7- esophagus diseases
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what type of epithelium lines the esophagus
non-keratinizing squamous (SSNKE)
2 types of esophageal obstruction
mechanical
functional
2 types of mechanical esophageal obstruction
atresia
stenosis
what’s atresia mechanical esophageal obstruction
birth defect where thin, non-canalized cord replaces part of esophagus usually near tracheal bifurcation → aspiration, suffocation, pneumonia
associated w/ fistula-connects esophageal pouch to bronchus or trachea
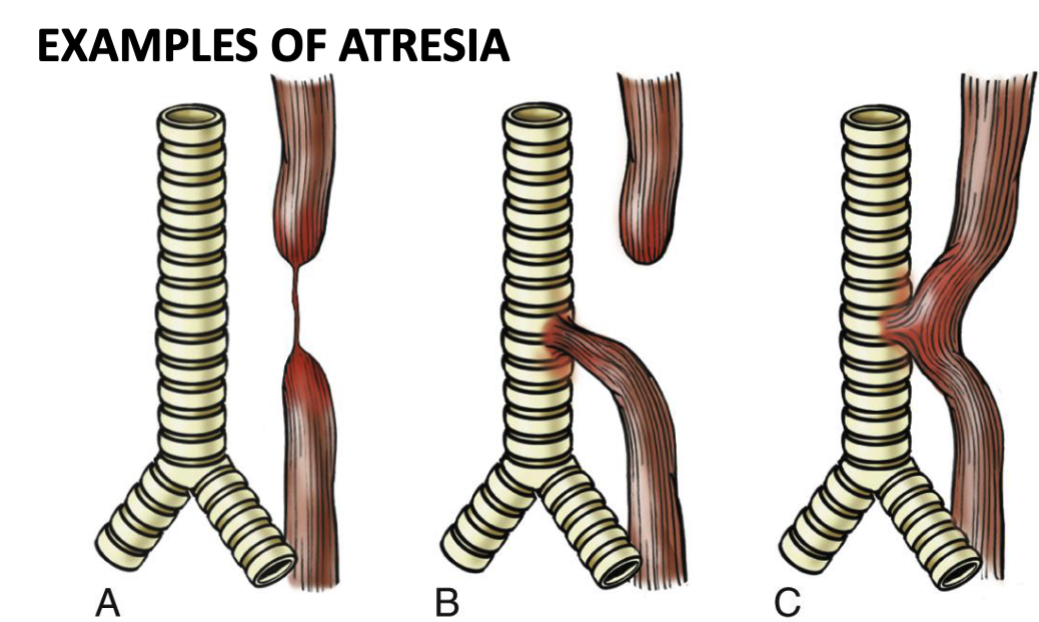
what’s stenosis mechanical esophageal obstruction
congenital/acquired (common) narrowing of esophagus → fibrous thickening of submucosa + atrophy of muscularis propria
2 common causes of stenosis mechanical esophageal obstruction
chronic GERD or irradiation
2 types of functional esophageal obstruction
achalasia: incomplete relaxation of LES, increased LES tone, esophageal aperistalsis
primary: unknown cause, failure of distal esophageal inhibitory neurons, can affect CN X
secondary: Chagas disease caused by Trypanosoma cruzi bacteria → failure of LES to relax, esophageal dilation, destruction of myenteric plexus
what’s esophageal varices
portal HTN → enlarged vessels that protrude in lumen of distal esophagus → can rupture + cause massive bleeding
esophageal varices is seen in 50% of which pts
pts w/ cirrhosis
what’s the first pass effect
venous blood from GI tract goes to liver via portal vein
2 causes of esophageal lacerations
Mallory-Weiss syndrome: acute alcohol intoxication w/ severe vomiting → linear + superficial esophageal tears into GI junction
Boerhaave syndrome: rupture of distal esophagus → can affect mediastinum + result in mediastinitis
which cause of esophageal laceration is most common
Mallory-Weiss syndrome
which cause of esophageal laceration requires surgery
Boerhaave syndrome
what’s esophagitis
inflammation of esophagus
3 types of esophagitis
infectious
eosinophilic
reflux (GERD)
3 common infections that cause infectious esophagitis
fungal (Candidiasis)
cytomegalovirus: presents w/ shallow ulcers + nuclear/cytoplasmic inclusions histologically
herpes simplex: presents w/ “punched out” uclers
symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis in adults vs. children
adults: experience food impaction + dysphagia
children: experience food intolerance or GERD-like symptoms
what’s the histopathology that indicates eosinophilic esophagitis
infiltration of eosinophils in superficial aspect of lamina propria + epithelium, distinguishing it from GERD or Crohn’s
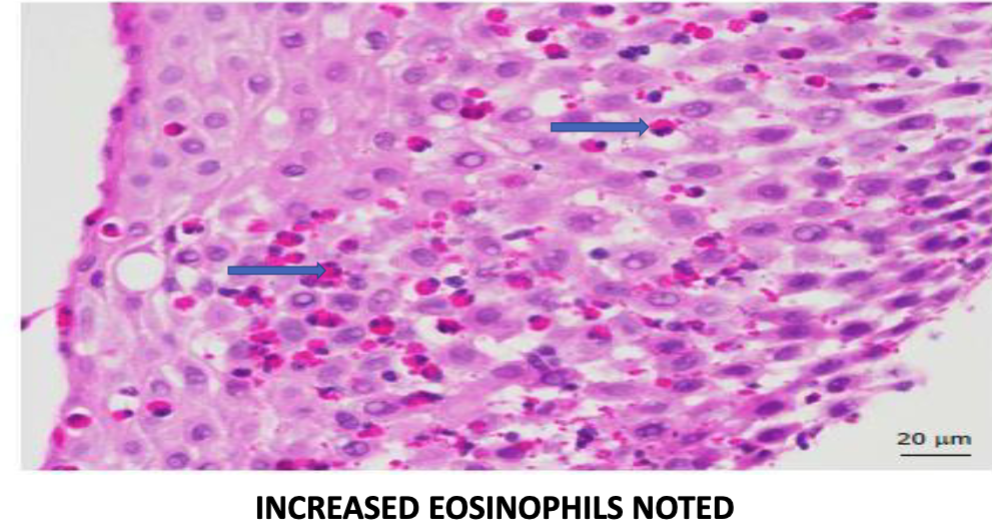
what’s the most common type of esophagitis
reflux esophagitis (GERD)
4 things that contribute to reflux esophagitis (GERD)
increased abdominal pressure
alcohol/tobacco use
pregnancy
hiatal hernia
3 symptoms of reflux esophagitis (GERD)
heartburn
dysphagia
regurgitation of sour tasting content
4 complications of reflux esophagitis (GERD)
esophageal ulcerations
hematemesis (vomiting blood)
stricture development
Barrett esophagus
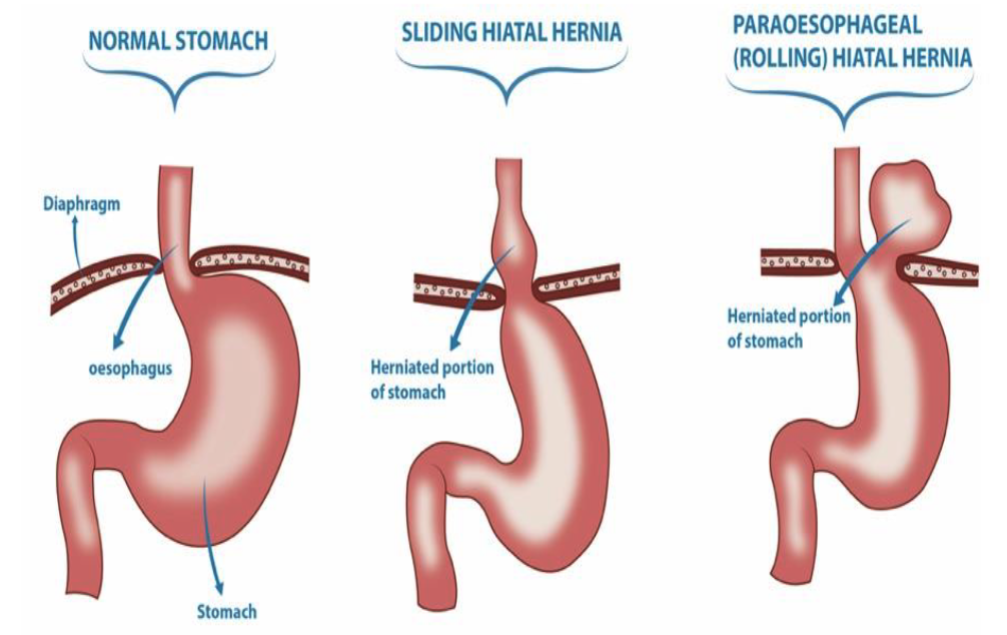
what are hiatal hernias
separation of diaphragmatic crura w/ protrusion of stomach into the thorax → can cause LES incompetence
2 symptoms of hiatal hernias
heartburn
regurgitation of gastric juices
2 types of hiatal hernias
sliding: stomach herniates through diaphragmatic hiatus
paraesophageal (rolling): stomach protrudes through separate defect alongside esophagus
Barrett’s esophagus involves metaplasia of what cells
lower 1/3 esophagus columnar squamous cells → tall, columnar glandular epithelium, resembling intestinal epithelium
Barrett’s esophagus increases risk for what
adenocarcinoma
esophageal adenocarcinoma can arise from which 2 conditions
Barrett’s esophagus
GERD
esophageal adenocarcinoma affects which part of the esophagus
distal/lower 1/3 of esophagus, can invade stomach
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma affects which part of the esophagus
middle 1/3
4 risk factors of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
alcohol/tobacco use
achalasia
frequent consumption of very hot beverages
Plummer-Vinson syndrome
what’s Plummer-Vinson syndrome
severe iron deficiency → esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in upper 1/3 of posterior cricoid area
Plummer-Vinson syndrome usually affects what type of people
middle aged + elderly women of Scandinavian origin