NRS 204: Safety, Mobility, Skin Integrity, and Functional Health
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Structure of skin
- Epidermis: Dermal papilla
- Dermis: Papillary dermis & reticular dermis
- Hypodermis: Subcutaneous fat cells
Sensory and motor integration: Control of voluntary movements
1. Sensory input
2. Planning and decision making
3. Coordination and timing: cerebellar input
4. Execution: corticospinal tract to skeletal muscles
5. Execution: extrapyramidal influence on posture, balance, and gait
6. Continuous feedback
Sensory and motor integration: Feedforward reflexes and feedback of info during movement
S
Safety Concept Definition
Minimize risk of harm to patients, families, communities and systems
Safety Concept Scope
Keeping patients safe to Patient injury or death due to injury
Safety definition
"freedom from accidental injuries; ensuring patient safety involves the establishment of operational systems and processes that minimize the likelihood of errors and maximize the likelihood of intercepting them when they occur."
Safe care
"avoiding injuries to patients from the care that is intended to help them."
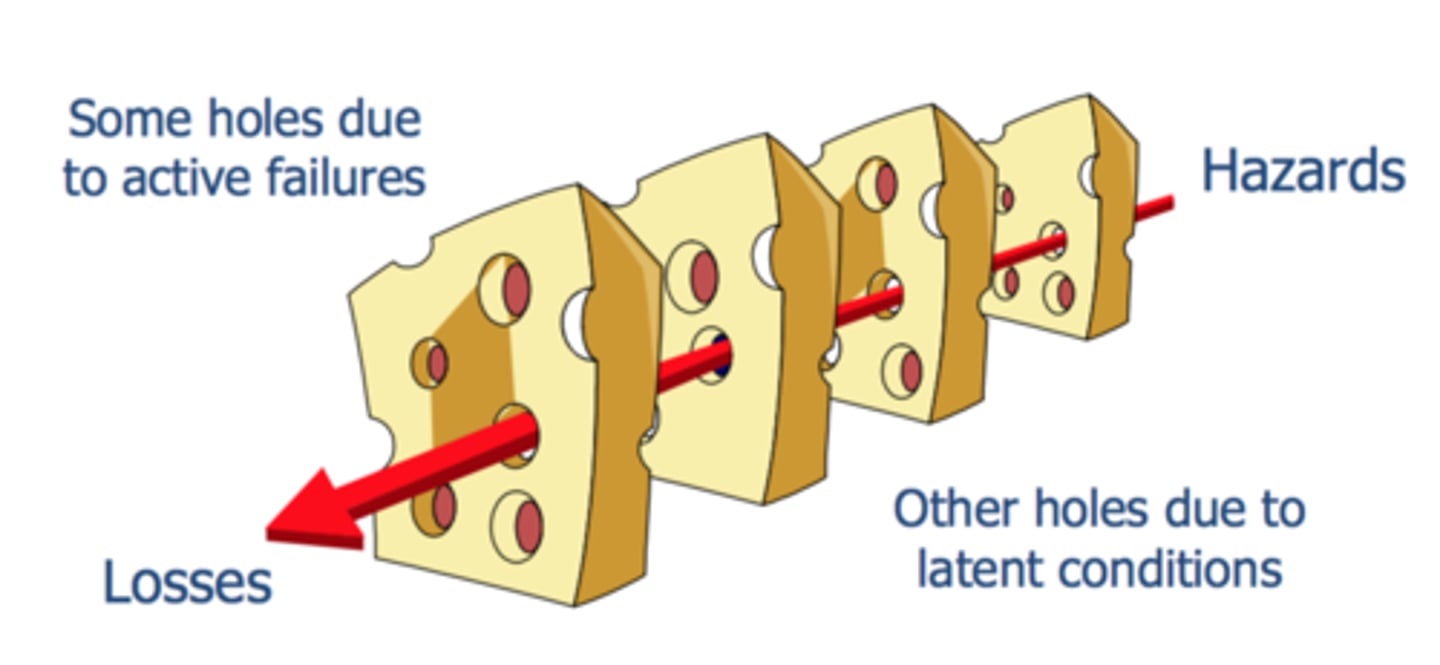
Reason's Swiss Cheese Model of Accident Causation
Categories of Errors
- Diagnostic
- Treatment
- Preventive
- Communication failure
Scope of errors: latent vs active
- Blunt end: Latent Errors. Organizational. System
- Sharp end: Active Errors. Direct Patient Care
Level of errors
- Near Miss
- Adverse Event
- Sentinel Event
- Never Event
- Near Miss: An event or situation that could have resulted in an accident, injury or illness, but did not, either by chance or through timely intervention
- Adverse Event: An event that results in unintended harm to the patient by an act of commission or omission rather than by the underlying disease or condition of the patient
- Sentinel Event: A patient safety event that reaches a patient and results in any of the following: death, permanent harm, severe temporary harm, or intervention required to sustain life
- Never event:
Preventable hazard that can result in injury or death - that should NEVER happen - considered sentinel events by JCAHO
Culture of Safety Definition
One in which a health care organization's leaders, managers and workers are committed to core values and behaviors that emphasize safety over competing goals
Human Factors
- Study of the interrelationships among people, technology, and the work environment
- Nurses' work is complex
- Multiple distractions
- Competing priorities
Typical vs. atypical findings: Atypical
• Alteration in tone:
Hypertonia • Hypotonia
- Alteration in strength:
• paresis • plegia
- Alteration in movement: Hyperkinesia • Hypokinesia
-phasia (speech)
-phagia (swallowing)
-taxia (coordination)
- trophic (development)
Benefits of mobility
• Muscles
• Tendons
• Joints
• Bones
• GI system
• Lungs
• Cardiovascular system
• Skin
Nursing interventions: Care of the restrained patient Mobility
• All restraints must:
• Be medically necessary (not coercive, punitive, or applied for the convenience of the nursing staff.)
• Benefit the patient and/or ensure the safety of others.
• Be used only when less restrictive interventions are not effective
• Be ordered by a licensed independent provider (LIP)
Nursing interventions: Care of the restrained pa,ent Monitoring and documenta,on
- All patients in restraints must:
• Be assessed at least every two hours, more if warranted, by an RN.
• Be provided with appropriate mobility, feeding, hydration, toileting, and safety interventions
• Remain free of injury
Mobility: Collaborative interventions
• Imaging studies
• Movement precautions
• Pain control
• Exercise therapy
• Mobility interventions
• Assistive devices
• Interdisciplinary collaboration for early mobility
Mobility: Movement precautions
• Hip precautions: • No hip flexion >90 • No crossing of midline
• Spinal precautions: • Keep spine straight
• Bleeding precautions: • Protect from injury
• Seizure precautions: • Protect from injury
Collaborative interventions: Skin
- Medications: • Ointment, cream, gel, powder
- Protective barriers: • Creams or dressings • Sunscreen!
- Wound care: • Dressing, debridement • Surgery, grafting
- Nutrition
- Infection prevention
- Phototherapy
Functional ability
The individual's ability to perform the normal daily activities required to meet basic needs; fulfill usual roles in the family, workplace, and community; and maintain health and well-being
Basic Activities of Daily Living (BADLs or ADLs)
Activities of personal care and mobility, including eating as well as hygienic and grooming activities such as bathing, mouth care, dressing, and toileting
Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADLs)
More complex skills that are essential to living in the community, such as managing money, grocery shopping, cooking, house cleaning, doing laundry, taking medication, using the telephone, and accessing transportation
Occupational health
Functional health also extends to one's abilities to do one's chosen work; this is nurtured by a nursing specialty called occupational health
Occupational therapy
Is a separate profession specialty that focuses on ADLs, IADLs, and occupational health
Physical assessment: Functional health
• Ask
• Performance-based assessments
• Mobility
• Demonstration/ return demonstration
• Published scales
Nursing interventions: Functional health
• Generalized assessment of BADLs and IADLs: • Self-reported assessment • Standardized functional assessment tools
• Crafting realistic self-care plans: • Medication schedules • Therapy plans • Follow-up care • Home set-up needs