Ms. Lusamba Mitosis and Cell Cycle Quiz
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is a chromosome?
A chromosome is a structure containing DNA.
Draw a chromosome
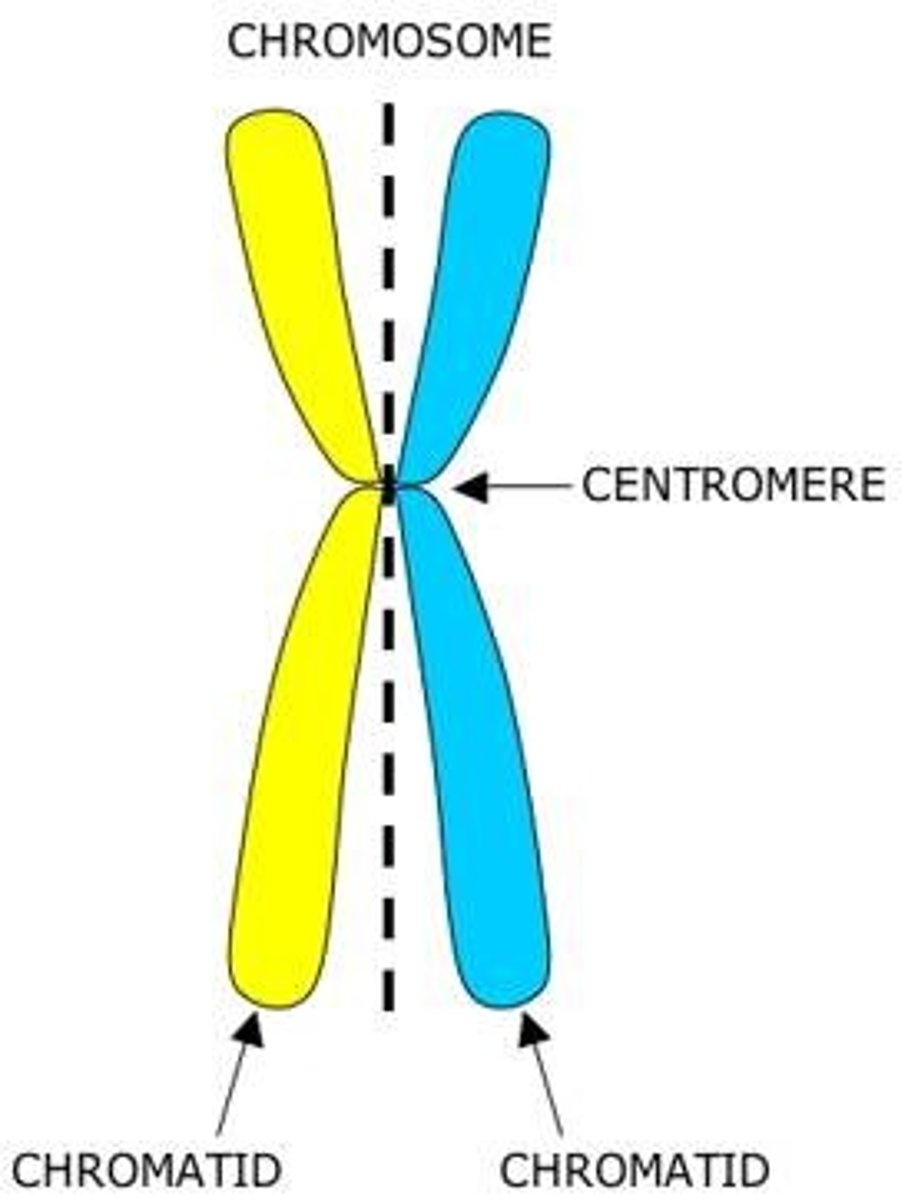
What is a chromatid?
Half a chromosome
Draw a chromatid
Just the yellow side or just the blue side

What joins chromatids into chromosomes?
Centromeres
What surrounds the nucleus?
The nuclear membrane
What connects to the spindle fibers?
Centrioles
What are the steps of the cell cycle?
G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis
What phases make up interphase?
G1, S, G2
What are the phases of mitosis? Which has early and late phase?
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Prophase has early and late
What happens in G1?
Cell increases in size, and enzymes, cytoplasmic organelles, and others double in number
What happens in S?
Replication of DNA
What happens in G2?
Cell assembles special structures
Cell spends ____% of it's time in interphase
90%
How can you identify interphase?
The nucleus is clear and surrounded by the nuclear membrane. Two centrioles are together outside the nucleus.
How can you identify metaphase?
Chromosomes line up in the middle along the metaphase plate
How can you identify prophase?
Centrioles are spreading apart, and spindle fibers stretch between them. The nuclear membrane is starting to come apart.
How can you identify anaphase?
Centrioles are on opposite sides of the cell (not to be confused with late prophase), and the spindle fibers are pulling chromatids apart from the middle of the cell
How can you identify telophase?
Cleavage furrow is visible, nuclear membrane is reforming, and chromosomes unravel
What is the nucleolus?
The part of the nucleus where chromosomes are
What happens in early prophase?
Nucleolus disappears, centrioles start to move to opposite sides of the cell, and a spindle of microtubules starts to form
What happens in late prophase?
Nuclear membrane fragments and microtubules enter the nuclear area. The spindle is completely formed. The spindles help separate the chromatids. The centrioles are at opposite sides of the cell.
What is another name for late prophase?
prometaphase
What happens in metaphase
The chromosomes are lined up in the middle of the cell. Each chromosome has a spindle fiber connected to its centromere
What happens in anaphase?
The microtubules shorten and pull the chromatids to opposite sides of the cell. Each side will have an equivalent and complete set.
What happens in telophase?
The nuclear membrane begins to reform. The spindle is disassembled, and the nucleus starts to become visible again. The cell "pinches" in.
How do the two nuclei at the end of mitosis differ?
They don't, they're identical
What is cytokinesis?
The division of the cytoplasm.
Cytokinesis usually overlaps with what phase?
Telophase
How does telophase work differently in plant cells?
Because of the cell wall, they cannot "pinch," so instead a cell plate forms across the middle of the cell, until there are two cells
What is a checkpoint in the cell cycle?
A control point in the cell cycle where the cell is signaled to "stop" or "go" to control the cell cycle
What are the three checkpoints?
G1, G2, Mitosis
Which checkpoint is most important?
G1
What are the potential results at the G1 checkpoint?
1) Cell gets told "go" and completes the cycle and divides
2) Cell gets told "stop" and exits the cycle. It is in the G0 phase
What is the phase when the cell doesn't divide and isn't a part of the cell cycle
G0
What happens at the G2 checkpoint?
DNA repair enzymes check the duplicated DNA. If it's a "go" then mitosis will start
What happens if the cell passes mitosis checkpoint?
It will go back to G1
What are some cells that are always in G0
Mature nerve cells and muscle cells
What are some cells that go to G0 but can be called back?
Liver cells