General Pathology Topic 1 : Introduction
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is this?
Hypostatic congestion
What is this?
Hemoglobin imbibition

What is this?
Bile imbibition
What is this?
Autolysis
What is this?
Bloat
What is this?
Autolysis
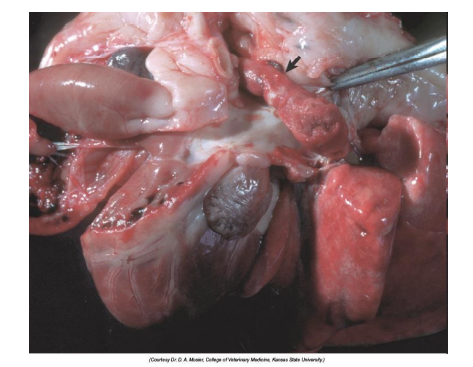
What is this?
Fat Clot
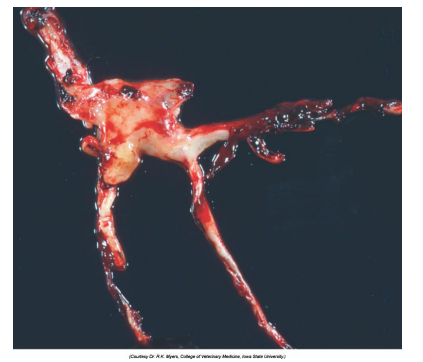
What is this?
Thrombus
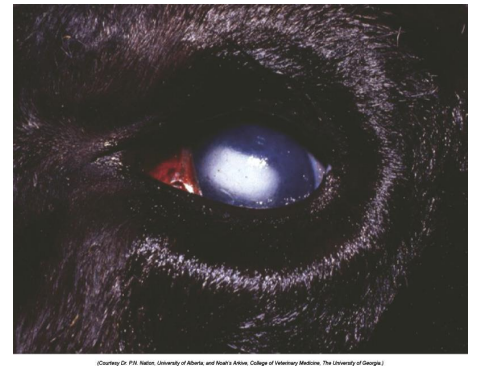
What is this?
Clouding of cornea
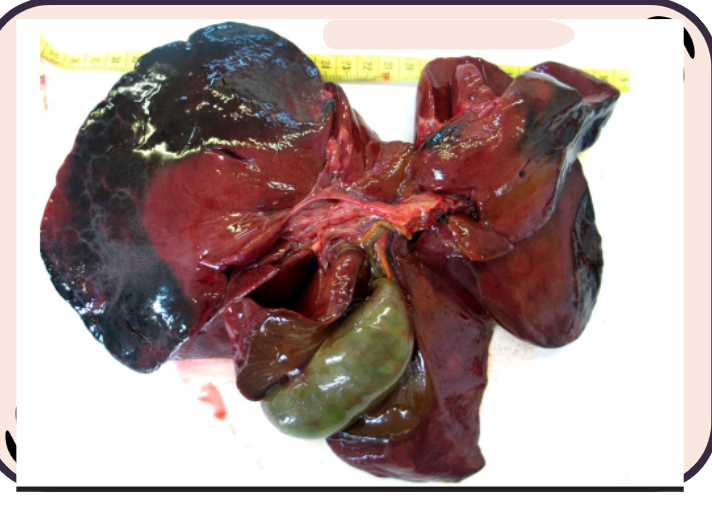
What is this?
Pseudomelanosis
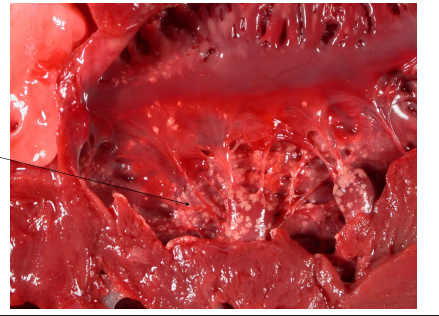
What is this?
Euthanasia artifacts

What is this?
Lungs: congestion
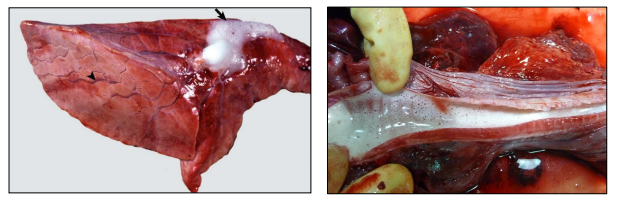
What is this?
Pulmonary edema
What is this?
Pulmonary edema
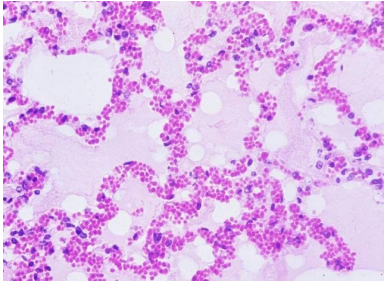
What is this?
Pulmonary edema
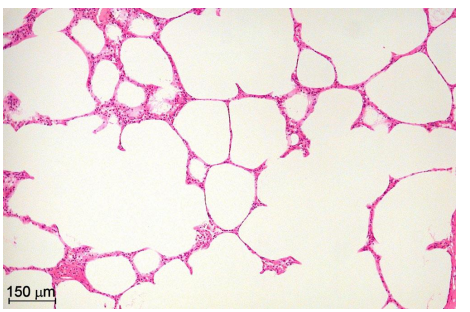
What is this?
Pulmonary emphysema
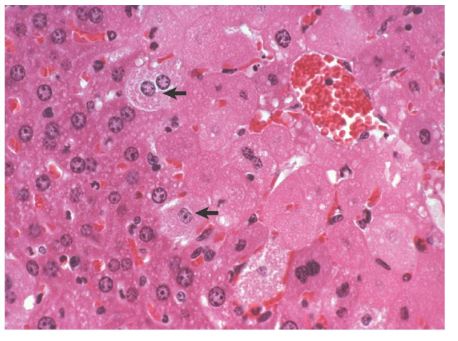
What is this?
Hydropic degeneration
What is this?
Hydropic degeneration
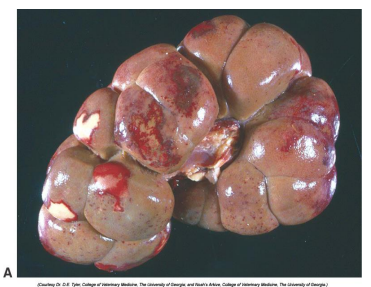
What is this?
Coagulation necrosis
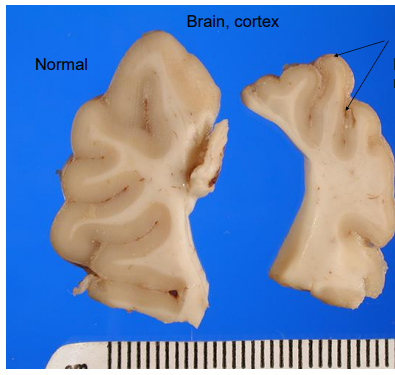
What is this?
Liquefactive necrosis
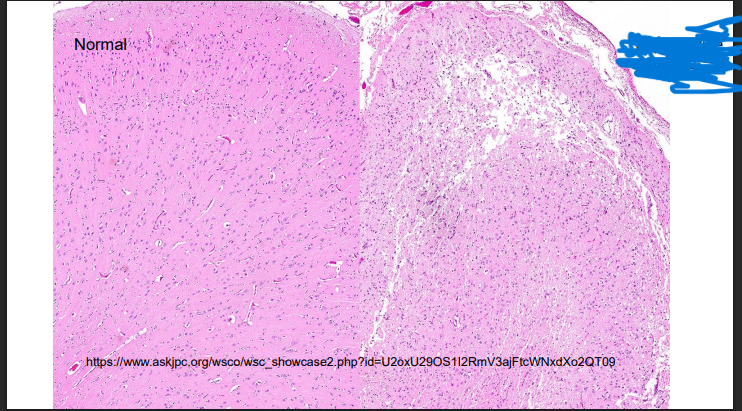
What is this?
Liquefactive necrosis
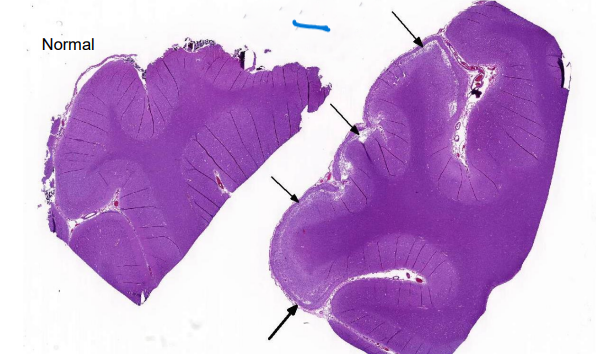
What is this? Give Disease diagnosis and possible cause
Liquefactive necrosis
Diseases dg: polioencephalomalacia
Possible causes – thiamine deficiency, lead toxicosis, etc.

What can you see and give a possible cause
Chronic abscess of the vertebrae
Liquefactive necrosis
cause – Arcanobacerterium pyogenes
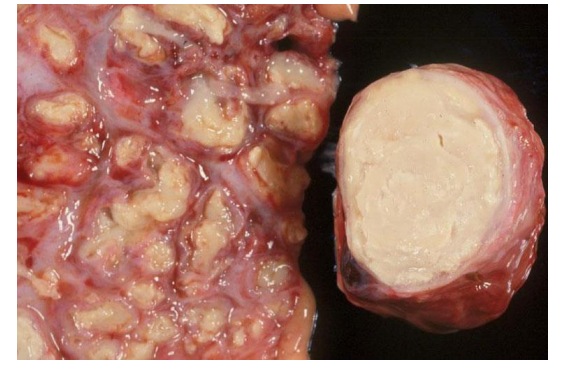
What is this?
Caseous necrosis

What is happening here and give a possible cause
Wet gangrene, mammary gland (longitudinal section through the teat), sheep.
Staphylococcal infection caused the gangrenous mastitis
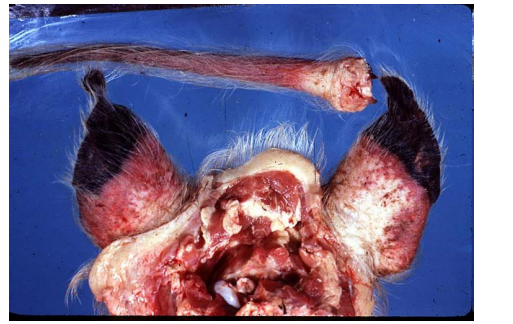
What is this?
Dry gangrene
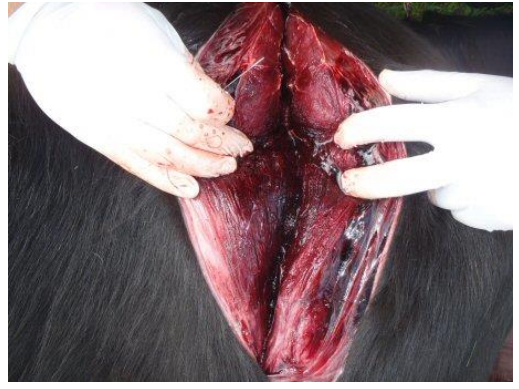
What is this?
Gas gangrene
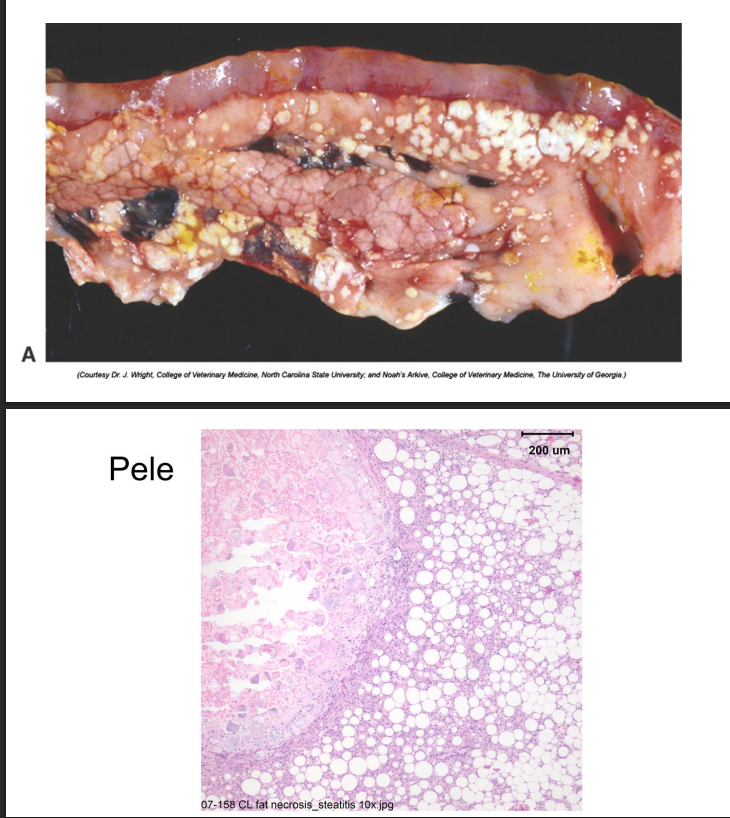
Fat Necrosis
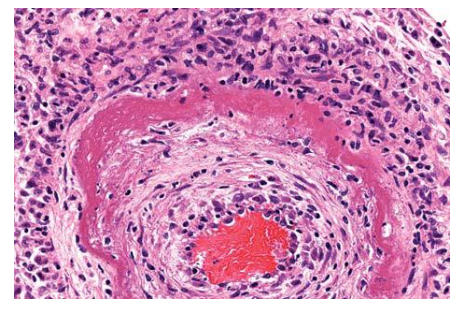
Fibrinoid necrosis
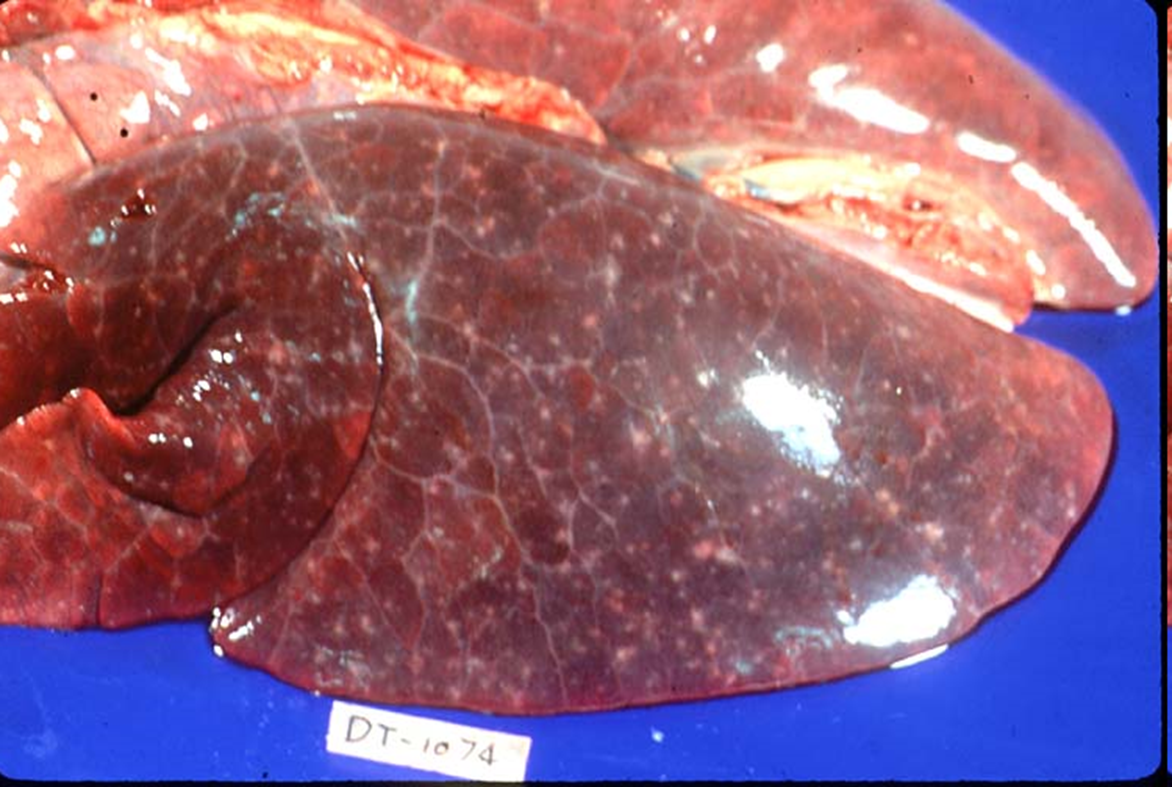
What organ is this? Give a morphological description, morphological diagnosis, possible etiology and the disease name
Organ -- Lung
Morph. description: Diffusely, left lung lobes are dark red
In the left lung lobes diffusely scattered there are multifocal white to gray, small to pinpoint foci.
Morph. dg.: Lung – necrosis, multifocal, moderate
Etiology -- toxoplasma gondii (protozoal organism)
Disease – toxoplasmosis
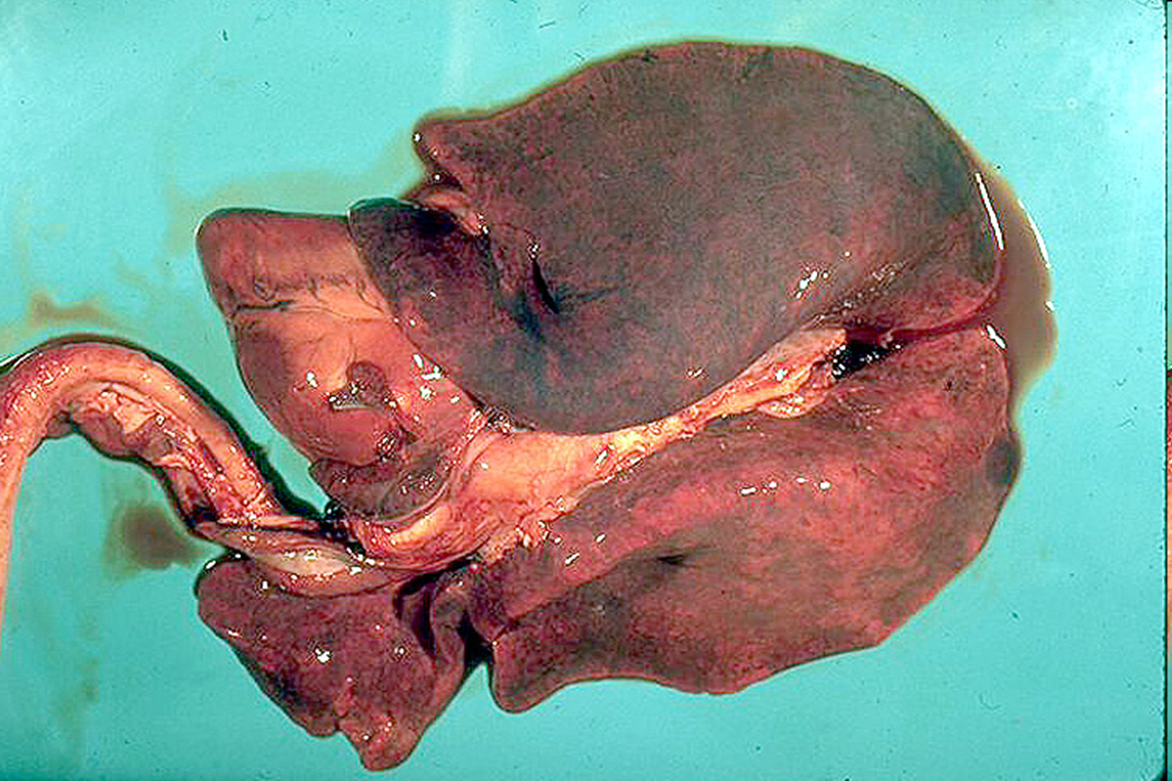
What organ is this? Give a morphological description, morphological diagnosis, disease diagnosis, and possible etiology
Organs – lung, heart, trachea
Morph. description:
All lung lobes are diffusely dark red, with right lung lobes more extensively red. There is a large amount of red-tinged fluid oozing from the lungs. In the left ventricle of the heart, there is a focally extensive pale yellow area occupying 90% of the left ventricular wall.
Morph. dg.:
Lungs – congestion and edema, diffuse, severe, acute
Heart – necrosis, focally extensive, acute, severe
Disease dg. -- white muscle disease
Etiology– vitamin E and selenium deficiency
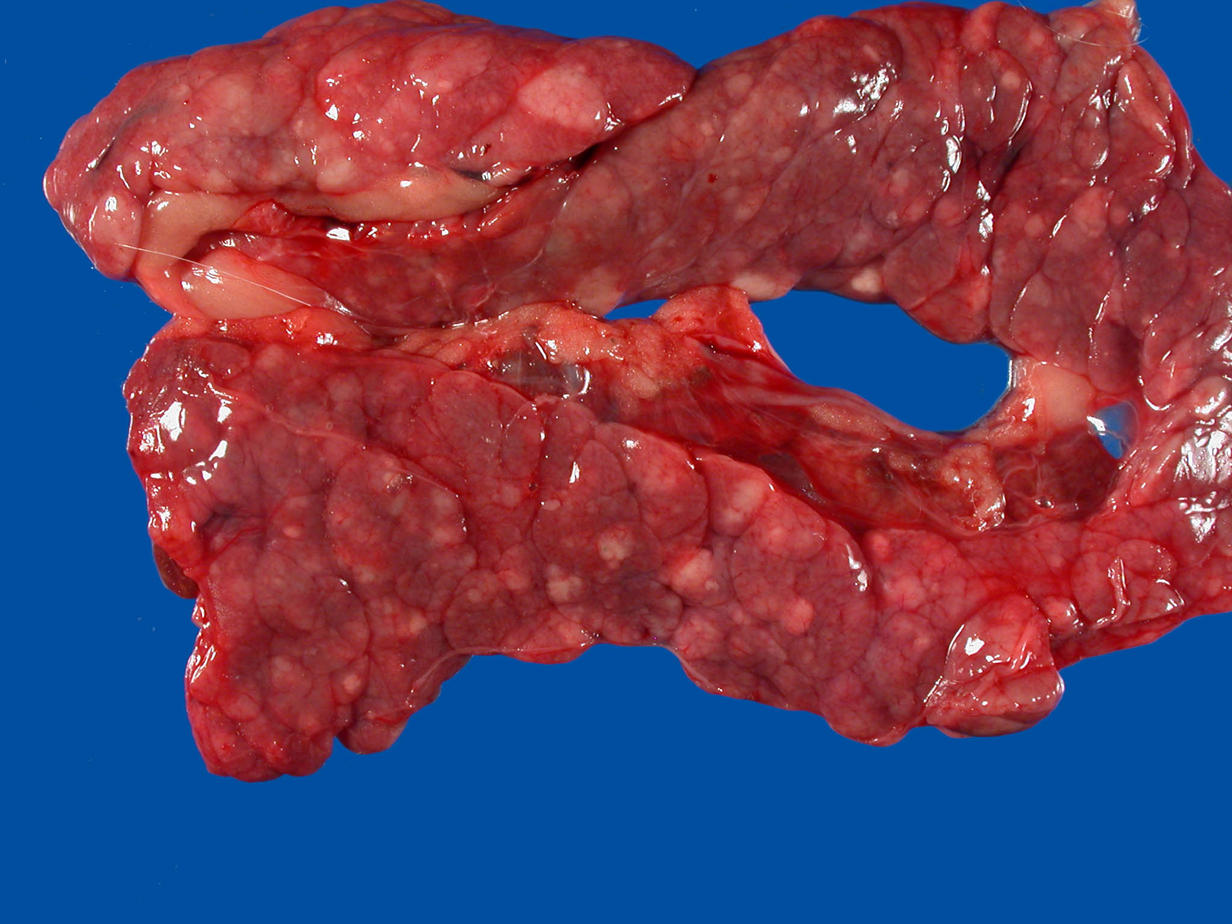
What organ is this? Give a morphological description, morphological diagnosis,
Organ – pancreas
Lesion description
Widely scattered within pancrease there are numerous nodules that are light gray, partially circumscribed, ranging in size from few mm to 2 cm in diameter.
Morph dg.
Pancreas – nodular hyperplasia, multifocal, severe, chronic
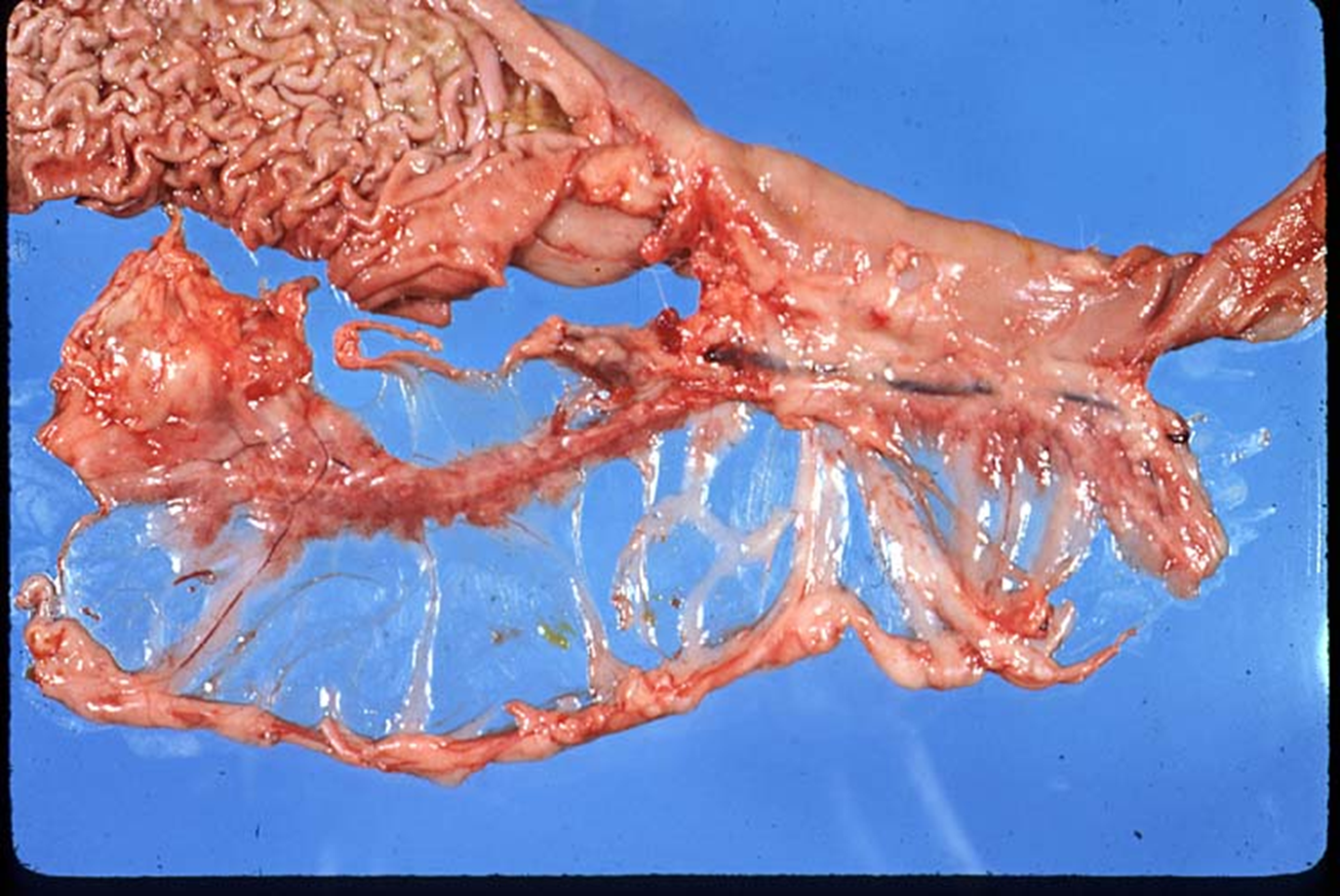
What organ is this? Give a morphological description, morphological diagnosis, and possible etiology
Organs -- stomach, duodenum, pancreas and omentum
Lesion -- the pancreas is almost completely absent. Remaining is a thin, strip of pale pink parencnhyma.
Morph. dg.:
Pancreas - atrophy, diffuse, severe
Etiology – immune mediated disease during which lymphocytes attack and destroy pancreatic acinar cells
What organ is this? Give a morphological description, morphological diagnosis, and possible etiology
Organs – heart (with pericardium opened), lungs
Lesion description – epicardial surface of the heart diffusely is covered with gray dull, few mm thick membrane that is ruptured in a few foci. Pericardium is thickened and gray-red, non-transparent. Lungs (right side lobes) ar diffusely red with small, indistinct gray foci few mm in diameter.
Morph. dg.
Heart – pericarditis, fibrinous, severe, subacute
Lung – pneumonia, moderate (possible diagnosis, not sure)
Etiology – systemic bacterial infection with septicemia
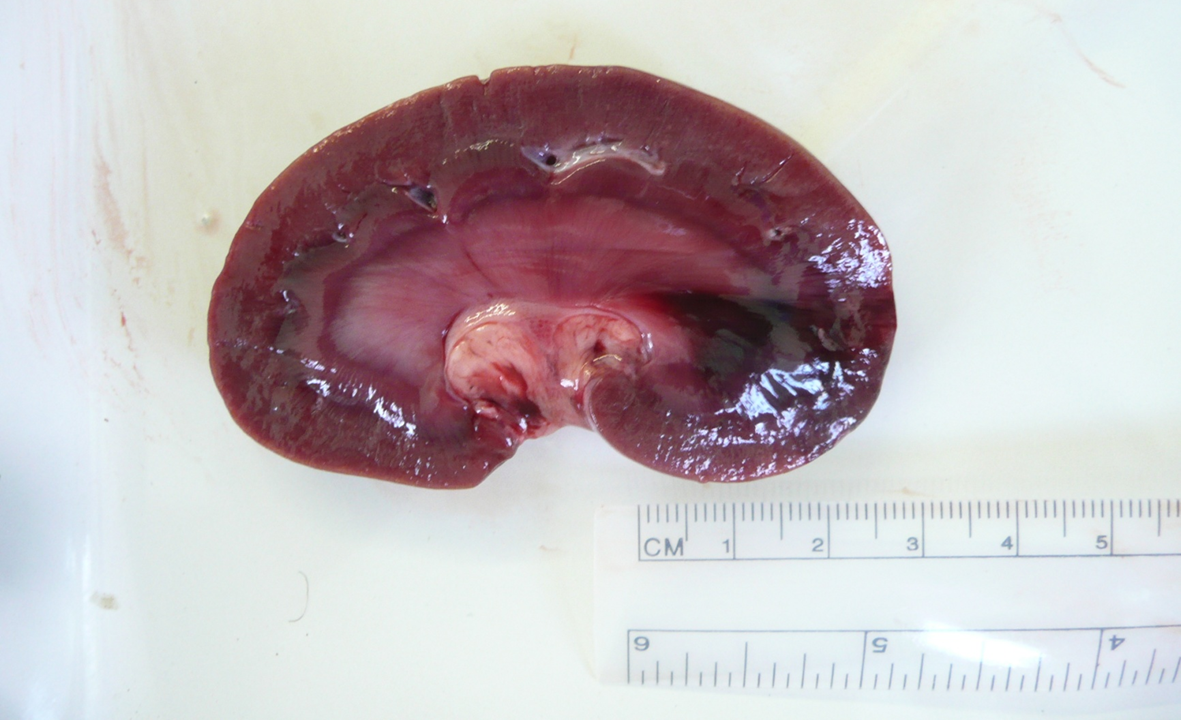
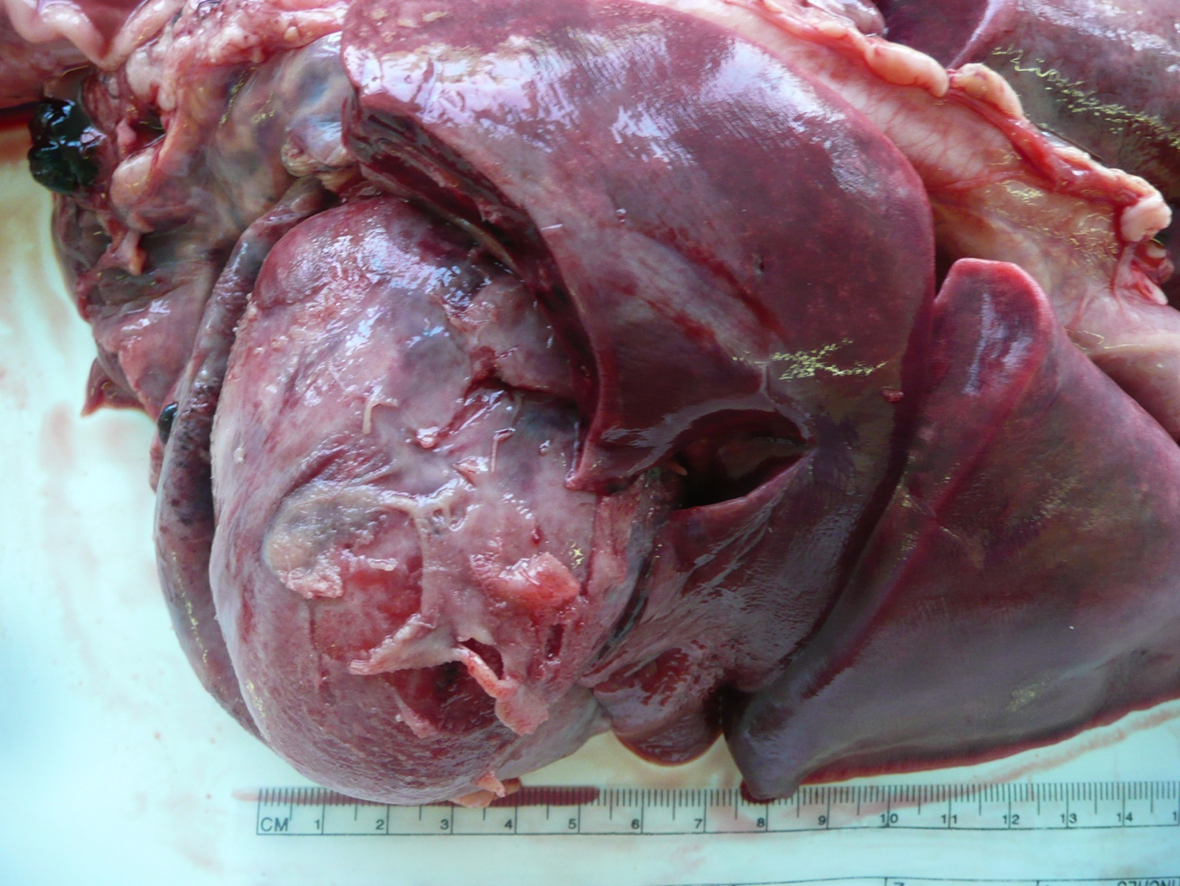
What organ is this? Give a morphological description, morphological diagnosis, and possible etiology and pathogenesis
Organ – kidney
Lesion description – at one pole of the kidney there is a well-delineated triangular dark red area with its tip in the medulla and approx. 2cm wide base in the cortex.
Morph. dg.
Kidney – infarct, focal, moderate, acute.
Etiology – septicemia
Pathogenesis – vascular damage due to septicemia cause formation of thrombi. Such thrombus have occluded a vessel (likely a vein) resulting in infarct (focus of ischemia and hemorrhage in this case).
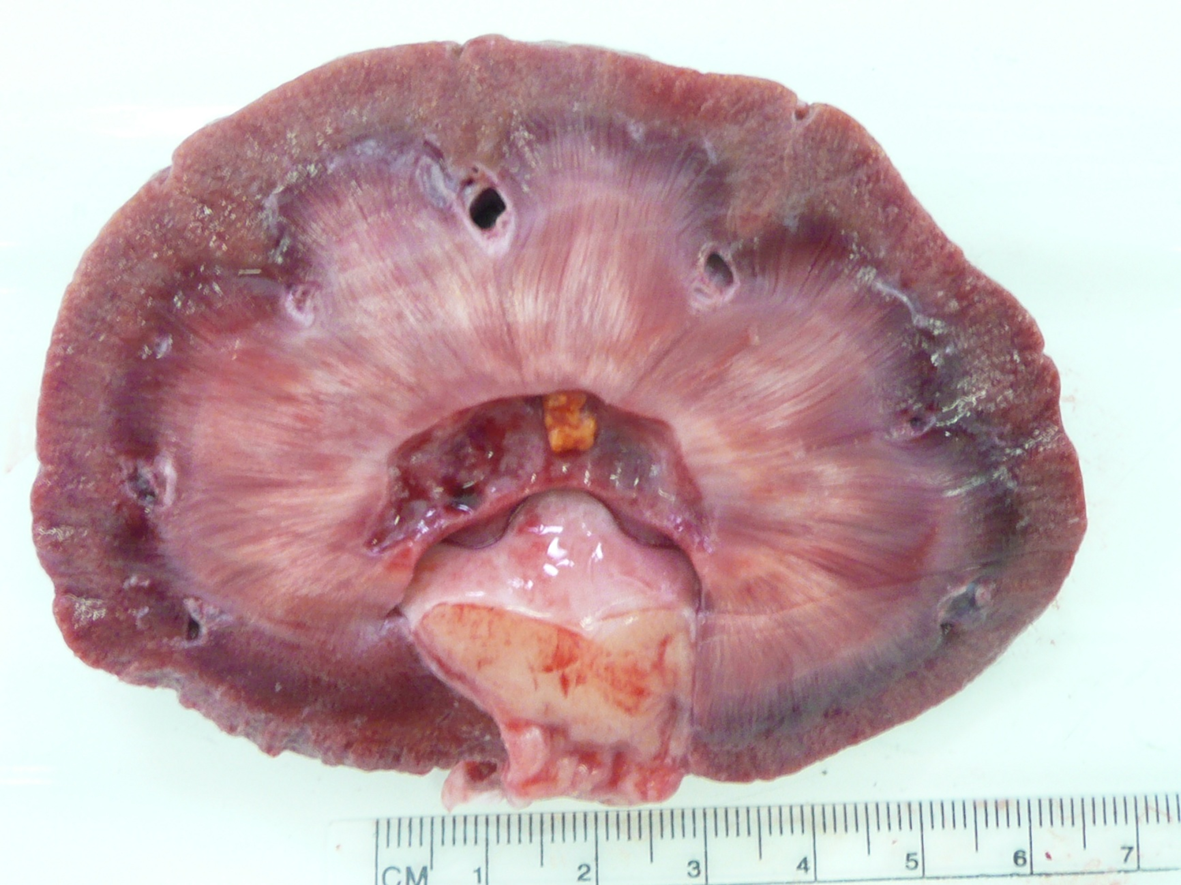
What organ is this? Give a morphological description, morphological diagnosis
Organ – kidney
Description – renal capsular surface is irregular, cortex is reduced in thickness in a few foci and inner medulla contains linear pale yellow streaks. Renal pelvis is dilated and contains yellow concretion, about 7x7mm in size with irregular surface
Morph. dg.: nephritis, tubulointerstitial, moderate to severe, chronic with hydronephrosis and nephrolith.
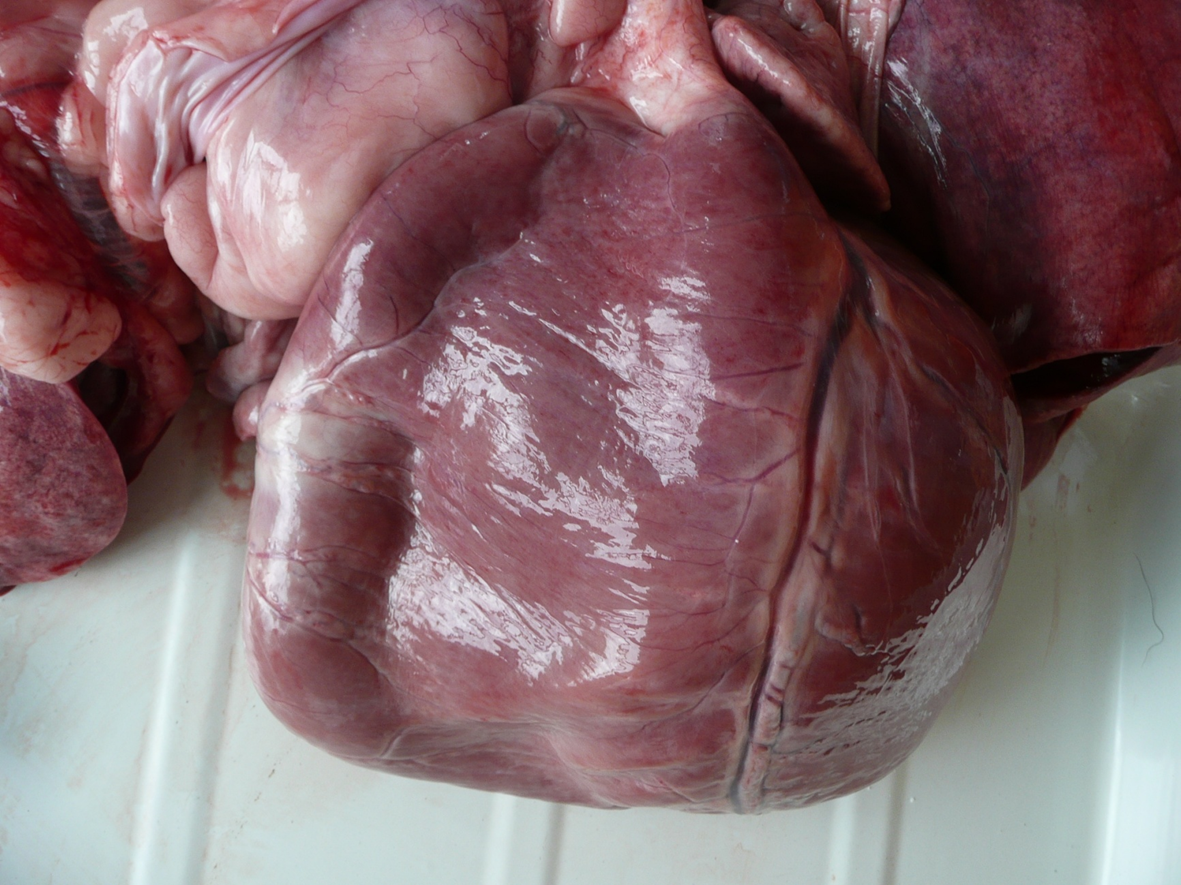
What organ is this? Give a morphological description, morphological diagnosis, disease diagnosis, and possible cause
Organ – heart
Description – the apex of the heart is square shaped. The lumen of the right ventricle is markedly expanded and the wall of the right ventricle is flaccid.
Morph. dg.
Heart – right ventricular dilation, severe
Ds. dg. – dilated cardiomyopathy
Cause – unknown, inherited, nutritional.

What organ is this? Give a morphological description, morphological diagnosis, disease diagnosis, and etiology
Organ – spiral colon and mesentery
Description – mesentery between colonic loops is expanded by clear, gel-like substance (material).
Morph. dg.
Spiral colon -- mesenteric edema (mesocolonic edema), acute, severe
Ds. dg. -- edema disease
Etiology – Stx2e-producing E. coli
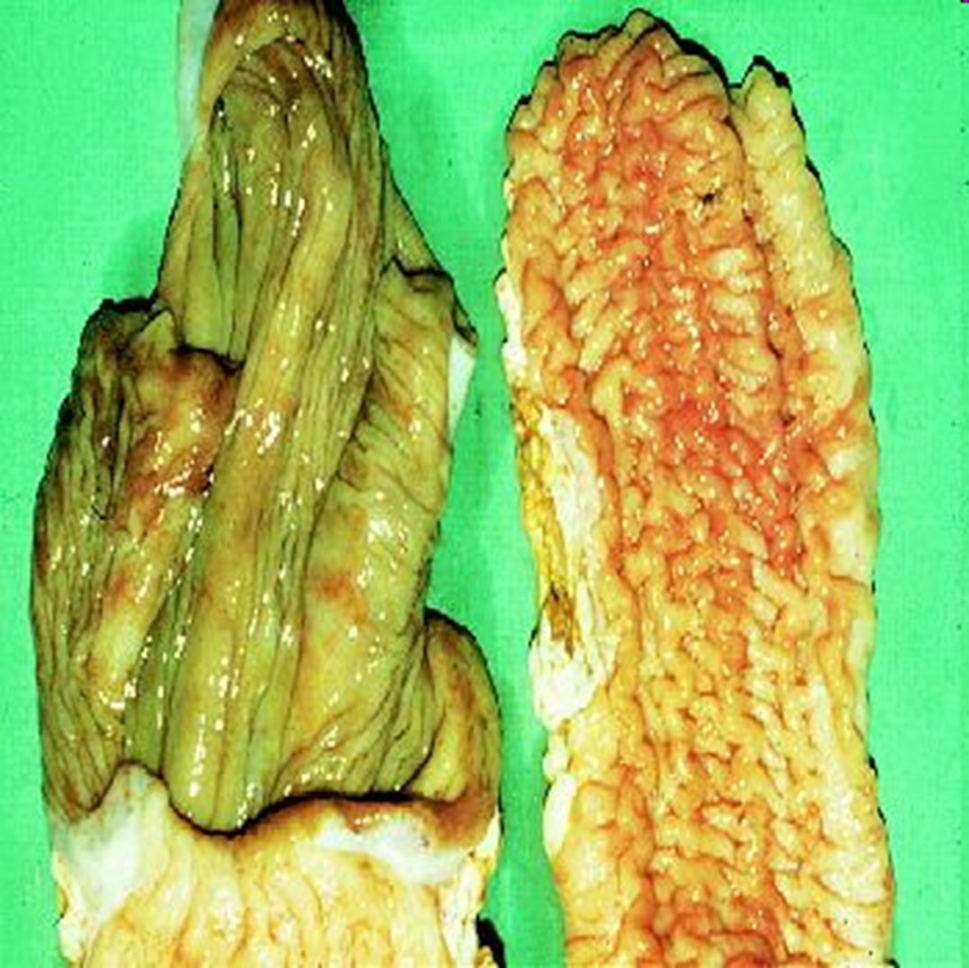
What organ is this? Give a morphological description, morphological diagnosis, disease diagnosis, and etiology
Organ -- ileum (normal on the left, abnormal on the right) (lumen is open so that mucosal surface is visable)
Description – mucosal surface of the ileum is markedly thickened, forming irregular folds.
Morph. dg.
Ileum – enteritis, granulomatous, diffuse, severe, chronic
Ds. dg. -- paratuberculosis
Etiology -- Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis
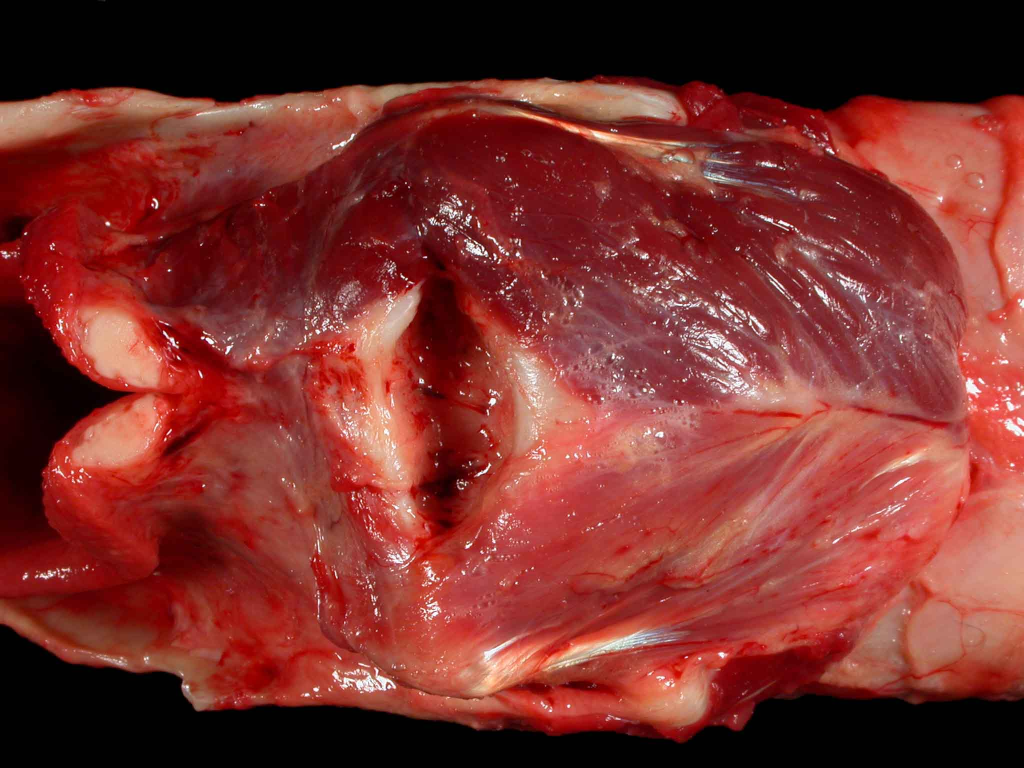
What organ is this? Give a morphological description, morphological diagnosis, disease diagnosis, and possible cause
Organ – larynx
Lesion description -- the laryngeal muscle is unilaterally reduced in size – it is pale pink, thin (left side).
Morph. dg.
Larynx – mm. crycoarytenoid dorsalis sinistra atrophy, diffuse, severe, chronic
Ds. dg. – laryngeal hemiplegia (common name «roarer»).
Cause – laryngeal recurrent nerve damage
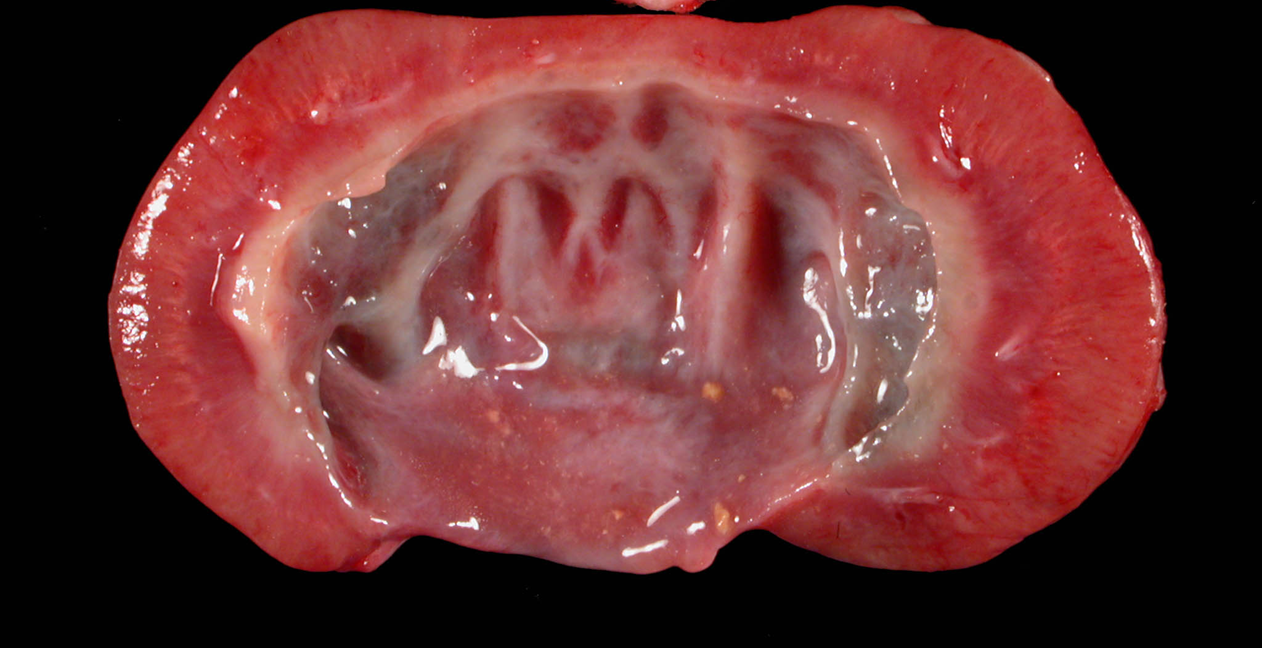
What organ is this? Give a morphological description, morphological diagnosis, disease diagnosis, and pathogenesis
Organ – kidney
Lesion description – renal pevis is widely dilated, renal medulla is narrow and thin (less than 1cm), renal cortex is of uneven thickness, segmentall reduced in thickness. There is small amount of yellow granular material present within renal pelvis.
Morph dg.
Kidney – hydronephrosis, severe, chronic, with medullary atrophy and nephroliths
Ds. dg.: nephrolithiasis.
Pathogenesis -- kidney stones have obstructed ureters resulting in accumation of urine in the renal pelvis and expansions of it (hydronephrosis).
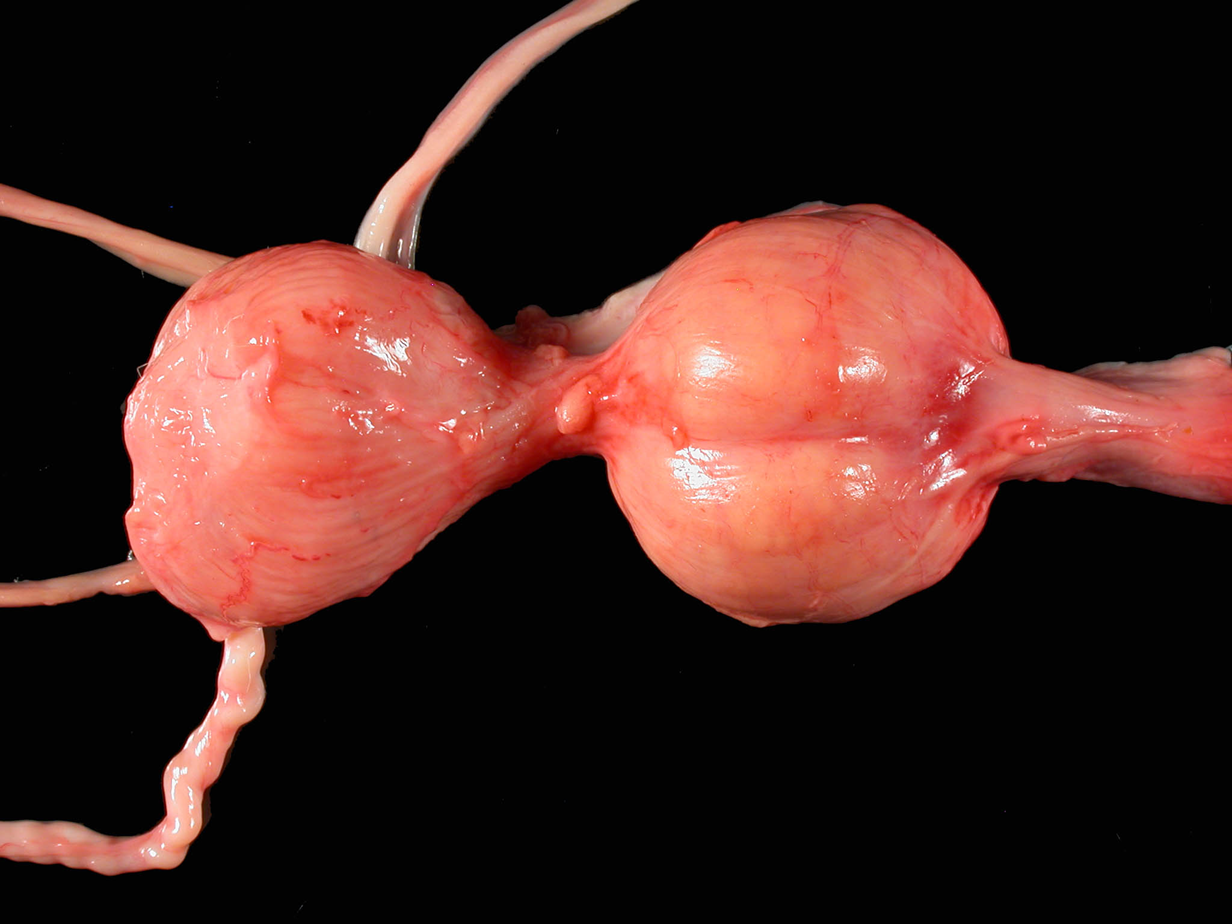
What organ is this? Give a morphological description, morphological diagnosis.
Organs – urinary bladder, prostate, ureters, ductus deferens, urethra
Lesion description – both lobes or prostate are symmetrically enlarged, ….. in size.
Morph. dg.
Prostate – hyperplasia, bilateral, severe, chronic
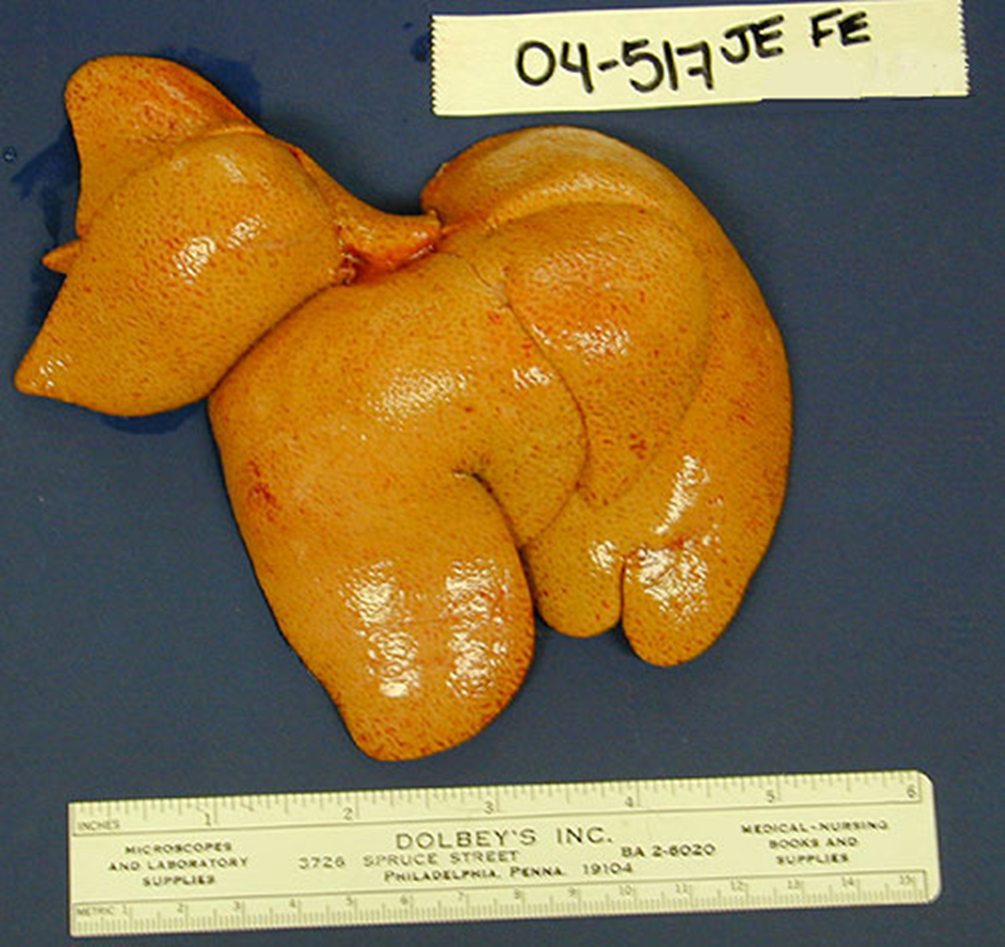
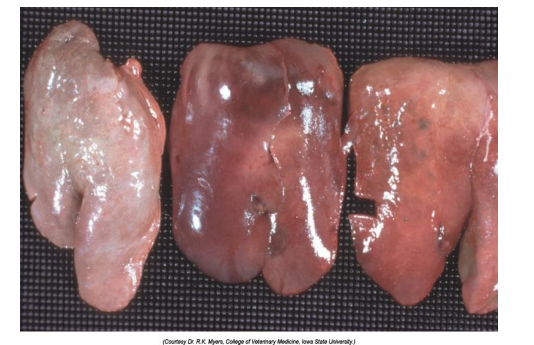
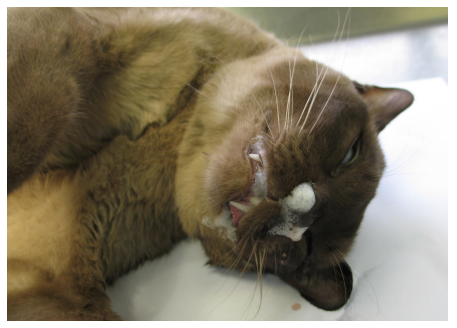
What organ is this? Give a morphological description, morphological diagnosis, and possible cause
Organ – liver
Description – the liver is diffusely yellow with slightly rounded edges. There are pinpoint red foci scattered regularly throughout with occasional larger foci.
Morph. dg.:
Liver -- hepatic lipidosis, diffuse, severe, chronic
Causes: sudden anorexia in an obese cat, diabetes, toxins