Brainstem Anatomy and Functions: Pons and Medulla Key Concepts
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
The pons is part of what brain region?
Metencephalon (with cerebellum)
Which ventricle contributes to CSF production in the pons?
Fourth ventricle
What structure connects the pons to the cerebellum for motor communication?
Cerebellar peduncles
Most important function of the pons?
Acts as a bridge for ascending and descending tracts
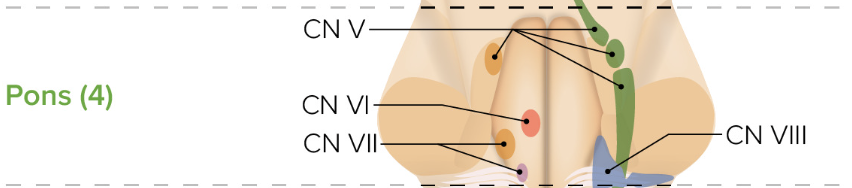
The pons holds nuclei for which four cranial nerves?
CN V, VI, VII, VIII
Which cranial nerves in the pons are major sensory and motor nerves of the face?
CN V (sensory) and CN VII (motor)
Which cranial nerve in the pons controls equilibrium and hearing?
CN VIII
Which cranial nerve in the pons controls eye movement?
CN VI
What cycle does the pons regulate that makes it clinically important?
Sleep and REM cycle
What autonomic roles does the pons play?
Controls autonomic functions and relays sensory information
Which brainstem region contributes to reticular formation and REM control?
Pons
MEDULLA Flashcards
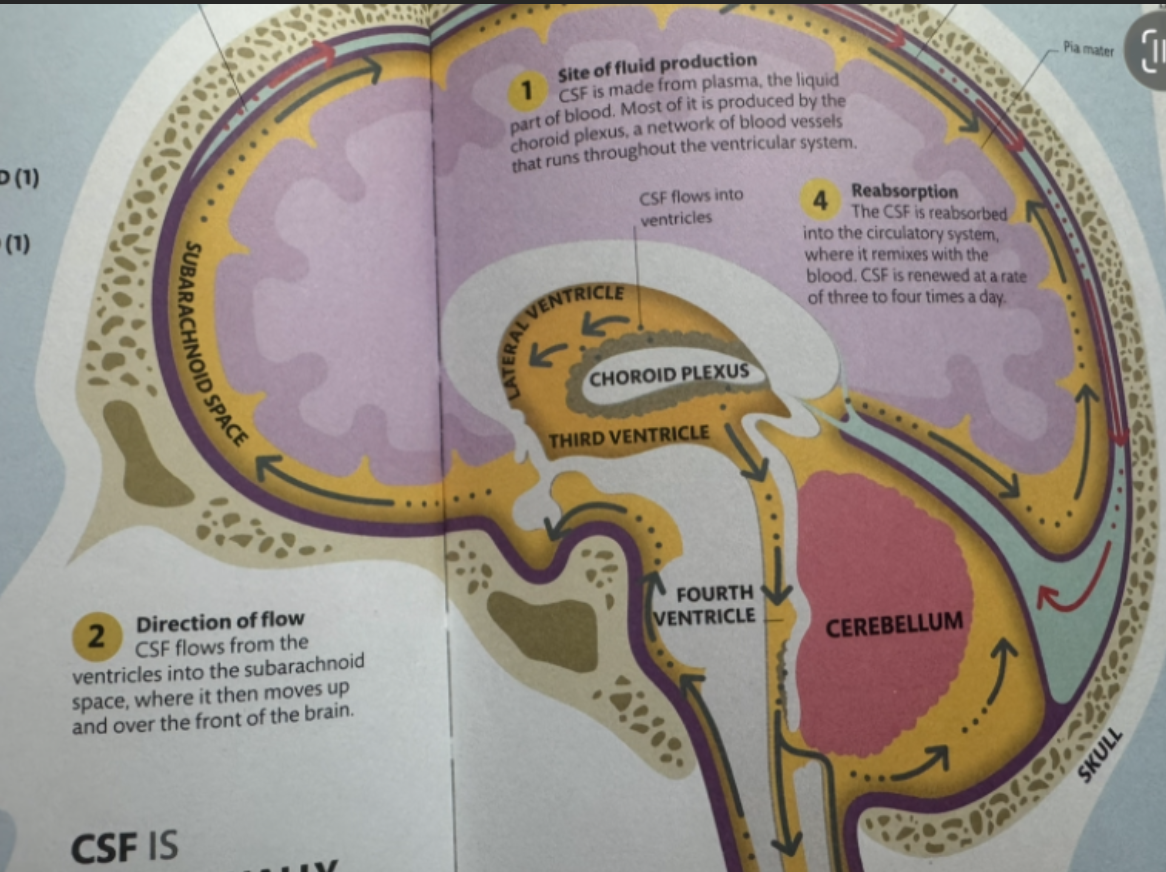
Which brainstem area forms most CSF and communicates with cerebral aqueduct and spinal canal?
Medulla (4th ventricle region)
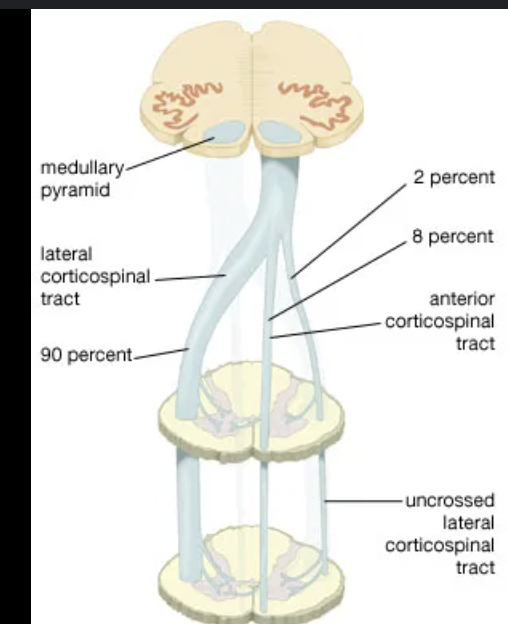
Which structures in the medulla house corticospinal tract decussation?
The pyramids
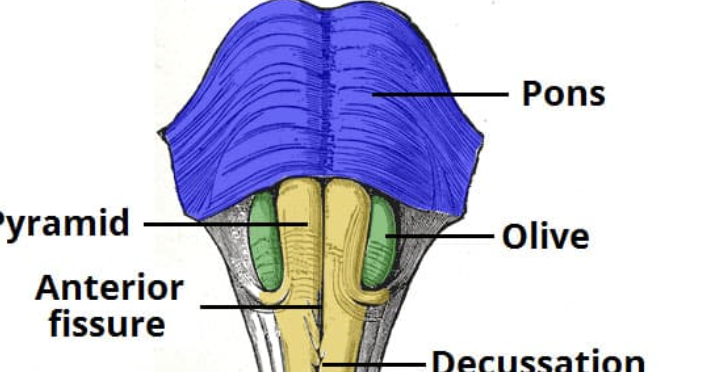
Which medullary structure relays proprioception information?
Olives
Which brainstem region contains life-support autonomic centers?
Medulla
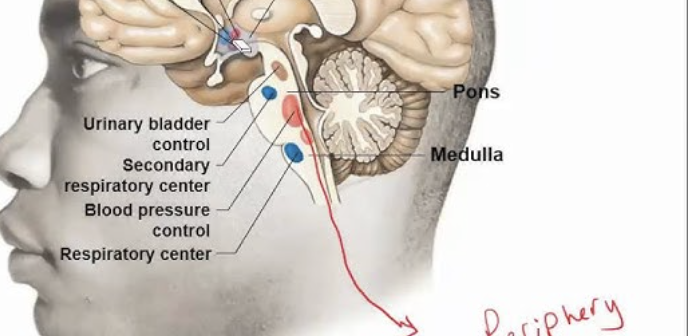
Name the three autonomic centers in the medulla.
Respiratory center, cardiac center, vasomotor center
What does the respiratory center control?
Breathing
What does the cardiac center regulate?
Heart rate and strength of contraction
What does the vasomotor center control?
Vessel diameter (vasoconstriction/vasodilation) and blood pressure
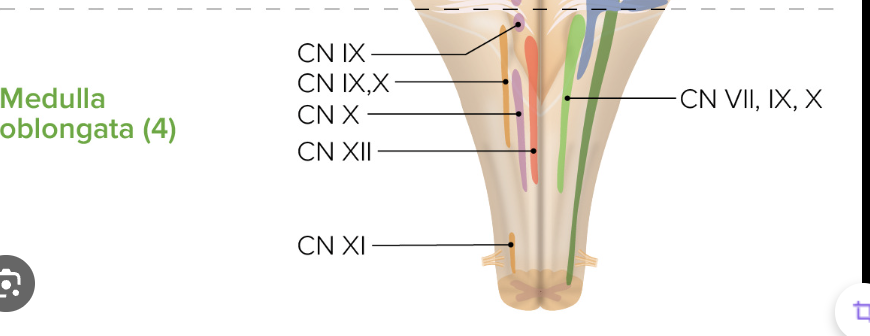
Which four cranial nerves have nuclei in the medulla?
CN IX, X, XI, XII
Which brainstem region contributes heavily to reticular formation arousal?
Medulla
Which substances can suppress medullary function?
Depressants like heroin, alcohol, and sleeping pills
A lesion affecting breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure likely involves which brainstem structure?
Medulla
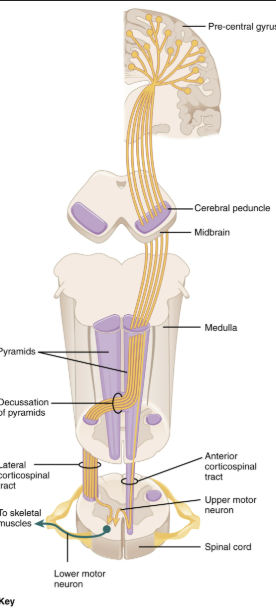
Damage to the pyramids in the medulla affects what pathway?
Corticospinal motor function (decussation)
A patient losing equilibrium, facial sensation, and REM control likely has a lesion where?
Pons
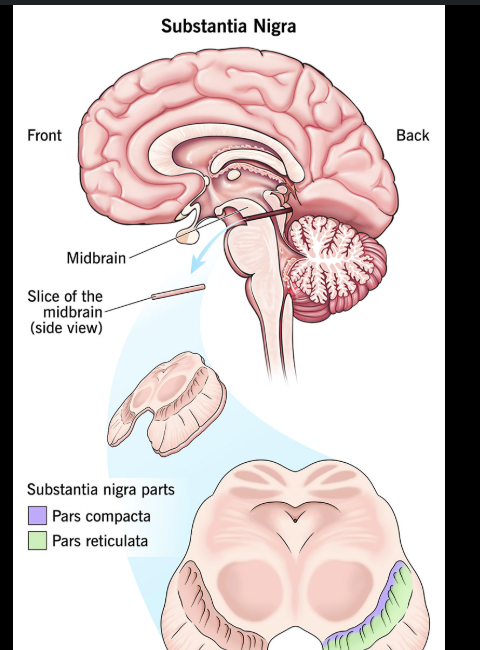
A patient with tremors and loss of fine motor control likely has dysfunction where?
Substantia nigra in the midbrain
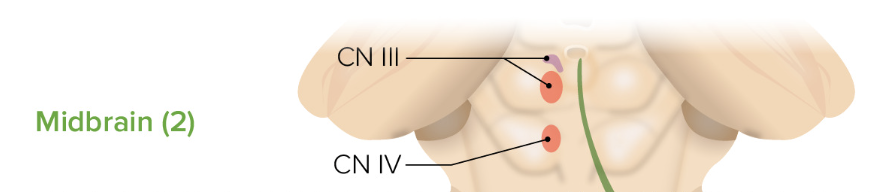
Which brainstem level would be affected in a patient with impaired eye movement and abnormal reflexes to sound?
Midbrain
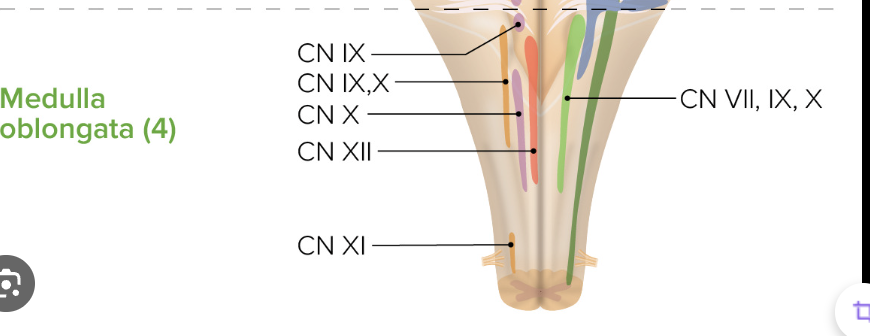
If cranial nerves IX-XII are impaired, where is the lesion?
Medulla
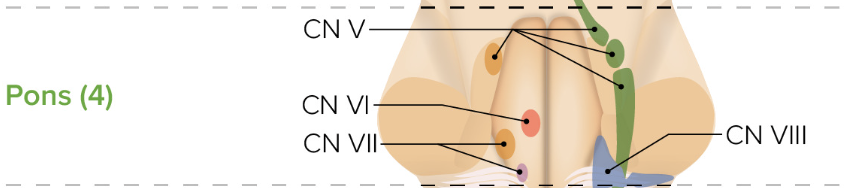
If cranial nerves V-VIII are impaired, where is the lesion?
Pons
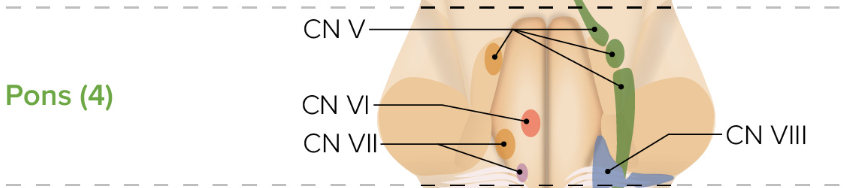
If a patient cannot move their eyes laterally, which brainstem level is damaged?
Pons (CN VI) or Medulla (tract connections depending on presentation