ANS 150 Exam 2 NCSU
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Ovary
Contains thousands of growing follicles
Each follicle contains an ovum or"egg"
Receives a rich supply of both blood vessels and nerves
Follicles
-grow in response to hormones called gonadotropins
-either die (become atretic) or ovulate and release their egg.
Corpus Luteum (CL)
-form from the tissue that remains after a follicle has ovulated
-produce a number of hormones associated with pregnancy
-progesterone is its (their) primary product
Corpus Albicans (CA)
-scar tissue left behind after corpus luteum dies or regresses
-avascular, non-functional tissue
Oviduct
Funnel shaped organ
• Specialized end near ovary called the fimbria
• Fimbria picks up ovulated eggs
-Anterior end called ampulla
-Posterior end called isthmus
-Fertilization and early embryonic development takes place in the oviduct in most animals
Uterus
Glandular inner lining surrounded by two layers of muscle
Longitudinal and circular layers
Responsible for maintenance of pregnancy
Also releases the hormone that regresses luteal tissue
Cervix
Thick, muscular organ
Serves to isolate the uterus from external environment during pregnancy
site of semen deposition in some animals
Vulva
External female genitalia
Outer portion of the vagina
Involved with recognition of receptivity and possibly with the production of female pheromones
Testicle
Series of tubules (seminiferous tubules)
Produce spermatozoa
Produce hormones (testosterone, androgens and others).
Epididymis
continuation of tubule in testicle
specialized for maturation and storage of spermatozoa
immature sperm enter epididymis
during their passage through epididymis they become mature
Secondary sex glands
Seminal vesicles, prostate and bulbourethral glands
Produce and secrete most of the liquid portion of semen
Composition of each is fairly specialized
Penis
Male reproductive organ
Specialized to deposit semen in female reproductive tract
central canal is the urethra
urethra is common exit for reproductive and urinary systems
Sheath
specialized pouch in which penis remains when not in use
in some animals, the lining of the sheath is involved in male pheromone production.
Female endocrinology
gonadotropins - stimulate ovary
sex steroids/prostaglandins - direct control of reproductive state
mammotropins - involved with lactation
Gonadotropins (LH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- produced by the pituitary gland
- stimulates final growth of follicles
- causes ovulation
- also stimulates corpus luteum
Gonadotropins (FSH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
- produced by the pituitary gland
- stimulates all stages of follicle growth, especially early periods
sex steroids/prostaglandins (Progesterone)
Progesterone
- produced by corpus luteum and the placenta (some animals)
- responsible for maintenance of pregnancy
- inhibits gonadotropin secretion
sex steroids/prostaglandins cont (Estrogen)
Estrogen (estradiol 17beta)
- produced by growing follicles, placenta and embryos
- has both positive and negative effects on gonadotropins
Estrogen (cont.)
- stimulates pre-ovulatory surge of gonadotropins
- prepares female for breeding and parturition
- responsible for female mating behaviors
sex steroids/prostaglandins cont (Prostaglandin)
Prostaglandin F2alpha
- primarily the uterus in the reproductive system
- responsible for luteal regression
- causes uterine contractions at birth
Mammotropins
Prolactin
- produced in the pituitary
- stimulates production of milk
Oxytocin
- produced by uterus and hypothalamus
- stimulates milk excretion
- stimulates uterine contractions
Reproductive Cycle (Stages)
Puberty
Estrous Cycles
Pregnancy (Gestation)
Lactation
Post-partum period (Rebreeding)
puberty
Puberty is generally defined as the age at which an animal is capable of adult reproductive function
Females - estrus, production of fertile eggs and maintenance of pregnancy
Males - libido, mating and production of fertile sperm
In most animals, it is the brain and production of gonadotropins, specifically LH that is the last function to mature during puberty
Ovaries and testes are capable of gamete and hormone production before puberty is reached
Estrous Cycle
repeatable sequence of events that results in female becoming sexually receptive
Estrous Cycle stages
-Begins with estrus (period of sexual receptivity)
-At estrus, estrogen is high and progesterone is low
-High estrogen causes preovulatory surge of gonadotropins
-LH surge causes ovulation
-Follicles release eggs
-Estrogen decreases
-Corpora lutea (corpus luteum) form
-Progesterone is produced from CL
-Gonadotropin secretion is decreased because of progesterone
-Progesterone and CL are maintained for 12 to 16 days
-Prostaglandin is released from non- pregnant uterus
-Corpora lutea are destroyed
-Progesterone decreases
-LH and FSH increase
-Follicles grow
-Estrogen increases
-At certain level of estrogens, females exhibit estrus and then ovulate
Pregnancy
-After ovulation, fertilization occurs and embryonic development occurs
-In most females, their bodies do not realize that they are pregnant until around 12 days after fertilization
-At day 12 embryo sends a signal to mother
-prostaglandins are not released from the uterus
-progesterone is maintained
-Embryo begins to differentiate
After embryo begins to differentiate and when it begins to take the shape and form of a young animal it is referred to as a fetus.
Fetuses are still differentiating, but they also are increasing in size very rapidly.
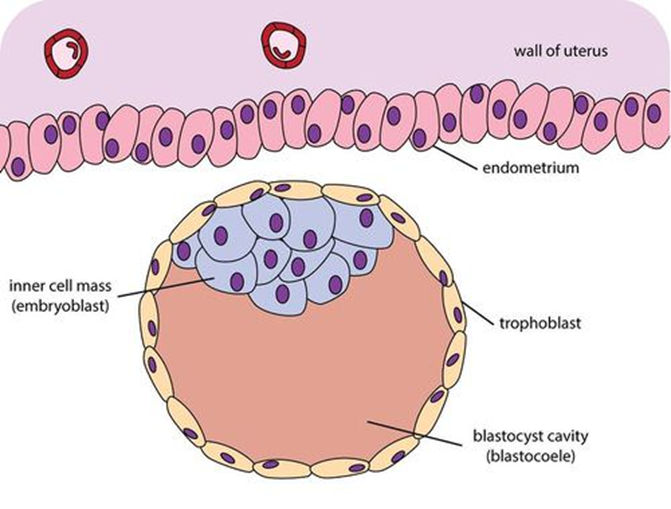
In the blastocys,
-inner cell mass become fetus proper
-cells within inner cell mass differentiate into bones, muscle, nerves, etc.
-trophoblast becomes placental membranes of fetus
parturition (birth process)
fetus initiates parturition
prostaglandins are released
progesterone decreases (except in the horse where it increases then decreases)
endocrine changes vary among species considerably
Lactation
neural reflex arc
physical stimulation of nipple during nursing causes prolactin and oxytocin release
prolactin - milk synthesis
oxytocin - milk ejection
Rebreeding
Suckling action of young prevents release of LH and FSH (via another reflex arc)
Once suckling is terminated by weaning or decreases in intensity, then LH and FSH increase and estrus results.
The one exception is the mare.
Male endocrinology
FSH and LH stimulate sperm production (spermatogenesis)
FSH and LH stimulate testosterone production (mostly LH)
process is fairly continuous, at least during the breeding season