final exam calculus 2
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
how do i get from the position → velocity → acceleration function?
derive
displacement formula
the integral of the velocity function from a to b


displacement being equal to the position function at “b” - the position function at “a” is rooted in what theorem of calculus?
fundamental theorem of calculus
total distance traveled formula
the integral of the velocity function with absolute value bars
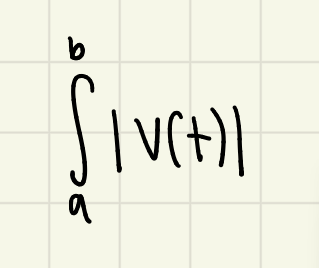
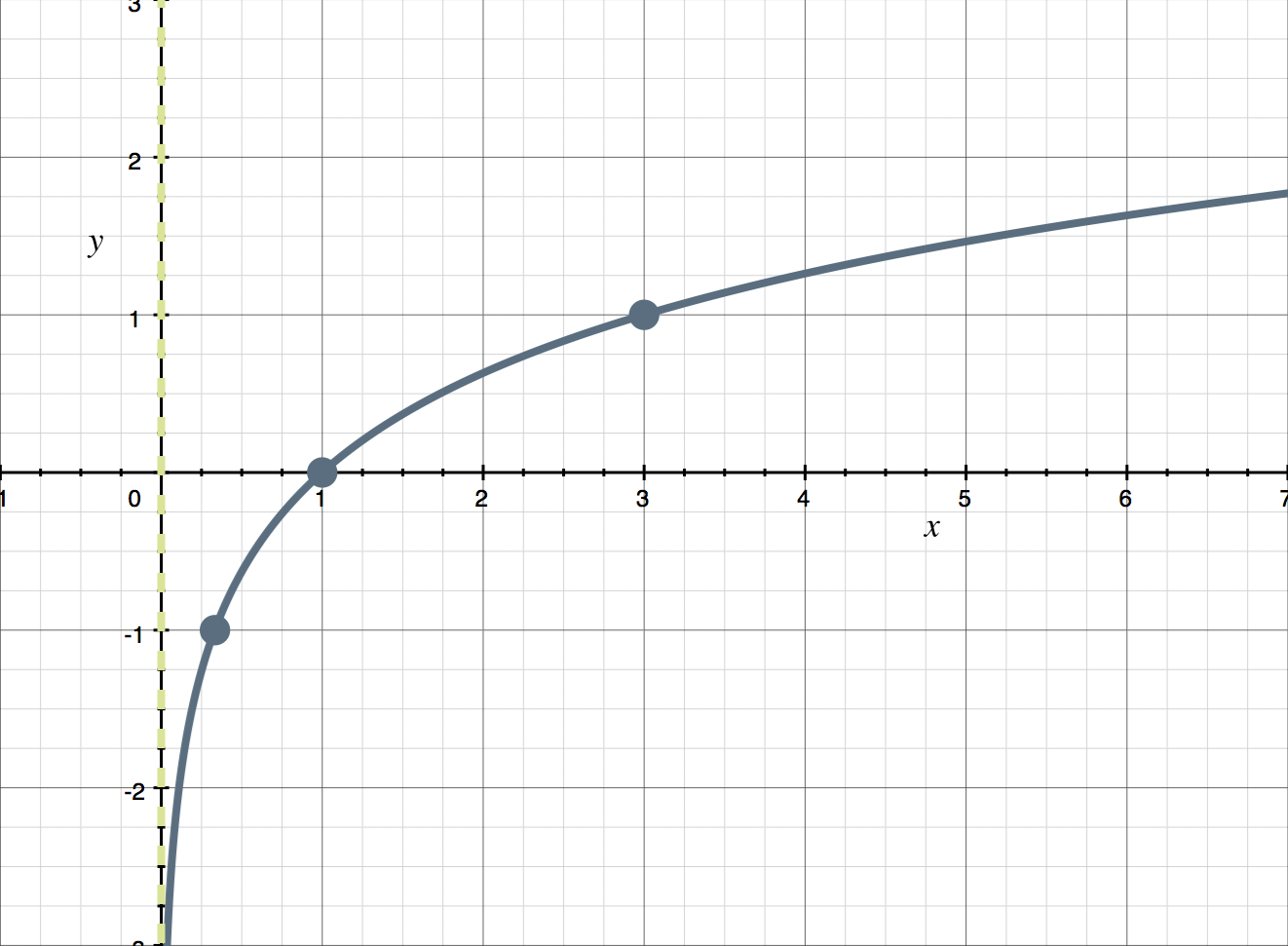
f(x)=x is what kind of graph?
linear

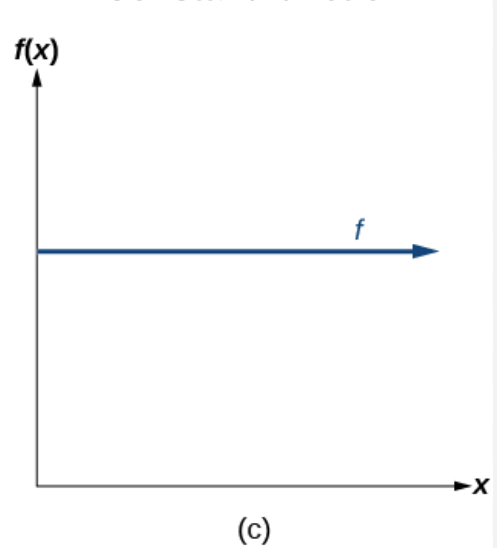
f(x)=c is what kind of graph?
constant (horizontal line)
f(x)=x² is what kind of graph?
quadratic (parabola)

f(x)=x³ is what kind of graph?
cubic
f(x)=square root of x is what kind of graph?
square root
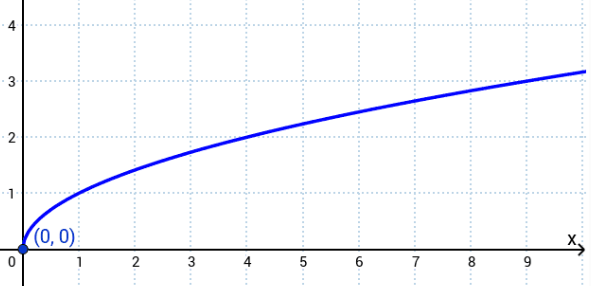
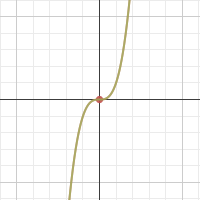
f(x)=cube root of x is what kind of graph?
cube root
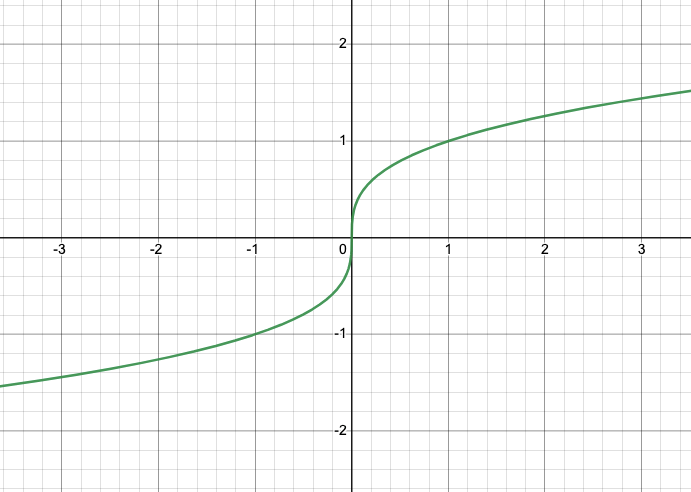
f(x)=|x| is what kind of graph?
absolute value

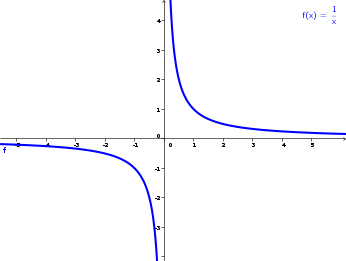
f(x)=1/x is what kind of graph?
reciprocal
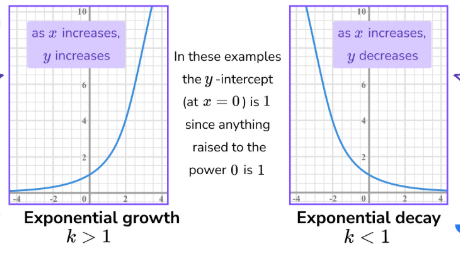
f(x)=a^x is what kind of graph?
exponential
f(x)=logax is what kind of graph?
logarithmic
mass (integral) formula
the integral from a to b of density

shell method formula
the integral from a to b of 2(pi)r times (top-bottom)
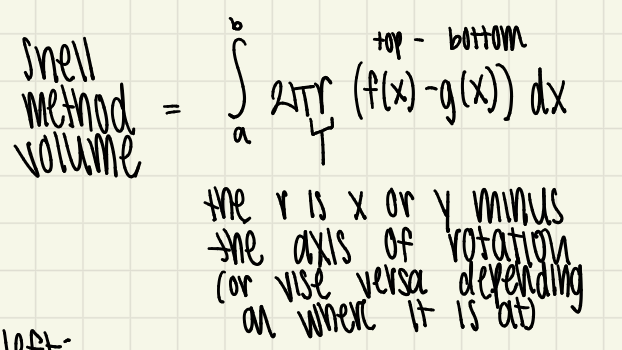
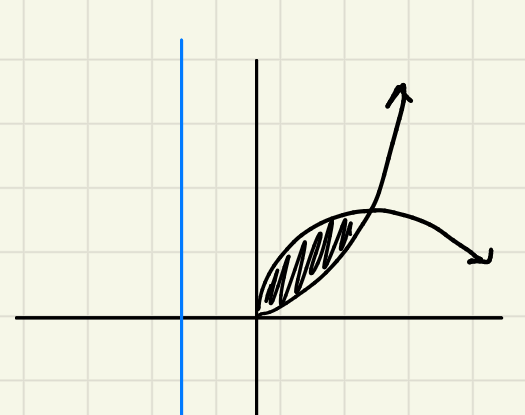
for the shell method: how would you write your “r” if the axis of rotation is to the left of the region?
r= x-axis of rotation
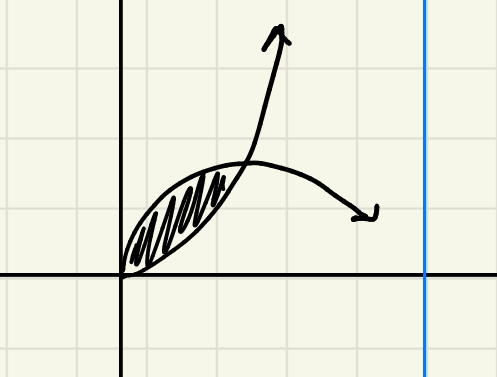
for the shell method: how would you write your “r” if the axis of rotation is to the right of the region?
r= axis of rotation -x
for the shell method: how would you write your “r” if the axis of rotation is below the region?
r=y- axis of rotation
for the shell method: how would you write your “r” if the axis of rotation is above the region?
r= axis of rotation - y

for the shell method the bounds will be ________ (perpendicular/parallel) to the axis of rotation?
perpendicular
when the axis of rotation is vertical: dx
when the axis of rotation is horizontal: dy
for the washer method the bounds will be ________ (perpendicular/parallel) to the axis of rotation?
parallel
when the axis of rotation is vertical: dy
when the axis of rotation is horizontal: dx
washer method formula
the integral from a to b of pi times the outer radius squared minus pi times the inner radius squared
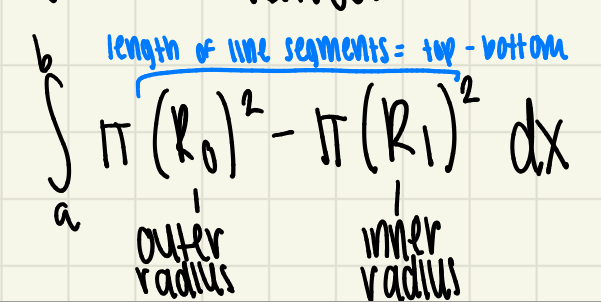
speed (from velocity function) formula
|v(t)|
disk method around the x-axis formula
the integral from a to b of pi times r(x)²

disk method around the y-axis formula
the integral from a to b of pi times r(y)²

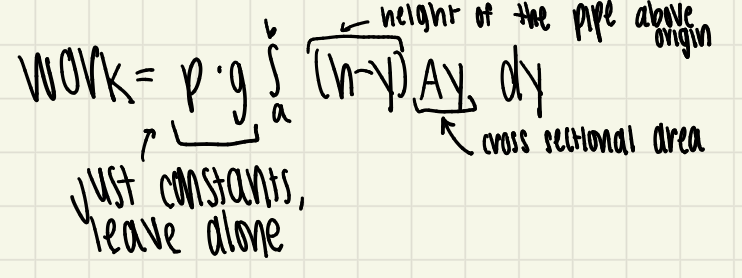
work formula