SZ 03 Neural correlates / dopamine hypothesis
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
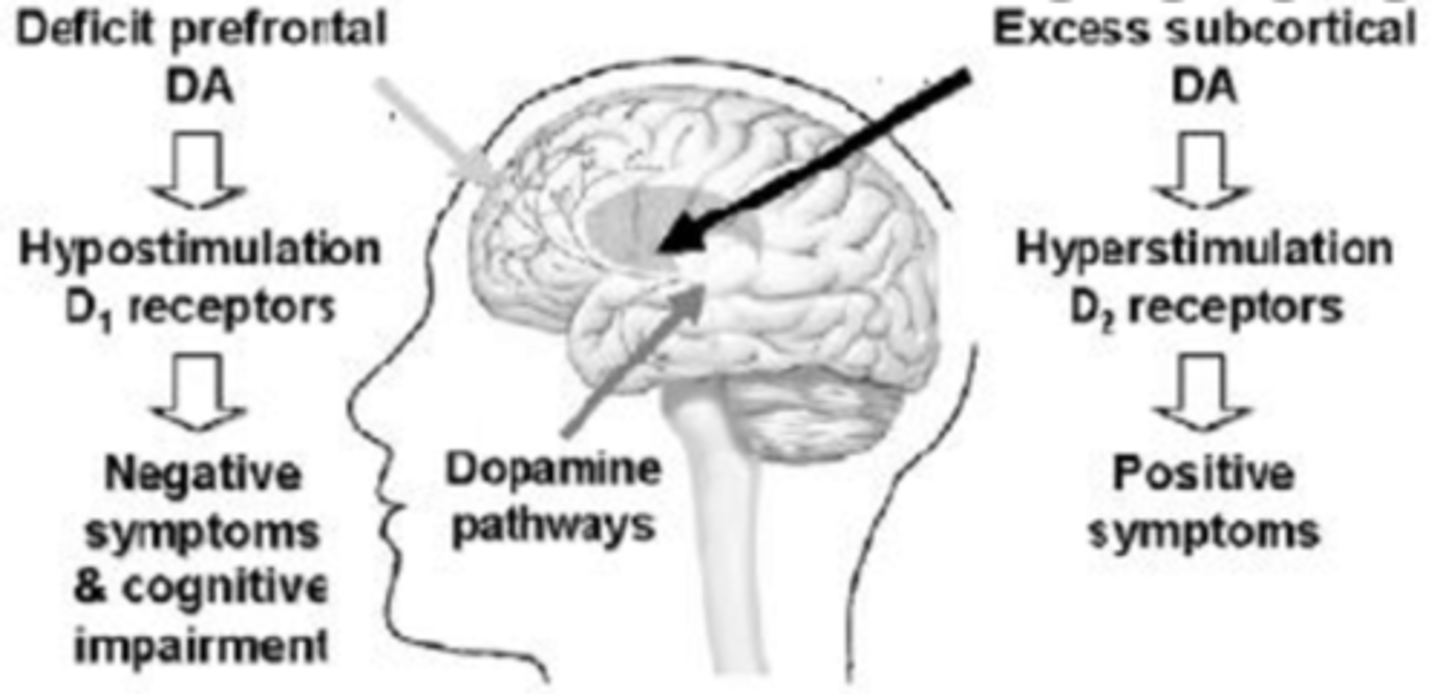
How does the dopamine hypothesis explain positive symptoms of schizophrenia? (3)
Positive symptoms caused by...
* High levels of dopamine (hyperdopaminergia) ...
* ...at D2 receptors ...
* ...in subcortex
How does the dopamine hypothesis explain negative symptoms of schizophrenia? (3)
Negative symptoms caused by...
* Low levels of dopamine (hypodopaminergia) ...
* ...at D1 receptors ...
* ...in prefrontal cortex
Explain why the findings of Howes' scanning study support the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia (3)
* Review of PET scans
* Moderate- high difference in levels of dopamine at D2 receptors between patients and controls
* Suggests that high dopamine causes positive symptoms
Explain why drug trials of antipsychotics (APs) support the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia (4)
(Bonus: why are trials especially strong evidence?)
* APs block dopamine (DA) receptors
* Reduce DA at D2 receptors
* APs are effective
* Suggests high DA was the problem / cause in the first place.
(Bonus: clinical trial = experiment => evidence of causal relationship, so strong evidence for role of DA)
Explain how schizophrenia could be due to glutamate instead of dopamine (3)
•High glutamate may be the ultimate / primary cause of DA dysfunction...
* ... and all symptoms of SZ
* So DA is a proximate / secondary cause