Strategy
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
According to Michael Porter, the essence of strategy is choosing what ————
not to do
Market segments and geographic areas represent which of the 5 elements of strategy?
Arenas
Speed of expansion and intervals between events refer to the ———— of the 5 elements of strategy
economic logic
To start your strategy, Roger Martin recommends
Do not make it complicated or leghty. Keep it short
Which strategic planning stage involves developing a mission and a vision and completing a SWOT analysis?
Strategy formulation
Motivating employees is a function of ————-
strategy implementation
Business Model
A story about how an organization created, delivers, and captures value is a simple explanation
purpose
why an organization exists
Internal factors
opportunities and threats are ———- to the organization
cost leadership
low profit margins per unit with large sales volumes to maximize profit
differentiation
exemplified by goods significantly different from competitors, higher prices, and higher margins
The focus (narrow market) concentrated on cost (cost focus) is best represented by which of the following examples
Neither Palacio de Hierro nor The Apple Store
Which of the following statements is not representative of a niche market
Weak market demand
In the 2×2 Matrix Guy Kawasaki presented in his TED Talk, in which quadrant do we want our company to be?
Lower right quadrant
In which Key Industry Success Factor do we find a superior work force and design expertise?
Skills related
examples of manufacturing- related Key Success Factors
Low cost production and lost cost plant locations
Purchasing high volumes and the availability of substitute products represents
Higher buyer bargaining power
Barriers to entry a market
Economies of scale, capital requirements, access to distribution channels
Industries characterized by increased investment, the creation of new jobs, and expanding market opportunities
expansion
Characteristics an organization developed over its years of operation that has made it a benchmark in the sector
resources and capabilities
A baseline against which performance can be evaluated to determine if improvements are needed/objectives met
benchmark
primary activities in the value chain
Inbound logistics
Operations
Outbound logistics
Marketing and sales
Service
The goal of the five sets of activities is to create value that exceeds the cost of conducting that activity, therefore generating a higher profit
support activities in the value chain
firm infrastructure, human resource management, technology development, procurement
Key aspects of dynamic capabilities
sensing opportuntities and threats
seizing opportunities
reconfiguring resources
strategy definition
The term comes from the Greek strategos - general of war or to plan the destruction of the enemy through the effective use of resources.
5 elements of strategy
arena
vehicles
differentiators
staging
economic logic
arena
where will be achieve?
which market segment?
which product categories?
which channels?
which geographic areas?
which core technologies?
which value creation stages?
vehicles
how will we get there?
joint ventures?
internal development?
strategic alliances?
licensing?
franchising?
mergers and acquisitions?
differentiators
how will we win in the marketplace?
image?
customization?
price?
styling?
reliability?
speed to market?
stage
what will be our speed and sequence of moves?
speed of expansion?
sequence of initiatives?
interval between events?
economic logic
how will we obtain our returns?
lowest costs through scale advantages?
lowest costs through scope and replication advantages?
premium prices due to proprietary product features?
premium prices due to unmatchable services?
ways to start a strategy
Accept angst (nervousnesss)
Can’t prove in advance that your strategy will work
Layout the logic of your strategy clearly
Watch the world unfold
Tweak,tone, and refine
Strategy is a journey
Keeit it shot (ideally fits on one page)
Do it, tweak it
strategic planning stages
Strategic formulation
Strategy implementation
Strategy evaluation
competitive advantage
Outperform rivals
These advantages allow a company to achieve and maintain superior margins, a better growth profile, or greater loyalty among current customers
Examples:
Access to natural resources not available to competitors
Highly skilled labor
Strong brand awareness
Access to new or proprietary technology
purpose
why do we exist?
mission
a plan for fulfilling your purpose
who we are
what we value
vision
what will the world look like when we’ve
what we want to become
goals and objectives
how we gauge our degree of success
business model
A story about how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value
SWOT analysis
A framework used to evaluate a company’s competitive position and to develop strategic planning
Internal factors: strengths, weaknesses
External factors: opportunities, threats
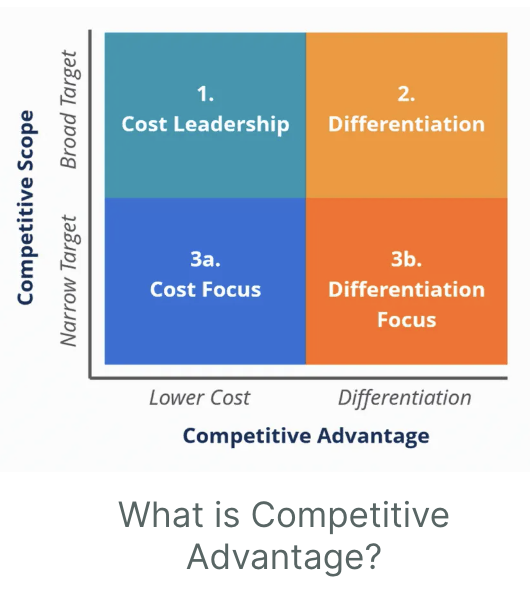
Cost leadership
The lowest cost manufacturer or provider of a good or service
Producing goods that are of standard quality for consumers, at a price that is lower and more competitive than other comparable products
Combine low profit margins per unit with large sales volumes to maximize profit
ex. Walmart
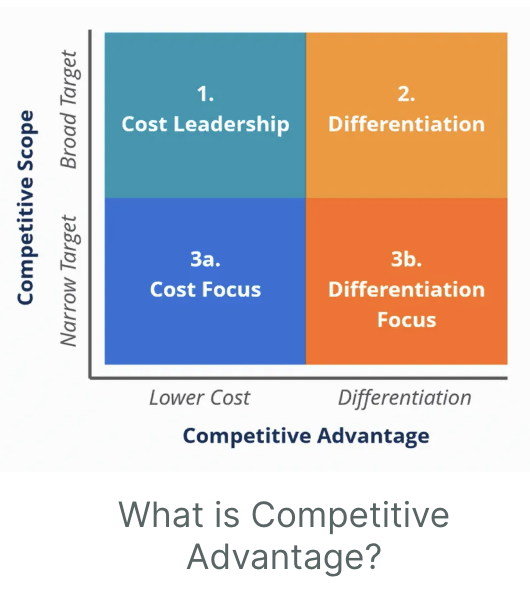
Cost Focus
Identifying the needs of a niche market and then developing products to align the specific need area
Lowest-cost producer in a concentrated market segment
ex. Whole Foods
Products are unique
Niche market with higher disposable income
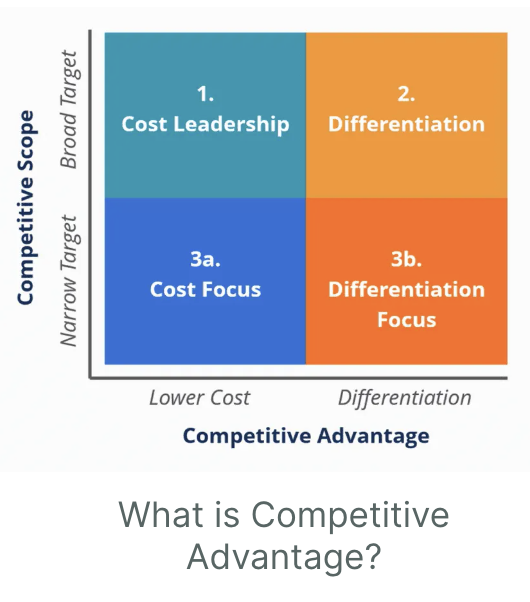
Differentiation focus
Identifying the needs of a niche market and then developing products to align the specific need area
Customized or specific value-add products in a narrow-targeted market segment
Niche
Minimal competition
Professionally and personally satisfying
High profile potential
Solves a practical need
Strong market demand
Product positioning
Target audience
Unique selling propositions
Product benefits
Competitors
Promotion
Position statement
What place do they occupy in the market?
How do their products or services rank against their competitors
Key Industry Success Factors
Key success factors (KSFs) are areas of critical performance, necessary for success in a specific industry
A firm cannot expect to be competitive in its industry without an understanding of the industry’s key success factors
Key success factors are a function of both customer needs and competitive pressures
technology-related
scientific research expertise, product innovation capability, expertise in a given technology, capability to use internet
manufacturing related
low-cost production efficiency, quality of manufacture, high use of fixed assets, low-cost plant locations, high labor productivity, low-cost product design
distribution-related
strong network of wholesale distributors/dealers, gaining ample space on retailer shelves, having company-owned retail outlets, low distribution costs, fast delivery
marketing-related
fast, accurate technical assistance, courteous customer service, accurate filling of orders, breadth of product line, merchandising skills, attractive styling
skills-related
superior workforce talent, quality control know-how, design expertise, expertise in a particular technology, ability to develop innovative products, ability to get new products to market quickly
Organizational capability
superior information systems, ability to respond quickly to shifting market conditions, superior ability to employ internet to conduct businesses, more experience and managerial know-how
other types
favorable image/reputation with buyers, overall low-cost, convenient locations, pleasant, courteous employees, access to financial capital
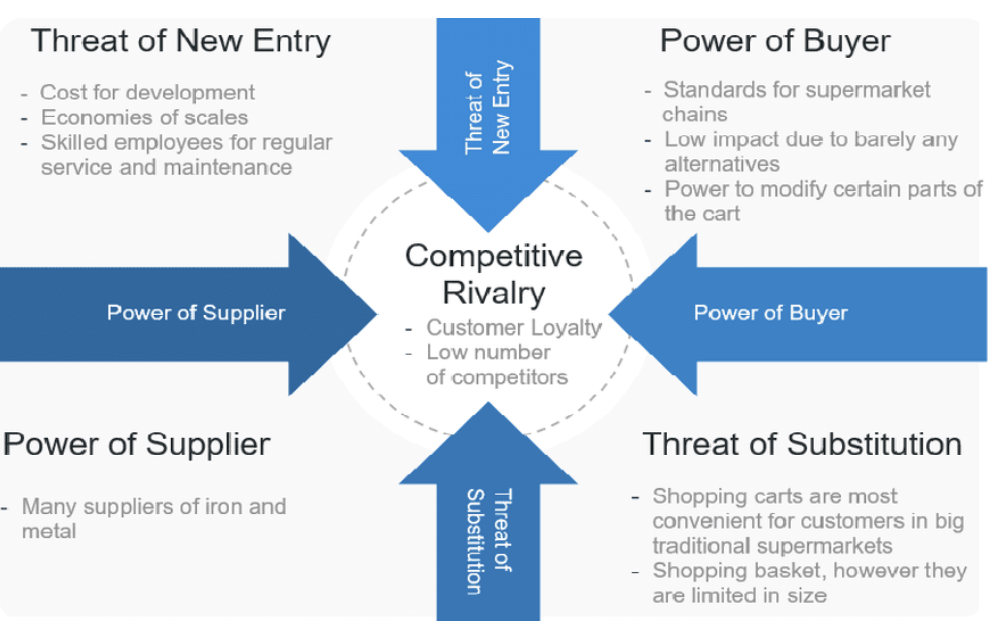
Porter’s 5 forces
threat of new entry
power of buyer
threat of substitution
power of supplier
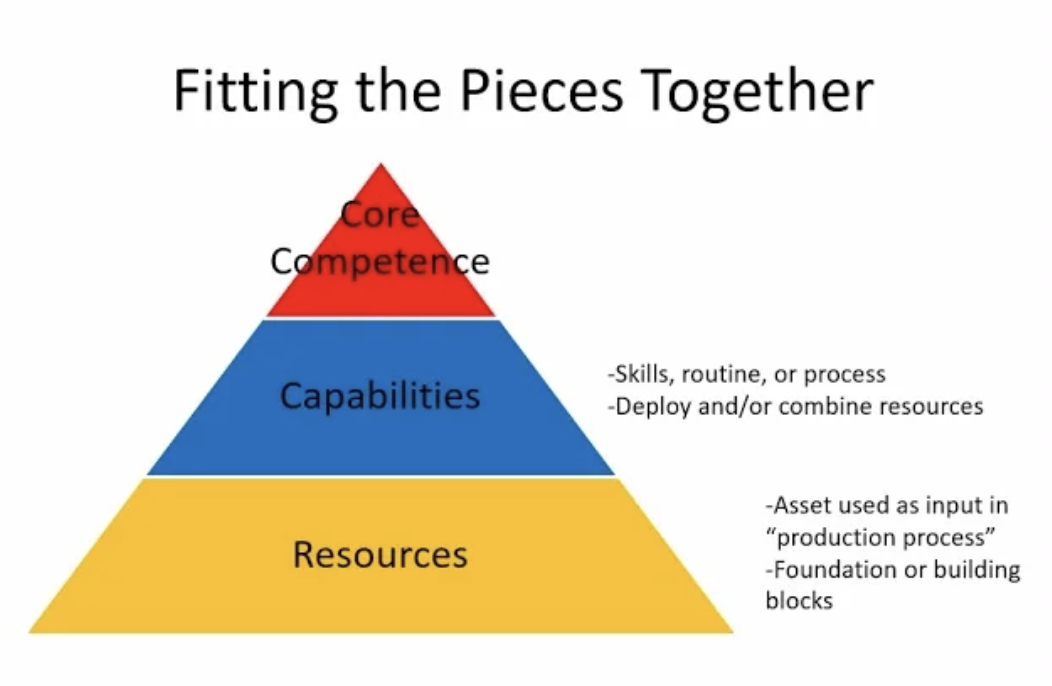
capabilities
skills, routine, or process
deploy and/or combine resources
The organization’s ability to effectively make use of its resources
resources
asset used as input in “production process”
foundation or building blocks
any factor that is necessary to accomplish a goal or carry out an activity
Assets that it uses to achieve its objectives
economic phases
expansion
recession
stable
contracting
expansion
Sectors of the economy that are experiencing rapid growth and development, driven by various factors such as innovation, consumer demand, technological advancements, or societal shiefts
These industries are often characterized by increased investment, the creation of new jobs, and expanding market opportunities
As these industries grow, they often reshape existing market, disrupt traditional industries, and create new economic opportunities
ex. Technology & software, renewable energy & sustainability, healthcare & biotechnology, e-commerce & digital retail, financial technology (FinTech)
recession
Sectors of the economy that are experiencing declined or stagnation
This can result from reduced consumer demand, technological disruption, changing market conditions, or external factors like regulatory changes or global events (ex. pandemics or geopolitical crises)
During a recession, industries in decline often face reduced revenues, layoffs, closures, and less investment
ex. Traditional retail, fossil fuels (coal and oil), print media, cable tv, automobile (traditional vehicles)
stable
Sectors of the economy that tend to remain resilient and maintain consistent demand, even during economic downturns or periods of volatility
These industries are often characterized by essential products or services that people or businesses need regardless of economic conditions
As a result, they experience relatively steady growth, predictable revenue streams, and lower susceptibility to market fluctuations
ex. healthcare, utilities, consumer staples, public sector and government services, funeral and death
contracting
Sectors of the economy that are shrinking or experiencing prolonged decline in terms of revenue, job opportunities, or market demand
These industries face significant challenges due to factors like technological disruption, changing consumer preferences, regulatory changes, or shits in global trade dynamics
As a result, businesses in these sectors may close down, lay off workers, or face reduced investment
ex. Blockbuster
resources and capabilities
These characteristics that the organization has established and developed over its years of operation have made it a benchmark in the sector(s) in which it operates
benchmark
A standard or point reference used for measuring and comparing the performance, quality, or process of an organization, product, or service
A baseline against which current or future performance can be evaluated to determine if improvements are needed or if objectives have been met
ex. customer-related, HR related, finance-ROI, sustainability-related
activist investor
An activist investor is an individual or institutional investor who buys a significant stake in a publicly traded company with the aim of influencing how the company is run
Rather than being passive shareholders, activist investors actively push for changes in management, strategy, or operations to improve the company’s value, governance, or financial performance
hedge fund
A hedge fund is a type of investment fund that pools capital from accredited or institutional investors to engage in a wide range of strategies aimed at generating high returns, regardless of market conditions. Hedge funds are typically more and less regulated than mutual funds, allowing them to use advanced and sometimes riskier investment techniques
dynamic capabilities
An organization’s ability to integrate, build, and reconfigure its internal and external competencies to respond rapidly to changing environments
This concept is rooted in strategic management and emphasizes the firm’s capacity to adapt, innovate, and remain competitive in fast-moving or uncertain markets
Allow businesses not just to survive, but to thrive by consistently evolving their resources, processes, and strategies in alignment with external changes
It is important to identify what these capabilities are within the company and promote/exploit them
Dynamic capabilities allow companies to change and evolve the company
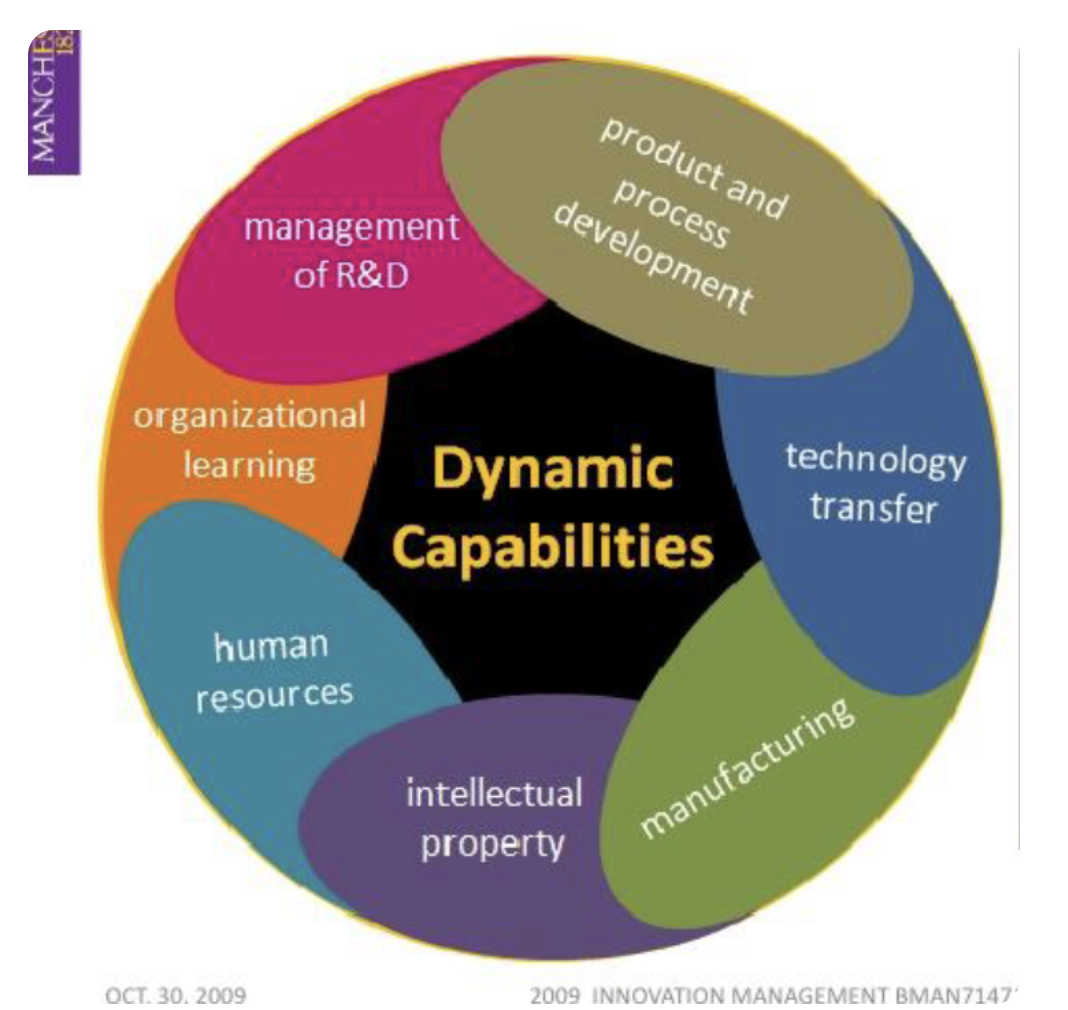
components of dynamic capabilities
Learning and Innovation
Entrepreneurial Management
Strategic Flexibility