IPC EXAM 1
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
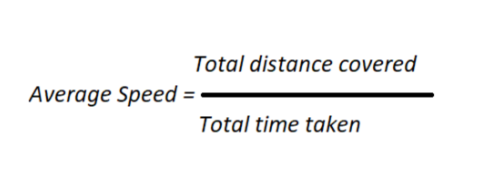
formula for average speed

formula for acceleration
f = mass X acceleration
formula for force
SI units for momentum
Kg m/s
SI units for speed/velocity
m/s (or whatever fits the equation, kg/s, m/hr, etc.)
SI units for distance and displacement
meters (or whatever fits the equation)
a scaler, always positive; when there is no motion it is zero
speed
a vector, can be positive or negative; shows speed and direction
velocity
a vector; can be positive or negative
acceleration
accelerates in a positive direction and/or increases speed
psoitive acceleration
changes towards a negative direction and/or decreases speed
negative acceleration
0 acceleration means there is
either constant velocity or no motion
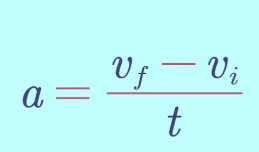
acceleration formula