C2 Atoms, elements and compounds
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What is an element?
a substance made from only one type of atom, they are pure substances that can’t be broken down any further
What is an atom?
the smallest unit of matter
What is a molecule?
group of two or more atoms bonded together. the atoms can be the same or different
What is a compound?
a substance made from two or more elements chemically bonded together
What is a mixture?
a combination of two or more substances that aren’t chemically bonded together
Draw the structure of an atom
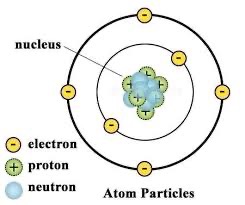
Describe the structure of an atom
atoms contain a positively charged nucleus made of positively charged protons and no charge neutrons surrounded by negatively charged electrons arranged in shells
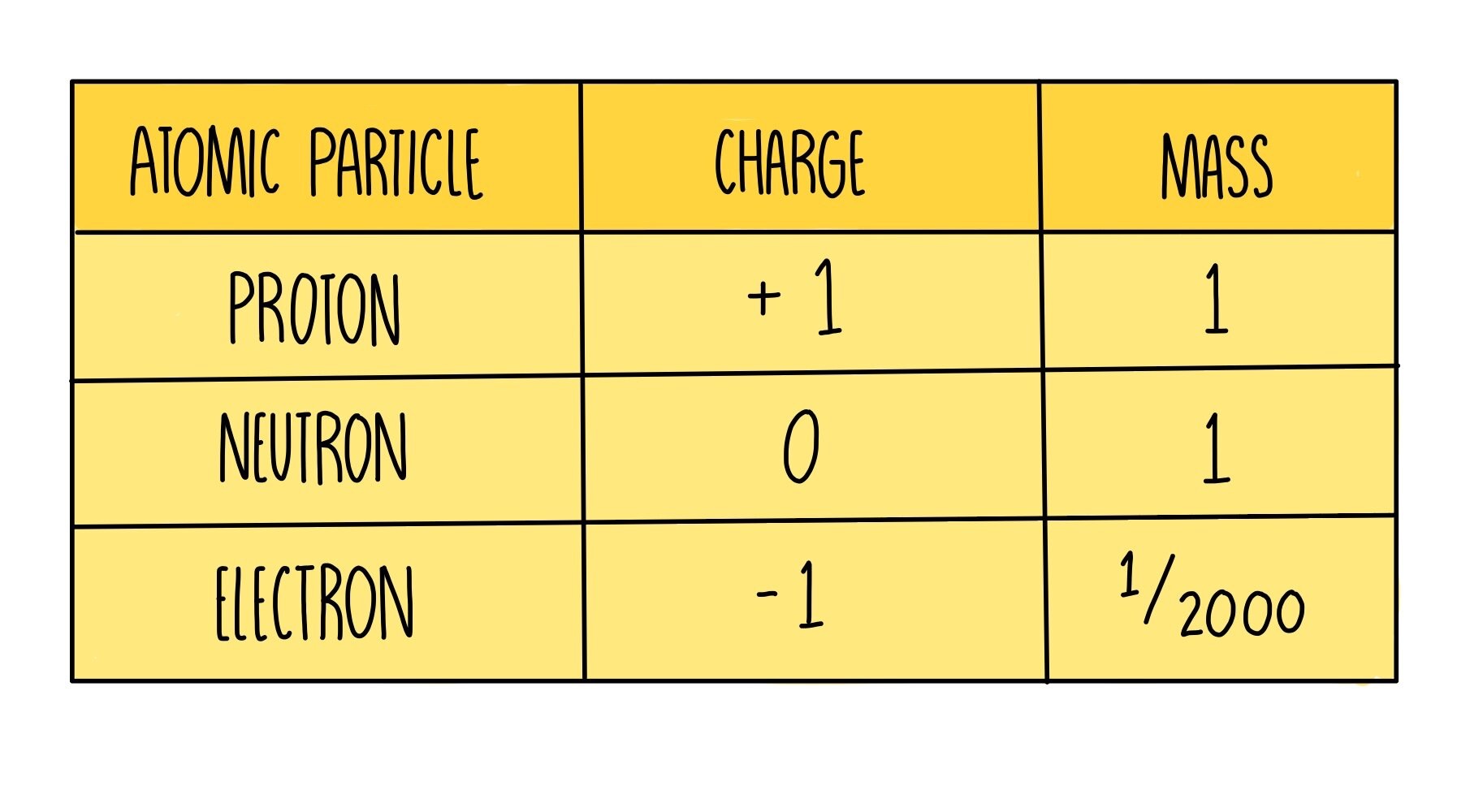
Fill in this table
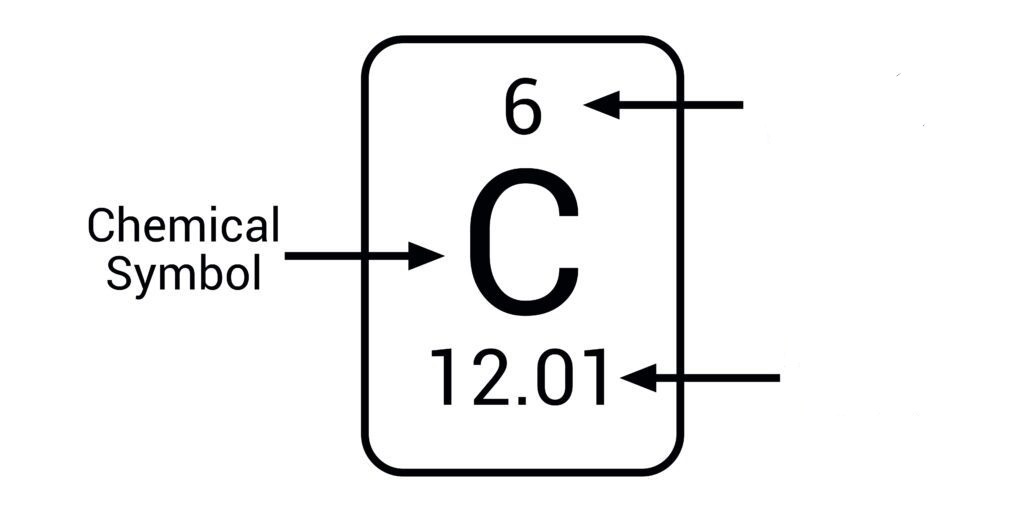
Which of these is the atomic number and which is the mass number?
Smaller number=atomic number
Bigger number=mass number
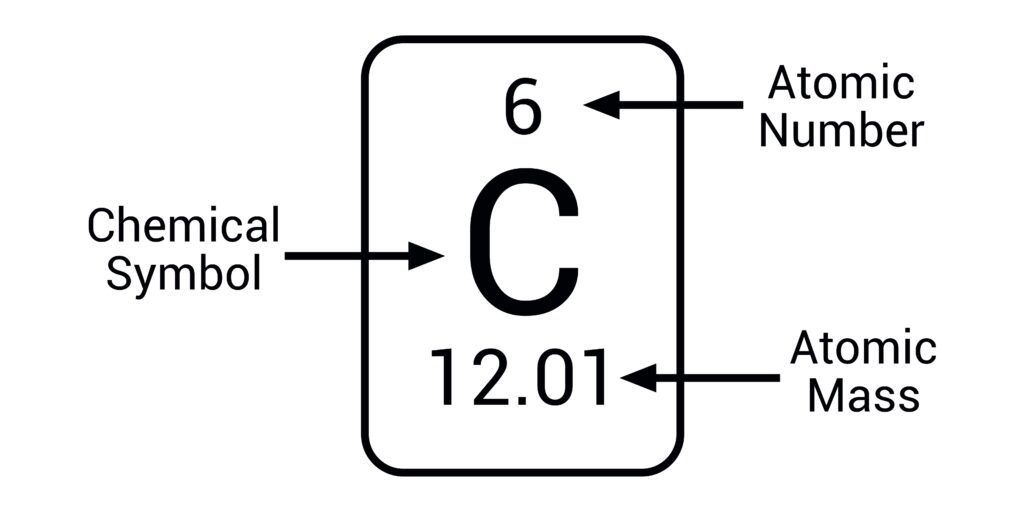
What is the proton number/atomic number?
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
What is equal to the number of protons?
number of protons=number of electrons
What is the mass number/nucleon number?
the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
How to find number of protons, electrons and neutrons?
protons= atomic number
electrons=number of protons (atomic number)
neutrons= mass number - atomic number
What is the electron configuration based on?
atomic number
Electron configuration rule
1st shell=2
2nd shell=8
3rd shell=8
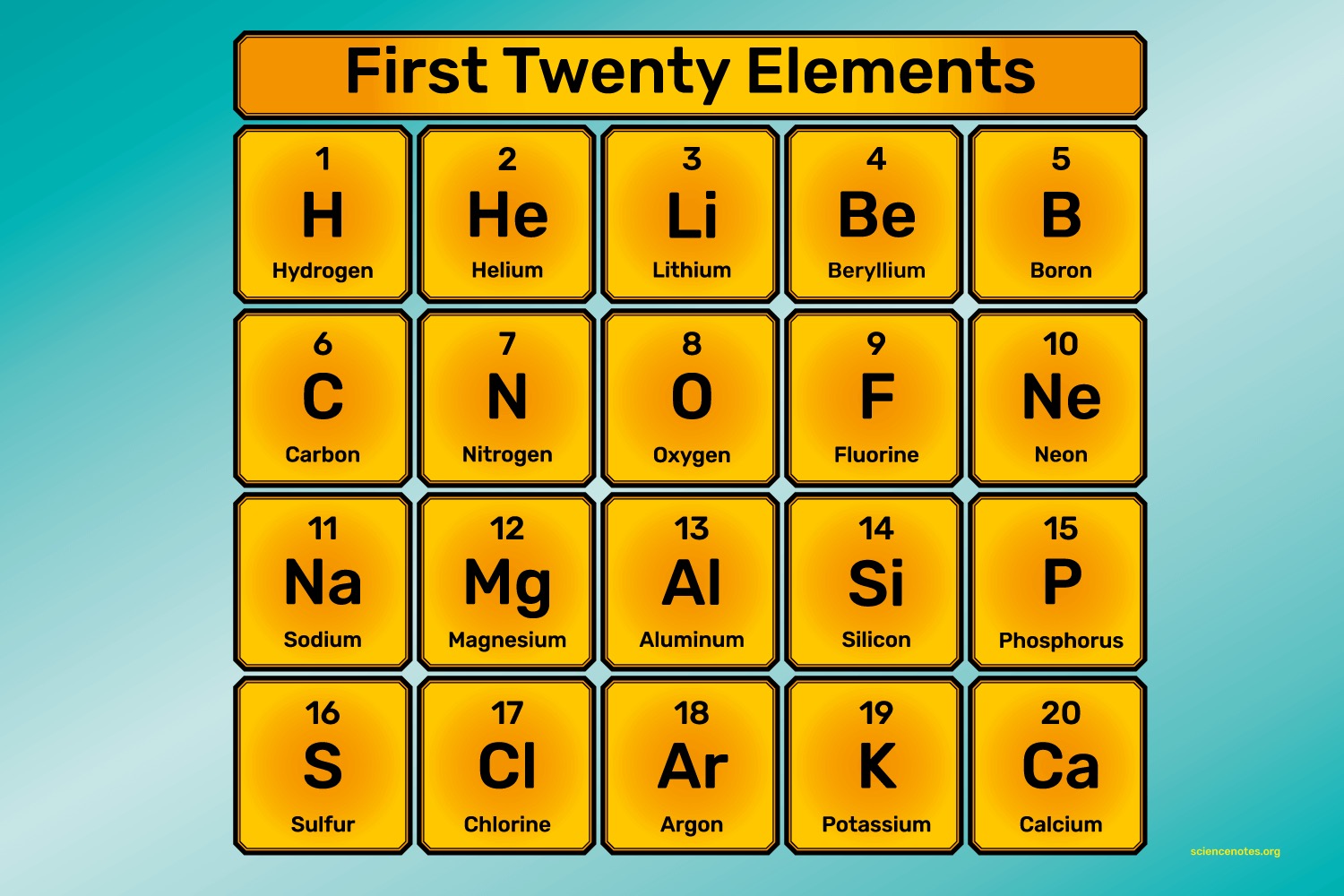
Find the electron configuration for the first 20 elements
Hydrogen (H): 1
Helium (He): 2
Lithium (Li): 2, 1
Beryllium (Be): 2, 2
Boron (B): 2, 3
Carbon (C): 2, 4
Nitrogen (N): 2, 5
Oxygen (O): 2, 6
Fluorine (F): 2, 7
Neon (Ne): 2, 8
Sodium (Na): 2, 8, 1
Magnesium (Mg): 2, 8, 2
Aluminum (Al): 2, 8, 3
Silicon (Si): 2, 8, 4
Phosphorus (P): 2, 8, 5
Sulfur (S): 2, 8, 6
Chlorine (Cl): 2, 8, 7
Argon (Ar): 2, 8, 8
Potassium (K): 2, 8, 8, 1
Calcium (Ca): 2, 8, 8, 2
In a periodic table, what is each row/going across called?
a period
In a periodic table, what is each column/going down called?
a group
What is group VIII (8) called and what do they have?
noble gases have a full outer shell
What does the group number in Groups I to VII (7) tells you?
the number of electrons in the outer-shell
What does the period number tell you?
the number of occupied electron shells
What is an isotope?
atoms of the same element that have the same number of electrons and protons but different number of neutrons
Why do isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties?
because they have the same number of electrons in the outer shell and therefore the same electronic configuration
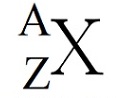
Interpret this symbol
X=element symbol
A=mass number
Z=atomic number
What is the relative atomic mass?
the average mass of atoms of a chemical element compared to one twelfth of a mass of carbon-12
How to calculate the relative atomic mass?
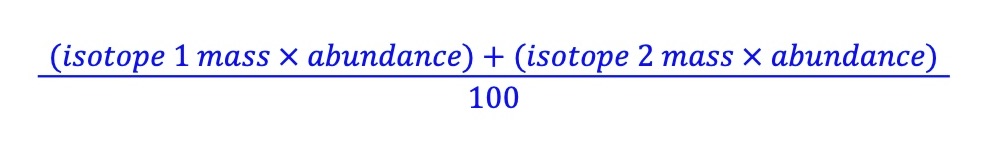
What is an ion?
an atom or molecule with an electrical charge due to loss or gain of an electron
What is the charge of an atom to start with?
neutral because there are the same amount of positive protons and negative electrons
What is an cation?
positive ions formed from the loss of an electron from a metal
How is a cation formed?
A metal always loses electrons to get a full outer shell, this means it ends up with more positive protons than negative electrons, the overall charge of the particle is now positive
What is an anion?
negative ions formed from the gain of an electron to a non-metal
How is an anion formed?
A non-metal always gains electrons to get a full outer shell, this means it ends up with more negative electrons than positive protons, the overall charge of the particle is now negative
What is an ionic bond?
a strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
-electrostatic attraction is the bond created between atoms/molecules of opposite charge
What do ionic bonds occur between?
a metal and non-metal/cation and anion
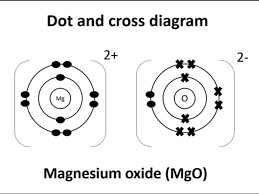
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for MgO
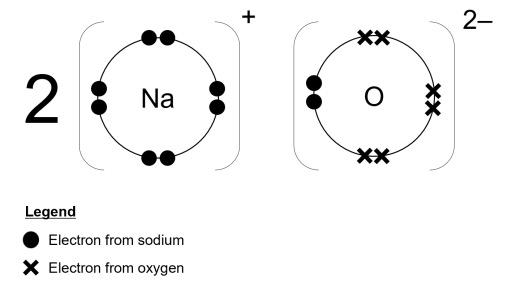
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for Na2O
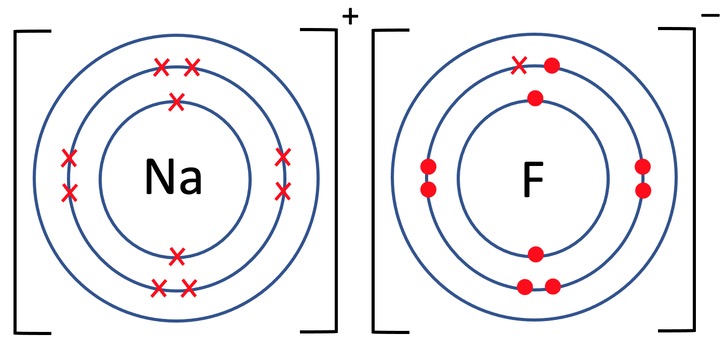
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for NaF
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for Al2O3

What are the properties of ionic compounds?
-high melting points and boiling points
-good electrical conductivity when aqueous or molten and poor when solid
-generally soluble in water
Explain why ionic compounds have high melting points and boiling points
the ionic bonds have very strong electrostatic attraction so more energy is needed to overcome them and change state
Explain why ionic compounds are good electrical conductivity when aqueous or molten and poor when solid
-good electrical conductivity when aqueous or molten because the ions are free to move around and carry charge
-poor conductor when solid because the ions are fixed in position and can’t move from one place to another
What is a giant lattice structure of ionic compound?
a regular arrangement of alternating positive and negative ion
What is the overall charge of a giant lattice structure of ionic compound?
neutral
Draw a giant lattice structure for sodium chloride
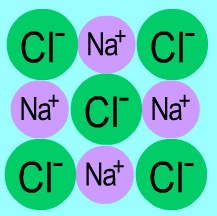
What is the overall charge for a giant lattice structure for sodium chloride?
neutral
What is a covalent bonding?
the sharing of electrons between two non-metals formed when a pair of electrons is shared between two atoms leading to noble gas electronic configurations
What is a covalent bond?
the electrostatic attraction between positive nuclei and negative shared electrons
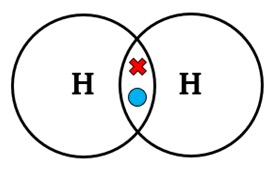
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for H2
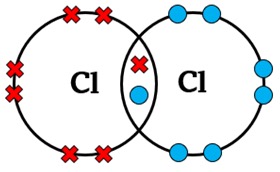
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for Cl2
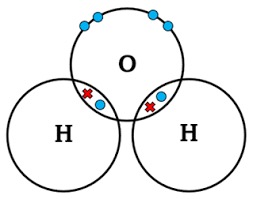
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for H2O
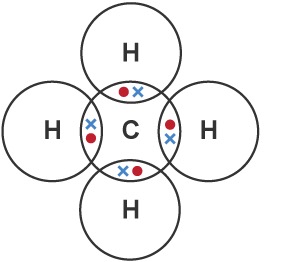
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for CH4
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for NH3
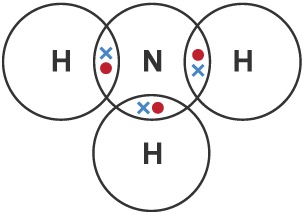
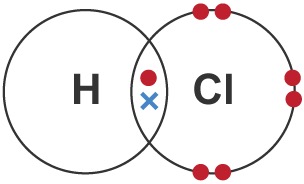
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for HCl
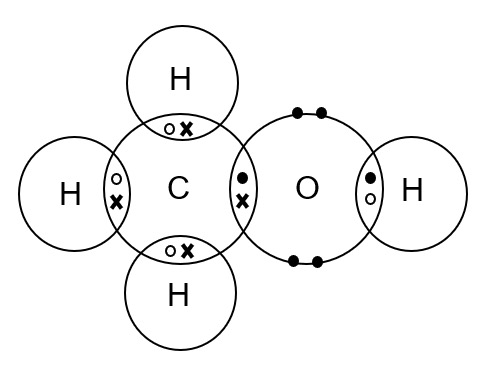
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for CH3OH
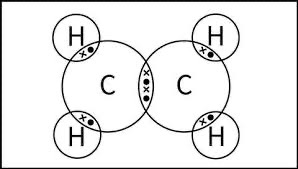
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for C2H4
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for O2
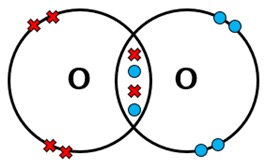
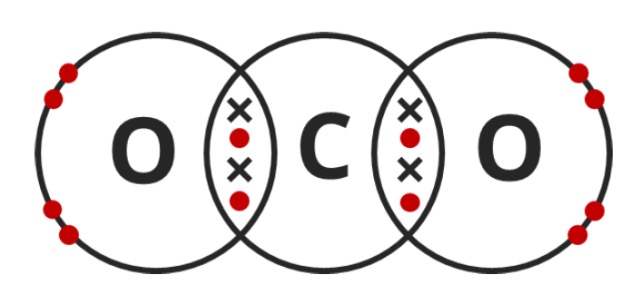
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for CO2
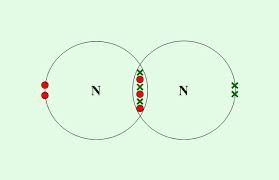
raw a dot-and-cross diagram for N2
What are the properties of simple molecular compounds (covalent)?
-low melting points and boiling points
-poor electrical conductivity
Explain why simple molecular compounds (covalent) have low melting points and boiling points
the covalent bonds within the molecules are very strong and hard to break but the forces between the molecules called the intermolecular forces are weak and need little energy to break and change state
Explain why simple molecular compounds (covalent) are bad electrical conductors
there are no free ions to carry charge
What is a giant covalent structure?
a substance where large number of atoms are held together by covalent bonds forming a strong lattice structure that extends itself in all directions
What is the giant covalent structure for diamond like?
Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to 4 other carbon atoms
-its structure is a tetrahedral 3D shape
Draw the giant covalent structure for diamond
Properties of diamonds and why
-hard due to many strong covalent bonds
-high melting point and boiling point
-doesn’t conduct electricity
What are diamonds used in? + why
cutting tools because its very hard due to rigid structure held together by strong covalent bonds
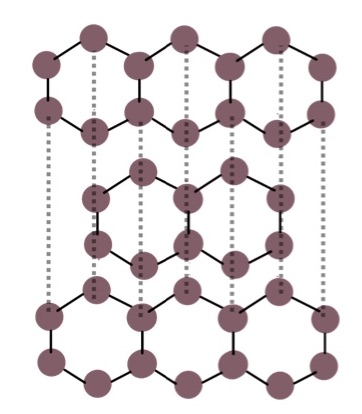
What is the giant covalent structure for graphite like?
Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to 3 other carbon atoms
-its structure consists of layers of hexagonal rings with no covalent bonds between the layers
Draw the giant covalent structure for graphite
Properties of graphite and why
-Soft because the layers are connected by weak intermolecular forces so they can slide over each other
-high melting and boiling points
-can conduct electricity as one electron from each carbon atom is delocalised and can carry charge
What is graphite used in? + why
lubricant-slippery as the layers can slide over each other due to weak intermolecular forces
conductor-can conduct electricity due to delocalised electron
What is the giant covalent structure for silicon(IV) oxide (silicon dioxide), SiO2 like?
-each silicon atom is covalently bonded to 4 oxygen atoms
-each oxygen atom is covalently bonded to 2 silicon atoms
What are the similarity between diamonds and silicon(IV) oxide?
-high melting points and boiling points- both have strong covalent bonds which require a lot of energy to break
-don’t conduct electricity- both don’t have free electrons or ions to move and carry charge
-hard and rigid-both have atoms bonded in a tetrahedral arrangement
What is metallic bond?
the electrostatic attraction between the positive ions in a giant metallic lattice and a ‘sea’ of delocalised electrons
What is the process of metallic bonding?
the delocalisation of outer electrons from the metal atoms
What does metallic bonding look like (diagram)?
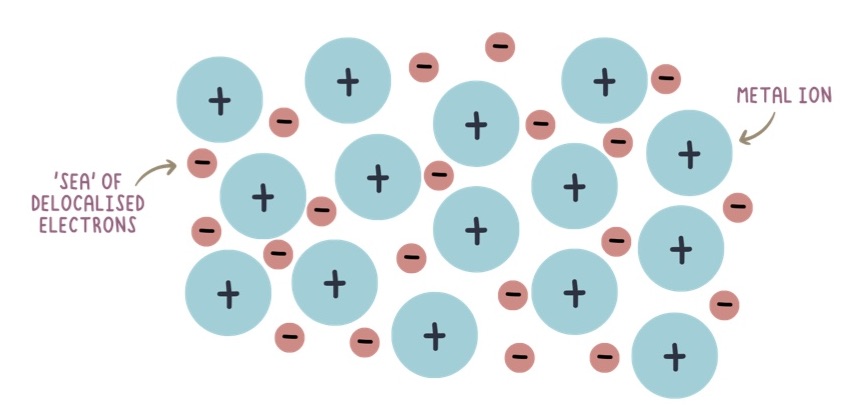
Why can metals conduct electricity?
the delocalised electrons can move around structure and carry charge
Why are metals malleable and ductile?
the positive ions are arranged in layers with a regular arrangement so the layers are able to slide over each other
Why do metals have high melting and boiling points?
strong electrostatic attraction between negatively charged electrons and positive metal ions so require a lot of energy to overcome the strong metallic bond