CYTOGENETICS: L2 (M)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Alleles Alter Phenotypes in Different Ways
Modification Of Mendelian Ratios
Geneticists Use a Variety of Symbol for Alleles
Neither Allele is Dominant in Incomplete, or Partial, Dominance
Codominance, The Influence of Both Alleles in Heterozygote
Multiple Alleles of a Gene may Exist in a Population
Lethal Alleles
Geneticists Use a Variety of Symbol for Alleles
Modification Of Mendelian Ratios
Alleles Alter Phenotypes in Different Ways
Neither Allele is Dominant in Incomplete, or Partial, Dominance
Codominance, The Influence of Both Alleles in Heterozygote
Multiple Alleles of a Gene may Exist in a Population
Lethal Alleles
Neither Allele is Dominant in Incomplete, or Partial, Dominance
Modification Of Mendelian Ratios
Alleles Alter Phenotypes in Different Ways
Geneticists Use a Variety of Symbol for Alleles
Codominance, The Influence of Both Alleles in Heterozygote
Multiple Alleles of a Gene may Exist in a Population
Lethal Alleles
Codominance, The Influence of Both Alleles in Heterozygote
Modification Of Mendelian Ratios
Alleles Alter Phenotypes in Different Ways
Geneticists Use a Variety of Symbol for Alleles
Neither Allele is Dominant in Incomplete, or Partial, Dominance
Multiple Alleles of a Gene may Exist in a Population
Lethal Alleles
Multiple Alleles of a Gene may Exist in a Population
Modification Of Mendelian Ratios
Alleles Alter Phenotypes in Different Ways
Geneticists Use a Variety of Symbol for Alleles
Neither Allele is Dominant in Incomplete, or Partial, Dominance
Codominance, The Influence of Both Alleles in Heterozygote
Lethal Alleles
Lethal Alleles
Modification Of Mendelian Ratios
Alleles Alter Phenotypes in Different Ways
Geneticists Use a Variety of Symbol for Alleles
Neither Allele is Dominant in Incomplete, or Partial, Dominance
Codominance, The Influence of Both Alleles in Heterozygote
Multiple Alleles of a Gene may Exist in a Population
Wild-type allele
Terminologies:
.
most frequently encountered allele in a population, arbitrarily considered as normal.
Mutation
Terminologies:
.
modification of genetic sequence
Loss of function mutation
Terminologies:
.
mutation that brought about diminished functionality of the gene
Null allele
Terminologies:
.
eventual loss of function of a gene due to mutation
Gain of function mutation
Terminologies:
.
increased activity of a gene due to mutation
Neutral mutation
Terminologies:
.
mutation in a gene that does not necessarily alter its activity
Recessive Allele
.
Lowercase and italicized
(p)
Dominant allele
.
Uppercase and italicized
(P)
Intermediate
Neither of the alleles are dominant nor recessive thereby expressing an _____ phenotype
Wild type allele is R1 = Red
Mutant allele is R2 = White
This type of mutation is loss of function
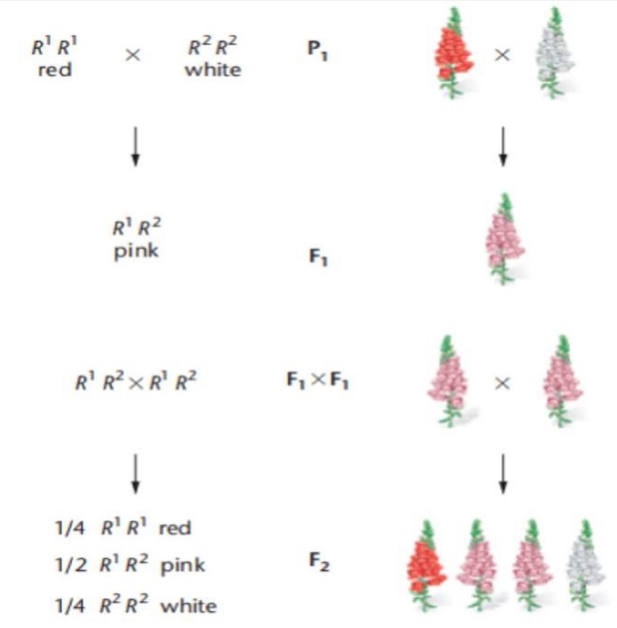
R1 = Red
Neither of the alleles are dominant nor recessive thereby expressing an intermediate phenotype
Wild type allele is __ = ___
Mutant allele is R2 = White
This type of mutation is loss of function
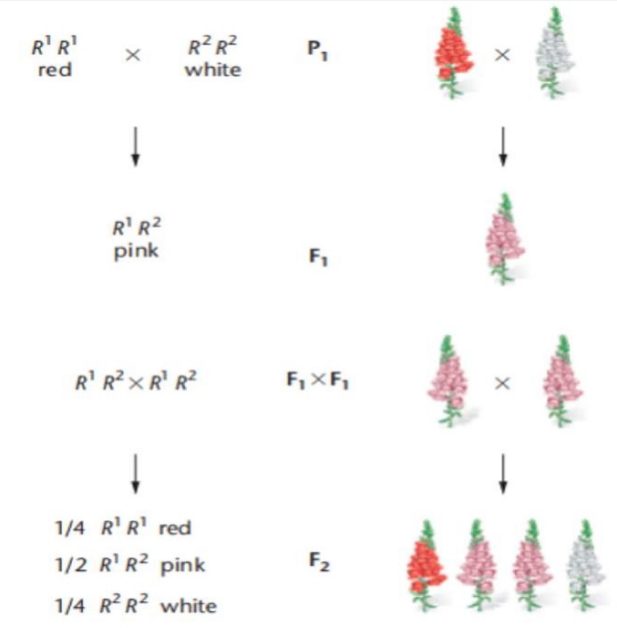
R2 = White
Neither of the alleles are dominant nor recessive thereby expressing an intermediate phenotype
Wild type allele is R1 = Red
Mutant allele is __ = ___
This type of mutation is loss of function
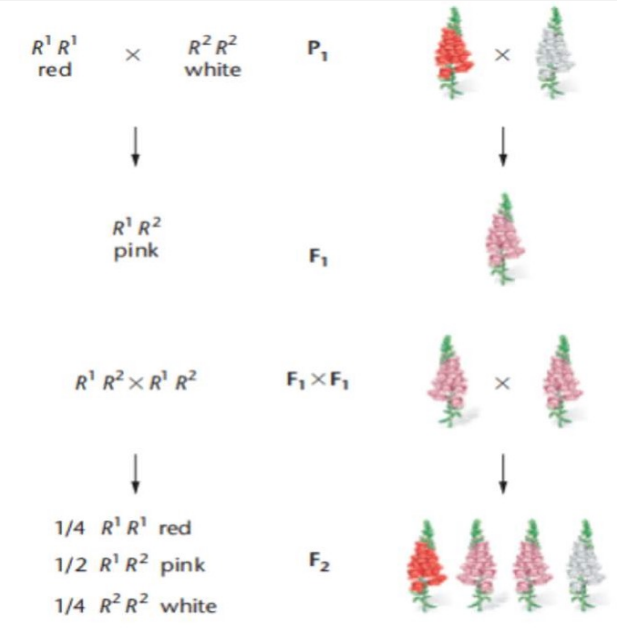
Loss of function
Neither of the alleles are dominant nor recessive thereby expressing an intermediate phenotype
Wild type allele is R1 = Red
Mutant allele is R2 = White
This type of mutation is
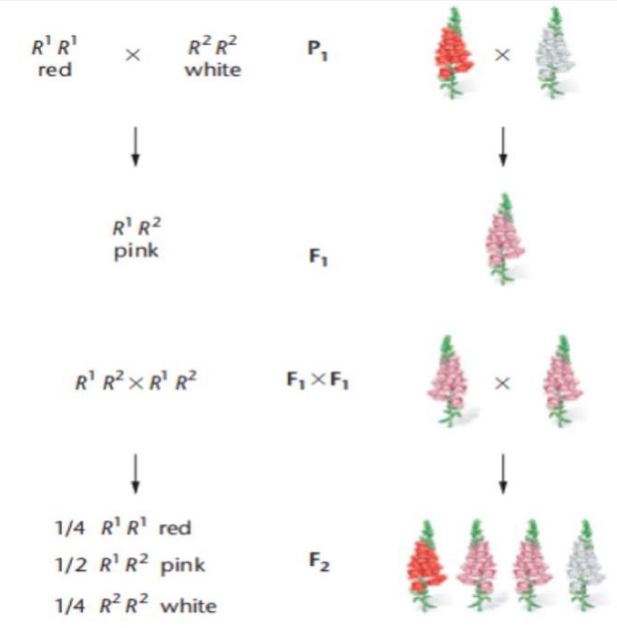
Codominance
_____, The Influence of Both Alleles in Heterozygote
In heterozygotes, both alleles are DOMINANT thereby expressing 2 distinct gene products.
Inheritance of both dominant genes (2 unit factors) leads to expression of 2 dominant phenotype
Ex. The MN Blood Group system
Genes at certain locus in chromosome 4 regulate the production of M and N substance (glycoprotein), inheritance of both genes lead to production of both glycoprotein.
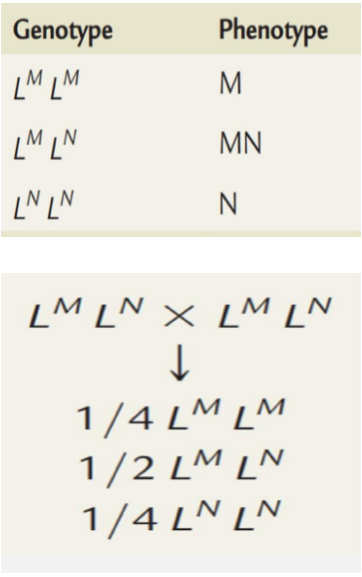
Dominant
Codominance, The Influence of Both Alleles in Heterozygote
In heterozygotes, both alleles are _____ thereby expressing 2 distinct gene products.
Inheritance of both dominant genes (2 unit factors) leads to expression of 2 dominant phenotype
Ex. The MN Blood Group system
Genes at certain locus in chromosome 4 regulate the production of M and N substance (glycoprotein), inheritance of both genes lead to production of both glycoprotein.
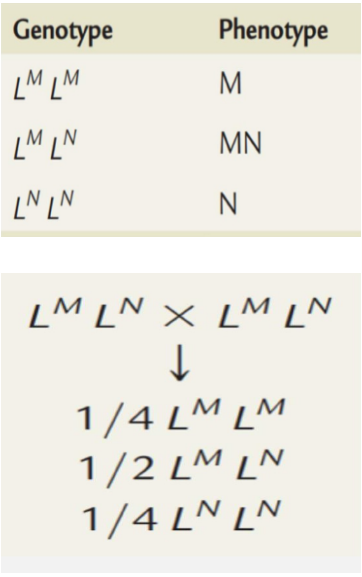
2 dominant phenotype
Codominance, The Influence of Both Alleles in Heterozygote
In heterozygotes, both alleles are DOMINANT thereby expressing 2 distinct gene products.
Inheritance of both dominant genes (2 unit factors) leads to expression of _ _____ _____
Ex. The MN Blood Group system
Genes at certain locus in chromosome 4 regulate the production of M and N substance (glycoprotein), inheritance of both genes lead to production of both glycoprotein.
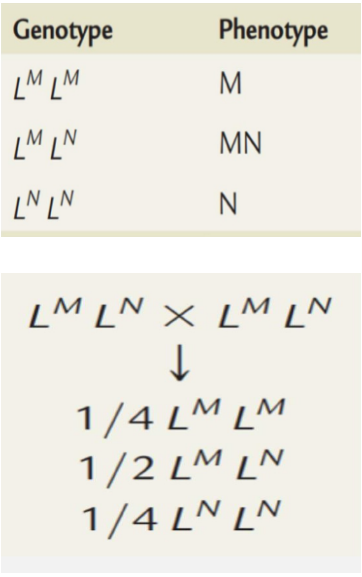
Multiple Alleles
_____ _____ of a Gene may Exist in a Population
_____ _____ - in a population of organisms, the presence of three or more alleles of the same gene
The ABO Blood Group
Simplest case of multiple alleles is that which three alternative alleles of one gene exist
Discovered by Karl Landsteiner
Four phenotypes of ABO Blood Group
A antigen (A phenotype)
B antigen (B phenotype)
A and B antigen (AB phenotype)
neither antigen (O phenotype)
The Bombay Phenotype
A rare variant of the ABO antigen system in which affected individuals do not have A or B antigens and thus appear to have blood type O, even though their genotype may carry unexpressed alleles for the A and/or B antigen
ABO Blood Group
Multiple Alleles of a Gene may Exist in a Population
Multiple alleles - in a population of organisms, the presence of three or more alleles of the same gene
The ___ _____ _____
Simplest case of multiple alleles is that which three alternative alleles of one gene exist
Discovered by Karl Landsteiner
Four phenotypes of ___ _____ _____
A antigen (A phenotype)
B antigen (B phenotype)
A and B antigen (AB phenotype)
neither antigen (O phenotype)
The Bombay Phenotype
A rare variant of the ABO antigen system in which affected individuals do not have A or B antigens and thus appear to have blood type O, even though their genotype may carry unexpressed alleles for the A and/or B antigen
Karl Landsteiner
Multiple Alleles of a Gene may Exist in a Population
Multiple alleles - in a population of organisms, the presence of three or more alleles of the same gene
The ABO Blood Group
Simplest case of multiple alleles is that which three alternative alleles of one gene exist
Discovered by ____ _____
Four phenotypes of ABO Blood Group
A antigen (A phenotype)
B antigen (B phenotype)
A and B antigen (AB phenotype)
neither antigen (O phenotype)
The Bombay Phenotype
A rare variant of the ABO antigen system in which affected individuals do not have A or B antigens and thus appear to have blood type O, even though their genotype may carry unexpressed alleles for the A and/or B antigen
A phenotype
Multiple Alleles of a Gene may Exist in a Population
Multiple alleles - in a population of organisms, the presence of three or more alleles of the same gene
The ABO Blood Group
Simplest case of multiple alleles is that which three alternative alleles of one gene exist
Discovered by Karl Landsteiner
Four phenotypes of ABO Blood Group
A antigen (_ _____)
B antigen (B phenotype)
A and B antigen (AB phenotype)
neither antigen (O phenotype)
The Bombay Phenotype
A rare variant of the ABO antigen system in which affected individuals do not have A or B antigens and thus appear to have blood type O, even though their genotype may carry unexpressed alleles for the A and/or B antigen
B phenotype
Multiple Alleles of a Gene may Exist in a Population
Multiple alleles - in a population of organisms, the presence of three or more alleles of the same gene
The ABO Blood Group
Simplest case of multiple alleles is that which three alternative alleles of one gene exist
Discovered by Karl Landsteiner
Four phenotypes of ABO Blood Group
A antigen (A phenotype)
B antigen (_ _____)
A and B antigen (AB phenotype)
neither antigen (O phenotype)
The Bombay Phenotype
A rare variant of the ABO antigen system in which affected individuals do not have A or B antigens and thus appear to have blood type O, even though their genotype may carry unexpressed alleles for the A and/or B antigen
AB phenotype
Multiple Alleles of a Gene may Exist in a Population
Multiple alleles - in a population of organisms, the presence of three or more alleles of the same gene
The ABO Blood Group
Simplest case of multiple alleles is that which three alternative alleles of one gene exist
Discovered by Karl Landsteiner
Four phenotypes of ABO Blood Group
A antigen (A phenotype)
B antigen (B phenotype)
A and B antigen (__ _____)
neither antigen (O phenotype)
The Bombay Phenotype
A rare variant of the ABO antigen system in which affected individuals do not have A or B antigens and thus appear to have blood type O, even though their genotype may carry unexpressed alleles for the A and/or B antigen
O phenotype
Multiple Alleles of a Gene may Exist in a Population
Multiple alleles - in a population of organisms, the presence of three or more alleles of the same gene
The ABO Blood Group
Simplest case of multiple alleles is that which three alternative alleles of one gene exist
Discovered by Karl Landsteiner
Four phenotypes of ABO Blood Group
A antigen (A phenotype)
B antigen (B phenotype)
A and B antigen (AB phenotype)
neither antigen (_ _____)
The Bombay Phenotype
A rare variant of the ABO antigen system in which affected individuals do not have A or B antigens and thus appear to have blood type O, even though their genotype may carry unexpressed alleles for the A and/or B antigen
The Bombay Phenotype
Multiple Alleles of a Gene may Exist in a Population
Multiple alleles - in a population of organisms, the presence of three or more alleles of the same gene
The ABO Blood Group
Simplest case of multiple alleles is that which three alternative alleles of one gene exist
Discovered by Karl Landsteiner
Four phenotypes of ABO Blood Group
A antigen (A phenotype)
B antigen (B phenotype)
A and B antigen (AB phenotype)
neither antigen (O phenotype)
___ _____ ______
A rare variant of the ABO antigen system in which affected individuals do not have A or B antigens and thus appear to have blood type O, even though their genotype may carry unexpressed alleles for the A and/or B antigen
Lethal Alleles
_____ _____
Genetic mutation which might lead to death
Genes function primarily for the expression/production of substances essential to life
Death
Lethal Alleles
Genetic mutation which might lead to _____
Genes function primarily for the expression/production of substances essential to life
Expression / Production
Lethal Alleles
Genetic mutation which might lead to death
Genes function primarily for the _____/_____ of substances essential to life