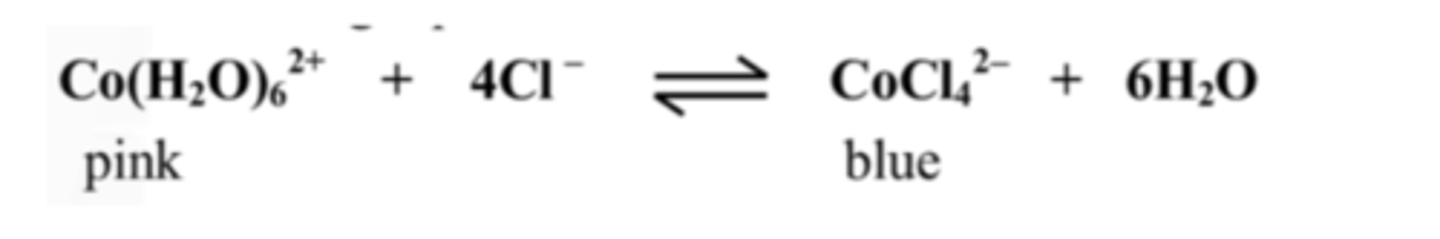Chemical Equilibrium Model Questions and Solutions
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is chemical equilibrium?
Where the forward reaction and the reverse reaction form at the same rate.
What colour would form in the above equation if the volume was
decreased?
Colourless would occur as high pressure (low volume) favours side with fewer molecules on the product side.

What colour would form in the above equation if the temperature was increased?
It would go green - less product formed.
The reaction is exothermic. If you supply heat according to Le Chatelier the system will adjust itself.

4. What would happen to the equilibrium constant in the above equation if a catalyst was used?
Nothing. Only temperature has an effect on the Kc.
A catalyst would speed up the rate of reaction but has no effect on equilibrium concentrations/yields.

5. Le Chatelier's principle predicts best yields for a reaction at low
temperatures and high pressure. Suggest reasons why these condition might not be suitable?
Low temperature will mean the reaction is very slow and this may be costly.
High pressure is difficult to maintain and can be unsafe as well as costly.
6. Why is chemical equilibrium described as a dynamic state?
The reactants are constantly forming the products and the products are constantly forming the reactants.
7. State Le Chatilier's principle
Systems at equilibrium react to minimise or oppose the applied stress
8. What effect does increasing the temperature have on the equilibrium constant, Kc
Increasing the temperature increases the Kc
9. How does an increase in temperature affect the pressure of an equilibrium mixture?
Increased temperature increases the pressure aster will be more collisions with the walls of the container.
10. Explain the effect on the Fe3+ ion concentration of adding KCNS to the equilibrium mixture above.
Adding CNS- will drive the reaction to the product side due to Le Chatiliers principle.
Therefore the Fe3+ concentration will decrease.
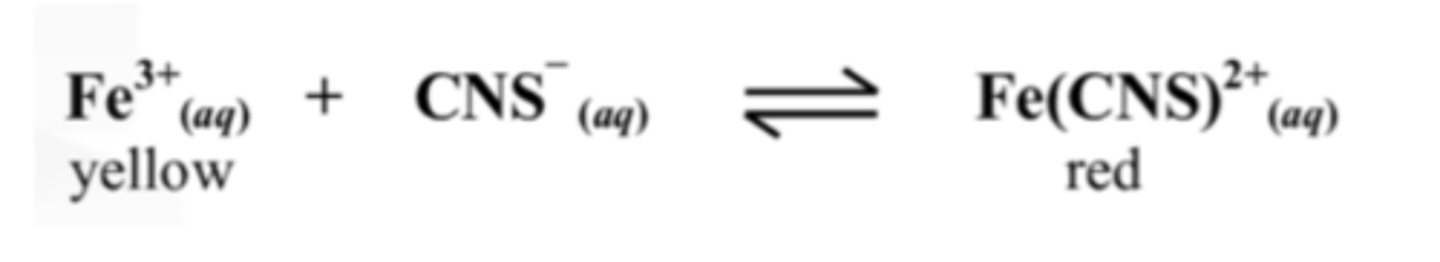
11. Explain why changing the volume has no effect on the equilibrium in the equation above
Both the reactants and products are aqueous.
Pressure only has an effect of they are gases.
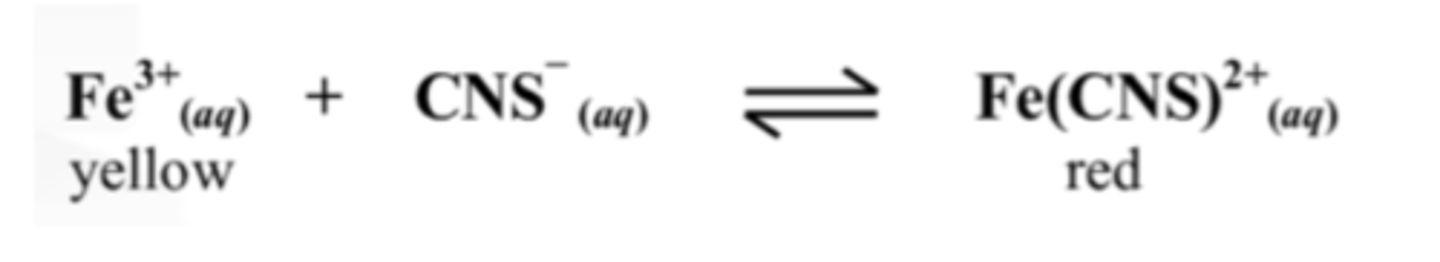
12. The red colour disappeared when placed in an ice bath.
State whether the equilibrium constant, Kc is bigger or smaller at the lower temperature
Smaller. The Kc increases with temperature increase.
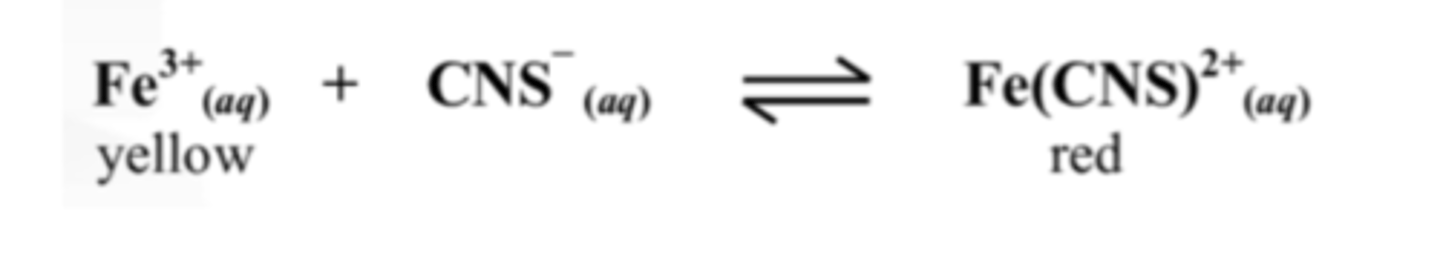
13. The red colour disappeared when placed in an ice bath.
State whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic.
The reaction is endothermic.
Cooling a substance favours the reactant side.
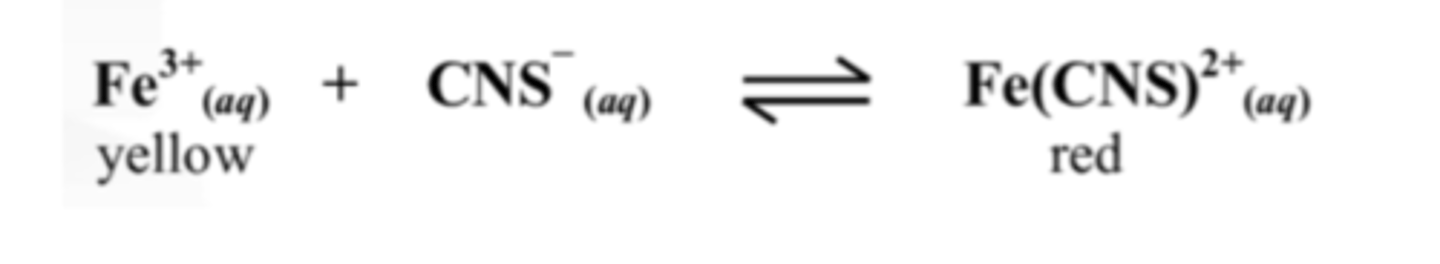
14. State and explain the effect on the equilibrium concentration of triiodide ions of adding a substance that reacts with iodine e.g. starch
The triiodide ions would decrease as the equilibrium would shift to the reactants to help restore the iodine concentration.
This occurs if an additional substance is being added to the equilibrium e.g. starch.

15. Explain the lilac colour in the test tubes A - D
Lilac is evidence of equilibrium as it is a colour in between pink and blue.
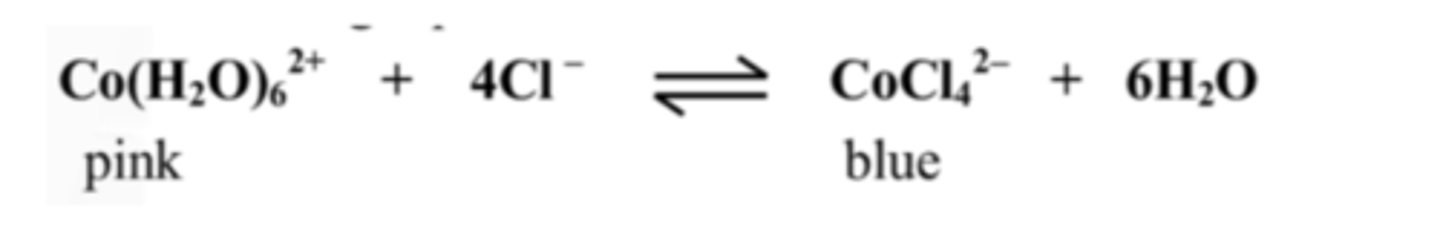
16. Explain the colour that appeared when adding water to test tube A
A pink colour forms as the reactions shifts backwards to decrease the H2O concentration.
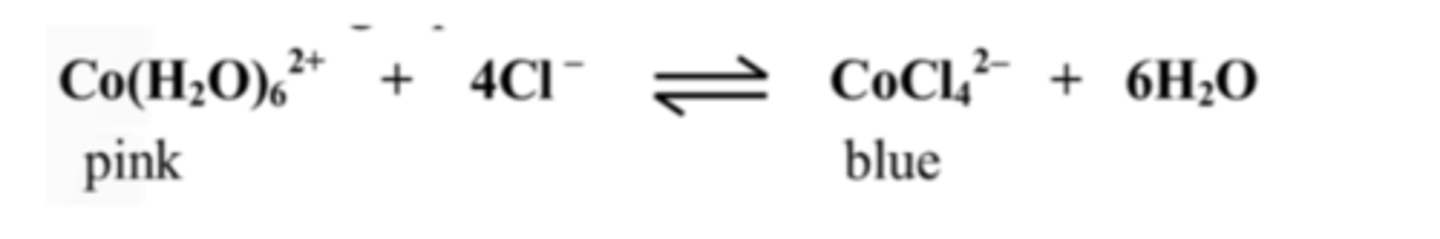
17. Explain the colour that appeared when conc. HCl was added to test-tube B
A blue colour forms as the reaction shifts forwards to decrease the Cl- ions.
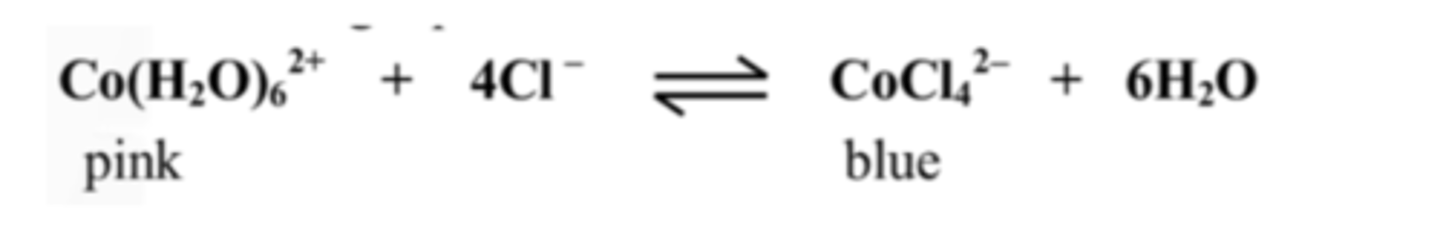
18. The solution went pink when placed in ice. Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? Explain your answer.
The reaction is endothermic.
Cooling a substance favours the reactant side.