Oxidation / Reduction
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Redox Reaction
A chemical reaction involving the transfer of electrons where one substance is oxidized (loses electrons) and another is reduced (gains electrons).
Leo says Ger (lose electrons oxidation - gain electrons reduction)
Redox Couple
A pair of substances related by their ability to be oxidized or reduced, e.g., NAD⁺/NADH.
Half-Reaction
A chemical equation showing either oxidation or reduction separately, detailing electron transfer.
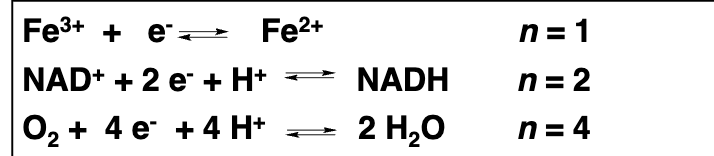
In the reaction Fe³⁺ + e⁻ → Fe²⁺, what is happening?
Fe³⁺ is being reduced to Fe²⁺ by gaining an electron.
Standard Reduction Potential (E⁰)
: A measure of a molecule’s tendency to gain electrons (be reduced) under standard conditions (1 M concentration, 25°C, pH 0).
E⁰’ means at standard temp and pH 7
if e is positive - reaction is spontanous (favourable) if E is negative its non spontanous (and not favourbale in that direction)

We don't know which way the reaction will go unless we have more info
Aox and Box are competing and the red ones are too.
Think of it in terms of A ox is A ox because in the reverse reaction electrons were lost, in the forward reaction electrosn were given to form Ared.
The difference in standard reduction potentials (E⁰′) of the two redox couples will determine which way electrons flow in a redox reaction.
If A_ox has a higher E⁰′ than B_ox, which species will accept electrons?

A_ox will accept electrons from B_red and will become A red.
What does a higher E⁰ value indicate about a molecule?
It has a stronger tendency to gain electrons (be reduced).
Electrons flow from the redox couple with the lower E⁰′ to the one with the higher E⁰′.
Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE)
The reference electrode used to measure standard reduction potentials, with E⁰′ = -0.42V
Spontaneous Redox Reaction
A redox reaction with a positive ΔE⁰′ value (ΔE⁰′ > 0), meaning it can proceed without input of energy.
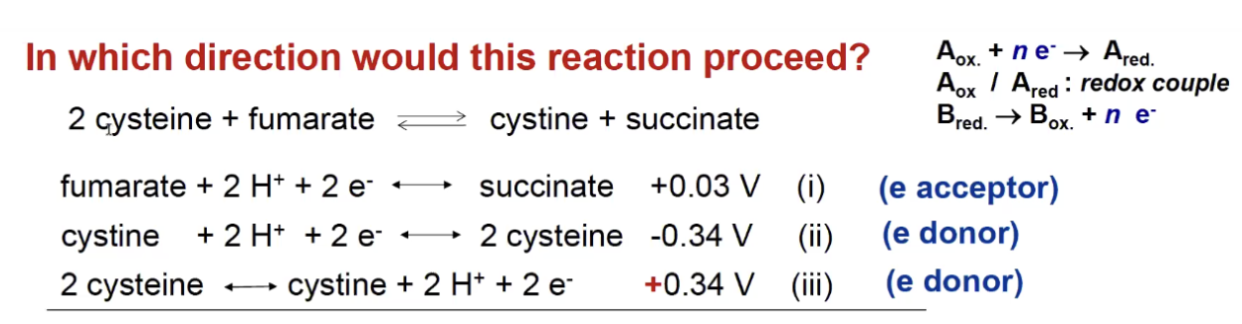
We look at fumarate and we see when fumarate grabs electron and becomes succinate th E is +0.03
Then we look at cysteine grabbing electrons and has E value of -0.34
If we compare the two equations we see that there is a competition between fumarate and cysteine for electrons - fumarate will grab electrons better than cysteine (more positive) whichever one grabs electrons better drives the reaction.
This tells us that fumarate gets reduced going from left to right.
The third line just tells us that cysteine is willing to give up electrons more than it is to grab electrons but dont worry about that.
The total standard redox potential will be calculated as +0.03-(-0.34)=+0.37
Stronger potential gets reduced
therefore the reaction is spontaneous un the forward direction
the one with the higher E value is the electron acceptor
Total standard reduction potential formula
ΔE°′=E°acceptor′−E°donor′
use it if u are givem two half reactions in redox pair and asked will the reaction go forward - or which molecule donates or accepts electrons.
Gibbs Free Energy (ΔG°′)
amount of energy available to do work; negative ΔG°′ means the reaction is spontaneous.
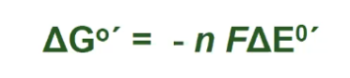
G gibbs formula - dont memorize understand tho
n is number of electrons, so if A grabs an electron and becomes A- (E=10) and B grabs electron and becomes B- (E=5)
So which grabs electrons more? A.
the bigger the difference between them, the faster the reaction will happen.
Strong Reductant
A substance with a low (more negative) E⁰′ value; it readily donates electrons.
strong oxidant is the opposite
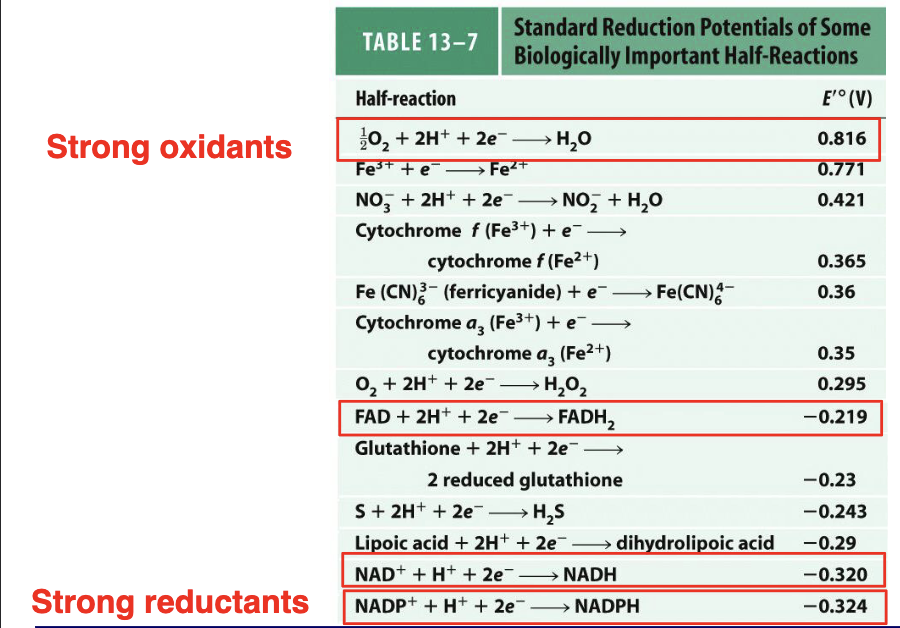
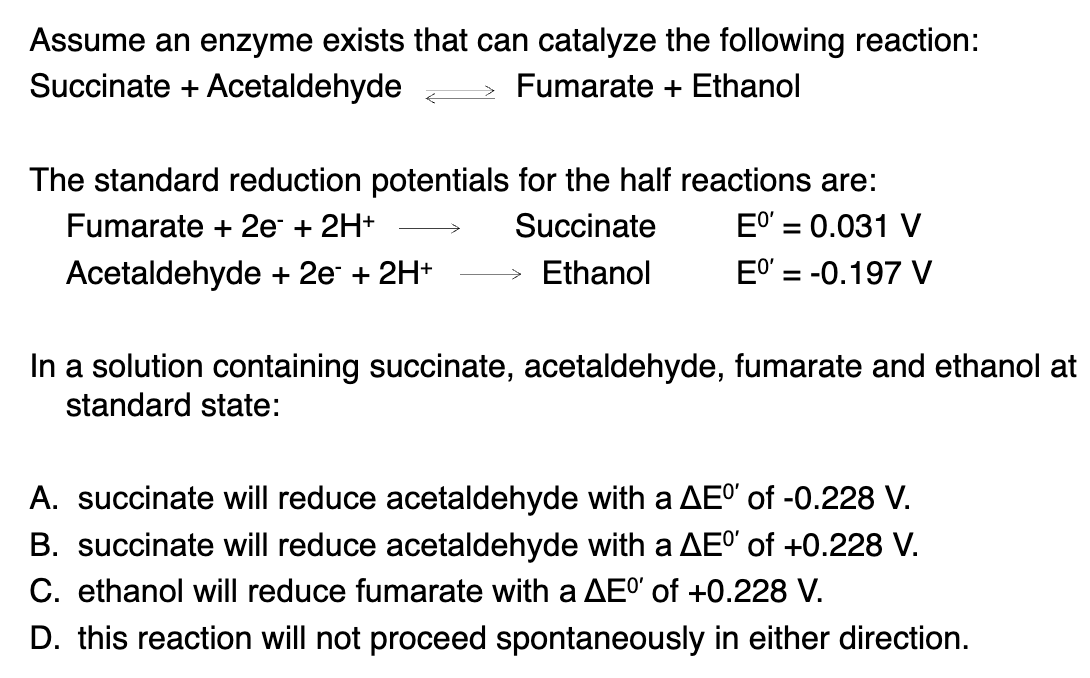
higher E value is more likely to accept electrons
acceptor-donor
0.031--(-0.197) = +0.228V
and we know that Fumerate is the oxidizer and will reduce into fumerate. so ethanol reduces fumerate.
so the answer must be C