
treatment of food with ionizing radiation
free radicals
ions with unstable oxygen- or hydrogen-containing molecules
gamma camera
another name for an Anger camera
gray (Gy)
the SI unit for radiation dose which is defined to be 1Gy=1J/kg=100rad
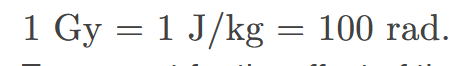
high dose
a dose greater than 1 Sv (100 rem)
hormesis
a term used to describe generally favorable biological responses to low exposures of toxins or radiation
ignition
when a fusion reaction produces enough energy to be self-sustaining after external energy input is cut off
inertial confinement
a technique that aims multiple lasers at tiny fuel pellets evaporating and crushing them to high density
linear hypothesis
assumption that risk is directly proportional to risk from high doses
liquid drop model
a model of nucleus (only to understand some of its features) in which nucleons in a nucleus act like atoms in a drop
low dose
a dose less than 100 mSv (10 rem)
magnetic confinement
a technique in which charged particles are trapped in a small region because of difficulty in crossing magnetic field lines
moderate dose
a dose from 0.1 Sv to 1 Sv (10 to 100 rem)
neutron-induced fission
fission that is initiated after the absorption of neutron
nuclear fission
reaction in which a nucleus splits
nuclear fusion
a reaction in which two nuclei are combined, or fused, to form a larger nucleus
positron emission tomography (PET)
tomography technique that uses 𝛽+ emitters and detects the two annihilation 𝛾 rays, aiding in source localization
proton-proton cycle
the combined reactions 1H+1H→2H+e++ve, 1H+2H→3He+γ, and 3He+3He→4He+1H+1H
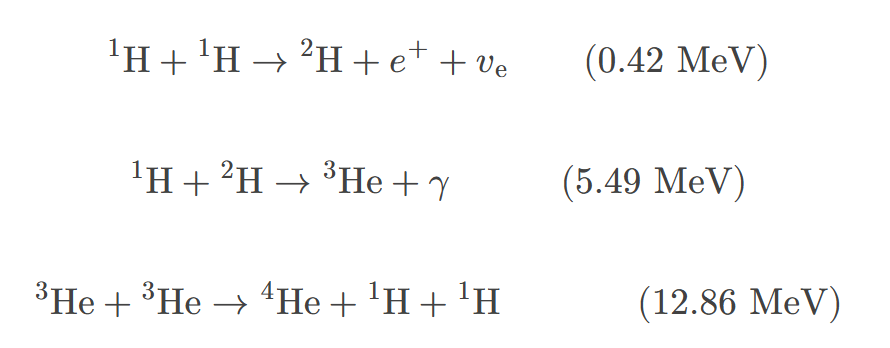
quality factor
same as relative biological effectiveness
rad
the ionizing energy deposited per kilogram of tissue
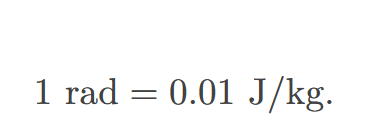
radiolytic products
compounds produced due to chemical reactions of free radicals
radiopharmaceutical
compound used for medical imaging
radiotherapy
the use of ionizing radiation to treat ailments
relative biological effectiveness (RBE)
a number that expresses the relative amount of damage that a fixed amount of ionizing radiation of a given type can inflict on biological tissues
roentgen equivalent man (rem)
a dose unit more closely related to effects in biological tissue
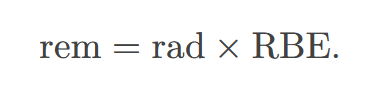
shielding
a technique to limit radiation exposure
sievert
the SI equivalent of the rem
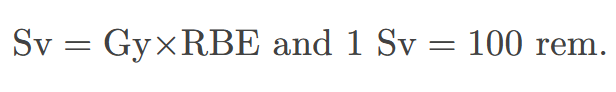
single-photon-emission computed tomography (SPECT)
tomography performed with 𝛾-emitting radiopharmaceuticals
supercriticality
an exponential increase in fissions
tagged
process of attaching a radioactive substance to a chemical compound
therapeutic ratio
the ratio of abnormal cells killed to normal cells killed
Overall effect of proton-proton cycle
is the conversion of hydrogen into helium, releasing energy.