Waves 1
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What is a progressive wave?
An oscillation that travels through matter (or sometimes a vacuum)
All progressive waves transfer energy from one place to another but not matter
Although particles in the matter vibrate, they do NOT move along the wave
Explain why sound is a progressive wave?
When you hear someone talking to you, vibrations travel to your ears. But the air particles do NOT move.
Instead they vibrate in a plane parallel to the direction of energy transfer as the wave passes through the air
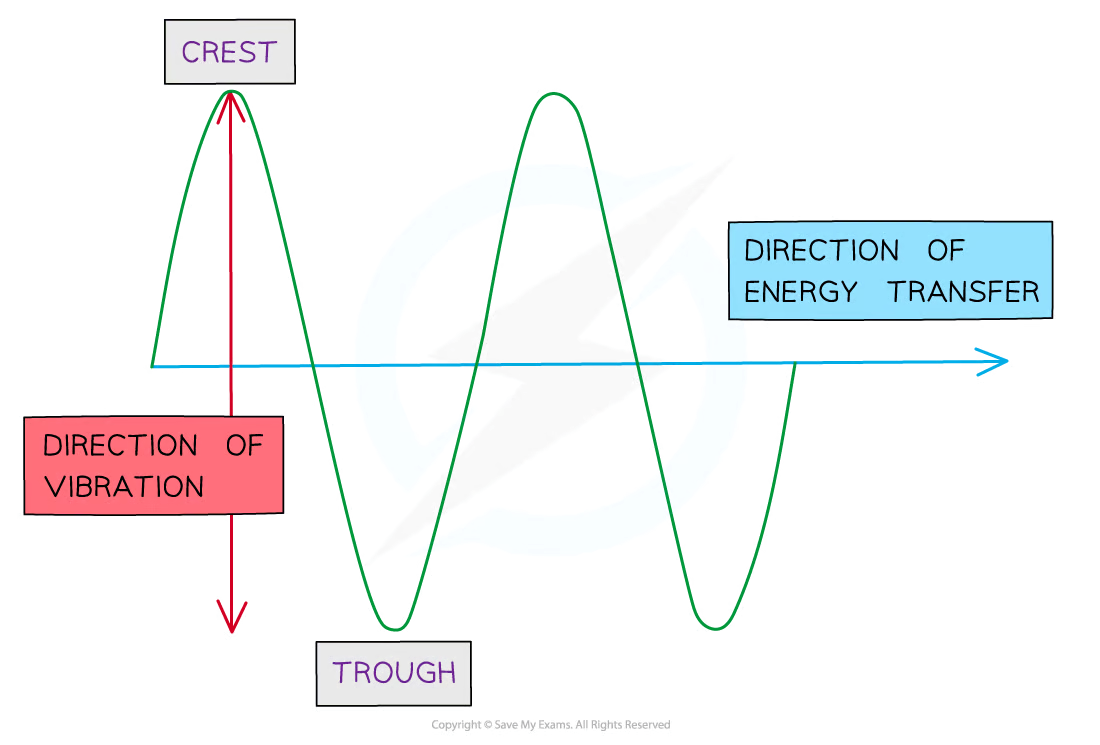
What is a transverse wave? Include diagram
The direction of oscillation of the medium are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer
Give 4 examples of a transverse wave?
Waves on the surface of water
Any Electromagnetic wave
Waves on stretched springs
S-waves produced in earthquakes
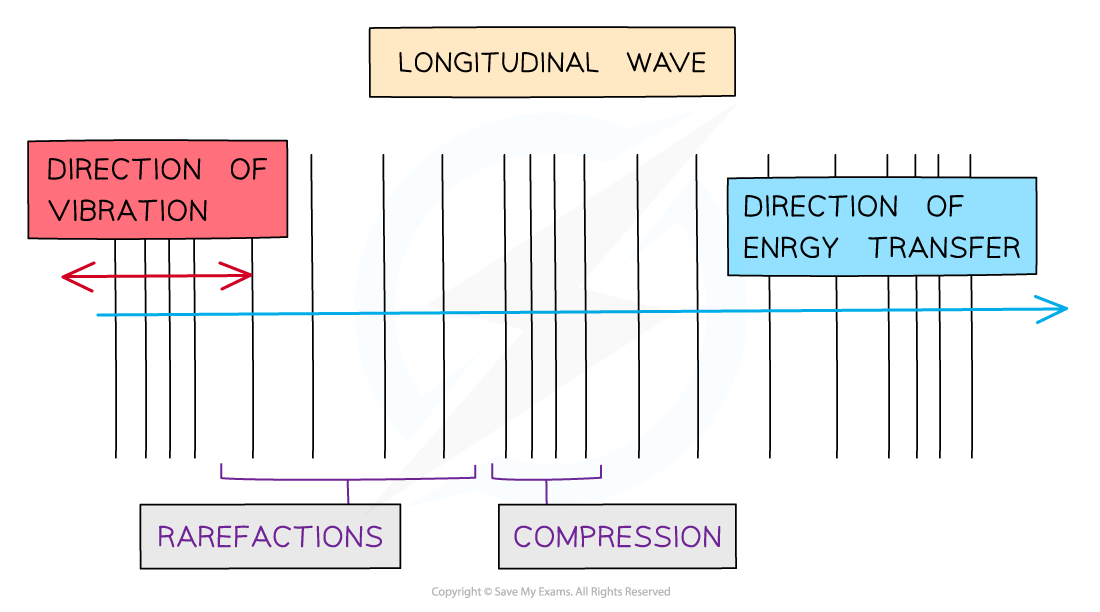
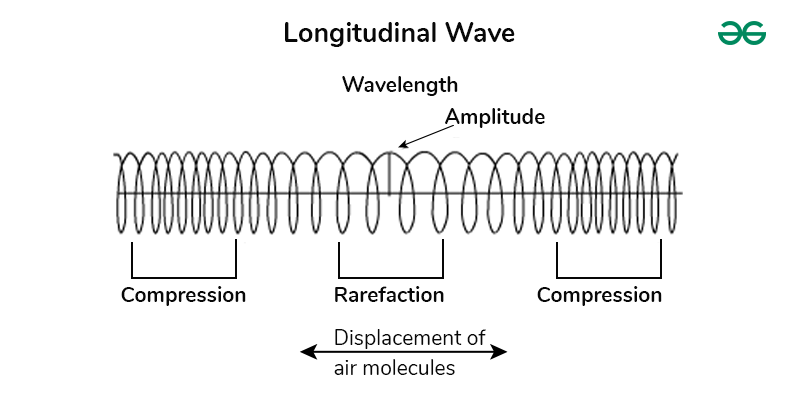
What is a longitudinal wave? Include diagram
The direction of oscillation of the medium are in parallel to the direction of energy transfer
Give 2 examples of a longitudinal wave?
Sound waves
P- waves produced in an Earthquake
Longitudinal waves can be described as having regions of compression and rarefaction.
What do these 2 terms mean?
Compression- Where the medium of particles are closer and there is a momentary decrease in volume of medium
Rarefaction- Where the medium of particles are further apart and there is a momentary increase in volume of medium
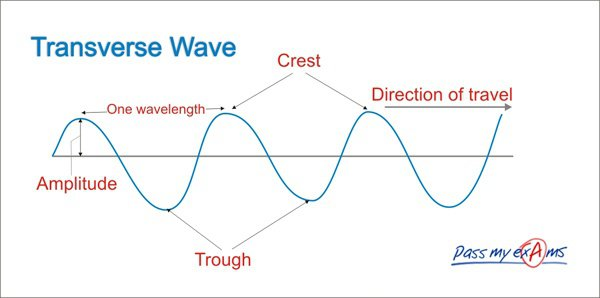
Sketch a displacement- distance of a transverse wave?
Sketch a displacement- distance of a longitudinal wave?
What is meant by displacement?
Distance from the equilibrium position in a particular direction ; a vector, so it can be positive or negative value (m/meters)

What is meant by amplitude?
Maximum displacement from the equilibrium position (can be positive or negative) (m/meters)

What is meant by wavelength?
Minimum distance between 2 points in phase on adjacent waves. The distance from one peak to the next peak or from one compression to the next compression

Define the time period of an oscillation? Include units and symbols
The period of oscillation and the frequency of a wave are reciprocals of each other
f (frequency/ Hz) = 1/ Time period (s)

Define frequency of an oscillation? Include units
The amount of complete waves each second
v (wave speed/ms^-1) =
f (frequency/Hz) X λ (wavelength/m)
How are Time period and Frequency related?
They are reciprocals of each other
State the wave equation. Define all terms and Units
v (wave speed/ms^-1) =
f (frequency/Hz) X λ (wavelength/m)
Derive the wave equation?
v= x/t = λ/T
v= λ/T = 1/T X λ
1/T = frequency
v= f X λ
What is a wave profile?
A graph seeing the displacement of the particles in the wave against the distance along the wave. Can be used to determine wavelength and amplitude
How do the particles displace overtime in waves?
They oscillate from their equilibrium position to a maximum positive position, back to the equilibrium and then to the maximum negative position and then back to the equilibrium position and then repeat
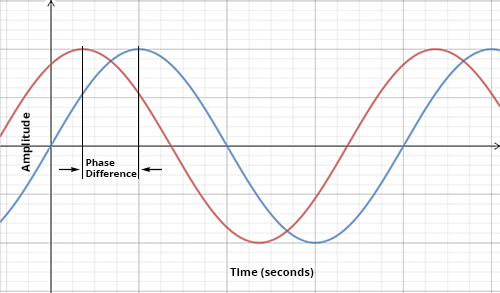
What is a phase difference? Include diagram
The difference between displacements of particles along a wave or the difference between the displacement of particles on different waves
What are the units of phases difference?
Measured in degrees representing 360° for a complete wave
OR
Measured in radians representing 2π for a complete wave
How can you convert degrees to radians?
° × π/180
How can you convert radians to degrees?
radians × 180/π
What does it mean if 2 particles are in phase?
If particles are oscillating perfectly in step with each other (they both reach maximum positive displacement at the same time)
What does it mean if particles are antiphase?
If particles are oscillating completely out of step of each other (one reaches maximum positive displacement when the other reaches maximum negative displacement)
Phase difference of 180° or π radians
How can phase difference be calculated for 2 points separated by a distance x on a wave?
Phase difference= Φ, x = path difference
Φ = x/λ × 360°
OR
Φ = x/λ × 2π
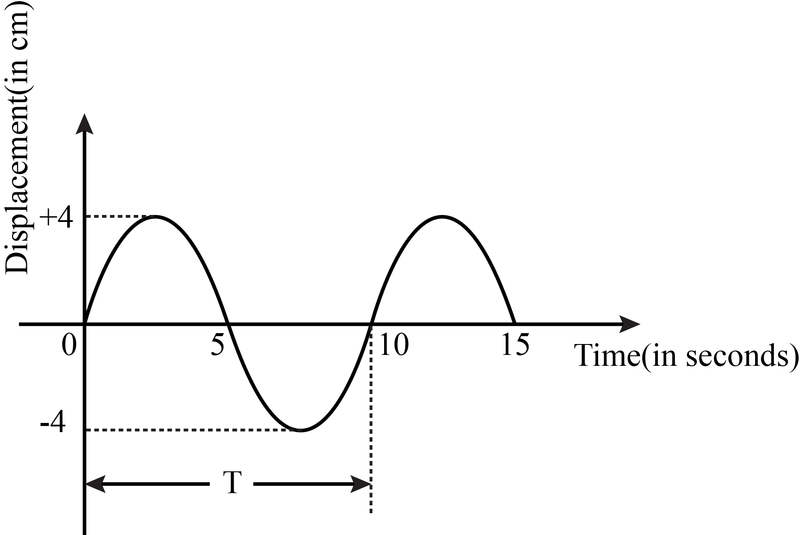
Draw a displacement- time graph with the Time period labelled?
5 = T/2
10= T
15= 3T/2
What piece of scientific equipment can be used to determine the frequency of a wave?
Oscilloscope
What is the reflection of a wave?
When a wave is travelling through a medium and meets a boundary and reflects back through the medium
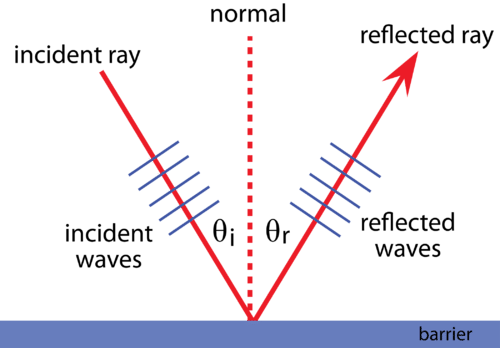
Sketch a diagram of reflection of a wave? Show incident and reflected wave
Angle of incident= Angle of reflection
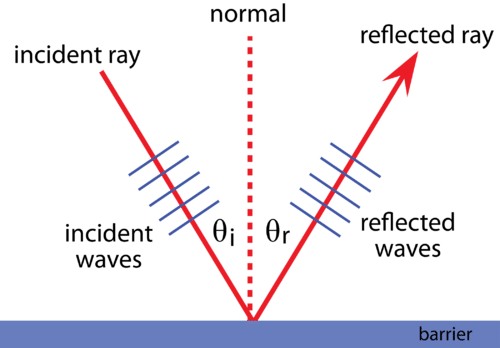
What does a ray show?
Rays are drawn 90° to the wave fronts
State the law of reflection?
The angle of incidence= the angle of reflection
(Measured from the normal)
When a wave is reflected, do the wavelengths or frequency change?
The wavelength and frequency do NOT change as it is still travelling through the same medium
What is refraction?
When a wave changes its speed as it passes from one medium to another
Sketch a diagram of refraction?
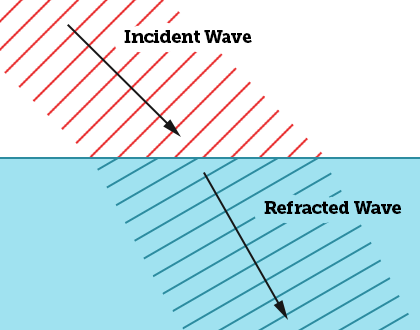
Why does the speed of a wave change when entering a new medium?
The frequency must remain constant
The wavelength is changing as it is a new medium
Wave speed must change as:
v= f ×λ
Describe what happens to the wavelength if a wave slows down upon entering a different medium?
The wavelength decreases as the frequency must remain constant
Describe what happens to the wavelength if a wave speeds up upon entering a different medium?
The wavelength increases as the frequency must remain constant
Generally, do waves speed up or slow down when entering a denser medium?
Speed up
Generally, do light waves speed up or slow down when entering a denser medium?
Slow down
What happens to water waves when they enter shallower waters?
When water enters shallower water, it slows down and the wavelength gets shorter
If a wave travels from a ‘fast’ medium to a ‘slow’ medium will the change in direction be towards or away from the normal?
towards the normal
What is diffraction? Include a diagram
Diffraction is the spreading out of a wave front as it passes through a gap.
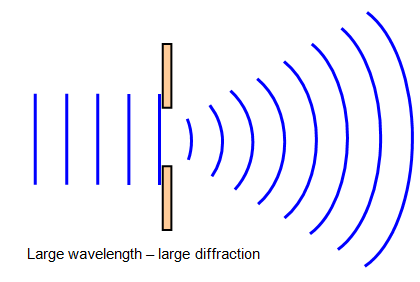
Do the speed, frequency and wavelength change when a wave is diffracted?
Yes
Under what conditions are diffraction most significant?
When the gap is the same size of the wavelength → Maximum diffraction occurs
When the gap is much smaller than the wavelength → little diffraction occurs
Explain why we need a smaller gap to observe diffraction in light compared to sound?
Light has a much smaller wavelength compared to sound, so it does not diffract through a large area
Diffraction needs the gap to be the same size of the wavelength to be most effective
What does polarisation mean?
Particles oscillate along the direction of the wave- it is confined to a single plane
What does plane polarisation mean?
When the oscillations are limited to one plane
Sketch a diagram of plane polarised and unpolarised light? (Give definition of unpolarised light)
Unpolarised light travels in random directions in many planes
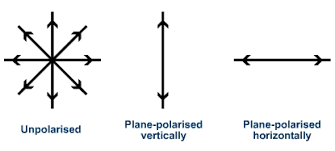
Explain why a longitudinal wave cannot be plane polarised?
The oscillations are always parallel to the direction of energy transfer. Their oscillations are already limited to only one plane (direction of energy transfer)
How can transverse waves become plane polarised?
When transverse waves reflect off a surface they become partially polarised. This means more waves oscillate in one particular plane but the wave is not completely plane polarised
How is intensity defined?
The intensity of a progressive wave is the radiant power passing through a surface per unit area
How is intensity of a wave calculated? Include units and terms
Intensity (Wm^-2) = Power ( W/ Watts) / Cross- sectional area (4πr²)
I= P/A
Explain why the intensity of a wave reduces as it spreads out from a point source?
The radiant power spreads out
Show that for a point source intensity and distance have an inverse square relationship? (diagram)
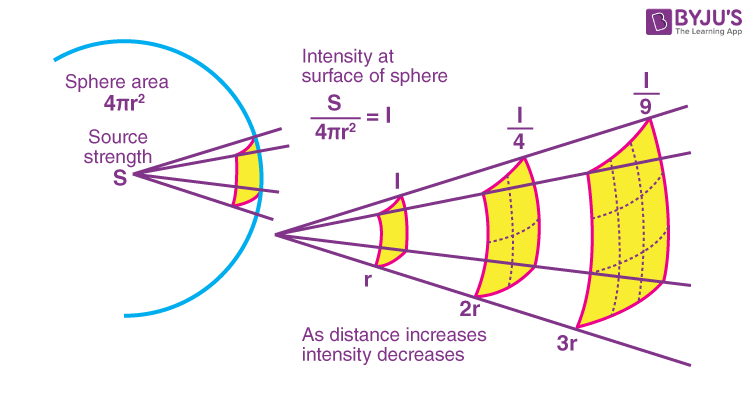
What happens to Intensity if distance doubles?
The intensity will be quartered
I= 1/ (2)²
What is the relationship between intensity and amplitude?
Intensity is directly proportional to amplitude²
I = k X A²
I/A² = k
(I/A²) 1 = (I/A²) 2
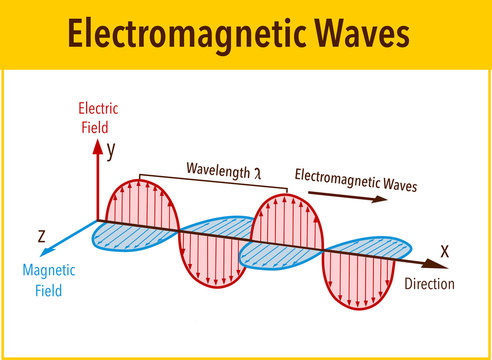
Is an electromagnetic wave transverse or longitudinal?
An EM wave is a transverse wave
What is the unique property of electromagnetic waves that allow energy to be transferred from the Sun to the Earth?
It does not require a medium to transfer energy (It can travel through a vacuum)
What is an EM wave (diagram)?
List the different types of EM waves in order of decreasing wavelength? (Include a range)
Radio waves= 10^6 → 10^-1
Microwaves= 10^-1 → 10^-3
Infrared= 10^-3 → 7×10^-7
Visible light= 7×10^-7 → 4 × 10^-7
Ultra violet= 1×10^-7 → 4×10^-7
X rays= 10^-8 → 10^-10
Gamma Rays= 10^-13 → 10^-16
How are X- rays and gamma rays classified?
By their origin, not their wavelength
List the key properties of an EM wave?
They can be reflected, refracted and diffracted
They can be plane polarised
They can travel in a vacuum
State the wave equation for EM waves? Define all terms and units
C (speed of light/ 3×10^8) = f (frequency/Hz) X λ (wavelength/m)
What does it mean if light is unpolarised?
The wave oscillates in random planes, all at 90 degrees at the direction of energy transfer
What does it mean if light is polarised?
Light only oscillates in one plane (only for transverse waves)
Polarising filters can be used to polarise light, Sketch a diagram to show the basic principle behind a polarising filter?
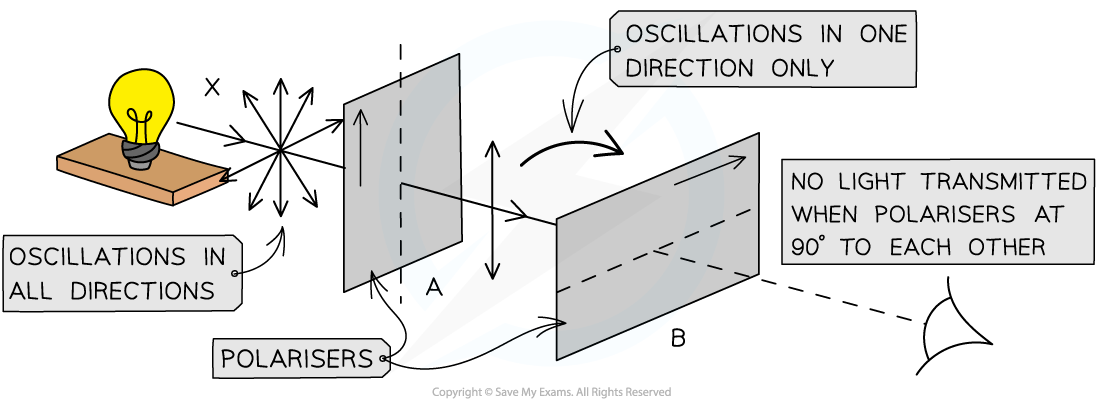
Describe an experiment that can be performed to show the polarisation of light and describe the expected results?
Take 2 polaroid filters, place them together and rotate them, you can observe the plane polarisation.
Unpolarised light passing through the 1st filter becomes polarised, if the 2nd filter is in the same place as the 1st then the light passes through.
However when it has turned 90 degrees, no light is transmitted and the intensity falls to 0
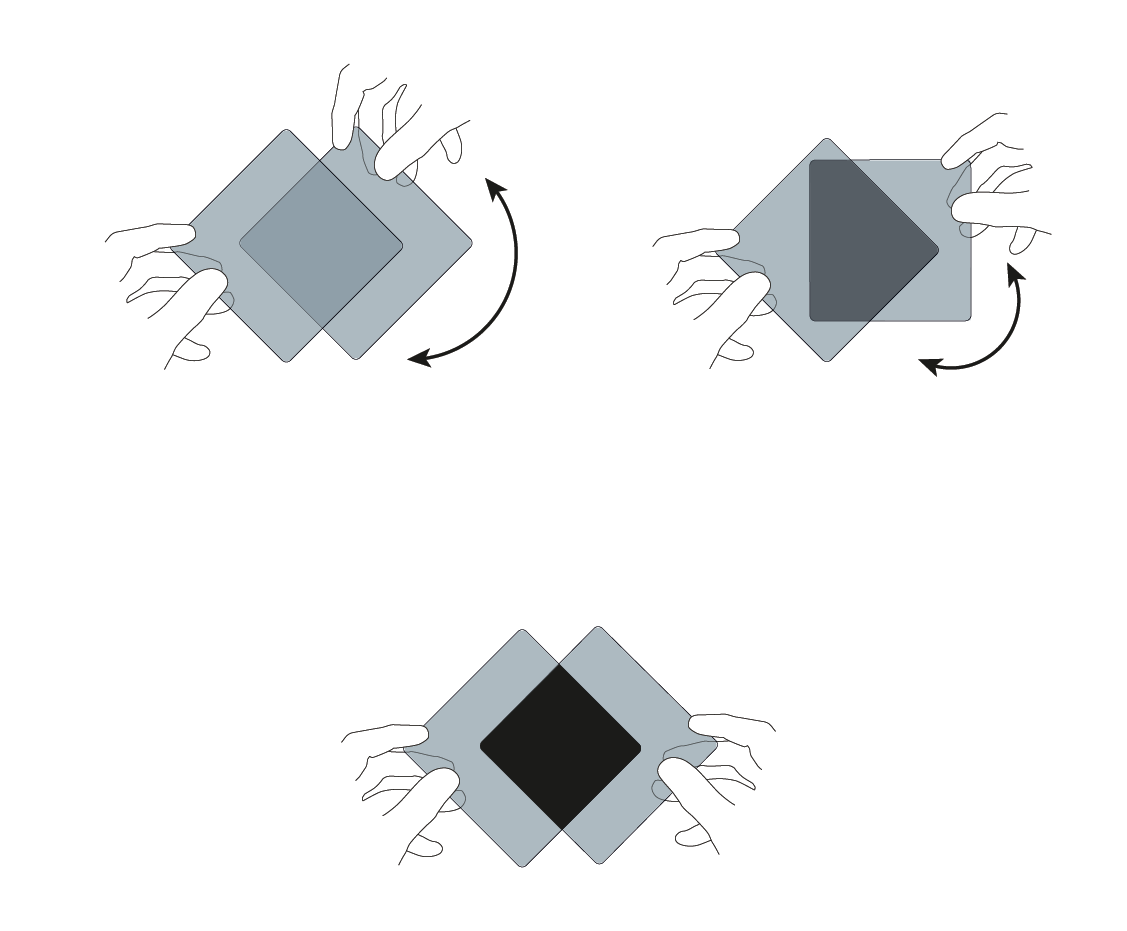
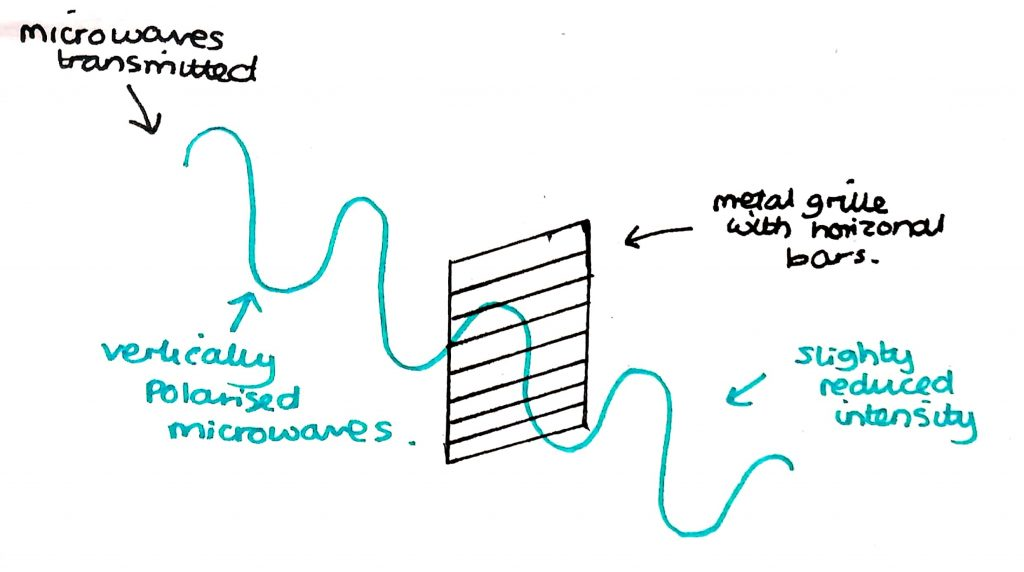
Describe an experiment that can be performed to show the polarisation of microwaves. Include a diagram
After the metal grill, less microwaves would be transmitted
How is refractive index calculated? Define all terms and units
n (refractive index) = c(speed of light) / v (speed of light through material)
refractive index is a ratio, no units
What does it mean if a material has a refractive index, n equal to 1?
It is the same speed of light through a vacuum
What factor decides how much the angle of refraction is through a material?
The density of material
More dense- slows down → further away from the normal
Less dense- speeds up → closer to the normal
From which point do you measure the angle of incidence, and the angle of refraction on a diagram?
From the normal
State the law of refraction? Define all terms and units
n1 X sinθ1 = n2 X sinθ2
n= refractive index
θ= angle between normal and incident ray
What is total internal reflection?
When the angle of incidence is bigger than the critical angle when the light moves from a higher refractive index to a lower one
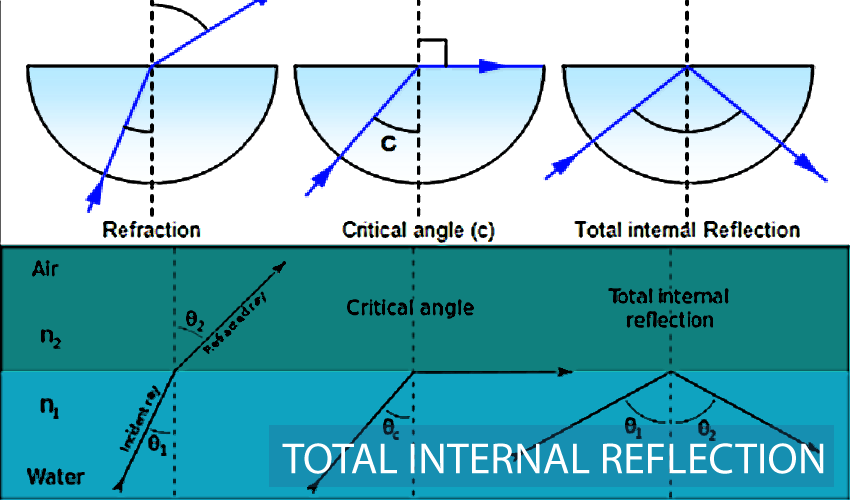
State 2 conditions required for total internal reflection?
Angle of incidence must be bigger than critical angle
The material change must be from a higher refractive index to a lower one
What is the equation for the critical angle?
n (refractive index) = 1 / Sin C(critical angle)
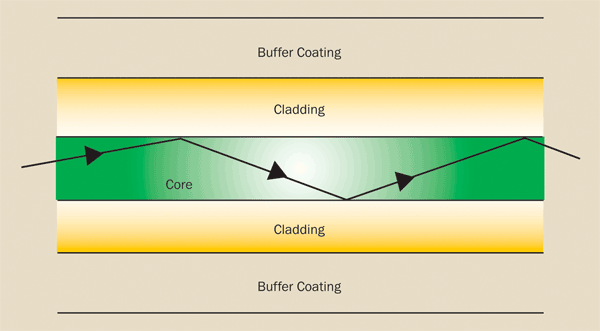
Describe the basic principle of an optic fibre. Include a labelled diagram?
The reflective index changes suddenly between the core and the cladding