L4 Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals approximation
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
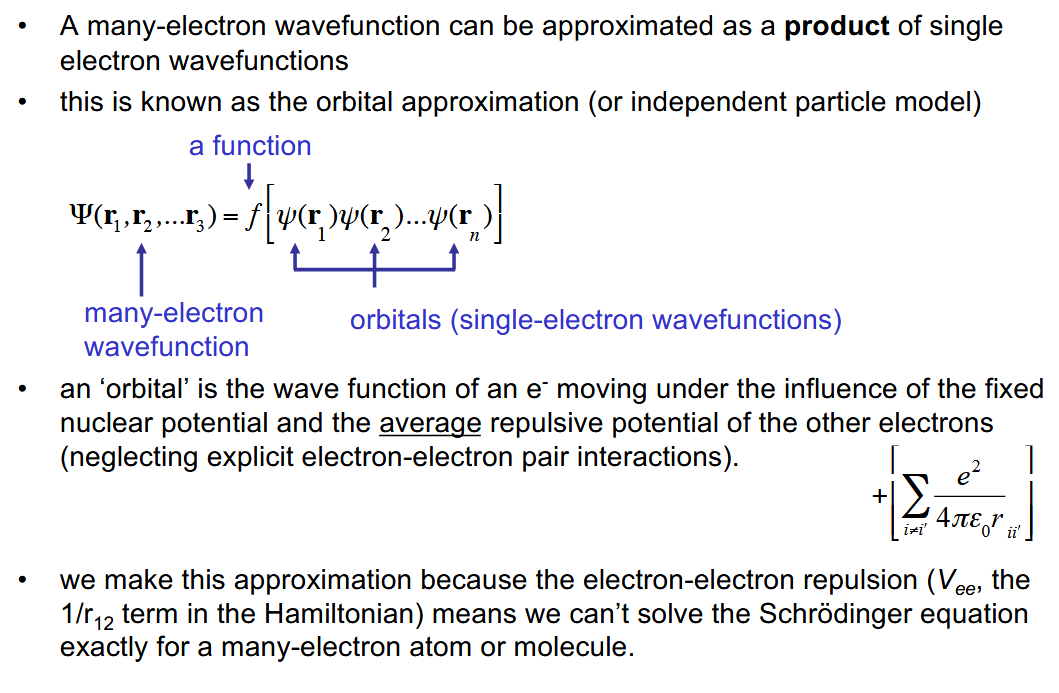
How can a many-electron (molecular orbital) wavefunction be approximated
As a product of single-electron wavefunctions. This approximation is needed as we CANNOT solve the Schrodinger equation exactly due to Vee (electron-electron repulsions).
The Linear Combination of Atomic orbitals (LCAO)
The wavefunction of a molecular orbital is (approximately) the sum of the atomic orbitals.
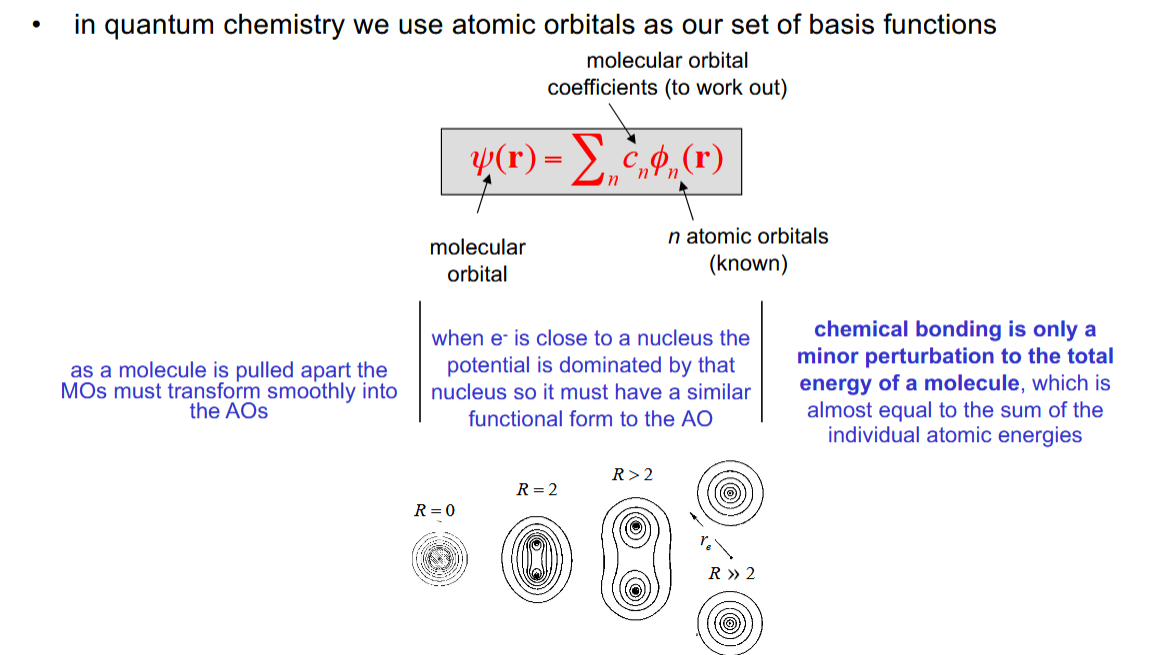
minimal basis set

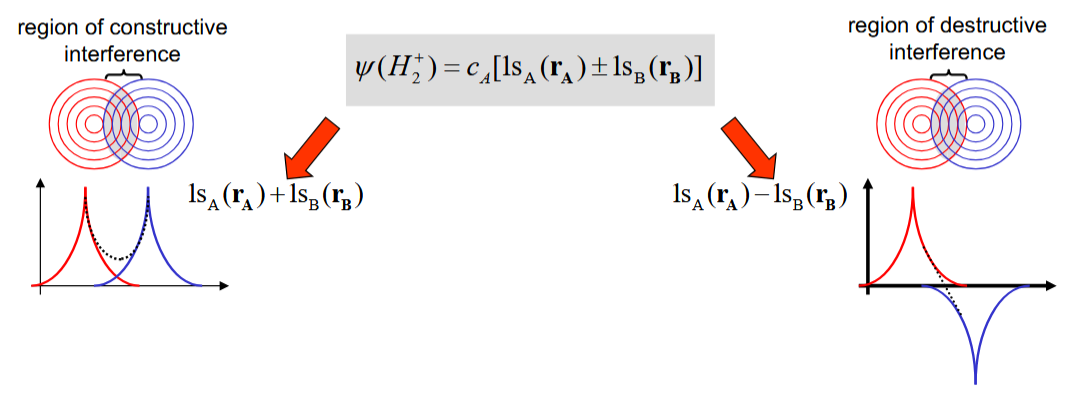
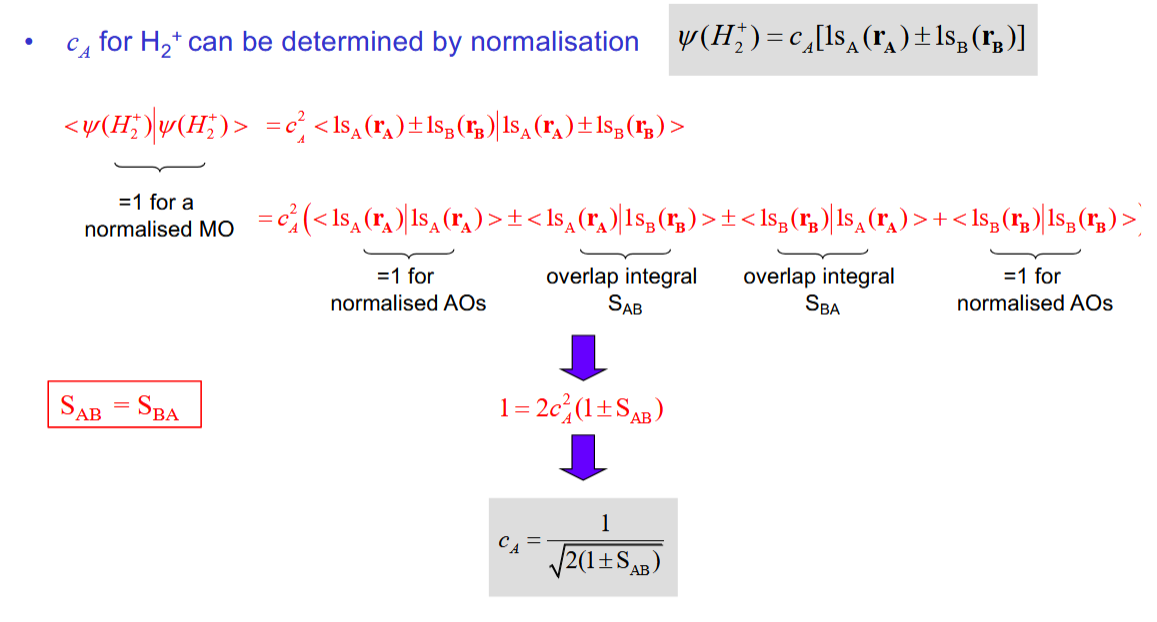
What is the significance of H2+ being centrosymmetric in terms of cA and cB
The electron should be no more likely to be around one atom than the other

Taking the sum of the orbitals vs the difference
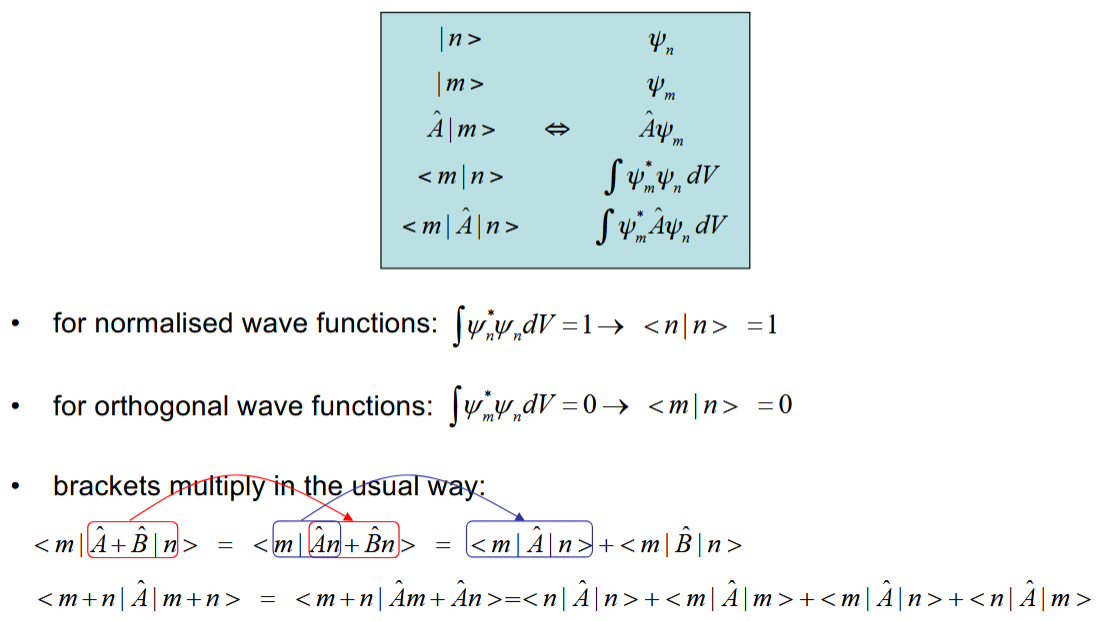
Dirac notation
Mainly for photochemistry - just a different way of writing wavefunction representations.
Operators get added before the line.
Two angled brackets introduced integration over all space.
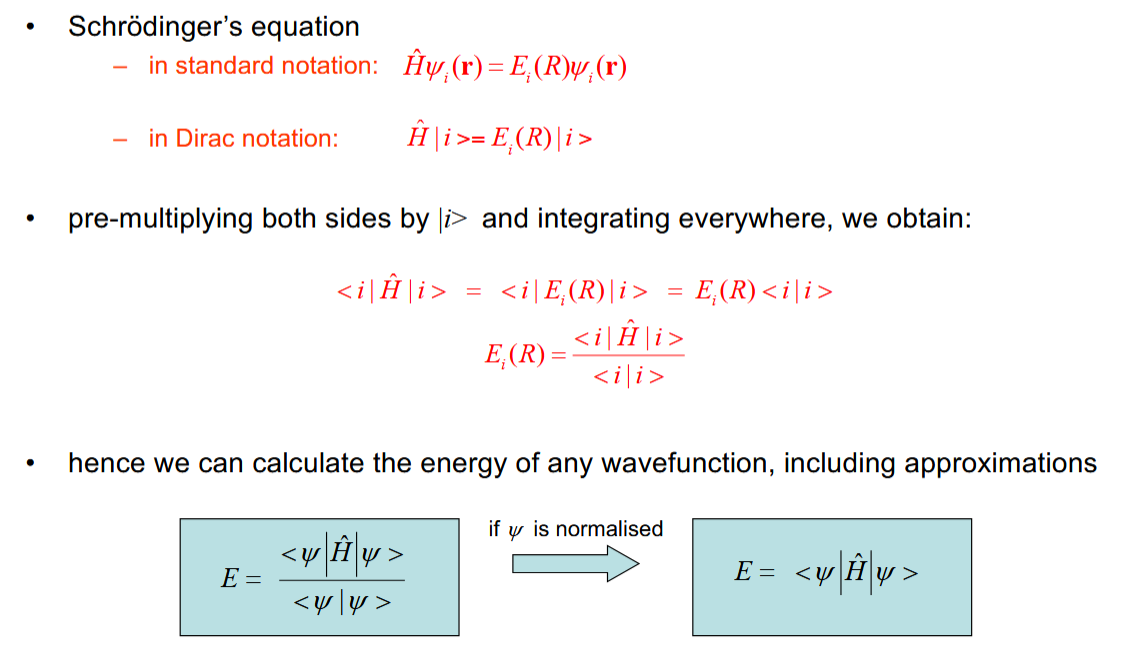
Calculating the energy of a wavefunction using manipulation of the Schrodinger equation
This allows you to make a guess of the wavefunction to calculate its energy
determining the molecular orbital coefficient cA
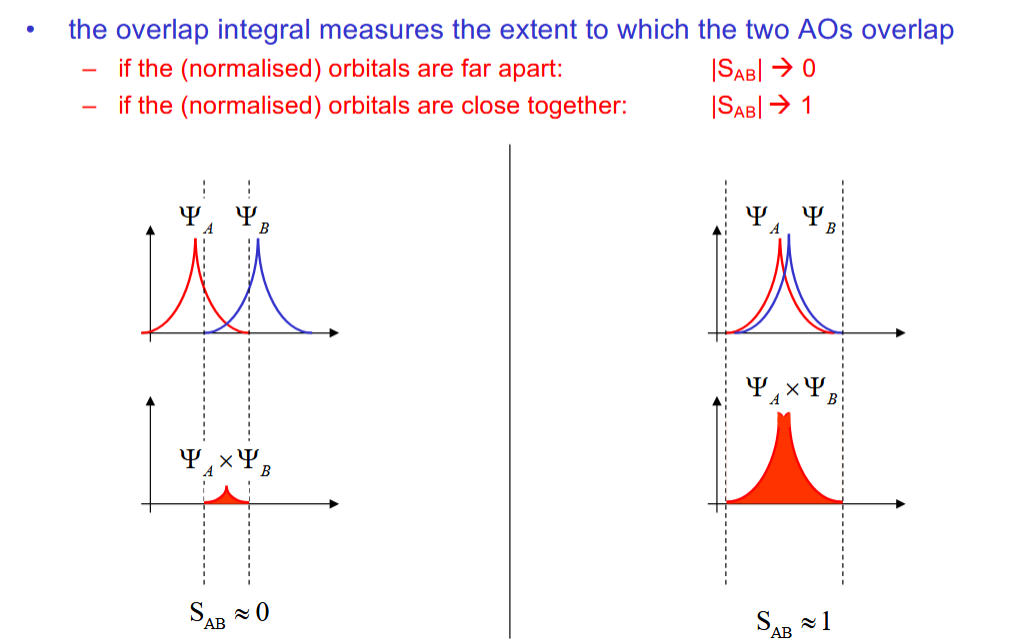
Overlap integral SAB
Measures the extent to which the two AOs overlap. Tends towards 0 as the overlap lessens
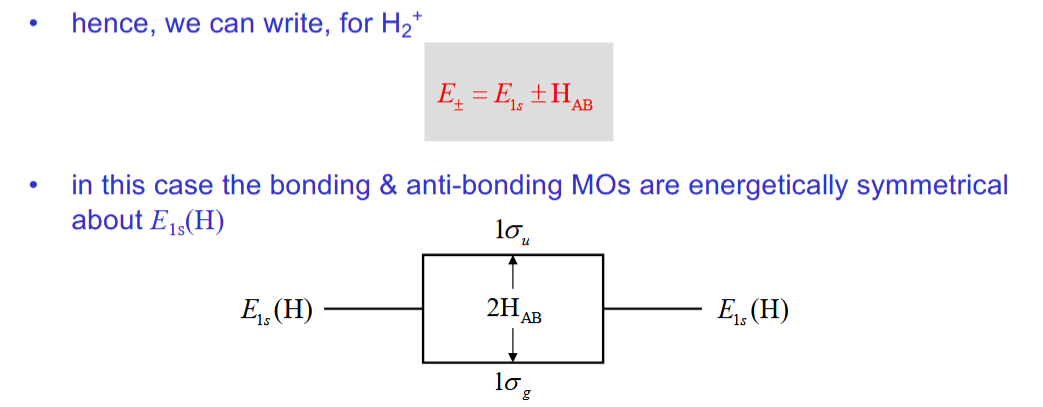
Determining the energy of the H2+ orbitals
Each of the 4 terms is negative
HAA = HBB and HAB = HBA
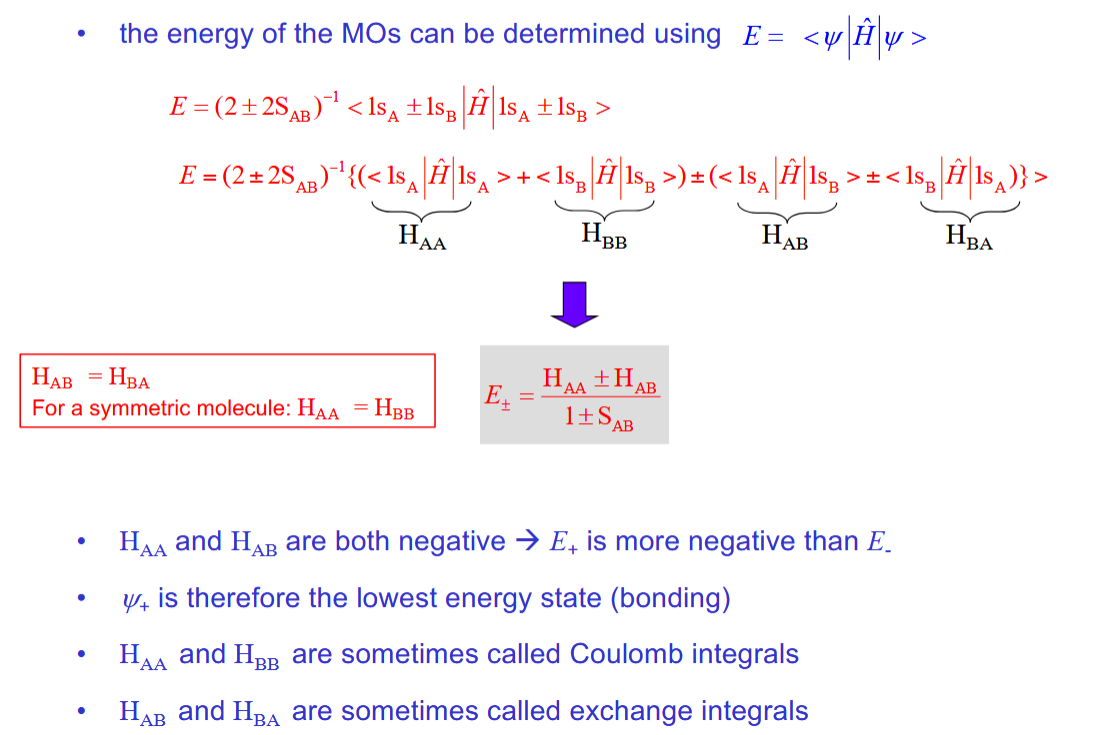
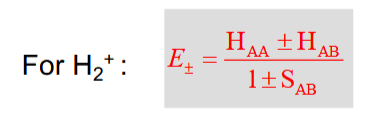
2 approximations to simplify this equation

What equation does this allow you to write