AP Biology Unit 3
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that speed up reactions, generally proteins.
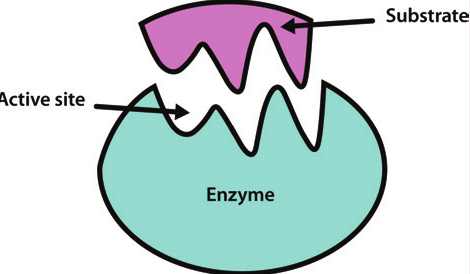
Substrate
The reactant molecule that binds to the enzyme.
Active Site
The region where the substrate binds to the enzyme.
Activation Energy
The minimum energy required to start a chemical reaction.
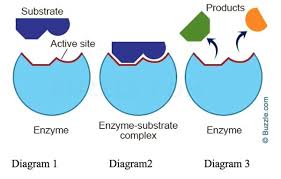
Enzyme-Substrate-Complex
A temporary molecule formed when the substrate binds to the enzyme.
Transition State
The highest energy point along the reaction pathway, a brief unstable state between the substrate and product.
Induced Fit Model
States that a substrate binds to an active site and both change shape slightly, creating an ideal fit for catalysis.
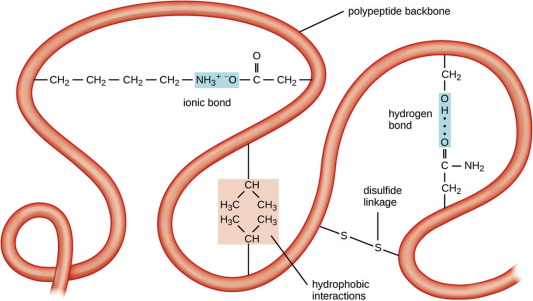
Primary Structure
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.

Secondary Structure
The local folded structures that form within a polypeptide due to interactions between atoms of the backbone.
Tertiary Structure
The overall three-dimensional shape of the polypeptide, resulting from interactions between the R groups of the amino acids. Includes the active site.
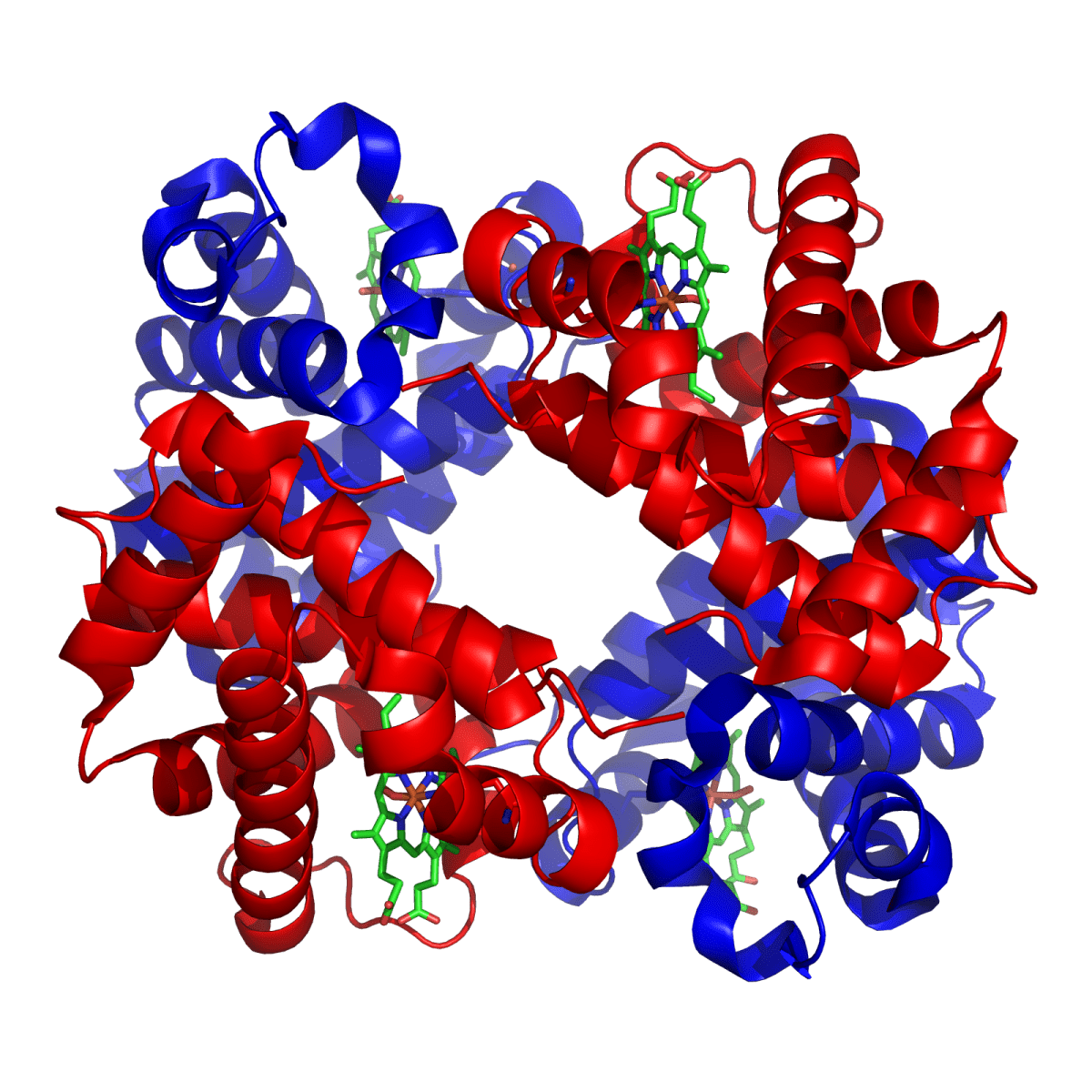
Quaternary Structure
The arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains within an enzyme.
Enzyme Catalysis
The process of enzymes speeding up chemical reactions.
Catalyst
Speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process.
Specificity
An enzymes ability to selectively bind to and catalyze reactions on a specific substrate or set of substrates.
Enzyme Inhibition
When an inhibitor binds to an enzyme and reduces/blocks enzyme activity.
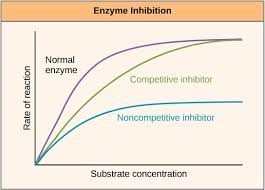
Competitive Inhibition
Competes with the substrate to bind to the active site & blocks the substrate from binding
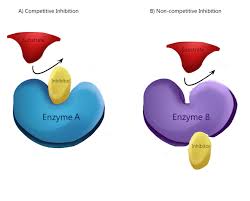
Non-Competitive Inhibition
Binds to a site that’s NOT the active site.Alters the enzyme’s shape and affects its ability to bind to the substrate and catalyze the reaction.
Allosteric Inhibition
Binds to a site that’s NOT the active site.Alters the enzyme’s shape and affects its ability to bind to the substrate and catalyze the reaction.
Environmental Impacts on Enzyme Function
Environmental factors such as temperature & pH can impact enzyme function, changes in these factors disrupt the enzyme’s structure slowing down its activity and possibly denaturation.These changes can alter the enzyme's active site, affecting substrate binding and overall catalytic efficiency.
Optimal pH
The specific pH level at which an enzyme exhibits maximum activity and catalytic efficiency, as deviations can lead to reduced effectiveness or denaturation.
Optimal Temperature
The temperature at which an enzyme functions most effectively, resulting in the highest reaction rate before denaturation occurs.
Denaturation
The process by which an enzyme's structure is altered, resulting in the loss of its biological activity. This can occur due to extreme temperature, pH changes, or other environmental factors.
Cellular Energy
The energy that cells use to power their various functions and processes. The energy is derived from the breakdown of food molecules and is stored in the form of a molecule known as ATP.
ATP
‘Adenosine Triphosphate’ (ATP) is the primary energy carrier in cells, providing energy for metabolic processes and cellular functions.
ATP→ ADP Cycle
The process by which cells store and release energy. ATP is reduced to ADP+Pi (inorganic phosphate) through hydrolysis and is regenerated back to ATP with energy (through cellular respiration OR photosynthesis).
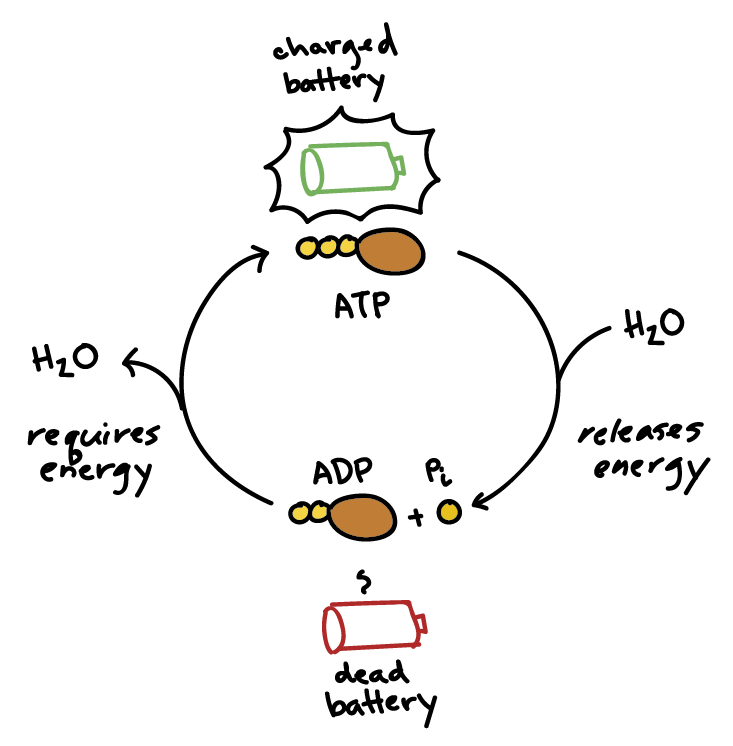
Energy Coupling
When energy produced by one reaction is used to drive another reaction. This energy transfer allows for cells to do work efficiently and help cause non spontaneous reactions.
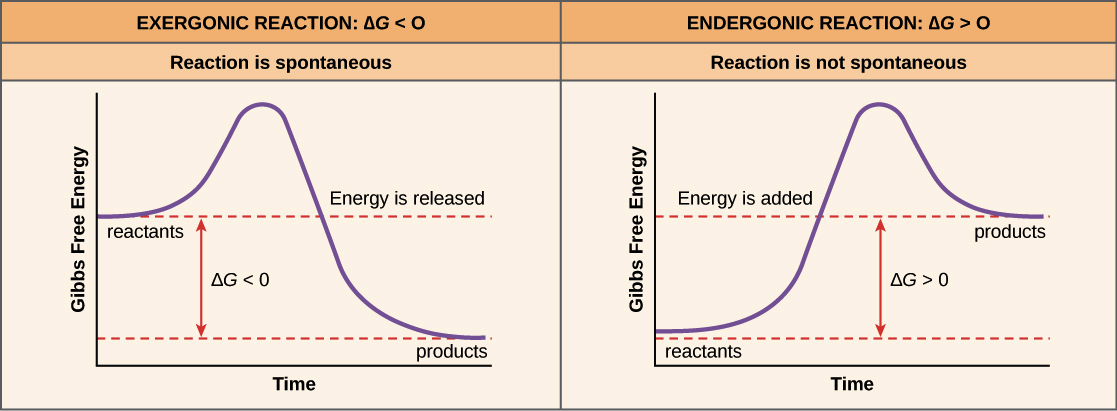
Non-Spontaneous Reactions
Doesn’t favor product formation and requires energy input or an external source to proceed
Spontaneous Reactions
Favors product formation under given conditions and doesn’t require energy input.
Exergonic Reaction
A chemical reaction that releases energy, often in the form of heat, or energy carriers (ATP) and occurs spontaneously.
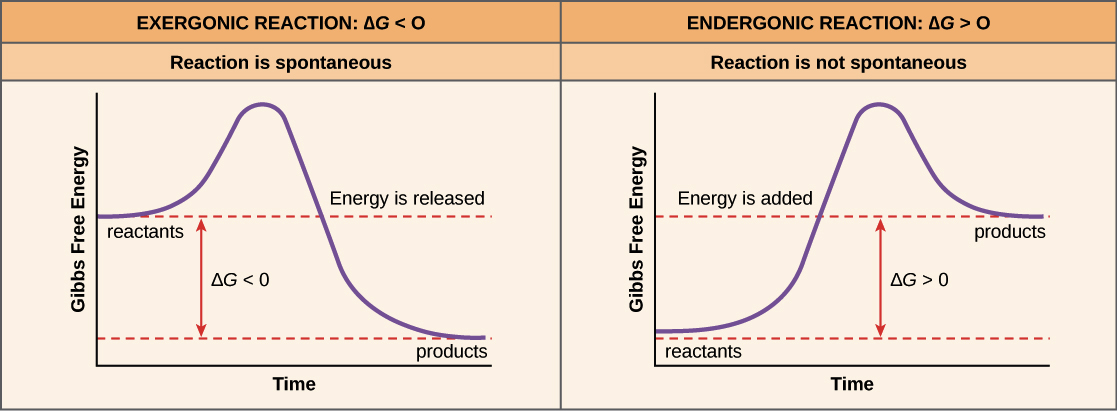
Endergonic Reactions
A chemical reaction that requires energy in order for it to occur
Laws of Thermodynamics
1st Law - Energy can’t be created or destroyed
Metabolic Pathways
A series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, converting substrates into products for energy. Can be categorized as ‘catabolic pathways’ or ‘anabolic pathways’ .
Catabolic Pathways
Breaks down complex molecules into simpler ones
Anabolic Pathways
Build up complex molecules from simpler ones.
Photosynthesis
The process of capturing light energy and converting it into chemical energy. Photosynthesis converts CO2+H2O → C6H12O6 + O2. It occurs in the chloroplast and it takes place in two main stages; light independent reactions and light dependent reactions.
Light-Independent Reactions
Calvin Cycle’
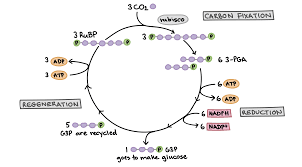
Converts CO2 → C6H12O6
Uses energy stored in ATP & NADPH from the light dependent reactions
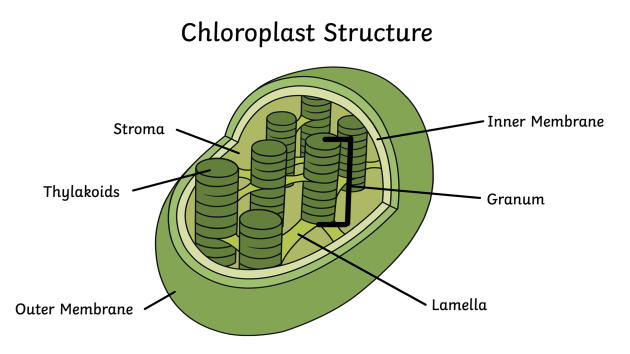
Takes place in the stroma
Calvin Cycle
A series of biochemical reactions in plants that convert carbon dioxide and other compounds into glucose using ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
Light-Dependent Reactions
Converts light into chemical energy
Occurs in the thylakoid membrane
Produces ATP & NADPH
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant cells that’s responsible for photosynthesis. Its structure consists of a double membrane, a internal membrane system (thylakoids), and a fluid-filled space (stroma).
Chlorophyll
A green pigment located in the thylakoid and its function is to absorb/capture light energy and start the process of converting it into chemical energy. It also excites electrons and drives the formation of ATP and NADPH through the Electron Transport Chain.
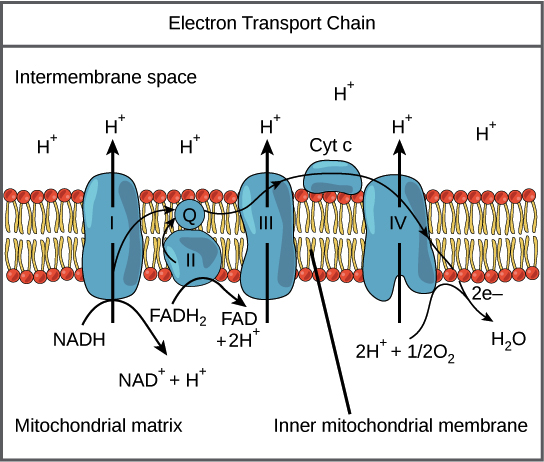
Electron Transport Chain
A series of 4 protein complexes the couple redox reactions creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a system known as Oxidative Phosphorylation.
Photosynthesis in Prokaryotes
Photosynthesis first evolved in prokaryotic organisms such as cyanobacteria. Around 3 billion years ago they evolved the ability to perform oxygenic photosynthesis and use water as an electron donor.
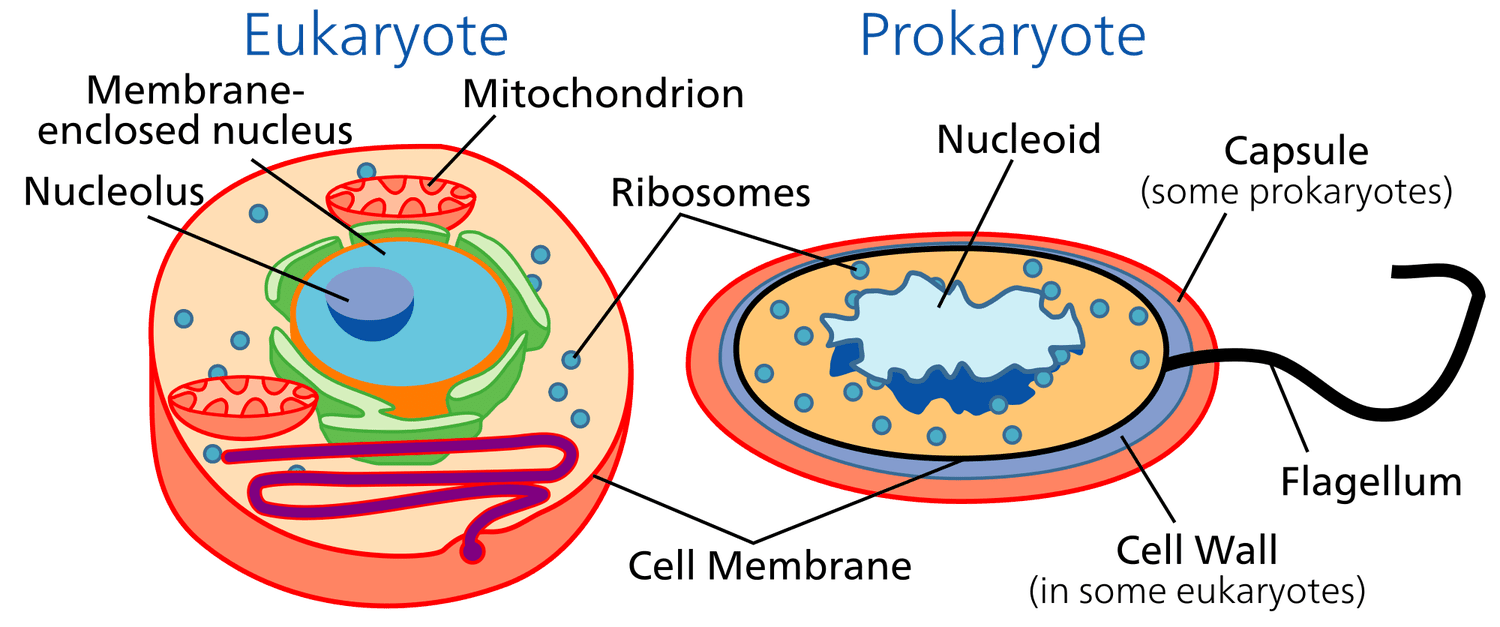
Binary Fission
A form of asexual reproduction where a bacteria divides into two identical daughter cell
Endosymbiotic Theory
Proposes that certain organelles such as mitochondria & chloroplasts were once free-living prokaryotic cells that were engulfed by an ancestral eukaryotic cell and formed a symbiotic relationship.
Cellular Respiration
A metabolic pathway that uses glucose to produce ATP. It’s carried out by both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The process can be divided into three stages: Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and Oxidative Phosphorylation.
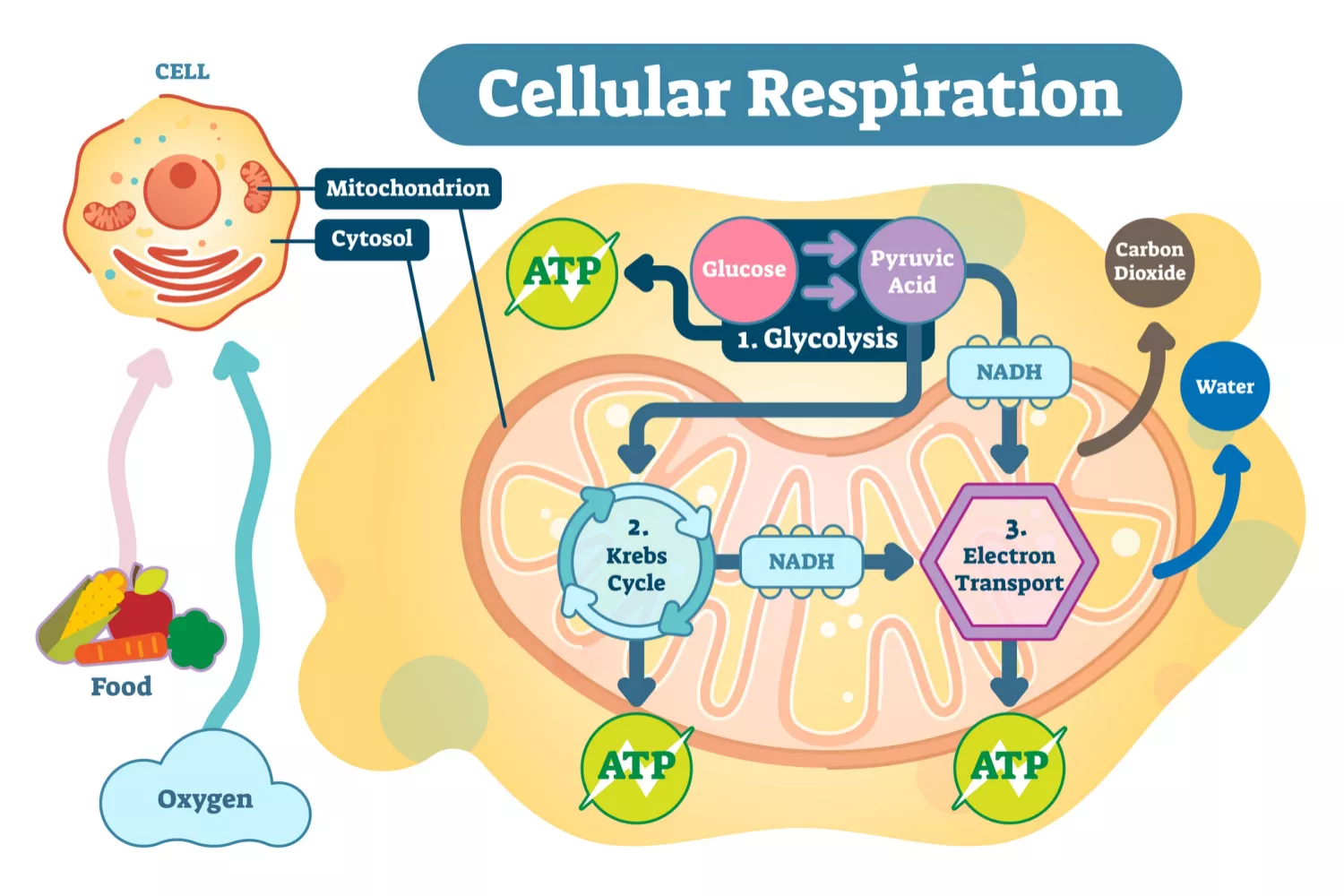
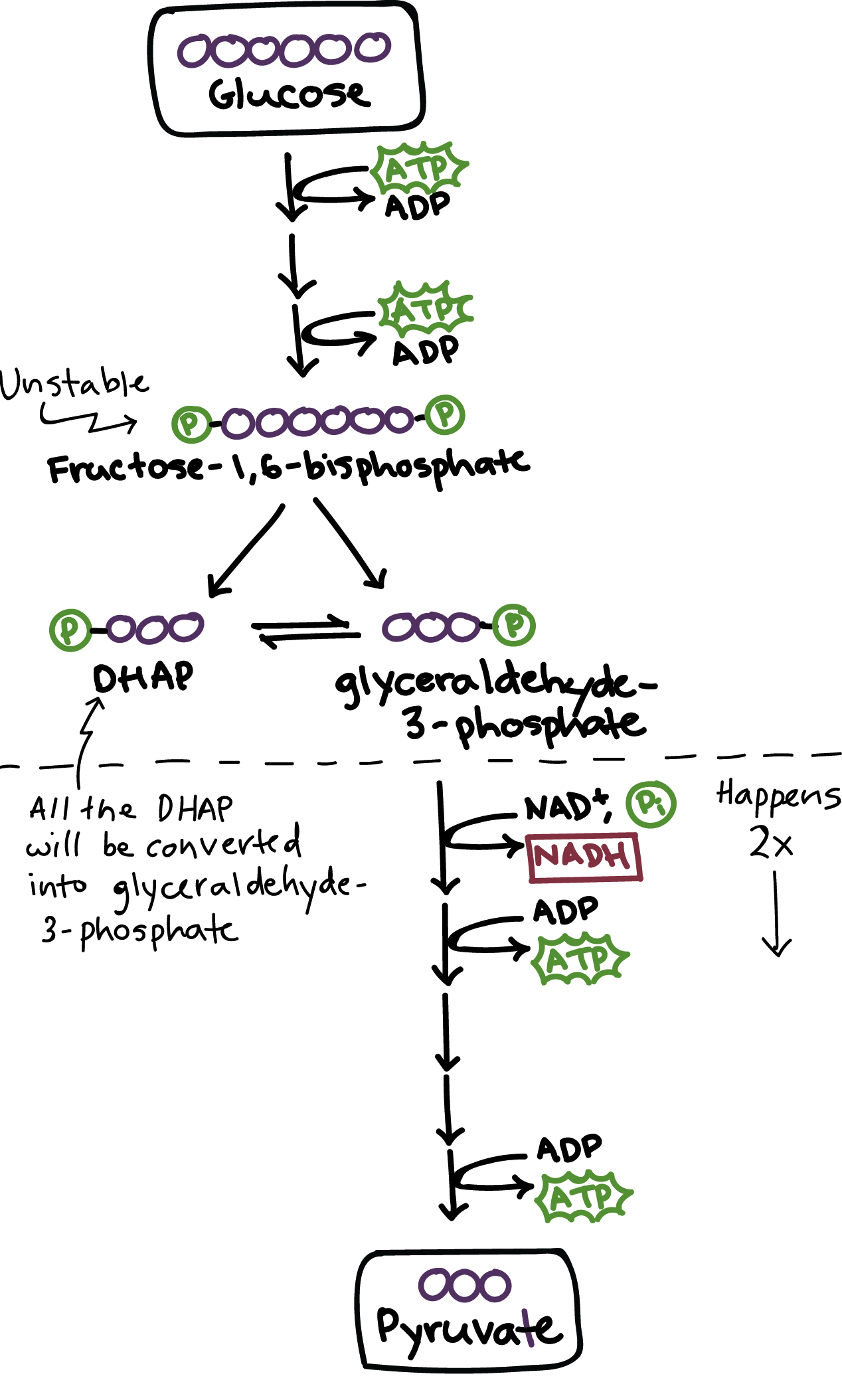
Glycolysis
Occurs in the cytoplasm
Inputs 2 ATP, 2 NAD+, 1 glucose
Outputs 4 ATP, 2 NADH, 2 Pyruvate
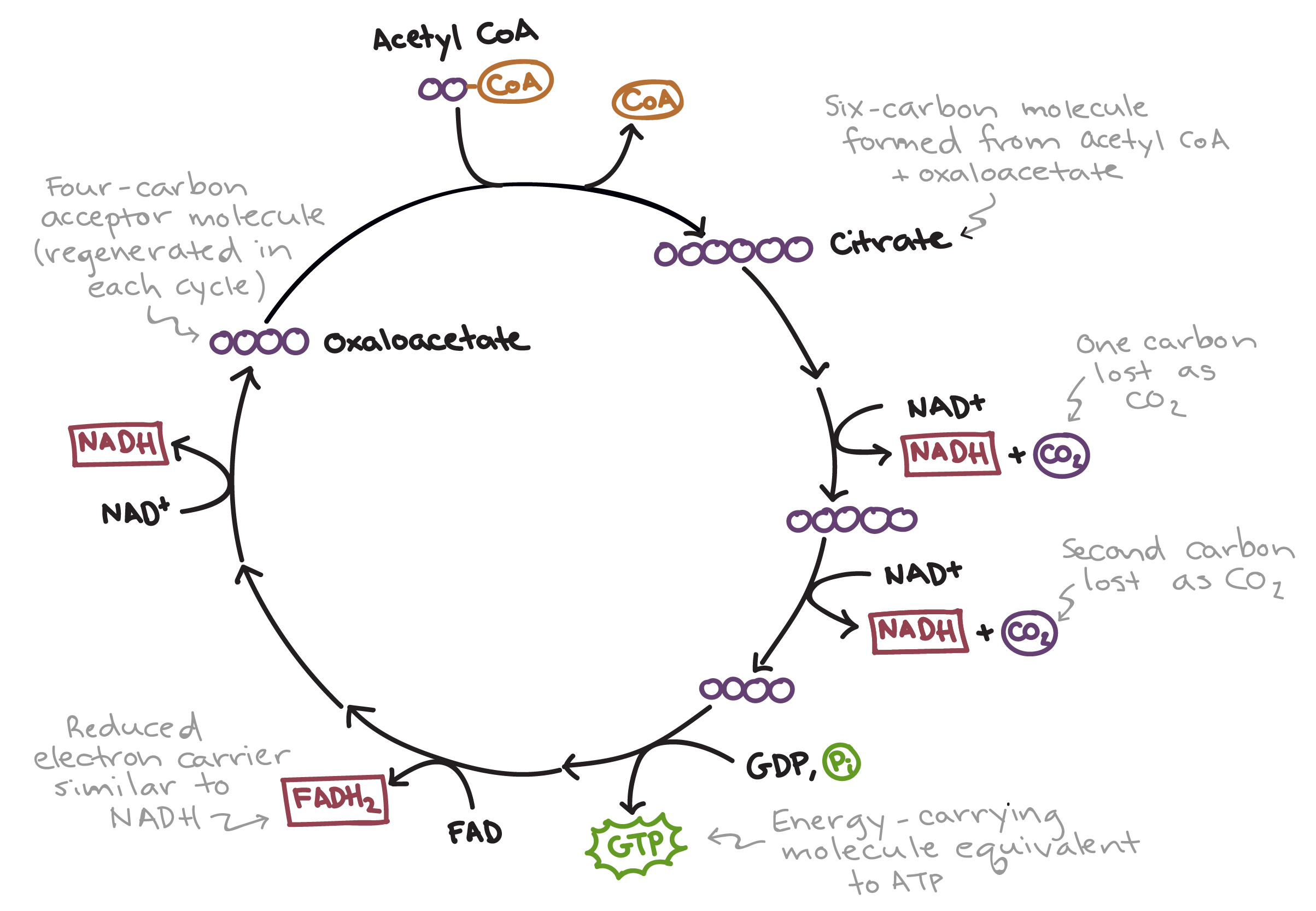
Krebs Cycle
Occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
Inputs 2 Acetyl CoA
Outputs ATP, CO2, FADH2, NADH
Electron Transport Chain & Oxidative Phosphorylation
Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane
Inputs NADH, FADH2, O2, ADP, Pi
Outputs ATP, H2O
Decouple OP from the ETC generates heat which can be used to regulate body temp
Fermentation
A process that produces energy in the absence of oxygen, glucose and other molecules are broken down to produce. Allows glycolysis to occur without oxygen producing organic molecules such as alcohol and lactic acid as waste products.
Photosystems
Protein complexes in thylakoid membranes that capture light energy for photosynthesis, primarily involving Photosystem I and II. They play a critical role in the light-dependent reactions, facilitating the conversion of light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
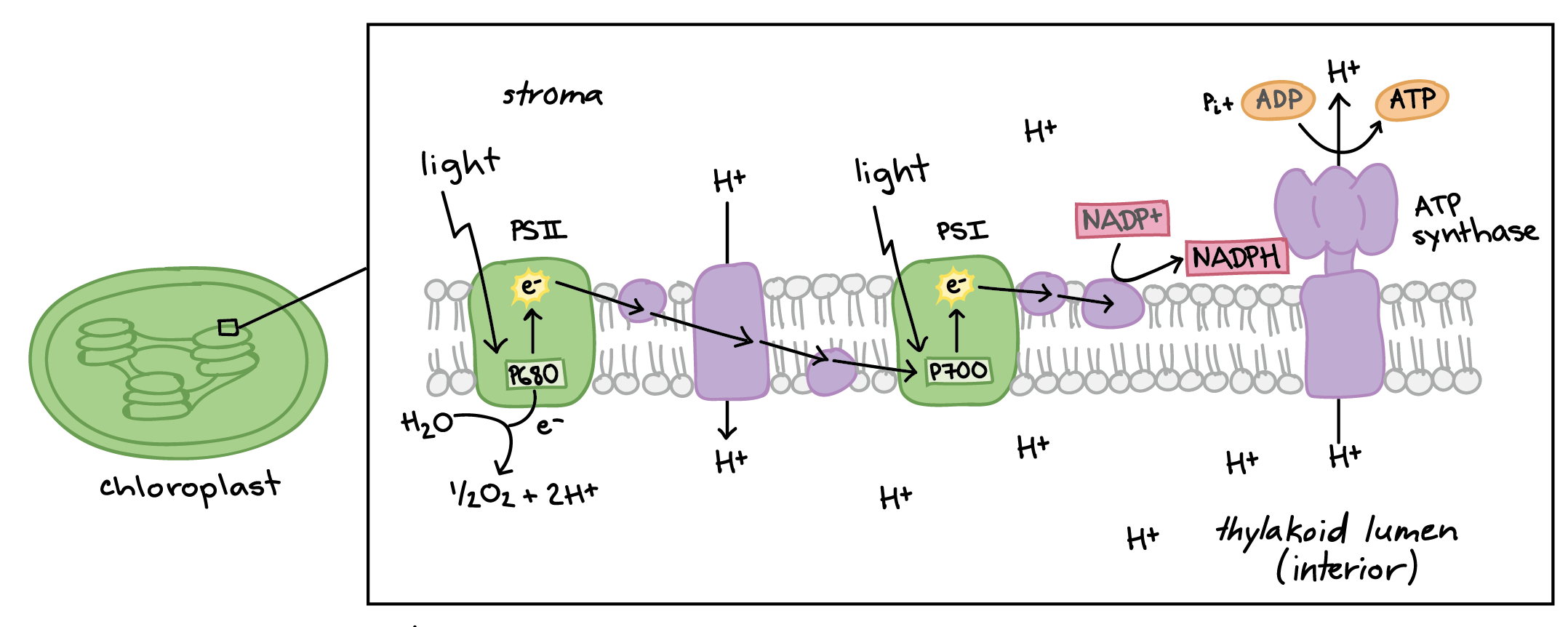
Photosystem II
This photosystem is the first in the light-dependent reactions. It absorbs light, excites electrons, and transfers them to an electron transport chain. PSII also splits water molecules, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
Photosystem I
This photosystem comes after Photosystem II in the light-dependent reactions. It absorbs light to excite electrons, ultimately contributing to the production of NADPH.
Fitness