APH CH 12 blood
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
blood is
connective tissue whose cells are suspended in liquid
blood functions to
transport substances between cells and the external environment
what does blood transpot
O2, CO2, nutrients, hormones, waste
platelets
close wounds
WBC
fights infections
blood distributes
heat
blood promotes
homeostasis
Average adult has _____ of blood
5L
body size, change in fluid (electrolyte concentration) and amount of adipose tissue
affect how much blood you have
Liquid Plasma is _____ of blood
55%
Liquid Plasma is clear, straw colored liquid composed of
water, carbs, proteins, amino acids, lipids, vitamins, hormones, electrolytes, cellular waste
Solid Portion - Hematocrit (HCT) is ______ of blood
45%
Solid Portion - Hematocrit (HCT) has
RBC, WBC and Platelets
Red blood cells aka
erythrocytes
Erythrocytes are ________ ______ in structure
biconcave discs
Erythrocytes have ______ that carry oxygen
hemoglobin
Erythrocytes do not have a
nucleus
Erythrocytes can not
make proteins or divide
males have
4.6 – 6.2 million RBC per cubic millimeter
females have
4.2 – 5.4 million RBC per cubic millimeter
Erythrocytes are produced in ______ and _______ as a FETUS
liver and spleen
Erythrocytes are produced in ______ _______ as INFANTS and ADULTS
bone marrow
Erythropoietin is a
hormone produced by the kidney that promotes the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow
Erythropoietin is controlled by
negative feedback
Average life span of a red blood cell is _____ days (removed by the spleen)
120
Sickle Cell Anemia causes erythrocytes to be
Hard, scarred, inflexible
◦Can’t carry as much oxygen
Sickle Cell Anemia symptoms include
fatigue, short of breath, painful joints
Sickle Cell Anemia diagnosis is higher in
African American Populations
◦Resistant to malaria
White blood cells aka
Leukocytes
Leukocytes protect against
disease
Leukocytes have ______ to _________ WBC per cubic millimeter
5,000 to 10,000
If you have more leukocytes than 5,000 to 10,000, it is an
infection
If you have less leukocytes than 5,000 to 10,000, it is
leukopenia
Leukocytes can indicate
typhoid fever, influenza, measles, mumps, chicken pox, AIDS, poliomyelitis
Types of WBC
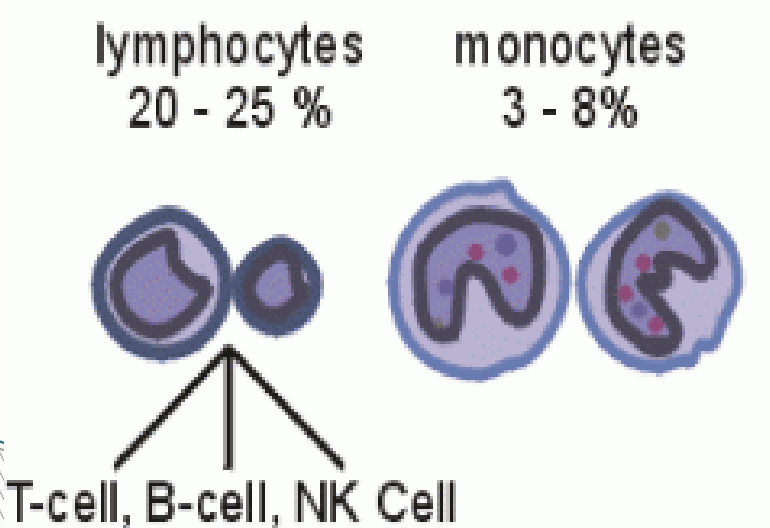
Lymphocytes
provides immunity (B & T cells)
Types of WBC
Monocytes
phagocytizes large particles
Types of WBC
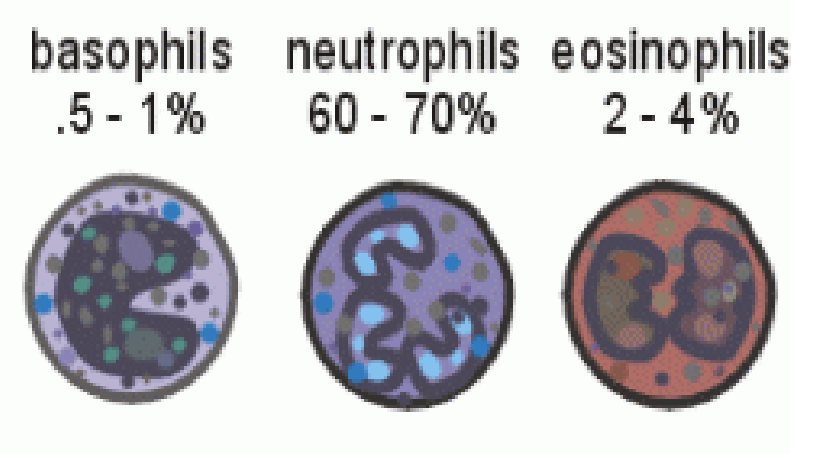
Basophils
releases heparin and histamine
Types of WBC
Neutrophils
Phagocytizes small particles
Types of WBC
Eosinophils
kills parasites, helps control inflammation & allergic reactions
leukocytes- agranular
leukocytes- granular
platelets aka
Thrombocytes
thrombocytes are
not complete cells (fragments)
thrombocytes come from
large cells in red bone marrow
thrombocytes lacks a
nucleus
thrombocytes help close breaks in
damaged blood vessels
thrombocytes initiate
blood clots
thrombocytes are ______- ________ per cubic millimeter
130,000 – 360,000
Hemophilia is a bleeding disorders in which
it takes a long time for the blood to clot
Hemophilia is passed down through families (inherited), often affecting
males
Blood pH – basic normal :
7.35 – 7.45
Blood Plasma
◦ Plasma Proteins – most abundant solute in plasma; comes from the ____
liver
Plasma Proteins
Albumins – (60%)
Helps maintain osmotic pressure
Plasma Proteins
Globulins – (36%)
Transports lipids, antibodies & fat soluble vitamins
Plasma Proteins
Fibrinogens (4%)
blood coagulation
Hemostasis is stoppage of
bleeding
Hemostasis
Vasospasm
smooth muscles in walls of a blood vessel contract, blood loss lessens
Hemostasis
Serotonin
vasoconstrictor released by platelets when blood vessels break to control bleeding
Hemostasis
Platelet Plugs
- Adhere to rough surface and each other
- Control blood loss from a small break
Hemostasis
Blood Coagulation – blood clot
- Clotting factors – biochemicals to promote and inhibit coagulation
- Fibrin – insoluble threads of protein produced by fibrinogen (a plasma protein)
- Positive feedback system – original action stimulates more of the same type of action
- Once a blood clot begins to form, it promotes more clotting.
Blood Clots
Thrombus
blood clot abnormally forming in a blood vessel
Blood Clots
Embolus
a blood clot that breaks loose and is carried away by the blood flow
Signs of a mismatched blood transfusion
◦Anxiety, difficulty breathing, red face, neck, chest, lumbar pain & death
Agglutination
clumping of red blood cells after a transfusion
Antigens
chemical found on all cells (including RBC) that stimulates body to produce antibodies
Antibodies
A protein made by the immune system that reacts with antigens
Type A – only have antigen __ on RBCs
A
Type B – only have antigen ___ on RBCs
B
Type AB – have both antigen __and antigen __ on RBCs
A and B
Type O – have neither antigen __and antigen __on RBCs
A and B
Most Common blood types
Type O (47%)
Type A ( 41%)
Rarer blood types
Type B ( 9%)
Type AB (3%)
Shortly after birth, if the antigen is absent, _______
antibodies are produced
Type A produces antibodies for
Antigen B
Type B produces antibodies for
Antigen A
Type AB doesn’t produce any antibodies
NEITHER antigen A or antigen B
Type O produces antibodies for
BOTH antigen A and Antigen B
Type A – donates to
A and AB
Type B – donates to
B and AB
Type AB – donates only to
AB
Type O - donates to
ALL
Type A – receives from
A and O (A preferred)
Type B – receives from
B and O (B preferred)
Type AB – receives from
ALL (AB preferred)
Type O – receives
only from O
Rh blood groups –
rhesus monkey
Rh factors (antigens)
◦antigen D is most important of the Rh antigens
Rh positive – antigen D is
present
Rh negative – antigen D is
not present (absent)
Only Rh+ can receive from Rh-
Rh- will have antibodies to Rh+
85% Rh
positive
15% Rh
negative
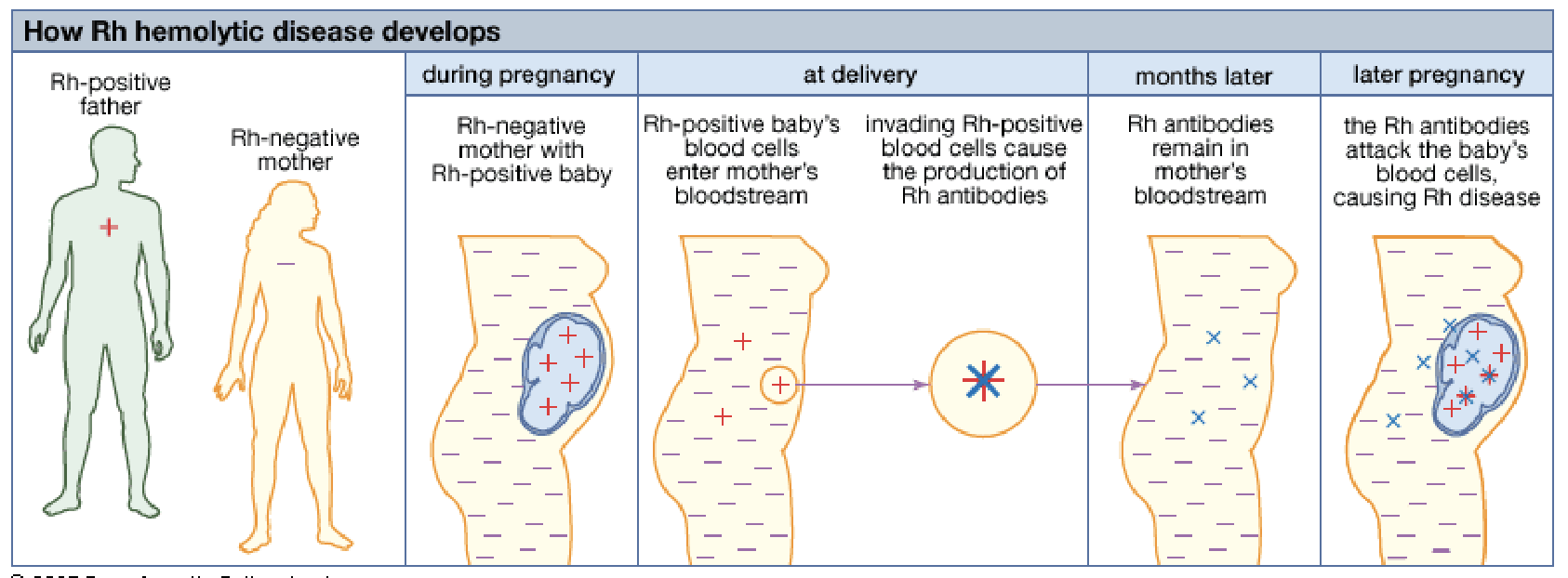
Erythroblastosis Fetalis
Pregnant mother: if mother is Rh- & fetus is Rh+
At birth (or miscarriage), placental membranes can tear.
Infant’s Rh + blood may enter maternal circulation.
This Rh+ blood stimulates production of anti- Rh antibodies.
If this woman becomes pregnant again with Rh + baby, the antibodies (for Rh+) cross the placental membrane, destroying fetal RBCs.
Erythroblastosis fetalis develops in fetus.
Erythroblastosis Fetalis