L1 - Non-covalent binding
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is a ligand?
a molecule that binds to a particular site on another molecule
What can association be driven by?
Contributions from charge-charge interactions, polar interactions and VDW
What is an important point about association?
Neither of the partner molecules are chemically modified by their interaction
Interactions are on the basis of affinity
What are the forward and reverse rate constants for protein-ligand binding?
kF and kR
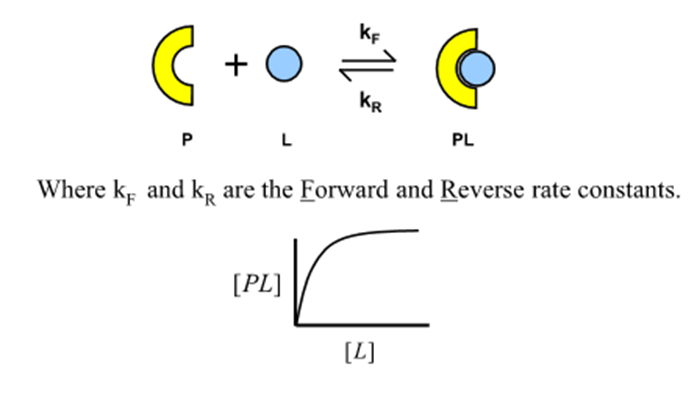
What is the rate of formation of the protein-ligand complex for a given ligand concentration?
d[PL]/dt
What is the rate of dissociation?
-d[PL]/dt
What happens at equilibrium?
kf [P][L] = kr [PL]
o The concentration of the species in the reaction mixture do not change with time
o Rate of forward = rate of reverse
Why will the protein-ligand complex saturate?
There is a fixed amount of protein
What is the equilibrium dissociation constant?
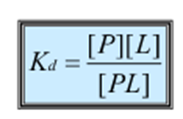
At equilibrium the rate of formation of PL = ?
The rate of destruction of PL
The concentrations are fixed
How the equilibrium dissociation constant be measured?
o Measuring both forward and reverse rate constants
o Or by allowing the reaction to proceed to equilibrium and then measuring the concentration of free protein [P], free ligand [L] and the protein ligand complex [PL]
Lower the Kd,
Greater the affinity
What is the binding function?
The average number of bound ligand molecules per macromolecule
What does the binding function = ?

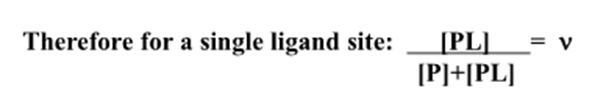
How do you find the fractional saturation?
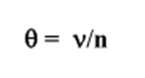
n = total number of binding sites on the protein
For a macromolecule with a single binding site what does the fractional saturation = ?
The binding function
What is an expression for the binding function in terms of the equilibrium binding constant and the free ligand concentration?
Scratchard general equation for n binding sites
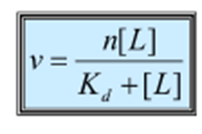
What do you assume about the Scratchard equation?
Assume binding sites are equal and independent
Do not interact with each other
Binding at one site does not affect binding at other sites on the protein
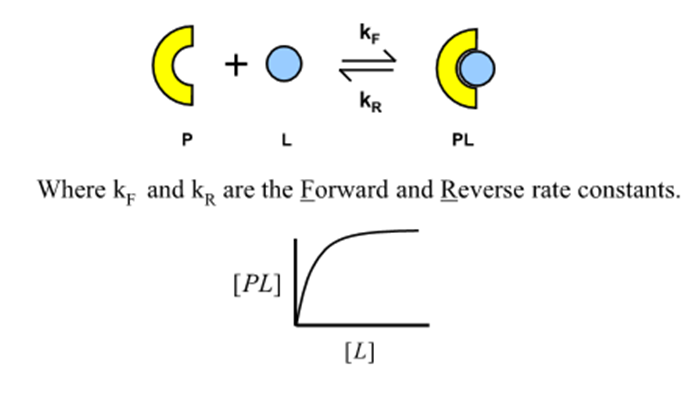
What is a simple plot?
Fractional saturation vs free ligand concentration
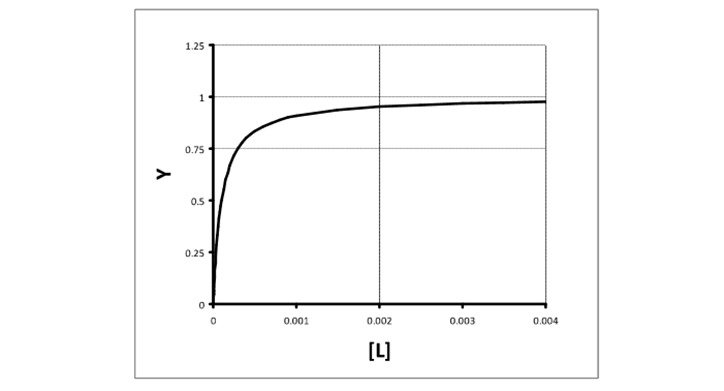
How do you find Kd of a simple plot?
free ligand concentration at which half saturation occurs
What is a more accurate way to find Kd?
From a straight line graph (Scratchard Plot)
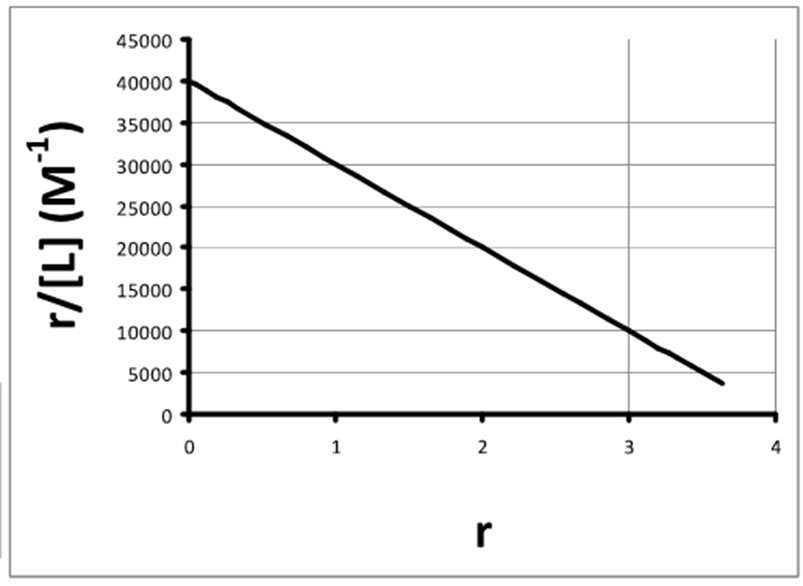
What is the equation for a Scratchard plot?
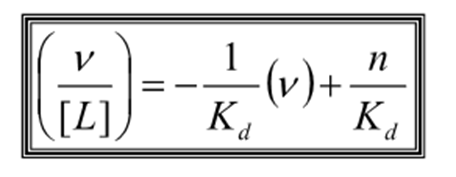
How do you find Kd from a Scratchard plot?

What happens when the binding function/ ligand concentration = 0 (ie y = 0) and what can this be used to find?
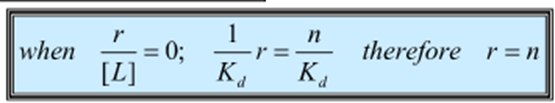
o The number of binding sites can be found from where the line meets x axis (4 for this graph)
o No longer need to go to saturating ligand concentration to access Kd
When can we calculate Kd?
When we know the amount of ligand bound
What are the assumptions for calculating Kd?
o Equilibrium has been reached
o If there are multiple bind sites on the macromolecule, these sites are not interacting (they are independent)
What does a Scratchard look like with multiple independent binding sites?
non-linear
Sites with highest affinity occupied at lower ligand concentrations
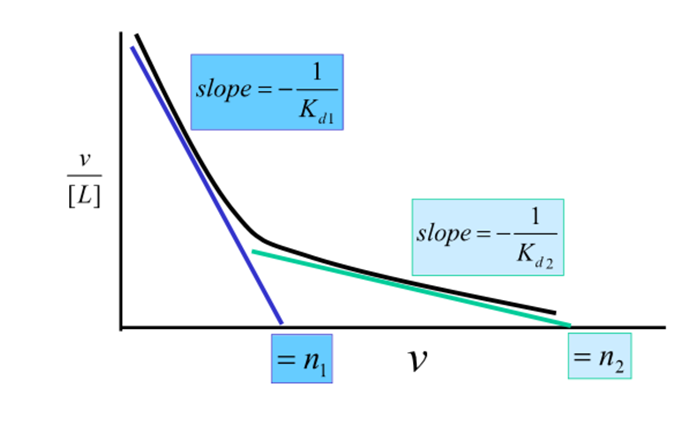
When is interpreting plots difficult?
Interpreting plots is difficult unless there is a large difference in Kd values of the sites
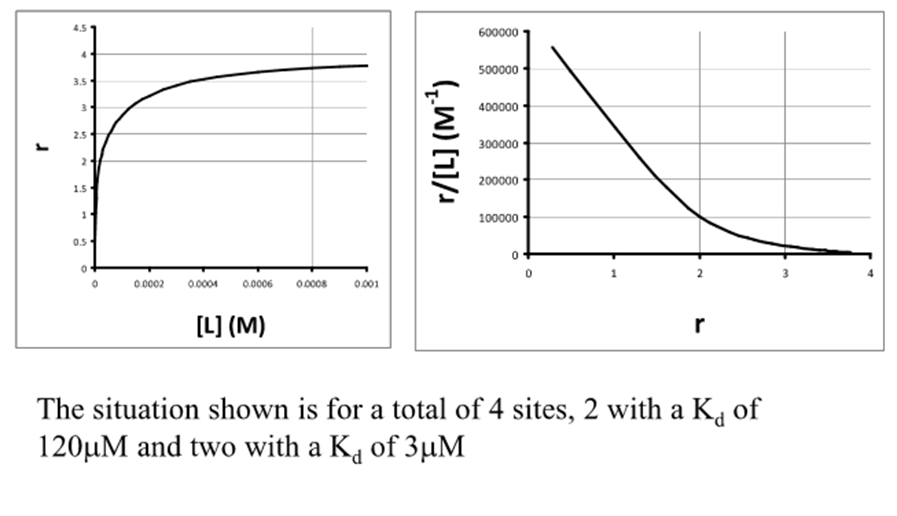
Summary
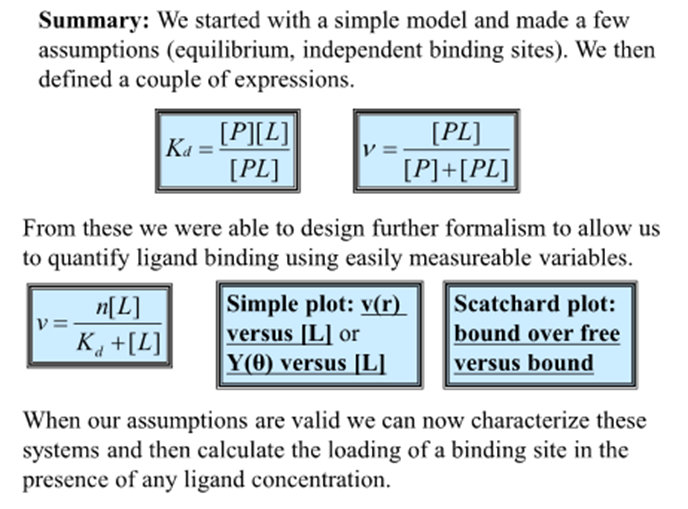
How do we define Kd?
We define Kd in terms of [P}, [L], and [PL] so all of these are present at all times in a ligand binding experiment
In an experiment, we will often have a known total protein concentration and titrate a known total ligand concentration and be able to measure [PL]
