Thermal Energy Transfer: Conduction, Convection, and Radiation in Physics
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is thermal conduction?
The transfer of kinetic energy between particles of objects in thermal contact.
How does thermal conduction occur between two objects?
Higher temperature particles from one object transfer energy to lower temperature particles of another object, leading to thermal equilibrium.
What is the role of solids in thermal conduction?
Solids are typically the best conductors due to the closeness of their particles, allowing for easier energy transfer.
What are good thermal conductors and insulators?
Metals are good conductors, while materials that reduce energy transfer are known as insulators.
What does a high thermal conductivity value indicate?
A high value indicates a good thermal conductor, while a low value indicates a thermal insulator.
What is the formula for calculating thermal conductivity?
The formula is ΔQ/Δt = k A (ΔT/Δx), where k is thermal conductivity, A is cross-sectional area, ΔT is temperature difference, and Δx is thickness.
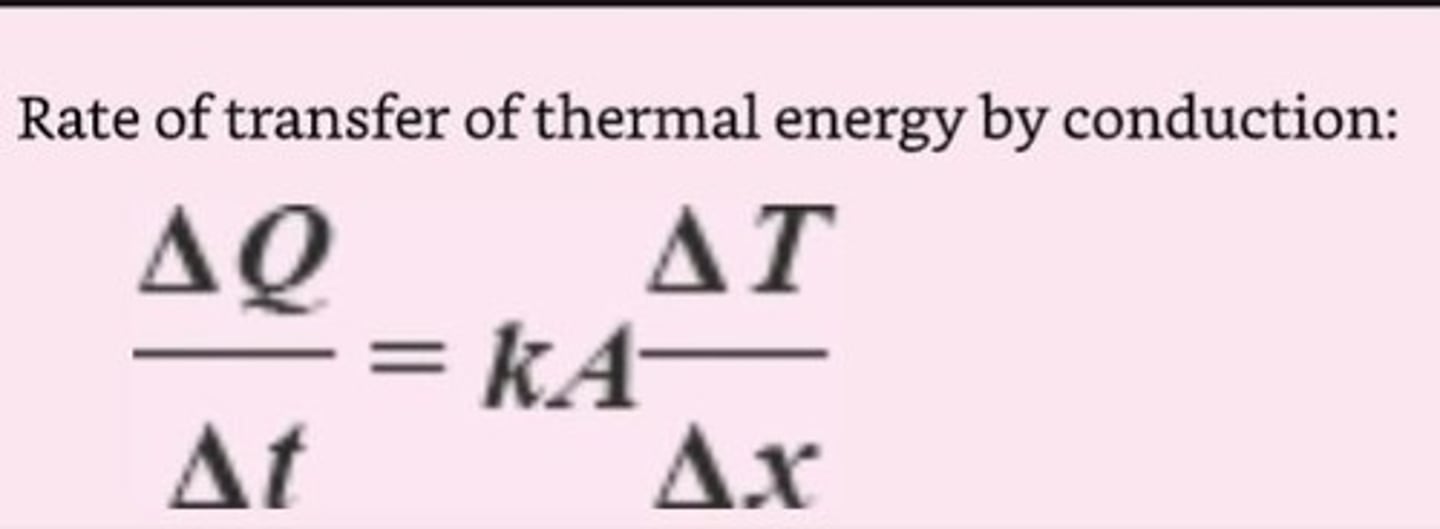
Why is air considered a good insulator?
Air is a good insulator because it limits thermal energy flow, often used in modern windows with air trapped between panes.
What is thermal convection?
Thermal convection is the transfer of energy due to fluid density differences, causing currents to flow from higher density to lower density regions.
Give an example of convection currents in everyday life.
Room heaters are placed near the floor while air conditioners are near the ceiling to create convection currents.
What is the Stefan-Boltzmann law?
It describes the rate of energy transfer by radiation from an object acting as a black body, defined as L = σ A T^4.
What does the symbol L represent in the context of thermal radiation?
L represents the rate of energy transfer, also known as luminosity, measured in Watts.
How does temperature affect the power output of a star?
Higher temperatures increase power output and result in emission of higher frequency/shorter wavelength electromagnetic spectra.
What is Wien's Displacement Law?
It relates surface temperature (T) to the wavelength (λmax) at which maximum power is received.
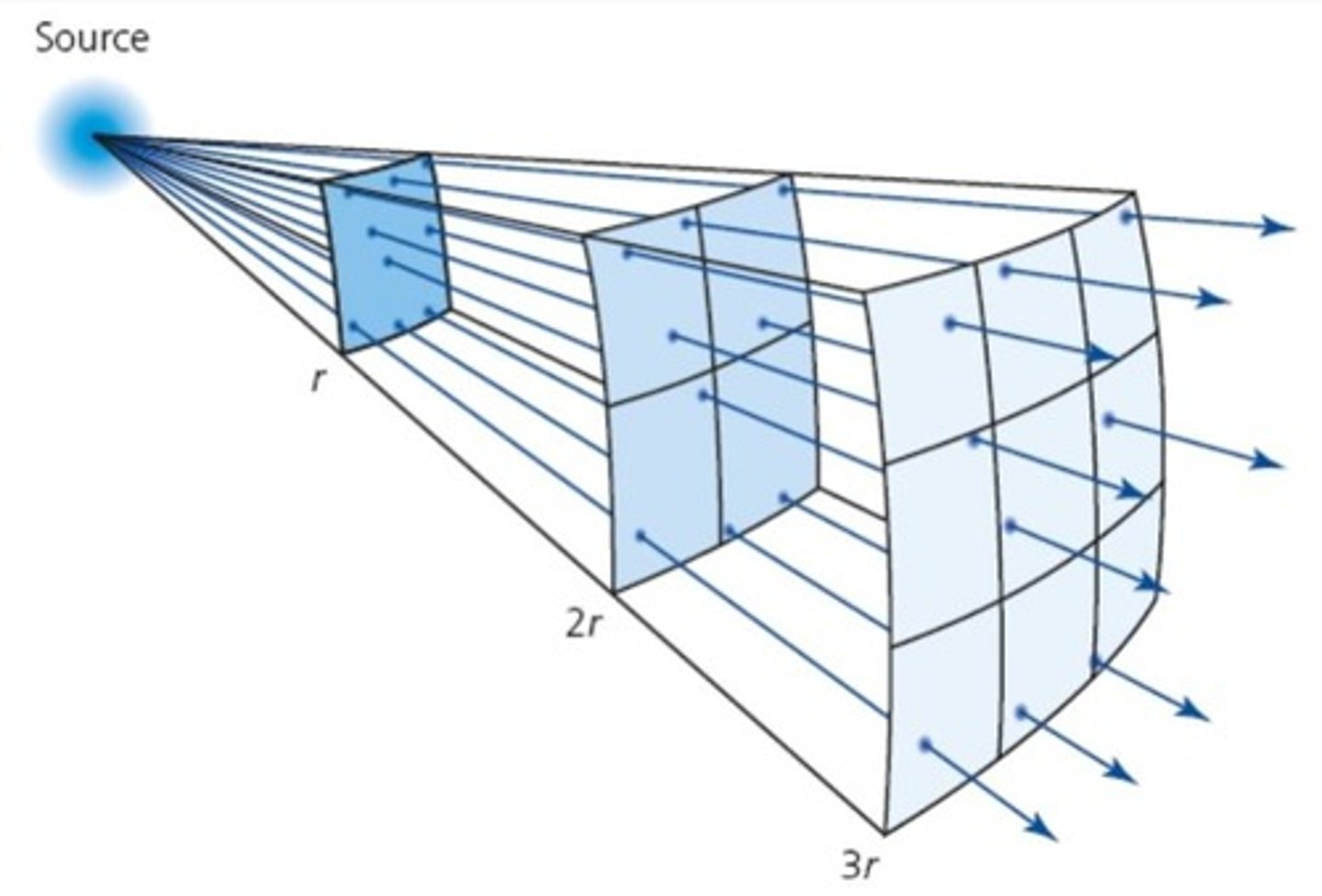
What is the relationship between intensity and distance in thermal radiation?
Intensity is based on an inverse square relationship, similar to gravity.
What is the significance of a black body in thermal radiation?
A black body is a perfect absorber and emitter of thermal radiation, used as a reference in calculations.
How can the power output of the Sun be calculated?
Using the Stefan-Boltzmann Law with the Sun's radius and temperature.
What is the typical temperature of the Sun?
The Sun's surface temperature is approximately 5780 °K.
What is the effect of thickness on thermal transfer rates?
Thicker materials typically have a lower thermal transfer rate, affecting overall energy efficiency.
What is the qualitative description of thermal energy transfer by radiation?
It involves the transfer of thermal energy through electromagnetic waves, primarily in the infrared and visible spectrum.
What happens to the radiative power output of an object as its temperature increases?
The radiative power output increases with higher temperature.
What is the significance of the wavelength of 5.8 x 10^-7 m in thermal radiation?
It corresponds to the maximum power emitted by an object at a specific temperature, which can be calculated using Wien's Displacement Law.