Introduction to English Linguistics Flashcards
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards for Introduction to English Linguistics, covering key terms and concepts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Language
A code for conveying information through symbols and syntax. relations are arbitrary
Syntax
the set of rules and principles that govern how words and phrases are arranged to form well‑formed sentences.
The sailors spoled the girls with binoculars.
Differential
Interdependence of meanings
Language sign is arbitrary, but
but not rsndom; not obvious relations between sound or shape and meaning.
Onomatopoeia
a word that sounds like the noise it describes.
e.g. moo, boom, splash

Word in a language
symbol within a differential system
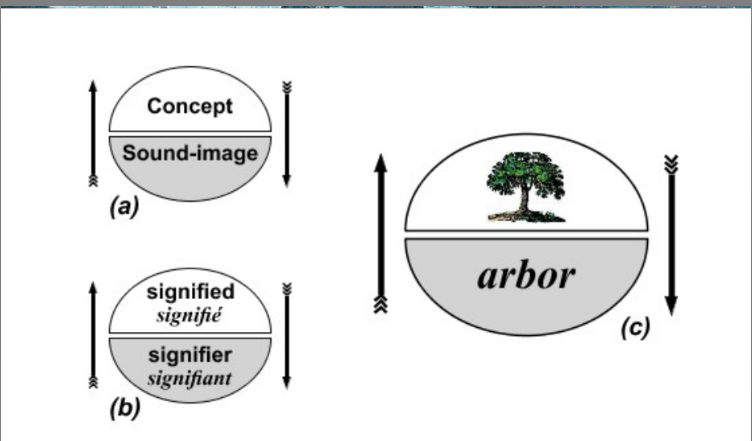
Saussure (Language as a Set of Signs)
Binary combinations of form (letters/sounds) and meaning (concepts).
Words are: 1 arbitrary, 2 conventional, 3 associative
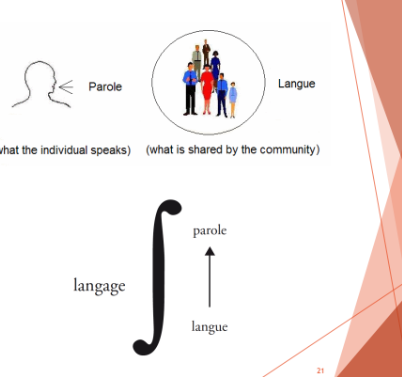
structural Linguistics
focus on language system(langua)
Not the actual language used by individuals (parole)
Goal: analyze elements in language system and their relations (e.g mat, bat, cat…)
3 main function of language
Expressive
representative
appellative
Linguistic symbols(function and form)
Symbols have function and form, e.g. Mary swims.
Form: Sequence of 9 sounds in linear sequence make up a linear(noun, verb…)
of 2 words
Function: The words are constituent parts of the sentence(subject, predicate…)
Language has structure (linear and hierarchical sequences)
Can be represented as tree diagram
Hierarchial Structure
Some elements in a sentence are 'weightier' than others and govern less 'weightier' bits.
Linguistic units are constructed according to rules
Rules of sound sequencing
Rules of word sequencing, etc.
Speakers of the same language must know the same rules.
Rules are descriptive not prescriptive.
Native speaker knowledge of rules is unconscious.
Description (our focus)
Describing how language is actually used: what you find in practice
E.g. the previous sentence, which contains both a double negative and the stigmatized form ain’t
Prescriptive
Prescribing rules for the use of language: what you (allegedly) should or should not do
E.g. Do not use double negatives as in the sentence…
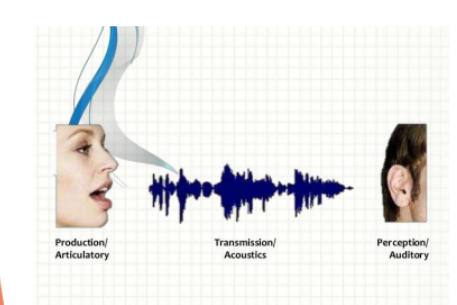
Phonetics
The study of sound systems of languages; What sounds are distinctive in a language
Articulatory
Acoustic
Auditory
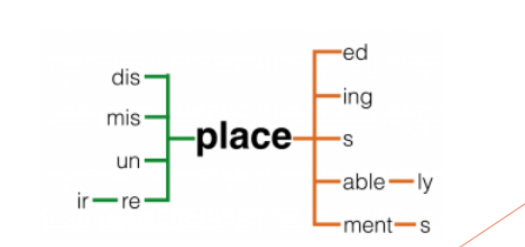
Lexis and Morphology
The vocabulary of language and its structure; The study of the internal structure (grammar) of words.
Syntax
the set of rules and principles that govern how words and phrases are arranged to form well‑formed sentences.The sailors spoled the girls with binoculars.
Why can you say “John sent a text to me” but not “sent me text a John to”?
Semantics
The study of the meaning of words, clauses, and sentences.
How is it related to syntax and lexis?
Subfields/ disciplines of linguistics
1.Phonetics
2./Phonology
3.Morphology
4.Syntax
5.Semantics
6.Pragmatics
7.Text
8.Sociolinguistics
Pragmatics
The study of how the context of an utterance is used to interpret it.
The study of how context contributes to meaning.>> A: Do you want some fudge brownies? B: There‘s got to be 2.000 calories in there.

Sociolinguistics
The study of how language is used in social context.
Language use and social class
Language use and gender
Multilingualism, etc
Psycholinguistics
The study of how language is acquired, produced, perceived, and stored in the brain.
Applied Linguistics
Generating knowledge that can be used to solve real-world problems
E.g. Creating writing systems for languages which do not have them
Language or Code?
Variety or code: neutral terms for a distinct system, with grammar, vocabulary, etc.
Language (sub)Varieties
Dialect
Standard
Accent
Register
Dialect
patterned verbal choices in the language of speakers from a neatly defined geographical region that affect pronunciation, lexis and grammar
A sub-variety of a language based on social groups and status.
e.g. geography, social class.
Dialects differ from each other on a range of linguistic levels
Standard Language
A sub-variety or dialect of a language with high social status.
Accent
A way of pronouncing a variety of a language.
e.g. RP
Register
A sub-variety of a language based on social situations.
e.g. chat, essay, prayer, occupations
Arbitrariness
The lack of a direct relationship between the form of a linguistic sign and its meaning.