Identity Theory
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Define type identity theory
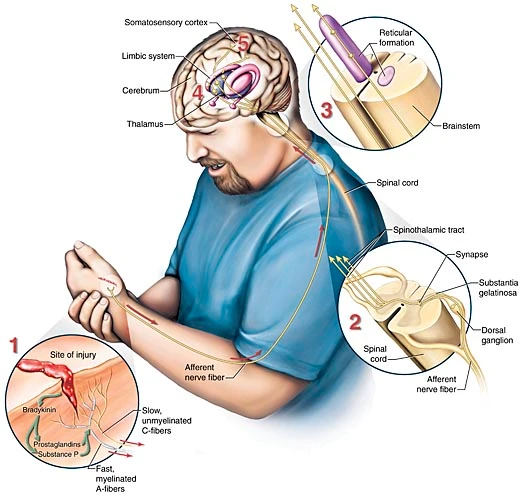
Belief that all mental states are identical to brain states although ' mental state ‘ and ‘ brain state ‘ are not synonymous . They are not analytically reducible they are ontologically reducible

What is the difference between analytic and ontological reduction ?
Analytic - the statement “ I’m angry translates to I’m shouting and kicking
Ontological - the statement “I’m angry “ not the same as neurons firing form my brain
Scientific research can show they’re the same
What does it mean to be philosophically complete
The most simple yet still complete theory is the best . However it still needs to explain everything
How is ontological reduction different to the type of reduction used by behaviourists ?
Behaviourism is an analytic reduction as it reduces behaviour to dispositions referring to certain emotions such as sadness , happiness in which behaviour such as crying or smiling is used to justify behaviourism

what is the type type identity theory
Mental states are brain states and each type of mental state can be defined with a type of brain state . Fully understood and reducible as a specific brain state
E.g. Pai
n = firing c fibres
Happiness = diffusion of dopamine /serotonin
Strength and weakness of type type identity theory
Strength - explanatory power
Weakness - multiple realisability
what is the type token identity theory
Belief that a specific mental state can be realised by different brain states

Strength and weakness of type token identity theory
Strength - flexible
Weakness - lacks explanatory power

what is the token token identity theory
Belief that every thought is unique , every brain state therefore unique
weakness of token token identity theory
lacks any explanatory power
Explain the criticism of indivisibility
Descartes claims mind not divisible , brain divisible therefore cannot be the same
Explain the criticism of conceivability
A priori
P1. It is conceivable and therefore possible for a being with different physical constitution to have same thoughts/sensations
P2. Inconceivable , therefore impossible for something to have and not have a certain property
C. Mental properties can’t be the same as physical properties

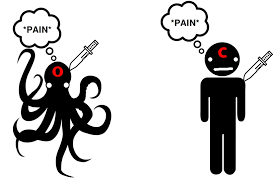
Explain the criticism of multiple realisability
P1. Type identity theory claims mental states are identical to brain states
P2. If type identity theory is correct mental states will always have a specific brain states
P3. However mental states can be conceived as different brain states in different species like aliens or octopuses
P4. Therefore , we can conceive of mental states being realised in multiple different brain states
C1. Mental states are not always identical to brain states
C2. Type identity theory fails

Define supervenience
x supervenes on y if there are no two metaphy
sically possible situations with the same y fact but different x facts
for example - the picture on a tv depends on pixels , in every universe will always depend on it
Give an example of supervenience
Chemistry supervenes on physics
Psychology supervene on biology

What is the common mistake with supervenience ?
x does not cause y

What is the name of a universe with the same physical facts but different phenomenal facts ?
Zombie universe
define ontological reduction
Mental states are brain states but the language we use to talk about mental states cannot be translated into neuroscientific language
Define a posteriori necessities
Propositions which are true in every possible world and are discovered by science / experience
E.g. water is H20
Mind type identity theorists think identities between mental and brain states are a posteriori necessities