FBLA International Business RESEARCH
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
190 Terms
Globalization
Broadening set of interdependent relationships among people from different parts of the world divided into nations. [interdependent relationship between different countries]
International Business
All commercial transactions between two or more countries. Only exists when funds move across boarders. (ex) I bought my plane ticket to Italy from American Airlines- this was NOT considered international business because the funds went to the same country. If I bought my ticket from a foreign country it would be considered international trade.
Two Types of International Business and Differences Between them
Public = has shareholders
Private = does not have shareholders
In what ways does international business influence domestic operations?
Physical
Societal
Competitive
(ex) banks- amount of public companies are changing
Fiat- biggest Italian car producer 10% owned by son 10% US stock and 80% Italy
Why engage in international business?
Why is it important to study?
Expand sales
Acquire Resources (better resources, services, products)
Minimize Risk (diversity among diff countries taking advantage of business cycle)
Important to study because = today global events affect almost all companies everywhere.
Reasons for Growth in International Business/Globalization
1) Technology- increase and expansion
2) Transportation- quicker and lower costs
3) Increased Global Competition
4) Communication- control from afar
5) Consumer Pressure
6) Liberal govt policies on trade
7) Development of institutions that support Int'l trade
*essay
Modes of International Business
Importing & Exporting = (trade) merchandise is most common but services are also traded. (ex) merch: Italy exports wine, the physical finished product, to the US. (ex) service: tourism and transportation, turn key operations, licensing and franchising (bud wiser gave peroni license to sell bud wiser in Italy (licensing)
Investments = factors of production can be a direct investment (control- joint ventures) and portfolio investments (no control)
Two Types of Investments
Direct Investments (control) joint ventures- new activity started by 2 or more partners
Portfolio Investments (no control) stocks
Example of a French export would be a visit by a
**US citizen to Euro Disney in France
xxx French Citizen to Disneyland in the US
When one party allows another party the use of a trademark and assist that other party on a regular basis the arrangement is known as a
Franchise
MNE
Multinational Enterprise is a global approach to markets and production
Types of Ownership
Propritorship = one owner
Partnership = 2 or more owners
Cooperation
(all three of these could go global)
(ex) nestle chocolate brand is so globalized that you no longer associate it with one country (switzerland)
Offshoring
transferring production abroad (seen as controversial)
Antiglobalists 3 thoughts on Globalization
1) threats to national sovereignty
2) promotes growth that causes environmental stress
3) increase income unequally (skews income distribution)
Why is it important to understand cultural environments facing business?
It is important for companies to unlearns and be sensitive to constantly changing environments.
Major Cultural Issues Occur in International Business when:
Employees:
1) have subconscious reactions
2) assume all societal groups are similar
3) can't adjust / accept foreign culture
4) insensitive to consumer preferences
(ex) we eat at 6 in US in Italy they eat later. US news is on at 6 but is not in Italy
Cultural Factors
Behaviour affecting business
Identification and Dynamics of Cultures
Cultural Awareness
Strategies for dealing with cultural differences
Cultural Awareness (Attire, Religion, Language)
Attire: Italians dress more formal than US
Religion: Italians primarily Catholic
Language: Italians have two ways of speaking informal and formal
Culture
learned set of norms based on attitudes, values, and beliefs of a group of people (Points of reference: national, geographical, language, religion) * International business often changes cultures (ex) McDonalds has to change their menu in diff countries to adapt
Different types of cultures people belong to
national, ethnic, professional, and organizational
Difference between Ascribed versus Acquired Status
*on exam
Ascribed = status you cannot change (where you come from, gender, family, caste, ethic)
Acquired = can change status (religion, political affiliations)
Social Stratification Systems
Individuals Status with the culture
Ascribed Group Membership
Acquired Group Membership
United States "Values"
*he said important slide
1) Success (compentence)
2) Intolerance for discrimination of: Gender, Race, Age, Religion
3) US values seem radical to foreigners: It is important that int'l business spend resources to determine what foreign cultures can ethically/effictively conduct in business (ex) case study chapter 2 w/ Saudi
Common Cultural Differences:
Work Ethic, Materialism, Leisure (US not as relaxed as Italians) , expectation of success and reward, assertiveness and masculinity index (Japan vs. Sweden)
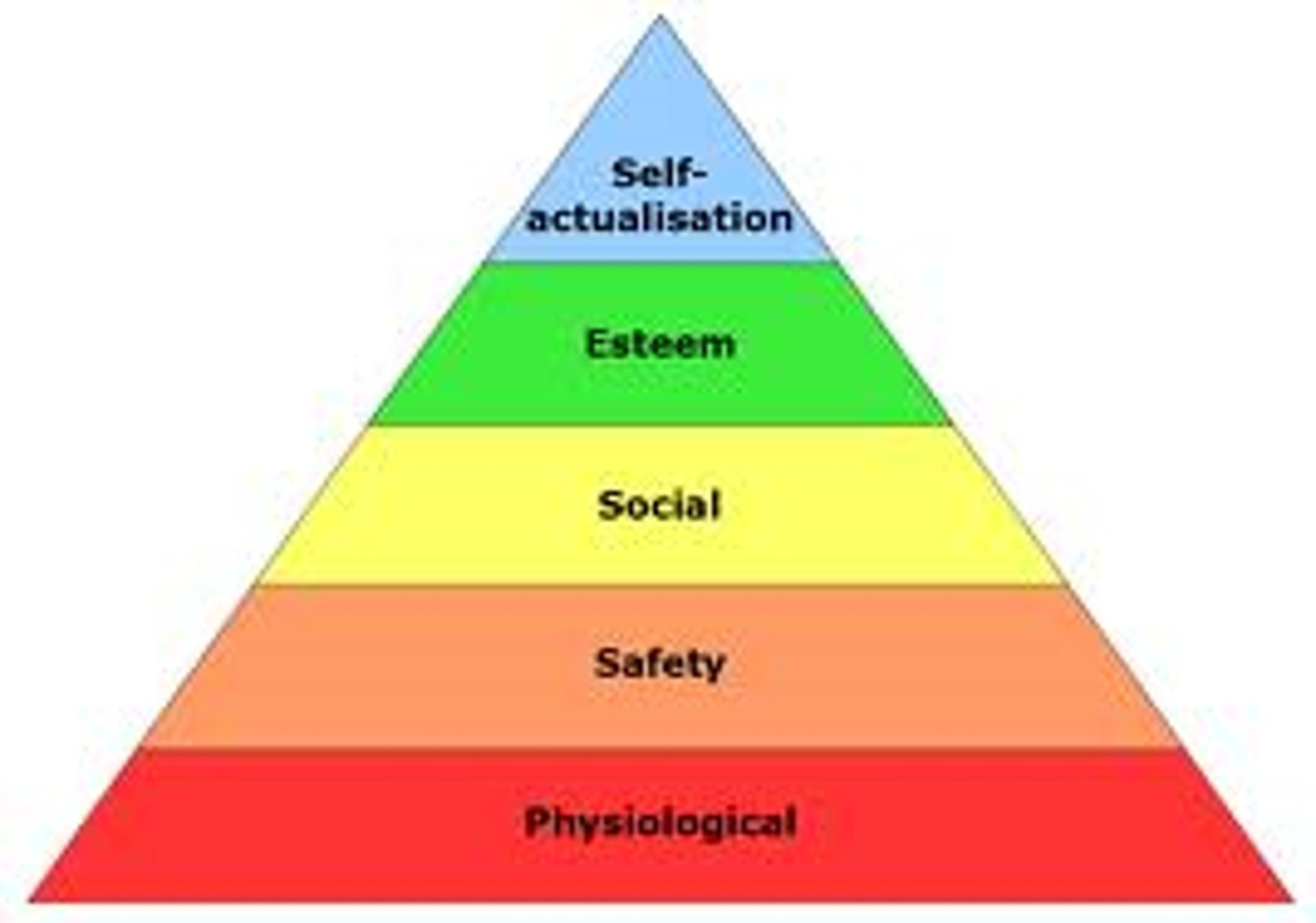
Hierarchy of Needs Pyramid
Physiological, Security, Affiliation, Esteem, Self-Actualization.
Once you achieve one level you are no longer motivated to achieve that level so you go to the next level. *in italy the most important is security of the job and security not being fired, Japan's most important is affiliation, US//UK is esteem
Relationship Preferences: Power Distance
Relationship between superiors and subordinates (Distance tends to be greater for Italy compared to US)
Relationship Preferences Individualism vs. Collectivism
US = very individualistic
Japan = collective
Relationship Preferences: Risk Taking Behaviour
1) Uncertainity / Avoidance
2) Trust (ex) you have to pay within 30 days that trust is gone if you don't pay
3) Future Orientation (US sees future others focus is the past)
4) Fatalism
(Certain countries in the world accept greater risks US is more risky than Italy) - US stock exchange: 5 million companies where as Italy has 250 companies
Mono chronic (how we process information)
People are expected to do one thing at a time, and they will not tolerate lateness or interruptions. - UNITED STATES
Poly chronic (how we process information)
where time is seen as cyclical (reoccuring) , punctuality is unimportant and interruptions are acceptable - ITALY
Low Context Culture (how we obtain information)
Immediately to the point (ex) I want to buy a pair of shoes. I call and am able to immediately pick them up later that day. (UNITED STATES)
High Context Culture (how we obtain information)
Not as immediate to the point (ex) I call to get a price on new tires for my car but end up chatting to the sales person about the upcoming soccer game for fifteen minutes then move on to my question about the tires. (SAUDI ARABIA)
Cultural Orientation (diff attitudes towards diff cultures) : Polycentrism
Sees many counties as the center and conducts business in the way of the local people (regional managers conduct business in a local manner)
Cultural Orientation :(diff attitudes towards diff cultures) Ethnocentrism
Belief that ones own culture is superior (ignores important local factors) (ex) President of Toyota thinks their country is better than all others. Ethno = Race
Cultural Orientation: (diff attitudes towards diff cultures)Geocentrism
Balanced between home and host country (ex) Home country of Apple is US and Host country of Apple is Italy
****START CHAPTER 3
Political System
When many people organise the government. Integration of the parts of society into a viable functioning unit.
Leaders of Italian Government
President = Mattarella [unlimited 7 year terms]
Prime Minister (Presidente del Consiglio) = Renzi [unlimited 5 year terms]
Political Ideology
The body of ideas, theories, and aims that constitute a sociopolitical program. Most modern societies have different ideologies. Brings the people and the political parts together.
Two Extreme Types of Ideologies
1) Democracy = system of govt that is controlled by the people through voting
2) Totalitarism = centralized government that is dictatorial
Democracy
-explain freedoms, elections, terms
Freedom of:
1) opinion
2) press
3) expression
4)organization
Elections (Italians do not directly vote for parliament) Limited Terms for Elected Officials (Exists in Italy also). You get to be apart of the decision making process.
Independent Court System
High regard for individual rights
Respect for property
Non Political Bureaucracy
Politicians make the decisions
Indicators of Political Rights
1) Fair and Competitive Elections
2) Ability to vote for a representative with real power
3) Ability to organize political parties
4) Protects the rights of the minorities
Indicators of Civil Liberties
1) Freedom of the Press
2) Equality for all individuals
3) Social Freedoms
4) Freedom from government indifference or corruption
*(A persons right to only be subject to laws for the good of the people)
Who governs the Vatican?
No separate government. All powers are given to the Theocratic Relationship (Italy) TOTALITARIANISM
Totalitarianism
1) Theocratic (God/religious) or Secular (non religious)
2) Order imposed through Military power
3) Single party in power
4) Neither recorginizes or permits opposition (resistance to totalitarianism rule)
Fascism or Communism
Four People who Formed Italy
Garibaldi = general
Cavour = Prime Minister
King Victor Emanuel II = King
Mussolini = Former Dictator
What was the last area to be added to Italy?
Rome 1870
Who convinced King Victor Emanuel II to give him the power?
Mussolini (dictator)
When did Italy enter into WWI and WWII?
WWI = between allies (UK, US 1917, Italy 1915) and central powers (Germany, Austria, Hungary)
WWII =Axis Powers (Germany, Italy 1940 and Japan) Allie Powers (UK, France, Australia, US1941)
April 25th Significance
Italian Holiday Representing the end of WWII
Italy: Institutions
Presidente della Republica = Elected by Parliament
President of the Council of Ministers = No direct elections
Proportional System
several members of parliament are to be elected per area. citizens vote (if you get 10% of vote you get 10% of the seats) US has this
Majoritarian System
only one member of parliament is to be elected per constituency. believing in decision by a majority.
Italy History
1) Started as a Kingdom
2) Venice
3) Roma
4) WWI
5) Mussolini (Fascism/Dictator)
6) WWII
7) Mussolini Arrested/Distrusted
8) Armistice (an agreement made by opposing sides in a war to stop fighting for a certain time; a truce)
9) Liberation (freedom from dictatorship)
10) Republic (king in exile)
11) Constitution
Three Parties in Italy
1) PD (democratic party)
2) PDL (centre right party)
3) 5 Star
Political Risks for International Business
Opinions of political leadership
Civil Disorder
External relations home / host country
Common Law
Uncodified Traditional / Precedent U.S. and U.K. (Based on tradition / how people behave normally) US has a lot of very big contracts but Italy does not
Civil Law
Codified Rules of Business are apart of that countries code.
Roman Law is the basis of Civil Law. Do not have the right to negotiate.
Civil Codes
Set of rules/ways to behave
Theocratic Law
Based on religious precepts
(Sudan/Pakistan)
Legal Issues for International Business
1) Worker relations
2) Employment practices
3) Antitrust (fair business practices) Prohibitations
4) Contractual Relationships
5) Environmental Practices
6) Patents, Trademarks, Intellectual Property Protection
7) Taxes and reporting requirements
Antitrust
Someone is prevented from having an extreme power (ex) Apple can not buy microsoft)
*****Chapter 4
Economic Issues for International Business
1) Type of economic system of the country
2) Market size, growth potential, and stability
3) Is the company's industry in public or private sector?
*important to know the other countries economic standpoint when doing international business
4) Govt. views foreign capital as competition or partnership with locals
5) Govt. controls private enterprise?
6) Is private sector expexted to help govt formulate economic objectves?
Key Economic Forces: Factor Endowments
Physical land, labor, materials we have. Countries with more of these tend to be more prosperous.
Key Economic Forces: Economic Indicators to tell how a country is doing
1) Growth
2) Inflation
3) Surpluses (Produce more than you consume)
4) Deficits
Key Economic Forces: Availability of Economic Infrastructure
(ex) access to hills, mountains, railroads, ect.
Factor Conditions: Inputs to the Production Process
1) Physical Resources
2) Human Resources
3) Infrastructure
4) Capital
5) Knowledge
Demand Conditions:
Market Potential
Market Potential:
1) Composition-needs of buyer
2) Size
3) Growth
Gross National Income (GNI)
*important slide
-The market value of final goods and services newly produced by domestically owned factors of production.
-GNI measures income received by a country both domestically and from overseas.
-Tool to measure a country from one economical point of view
-US uses GNI
-measured by % change
Market Value
What you can sell the good for
Final Good
A good or service consumed by the final user. (ex) Pillar done but house is not complete yet. This is NOT a final good
Newly Produced
(ex) If i sell a house (new) it benefits the Italian Govt, If it is used it does not benefit the Italian Economy
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
*important slide
- The value of production that takes place within a nation's borders (both domestically and foreign factors of production)
-Italy uses GDP
-has to be produced in home country in order to count towards GDP for that country
(ex) Ford produced in US = US GDP
Ford produced in Mexico = Mexico GDP
Difference between GNI and GDP
GNI = Considers the owner not the place of production. It focuses on how much a country produces and considers them only once.
GDP = Considers the place of production Instead of using the actual number they are provided as a percent change (ex) Italy has s GDP of 1.3% that means it went up in production by 1.3% since last year
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
*important slide- understand and be able to repeate
-The number of units of a currency required to buy one unit of another currency would buy. (How many units of one currency to you need to buy the same thing?)
-Tells how strong your currency/economy is
(ex) China you can buy a lot of things with a little bit of money that is why jobs get paid less
(ex) How many USD or Euros do you need to purchase something?
Market Economy
-Resources are primarily owned and controlled by the private sector
-Prices are determined by supply and demand (the market)
Command Economy
-Economic activity, including pricing and production decisions, determined by a central government plan
-Government owns and controls all resources
-Prices are determined by the government
Mixed Economy
-Some degree of government ownership and control
-No economy is purly market or command
-Europe is in the middle of command and market but moving more toward the market econ
Inflation
When you need more money to buy the same thing (the power/value of the currency goes down)
Surpluses, Deficits,
Balance of Payment
surplus = the amount of something left over when requirements have been met.
Deficit =an excess of expenditures over revenue in a given time period
Balance of Payment =encompasses all transactions between a country's residents and its nonresidents involving goods, services and income
Internal Debt
the part of the total government debt in a country that is owed to lenders within the country.
External Debt
the part of the total government debt in a country that is owed to foreign lenders
*****Start Chapter 5
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
an investment made by a company or entity based in one country, into a company or entity based in another country. (ex) an American company taking a majority stake in a company in China
-you have control in direct investment you do not have control in portfolio investment
Multinational Enterprise (MNE)
a corporation that has its facilities and other assets in at least one country other than its home country
-MNEs need to understand the impact of FDI in home / host country
What is the economic impact of a Multinational Enterprise?
-If i import something the balance of my country goes down
-If i export something the balance of my country goes up
Ethical Behavior 2 objectives
- develop competitive advantage
-avoid being perceived as irresponsible
-countries differ in ethical behavior
Relativism
the doctrine that knowledge, truth, and morality exist in relation to culture, society, or historical context, and are not absolute.
Normativism
universal standards of behavior
Bribes are used to
1) get govt. contracts
2) get officials do what they should do anyway
Problems with Bribery
1) affects performance of company and country
2) ruins government authority
3) damage reputations when disclosed
4) increases cost of doing business
Ethics and the Environment
-Sustainability
-Global Warming: the Kyoto protocol
****** Chapter 6
General Types of Trade Theories
-Descriptive
-Prescriptive
Descriptive
the natural order of trade (Laisses-Faire) let them do it no restrictions
Prescriptive
Government should interfere
International Trade Theories
1) Mercantilism
2) Absolute Advantage*
3) Comparative Advantage*
4) Factor proportions
5) Product life Cycle
6) Country similarity
Mercantilism:
dates
how it wealth measured
who?
goal?
-International Trade theory from 1500 to 1800 (most historical approach)
-Nations wealth is measured by its holding of treasure (gold)
-Marco Polo
-Nations Maximize exports Minimize imports
-Advantageous: Trade surplus with "colonies"
(ex) US exports to argentina but does not buy from argentina. eventually argentina will no longer be able to pay US
Mercantilism
favorable balance of trade
Favorable balance of trade exports > imports
Unfavorable balance of trade exports
Neomercantilism
countries that try to run favorable balances of trade by exporting a lot and importing as little as possible they do this for social or political gains (ex) china
Absolute Advantage
**ESSAY
dates?
how is wealth measured?
who?
goal
-1776
- Wealth is measured by how many goods are available to citizens
-Adam Smith "Invisible hand"
-Goal is to maximize goods and services available to citizens (not treasure) all around the world
-Different countries produce some goods more efficiently than others (ex) Italy & wine, UK and Germany & beer, you cannot produce certain goods in certain areas