Nutrition Exam 2
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
type 1 DM (born with it)
type 2 (aquire it thorugh lifestyle)
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
3 types of Diabetes
Most often diagnosed in children or adolescents
o Pancreas is unable to produce insulin
o It is thought to be an autoimmune disease
type 1 DM
Accounts for more than 90% of all cases of diabetes mellitus
o Cells are insulin resistant
Typically over age 40 and overweight or obese when diagnosed
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Type of diabetes that occurs in some women during pregnancy.
• Resolves after pregnancy
• Complications for infant:
o can cause fetal or infant illness or death
o high birth weight (macrosomia) of infant
o low blood glucose post-delivery
o diagnosis of DM later in life
Gestational diabetes
high birth weight of infant
macrosomia
Dark patch or rough skin which is marker for type 2
Acanthosis Nigricans
Poly
Urea
Dipsia
P something
Gestational diabetes (signs) (3 polys)
Resistant to digestion by human enzymes
Mostly composed of polysaccharides
exception is lignin; not technically a
carbohydrate
Reduces risk of diverticulosis
Dietary fiber
Soluble fiber
Insoluble fiber (decrease transit time)
Two types of dietary fiber
Some people have intolerance to the protein gluten
intolerance to gluten that results in autoimmune response
Celiac disease
carbohydrate can adhere to enamel of teeth
o bacteria metabolize carbohydrate in mouth
o lactic acid produced by bacterial fermentation degrades tooth enamel
Process by which dietary sugar can lead to dental
decay
Some people unable to digest lactose due to loss of
function of enzyme lactase (so cannot breakdown lactose)
Lactose Intolerance (why)
Triglycerides
Phospholipids
Sterols (ex: cholesterol)
3 major categories of lipids
Are CHO (Difference from carbs is that they can be polymerized)
Composition of Fat/Lipids
The chain has a carboxyl group on one end and a methyl group on the other
The carboxyl group (COOH)
Hydrophilic
The methyl group (CH3)
Hydrophobic
Ends of the fatty acid chains
Phospholipids
Triglycerides
Fatty acids are components in
mono = 1 C=C
Poly = 2 or more C=C
Saturated and unsaturated same as ochem
Solid at room temp
Since they are straight and stack
Saturated characteristics
Liquid
Since they have bends (due to double bonds) which is why they are liquid
Mono saturated characteristics
Liquid
Poly saturated characteristics
2 types
Omega 6
Linoleic acid (parent)
Omega 3
Linolenic acid (parents) (ALA)
Benefits
Reduce inflammation
Reduce free radicals (serve as anti-oxidants)
Help in cellular repair
a lot more
Over 60% of 3.5 pounds of fat in brain is made of omega 3 (most of your brain is made of omega 3 like fish oil)
Essential fatty acids
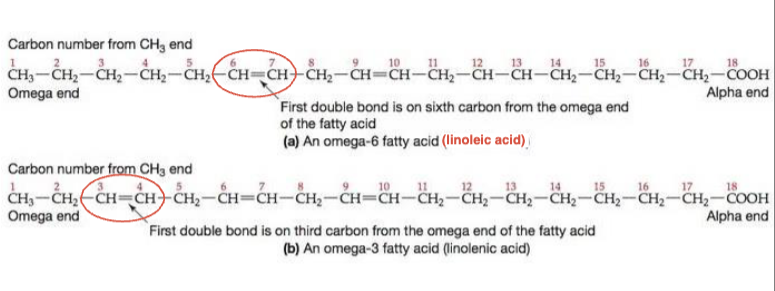
omega 3: has first C=C 3 C away from omega end (methyl)
omega 6: has first C=C 6 C away from omega end (methyl)
how to ID and differentiate both omega 3 vs 6
methyl end
which end is the omega end
carboxylic acid end
which end is the alpha end
linolenic
is omega 3 linolenic or linoleic acid
linoleic
is omega 6 linolenic or linoleic acid
4 parts omega 6
1 part omega 3
ideal consumption ratio for omega 3 vs 6
omega 3
Eicosapentanoic (EPA) found in which 3 or 6
omega 3
Docosahexanoic acid (DHA) found in which 3 or 6
omega 6
arachidonic acid found in which 3 or 6
2 servings of cold water fish every week to get essential fatty acids
how much EPA and DHA to eat
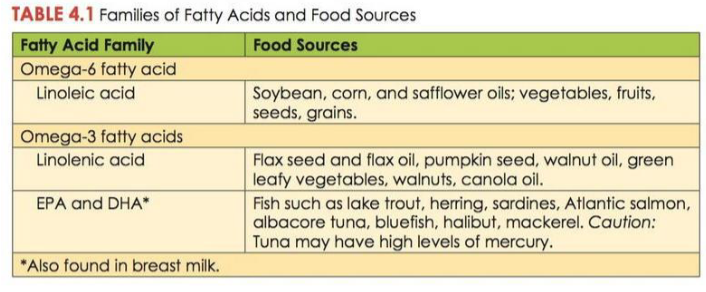
this
MEMORIZE THIS TABLE
Process of adding hydrogens to unsaturated fats
• Makes solid at room temp.
• Common dietary sources
MAKES FOOD LAST YEARS (cookies)
Hydrogenation
produced through addition of hydrogen atoms to double bonds of fatty acids
Small amount of naturally occurring trans fatty acids are found in:
• dairy milk and meat
Trans fatty acid (man-made/synthetic)
cis have bends
trans have no bends
cis vs trans fatty acids
3 carbon back bone (glycerol), with 3 fatty acid chains attached
primary form of lipid found in body
Triglyceride
compounds that assist the body in transporting fat through watery substance
• Chemically similar to triglycerides
• Three-carbon glycerol backbone
• Two fatty acids bound to first two carbons
• Third carbon has phosphate group bound to it
HAVE HYDROPHILLIC HEADS
HYDROPHOBIC TAILS
FUNCTION AS EMULSIFIERS
Phospholipid
Four-rings
steroid nuclus
cholesterol/sterols
Liver makes most of cholesterol in the body
It is non essential
Below 300 mg a day
What makes the miost cholesteroil in the body
Flavor and satiety
Essential fatty acids can protect the heart
Storage of energy (9kcal)
Steroid hormone prod
lipid functions
Linoleic acid
Linolenic acid
Both are precursors to eicosanoids
Which have strong physiological effects
Relaxing blood vessels and promoting clotting
what are both essential fatty acids precurssors to
Fat is required for absorption of fat soluble vitamins
Vit KADE
Fat soluble vitamin absorption decreases when there is incomplete fat absorption or fat malabsorption
Absorption/transport of lipids
Protects vital organs
Insulates skin
Organ protection of lipids
Phospholipids and cholesterol are major components of cell and organelle membranes
Cell membrane structure (phospholipids and cholesterols role)
Estrogen
Testosterone
Aldosterone
And VIT D
Cholesterol serves as important role to be precursor to these hormones
satiety
• fat slows stomach emptying
is fat satiating
Saturated fatty acids
• Beef, pork, poultry with skin and other meats
• Cheese, butter, and other dairy products
• Palm and coconut oils (tropical oils)
• Unsaturated fatty acids
• Vegetable oils
• Nuts and seeds
• Fish
• Cholesterol
• Only found in animal products
Primary Sources of Fat in the Human Diet
fat requirements
Fat mimetics
1. Carbohydrate-based
• Add creaminess, bulkiness, and moistness
• maltodextrins, modified food starches, cellulose, and gums
• 1-4 kcal per gram
2. Protein-based
• denature under high heat
• used in frozen desserts
• 4 kcal per gram
Fat substitute
3. Fat-based
• Non-digestible/partially digested
Fat Replacers
Marketed as weight loss drugs
Side effects:
anal leakage
reduced fat soluble vitamin A, D, E & K absorption
malabsorption of oral contraceptives
Fat blockers
Leading cause of death in US
Modifiable risk factors
• high blood pressure
• high cholesterol
• cigarette smoking
• diabetes
• poor diet and physical inactivity
• overweight and obese
Risk increases by overconsumption of nutrients that raise blood cholesterol
Fat
Saturated fat
Trans fat
Heart disease and fats
Primary type of heart disease linked with fat intake is atherosclerosis
Build up of fatty deposits and streaks in the arteries
May reduce blood flow to areas of the heart causing ischemia
cardiovascular disease
Artery becomes completely blocked
aka heart attack
myocardial infarction
blockage of artery supplying blood to brain
Stroke
Spherical structures that are composed of lipids and proteins
Transport lipids through emulsification
Outershell is monolayer
Proteins
Phospholipids
Their hydrophobic and phillic ends make them be able to transport lipids in the body
Lipoproteins
1. Chylomicrons
2. VLDLs
3. LDLs
4. HDLs
The blood contains four types of lipoproteins.
made in cells of small intestine
transport dietary lipids to the liver
Chylomicrons
synthesized in the liver
contain both triglycerides and cholesterol
deliver triglycerides to other tissues
Very low-density lipoproteins (VLDLs)
formed after VLDLs deposit triglycerides in other tissues
cholesterol rich
deliver cholesterol to other tissues, including blood vessels
• “Bad Cholesterol”
Begins journey as VLDL
Low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)
made mostly in the liver, but also in the small intestine
removes excess cholesterol from cells
return to liver for elimination (to be recycled into bile)
“Good Cholesterol”
High-density lipoproteins (HDLs)
USDA’s 2015 Dietary Guidelines for Americans
o 20 - 35% of daily calories from fat
from AMDR
Recommendations for Dietary Intake of Fats
30–35 % calories from fat
o growth and nervous system development depend on adequate fat intake
Recommendations for Dietary Intake of Fats (children under 2)
polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fatty acids
saturated fats linked to cancer/heart disease
which fat is healthy
CHON
Composition of proteins (what molecules its made of)
ino acids have a central carbon connected to four side groups
Amino group
Acid group (carboxyl)
Hygrogrn group
R group
Central carbon is alpha carbon
structure of amino acids
essential and non essential
2 catagories of amino acids
Must be acquired from our diet
essential amino acids
Normally made by body in adequate amounts
Nonessential amino acids
Transfer of amino group from one molecule to another to create an amino acid
Lets you make nonessential ones from essential ones
Transamination
usually non essential amino acids that under certain conditions become essential
Conditionally essential amino acids
incorrect AA sequence can lead to improper function like sickle cell
Shape dictates protein function
500 exist
20 make our genome
how many amino acids exist and how many make up our genome
ID comes from the R group
How are Amino acids ID’d or different
Peptide bonds link amino acids together
They start linking through dehydration synthesis from the carboxylic group
So amino 1 would be at the exposed amino end (N terminus)
Amino acids are added to the carboxylic group (C Terminus)
how are peptide bonds formed between amino acids
Heat
Acid
Enzymes
Agitation
Alcohol
electrolysis
Salting
how are proteins denatured
Proteins in blood maintain optimal balance between fluids inside and outside cells and blood vessels
Hydrostatic pressure causes water to leave blood capillaries
Osmotic pressure pulls water back in
Proteins in blood are solutes
Like Na
These proteins in the blood albumin and solutes work together to pull water back in
Albumin
Edema
Develops when blood albumin is low
Hydrostatic usually wins
Fluid Balence with proteins
chyl
When chylomicrons enter the lymph it becomes?
7.35-7.45
Proteins help us maintain this
The body PH is usually?
foreign substances that enter body and trigger immune response
Can be both good or bad things
Antigen
proteins made by immune system to fight antigens
Antibodies
Skin
Mucus
Proteins form first barriers against immune invaders
Messengers that help regulate body functions and systems
Made of lipids and proteins
Hormones
sodium/potassium pumps
Retinol-binding protein
Protein Transport
Tyrone Argued for Pro Glute Cycling
tyrosine
arginine
proline
glutamine
cysteine
What are the non essential amino acids that are conditionally essential
carbs
fats
protein
primary secondary and tertiary energy resources for body
Protein synthesis
Protein breakdown
1. Protein synthesis
requires presence of essential amino acids in adequate amounts
Limiting amino acid (present in lowest amount relative to body’s needs)
2. Protein breakdown
Free amino acids become part of amino acid pool
Deamination
required for elimination of excess amino acids
occurs primarily in the liver
keto-acid used for energy production
amino group converted to urea
excreted in urine
Nitrogen balance
nitrogen consumed vs. nitrogen excreted
basis of many nutrition recommendations
If your pregnant you should have a positive N balance (or recovering)
If recovering from disease (negative)
Protein turnover
Intake exceeds excretion
Occurs during growth, recovery from illness, and during pregnancy
Positive nitrogen balance
Excretion exceeds intake or intake is inadequate to meet body’s needs
Occurs during AIDS, cancer, starvation, and low calorie diets.
Negative nitrogen balance
Provide all essential amino acids in amounts needed by body
Easily digested and absorbed
Includes: Animal Proteins and Soy
Complete proteins or high quality proteins Contain:
Value assigned to proteins that accounts for protein quality and digestibility.
Based on scale of 0 –100
Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Score
(PDCAAS)
dont have all essential aminos
ex. legumes, grains, veggies
COLLAGEN (missing tryptophan)
Incomplete Proteins
AA contents combined provide all EAA
Complementary proteins
additional source of protein for specific populations
vegatarians, underweights ppl
Supplemental Proteins
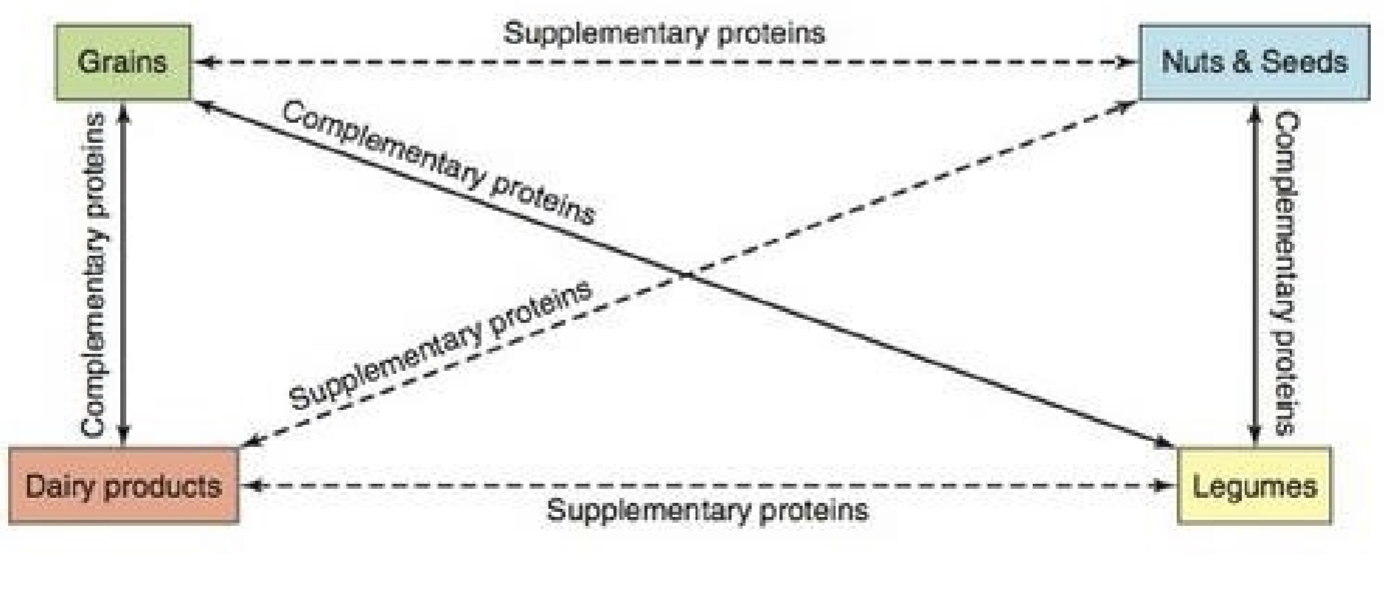
know this!!!!
complete protein
prevent bone loss
B VIT, Calcium, Potassium, VIT A, iron
isoflavones (phytoestrogens)
soy protein
DRIs for protein:
RDA: 0.8 g per kg of body weight (high-quality protein)
AMDR: 10% – 35%
Protein needs increase durring injuries, illnesses, and pregnancies
Recommendations for protein intake
benefits:
less risk of heart disease
less obesity risk
disadvantage is that they’re usually deficient in
VIT B12
Zinc
iron
calcium
VIT D
proteins
Health impacts of vegatarians
Disorder that occurs with inadequate protein and energy consumption
Most common deficiency in hospital
Greater concern internationally
Children more susceptible
PEM is most lethal form of malnutrition (WHO)
Protein energy malnutrition (PEM)
Condition of starvation characterized by emaciation, or skeletal appearance
Causes
Inadequate protein and calorie intake
Marasmus
Characterized by a swollen appearance, essentially the abdomen
Proposed causes
Low protein intake, altered gut bacterial populations
Frequent in children being weaned from breast milk to cereal
Kwashiorkor