Geography #8: Hot Desert Climate
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Case Study: Namib Desert Pg. 211-214
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What effect do cold ocean currents have on summer temperatures?
They may reduce summer temperatures due to the cooling effect of the ocean.
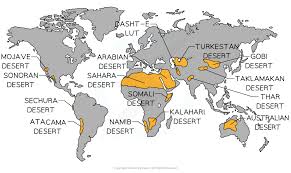
Where do hot deserts typically form?
Hot deserts form between 15° and 30° north and south of the equator.
What causes the formation of hot deserts in relation to atmospheric pressure systems?
High Pressure is the main influence in the formation of hot deserts.
What happens to air at the equator?
Air rises at the equator and moves north and south in the upper atmosphere.
What occurs when rising air cools in the upper atmosphere?
The air cools and starts to sink.
What is created at about 30° north and south of the equator due to sinking air?
A zone of high pressure is created.
Why is there high aridity in the zones of high pressure?
Due to the sinking air, warm air cannot rise, condense, and form clouds.
What is the location of hot deserts ?
15° - 30° north and south of the equator (tropical and sub-tropical).
What is the annual precipitation in hot desert climates?
Below 250mm.
What is the typical daytime temperature range in hot deserts?
Daytime temperatures can reach 50°C but average around 25°C.
What are the night-time temperatures like in hot deserts?
Night-time temperatures can drop below 0°C.
What is the diurnal temperature range in hot deserts?
The diurnal range can be large, up to 45°C.
What is the annual temperature range in hot deserts?
Around 15°C.
What are the seasons like in hot desert climates?
There are typically two seasons: summer and winter.
What is the humidity level in hot desert climates?
Humidity is low, often between 10-30%.
What are the prevailing winds like in hot desert climates?
The winds are offshore, blowing from the east across the land, and do not collect moisture.
What factor contributes to the hot desert climate year-round?
High pressure all year causes the air to descend and warm.
Why does precipitation not occur in hot deserts?
Precipitation does not occur because the air is not rising.
What influences the amount of rain in prevailing winds of hot deserts?
Prevailing winds often come from over land masses, so they contain little moisture.
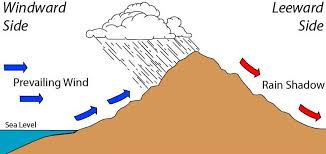
What is a rain shadow and how does it affect some deserts?
A rain shadow is when water rising from a large body of water is intercepted by a mountain range. Some deserts are in a rain shadow, resulting in little rainfall.
What happens to air at the equator as it moves toward the tropics?
The air moves north or south and then sinks.
What is associated with zones of high pressure where air is sinking?
Very low levels of rainfall and a large daily temperature range.
Why is there low rainfall in areas of sinking air?
There is no opportunity for moisture to cool and condense.
What is the tropical desert known for?
As the driest and hottest place on earth.
How is rainfall in hot deserts?
Rainfall is sporadic; in some years, no measurable precipitation falls.
What causes the dry conditions in hot deserts?
The dry conditions are due to the year-round influence of subtropical high pressure and continentality.
What defines a desert in terms of precipitation?
A desert is defined as any area that receives less than 250mm of precipitation in a year.
What are the two types of deserts mentioned?
Deserts can be hot or cold.
Give an example of a hot desert.
The Sahara Desert in Africa.
Give an example of a cold desert.
The tundra in North America.
Where are hot deserts generally found?
Hot deserts are found in sub-tropical and tropical latitudes.
What are the typical daytime temperatures in hot deserts?
Very high daytime temperatures, often over 50°C.
Why do hot deserts have low night-time temperatures?
Because of the lack of cloud cover to trap heat.
Where are deserts mostly found on continents?
Deserts are mostly found on the western edge of continents.
Why do prevailing winds lead to low moisture in deserts?
Prevailing winds in tropical regions blow off-shore from the east across the land, preventing moisture pickup.
What is the primary challenge for plants and animals in hot desert ecosystems?
Its extreme temperatures and lack of rainfall.
What is the biodiversity level in hot desert ecosystems?
It is low with 5,000-6,000 plant species, many invertebrates, and up to 20 species of birds.
Name two plant species found in hot desert ecosystems.
Cacti and yucca.
Name two animal species found in hot desert ecosystems.
Spiders and camels.
How do low-growing plants in deserts help with water conservation?
They avoid water loss due to strong winds.
What is the purpose of thick stems in desert plants?
To store water.
What type of roots do desert plants have to catch rain?
Shallow roots that spread out near the surface.
What is the advantage of long taproots in some desert plants?
They can reach water deep underground.
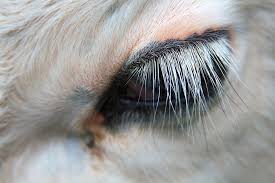
What adaptations do camels have to protect themselves from sand?
Camels have two sets of eyelashes and nostrils that close to protect themselves in sandstorms.
How do camels survive without food or water?
They store fat in their humps.
What are some adaptations that fennec foxes do to help lose heat?
Fennec foxes have large ears, helping them to lose heat.
They have thick fur which keeps their bodies cool in the hot day and warm in the cold night.
They are small and stay in cool burrows or hide under rocks or leaves to avoid the intense daytime sun.
Additionally, they are nocturnal, which allows them to avoid the heat of the day.
Why do many animals burrow?
To avoid intense daytime heat.
What adaptation do insects and reptiles have to minimize water loss?
They possess waterproof skin.

How do small leaves or needles help plants?
They reduce water loss due to its smaller surface area.
Why are some animals nocturnal?
To hunt at night and avoid daytime heat.
What is one adaptation of hot desert plants regarding water uptake?
Some hot desert plants have long, deep tap roots that reach 7 to 10 metres below the surface to access groundwater.
What does 'ephemeral' mean in relation to desert plants?
That some desert plants can change their behaviour based on environmental conditions, lying dormant until rain allows them to germinate.
How do desert flowers adapt their lifecycle in the hot desert?
They can lie dormant for years and germinate quickly after rain, completing their lifecycle in a few weeks and producing flowers for pollination.
What are the two distinct seasons in hot deserts?
The two distinct seasons are summer (35-40°C) and winter (20-30°C).
What type of plants adapt to arid environments?
Xerophytes
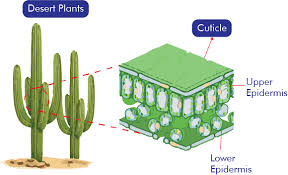
How do thick and waxy cuticles help desert plants?
They reduce transpiration, leading to less water loss.
What adaptation do some desert plants use to prevent water loss?
They drop their leaves. As the leaves are the main sites of transpiration, dropping them would conserve water in the dry seasons.

What is a specific adaptation of the acacia tree in deserts?
It has short, wide trunks that store water.
Why do desert trees have thick bark?
To be fire-resistant in extreme heat.
Where do some desert plants store most of their biomass?
Below the surface of the soil.
What is the benefit of biomass being below the soil surface?
Cooler temperatures below reduce the risk of vegetation shriveling up and dying.

What type of plants are cacti categorized as?
Succulents.
How do cacti prevent water loss and deter animals?
They have spikes.
What type of root system do many desert plants have?
Horizontal root systems that spread out.
What advantage do horizontal root systems provide to desert plants?
They maximize water absorption.
What are the characteristics of desert soils?
Desert soils are thin, sandy, rocky, grey in color, very dry, soak up water quickly, and may appear crusty.
What happens to water when it rains in desert soils?
Water is soaked up quickly by desert soils.

Why do desert soils appear crusty?
Due to the lack of rainfall, water is evaporated up to the surface, leaving salts behind.

What are xerophytes?
Plants adapted to live in hot and dry environments.
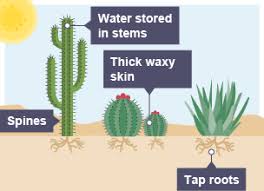
List one adaptation of xerophytes to reduce water loss.
Thick, waxy skin to reduce water loss and reflect heat.
How do some xerophytes store water?
In their large, fleshy stems.
What feature do cactuses have to protect their water reserves?
Spikes instead of leaves to reduce water loss as animals will wish to drink it.
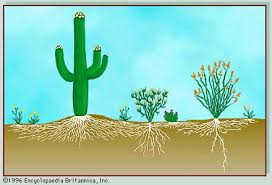
What is one root adaptation of xerophytes?
Deep roots to tap groundwater or long shallow roots that spread over a wide area.
What behavior do some plants exhibit during prolonged dry conditions?
They lie dormant for years until rain falls.

Why do cactuses have spikes?
To reduce water loss and protect stored water from animals.
What are deserts defined as?
Any area that recieves less than 250mm preciptation in a year.
What are the factors that influence the hot desert climate?
High Pressure, Prevailing Winds, Rain Shadow, Cold Ocean Currents
What do animals need to adapt for?
To be able to survive the extreme temperatures and lack of rainfall.

What are some examples of a xerophytic plant?
Cacti & Acacia Trees