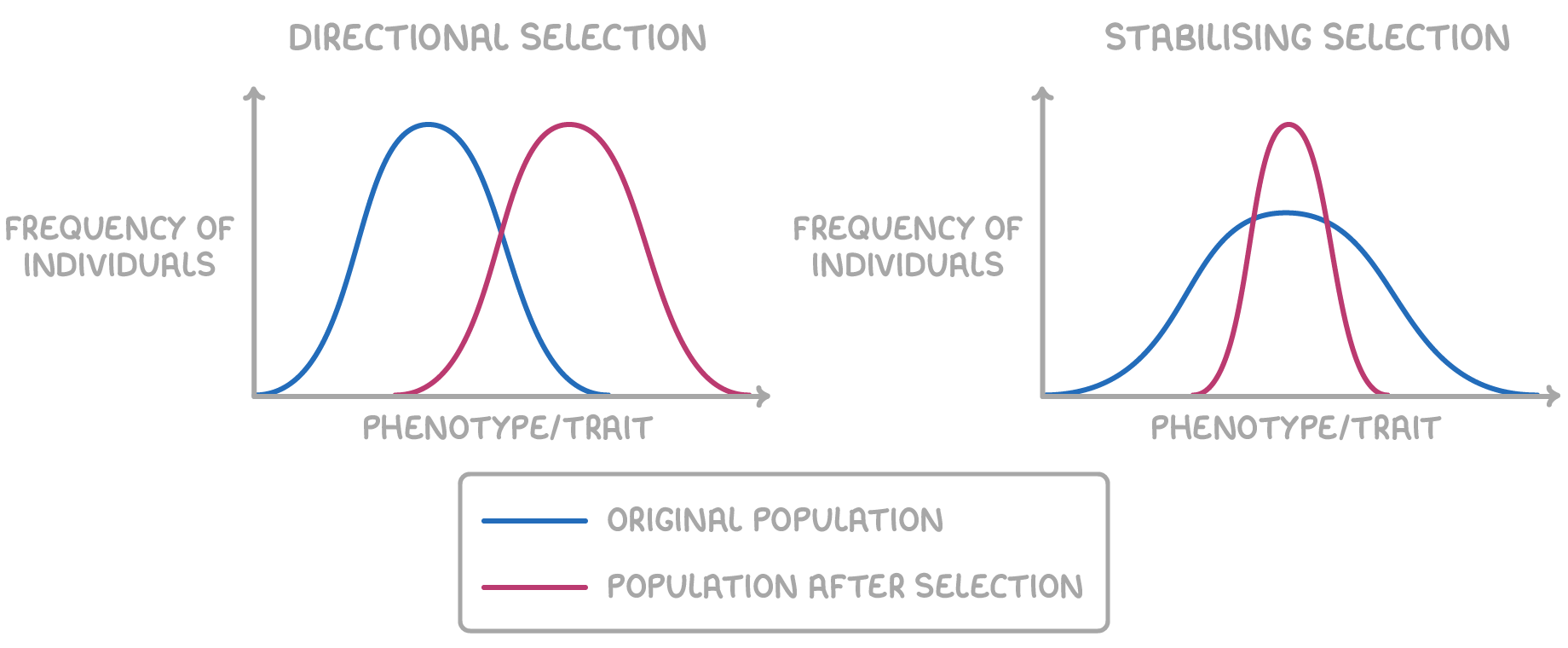
types of selection
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
how does a single bacterium become antibiotic resistant?
a bacterium becomes resistant due to a random mutation in its DNA
this means that the bacterium produces a protein that makes the antibiotic ineffective
the protein in the cell wall is no longer weakened by antibiotics
→ enzyme breaks down antibiotic and carrier protein pumps antibiotics out of cell
describe the process of antibiotic resistance:
a bacteria population has a gene pool w/ a wide variety of alleles
random mutation may introduce antibiotic resistant alleles, increasing variation
environmental pressure of antibiotic kills bacteria w/o antibiotic resistant mutation
differential reproduction occurs - only the antibiotic resistant bacteria survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous alleles to the next generation: heredity
over many generations, advantageous alleles increase in frequency, forming a population of antibiotic resistant bacteria
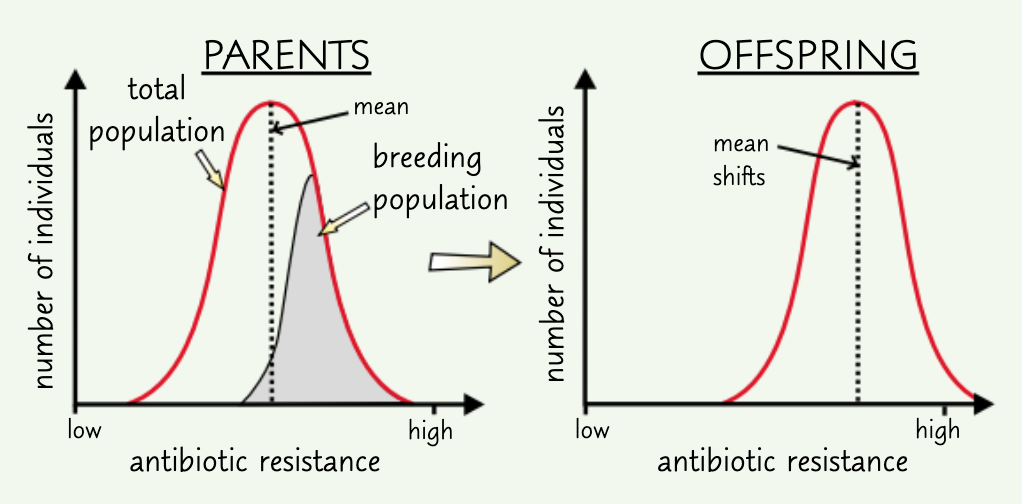
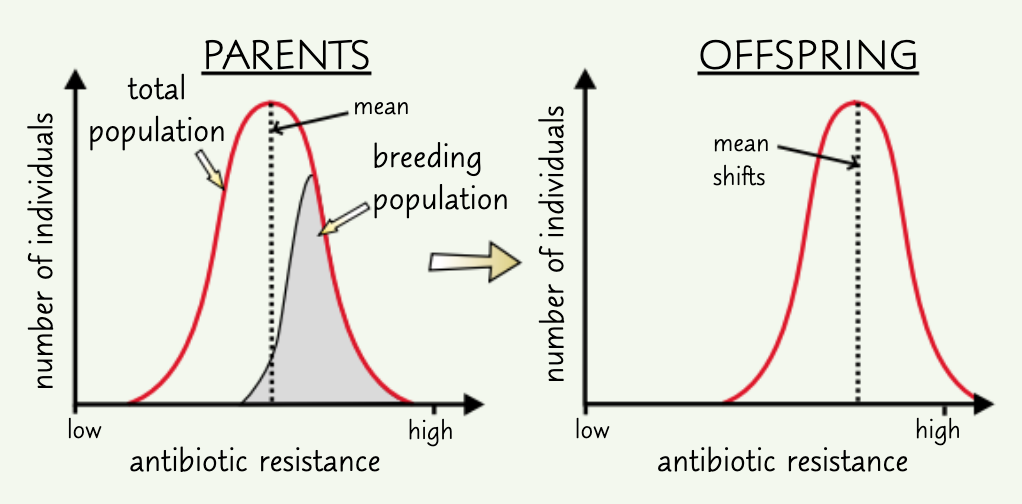
what is directional selection?
individuals w/ alleles for more extreme characteristics are more likely to survive and reproduce
due to a selection pressure - environmental change
on a graph, this shifts the mean frequency to the right
give an example of directional selection:
antibiotic resistance
what is stabilising selection?
individuals w/ alleles for characteristics towards middle of range are more likely to survive and reproduce
no selection pressure/environmental change
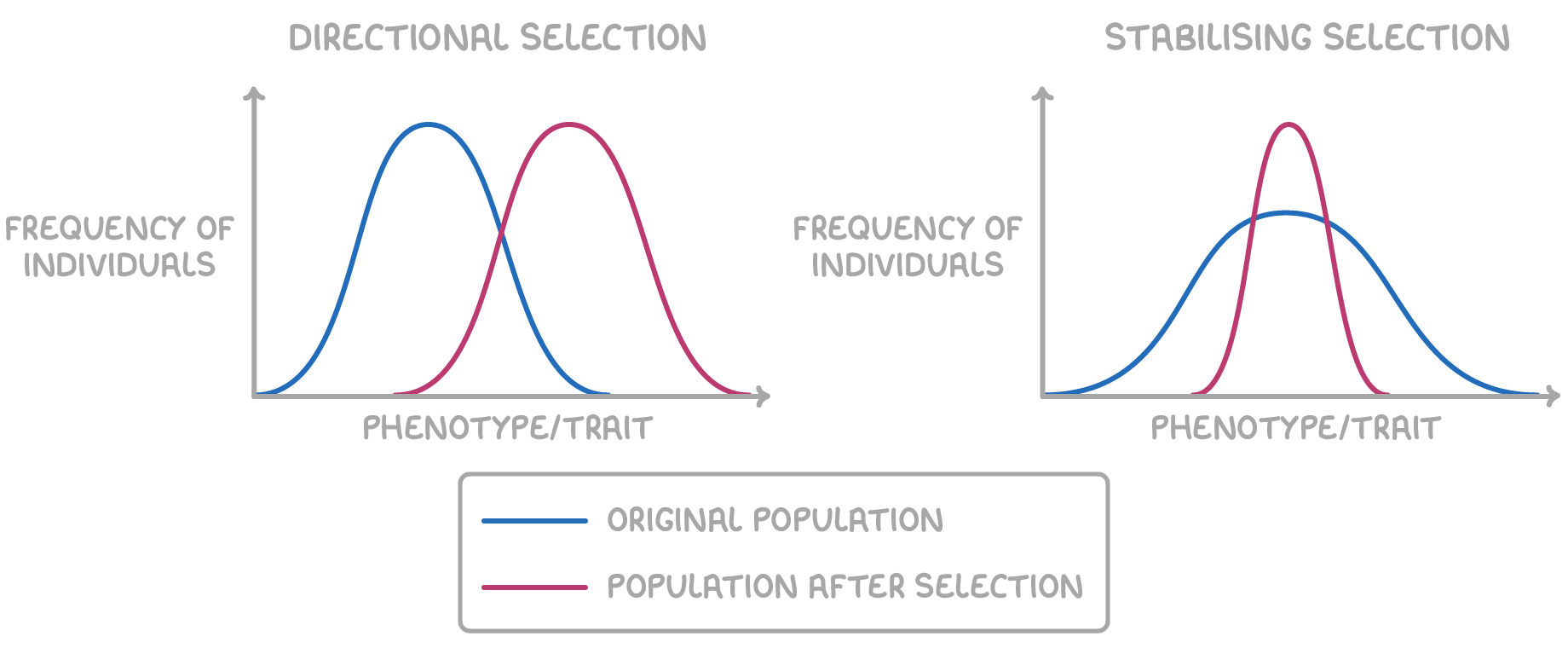
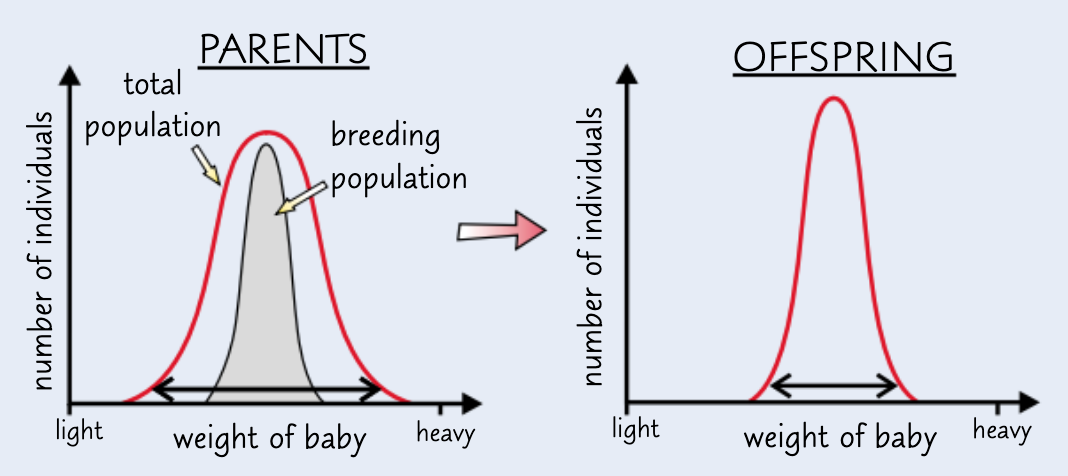
give an example of stabilising selection:
human birth weights
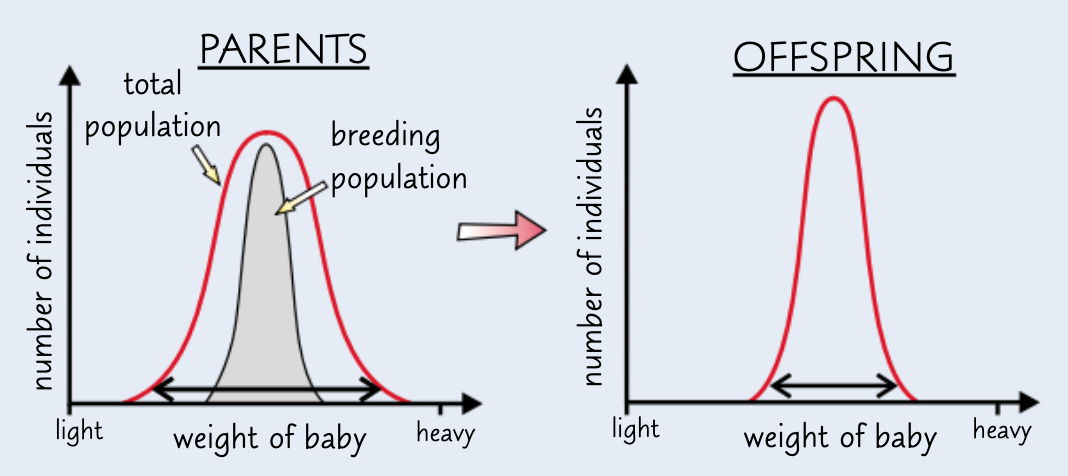
explain human birth weights in terms of stabilising selection:
very small babies less likely to survive - difficulty maintaining body temp → these alleles less likely to be passed on
very large babies less likely to survive - difficulty in childbirth → these alleles less likely to be passed on
→ conditions most favourable for medium sized babies ∴ human birth weights stabilise towards the mean w/ less variations at the extremes