Fasting Glucose - Exam 1
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What does this refer to
A laboratory test used to measure the concentration of glucose in the blood after an overnight fast (8–12 hours).
Fasting blood glucose (FBG) or Fasting serum glucose (FSG)
What does this refer to
To assess glucose metabolism, diagnose diabetes mellitus, and monitor treatment effectiveness.
Purpose of fasting blood glucose
What does this refer to
Screening for diabetes mellitus
Monitoring diabetic patients
Evaluating hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia
Indications for Fasting blood glucose
What does this refer to
Patient non-fasting
Severe illness or stress conditions that affect glucose metabolism
Contraindications (relative)
What does this refer to
Fast for 8–12 hours prior to the test
Avoid smoking, alcohol, or strenuous exercise before the test
Continue usual medications unless advised otherwise
Patient preparation
What does this refer to
Sterile syringe or lancet
Alcohol swab
Glucometer or laboratory analyzer
Capillary or venous collection tubes
Required Equipment
What does this refer to
Venous plasma (preferred)
Capillary whole blood (for point-of-care testing)
Specimen Type
What does this refer to
Verify physician’s order
Identify the patient using three identifiers
Explain the procedure
Ensure fasting status (8–12 hours)
Procedure Steps (1)
What does this refer to
Wash hands and wear gloves
Clean puncture site with alcohol swab
Collect the sample (capillary or venous)
Label the specimen correctly
Procedure steps (2)
What does this refer to
Transport immediately to the lab
Separate plasma within 30 minutes
Store at 2–8°C if analysis delayed (≤24 hours)
Specimen Handling
What does this refer to
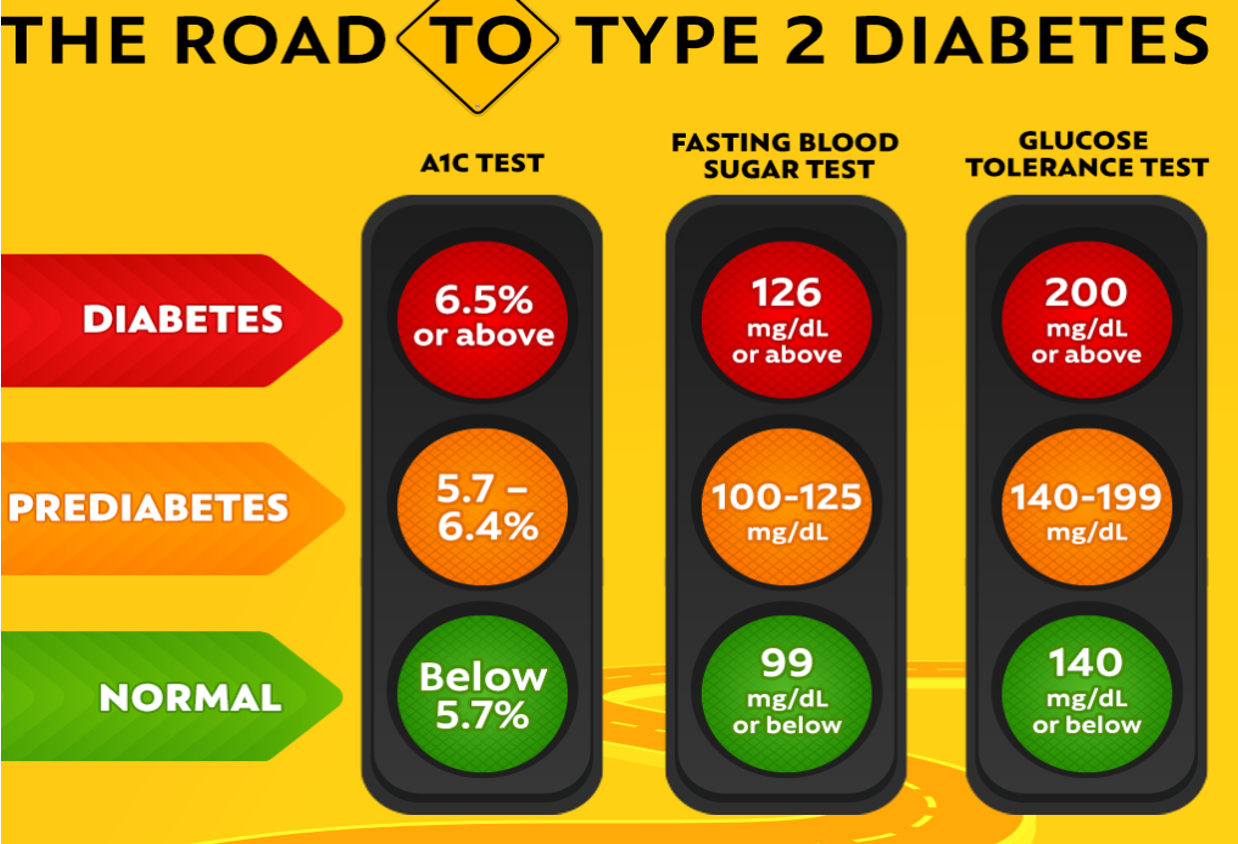
Fasting: 70–99 mg/dL (3.9–5.5 mmol/L)
Prediabetes: 100–125 mg/dL (5.6–6.9 mmol/L)
Diabetes: ≥126 mg/dL (≥7.0 mmol/L)
Normal Values
What does this refer to
Random check + signs and symptoms
Greater than or equal to 200 mg/dl = Diabetes
Random Plasma Glucose
What does this refer to
Elevated glucose suggests diabetes mellitus or impaired glucose tolerance
Low glucose indicates hypoglycemia.
Interpretation
What does this refer to
Inadequate fasting
Hemolysis
Delayed plasma separation
Improper labeling
Sources of Error
What does this refer to
Record:
Date
Time
Fasting duration
Glucose result
Any relevant observations.
Documentation
What does this refer to
Follow standard precautions and dispose of sharps and biohazard materials safely.
Infection Control
What does this refer to
Nothing to eat/drink X 8 hours (except water)
Usually done first thing in morning
Patient compliance
126+
Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG)
What does this refer to
Blood test
Average BS over past 3 months
What percentage of hemoglobin proteins in your blood are coated with sugar (glycated)
Higher= worse glycemic control
<5.7%= normal
6.5% += Diabetes
Hemoglobin A1C “Glycated Hemoglobin”