Cells & Microscopy Paper 1A CSA
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Where can the entire genome of an organism be found?
In the DNA present in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell

What is the maximum diameter of the nucleus in the cell labelled X? (When you use a ruler to measure image size, the image size is 2 cm)
10 μm
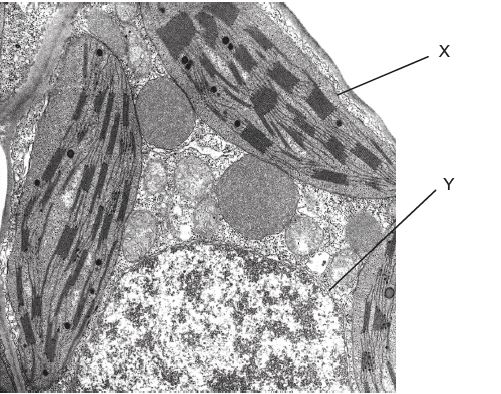
Which features do the two structures labelled X and Y have in common?
They are surrounded by a double membrane.
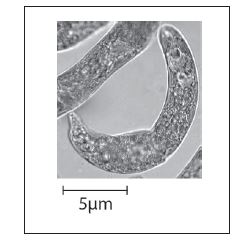
What is the magnification of the image?
× 3000
Which cell component is found in eukaryotic cells but not in prokartyotic cells?
Mitochondria for respiration
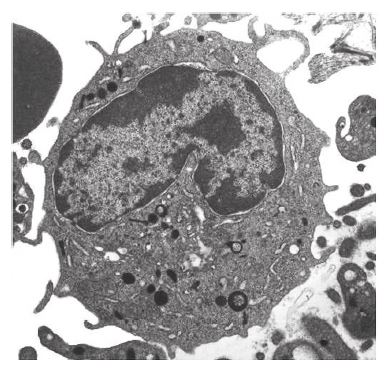
Which features can be found both within this cell and in a photosynthetic bacterium?
70S ribosomes
Which structure is found in animal cells?
Mitochondria

The images of the radiolarian, a single-celled marine organism, were produced using a light microscope (left) and a scanning electron microscope (right).
The resolution of the electron microscope is higher.
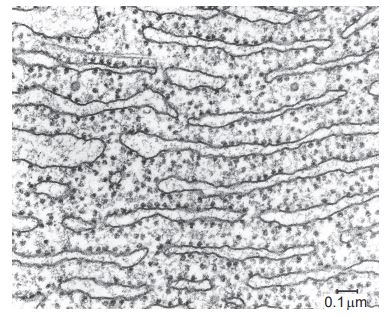
What function is performed by the part of the cell shown in the electron micrograph?
Synthesis of proteins
Which statement best contrasts light microscopes with electron microscopes?
Electron microscopes provide higher resolution than light microscopes, but specimens must be dead and chemically fixed.
Which statement best explains how fluorescent stains and freeze-fracture electron microscopy contribute differently to the study of cells?
Fluorescent stains allow visualization of specific proteins in living cells, while freeze-fracture electron microscopy reveals the distribution of membrane proteins in a split lipid bilayer.

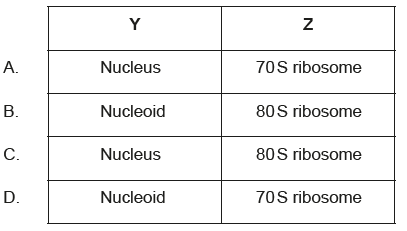
What are the structures labelled Y and Z?
Nucleoid and 70 S ribosome
Which is a feature of phloem sieve tube cells?
No nucleus
Which structures are only found in prokaryotic cells?
Flagella
A cell contains chloroplasts, plamsa membrane, and 80S ribosomes. What type of cell could it be?
Elodea cell
Which cell component arose first during the formation of the earliest cells?
Plasma membrane
More than 90 % of cellular cholesterol is located in the cell’s plasma membrane. What is the main role of cholesterol in the plasma membranes of mammalian cells?
To regulate fluidity
How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Eukaryotic cells are compartmentalized, whereas prokartyotic cells are not
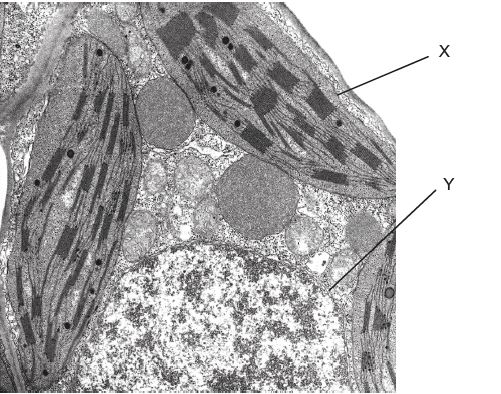
What is the name of the cell component labelled Y?
Nucleus
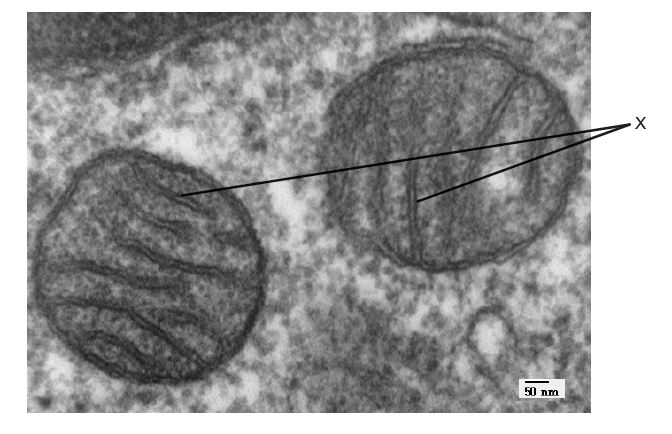
Which process is occurring on the structures labelled X?
Cellular respiration