Chapter 26-27 ("The Industrial Revolution" and "Imperialism in the 19th Century"))
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Origins and Growth of Industrialization (1750-1914)
Industrial Rev. began in Britain in the 18th Century
Marked the transition from manual labor & natural sources of power → mechanical power & machine-driven production
Results in new modes of Transportation, new economic policies, & new business procedures
Factory System
Factories grew due to dependence on large machinery
Steam power allowed factories to set up in cities with pools of cheap labor and access to transportation systems
The Industrial Revolution spread from Northern Europe to Southern Europe
Why?: Northern Europe had coal reserves and conditions suitable for industrialization
Differences between 1st Industrial Revolution and 2nd Industrial Revolution
1st: relied on steam power
2nd: used steel, electricity, and chemicals to steer progress
Chemicals
Cheaper paper
Fertilizer
Explosives (dynamite used for tunnels and excavation projects like the Panama Canal)
Tires, plastic
Aspirin and soap products (which improved health and hygiene)
Other Advances
Automobile
Telegraph
Telephone
Machine Gun
The Social and Economic Impact of Industrialization
Population increases due to food surplus, improvements in healthcare, and sanitation
Growing Middle-Class (doctors, lawyers, merchants)
Working Class-increased use of child labor (leads to increased injury and death among kids)
Improved Standard of Living
Increased wages
Improved living conditions in factories, mines, cities
More jobs for women
Women gained the right to vote with the 19th Amendment
Big Business
Laissez-faire: “hands-off” policy by governments towards business. Leave business alone.
Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Britain?
Britain had “coal and colonies”-natural resources for producing energy and a global trading network
A thriving merchant class
A banking system
A population surge due to new crops coming from America
Colonialism
A system in which people from one country settle in another, ruling it while maintaining connections to the mother country
Current Use: used to describe the contemporary exploitation (imperialism) of weaker countries by imperial powers
Tariffs
Modern form of imperialism?
Based on this cartoon, what was the Scramble for Africa?
The splitting of Africa between the European countries for its Natural Resources
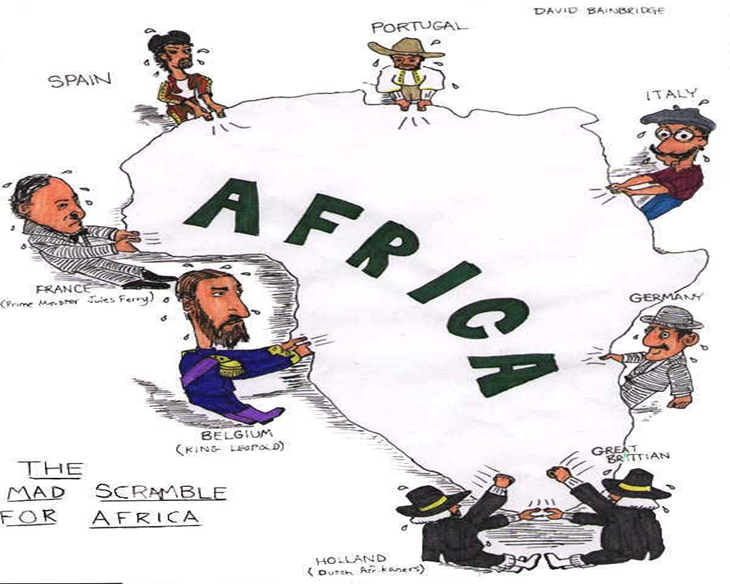
What’s the meaning of this Cartoon?
The Berlin Conference/The scramble for Africa/The European powers choosing how to divide up Africa’s land among themselves

Why do imperialists want Africa?
for Natural Resources
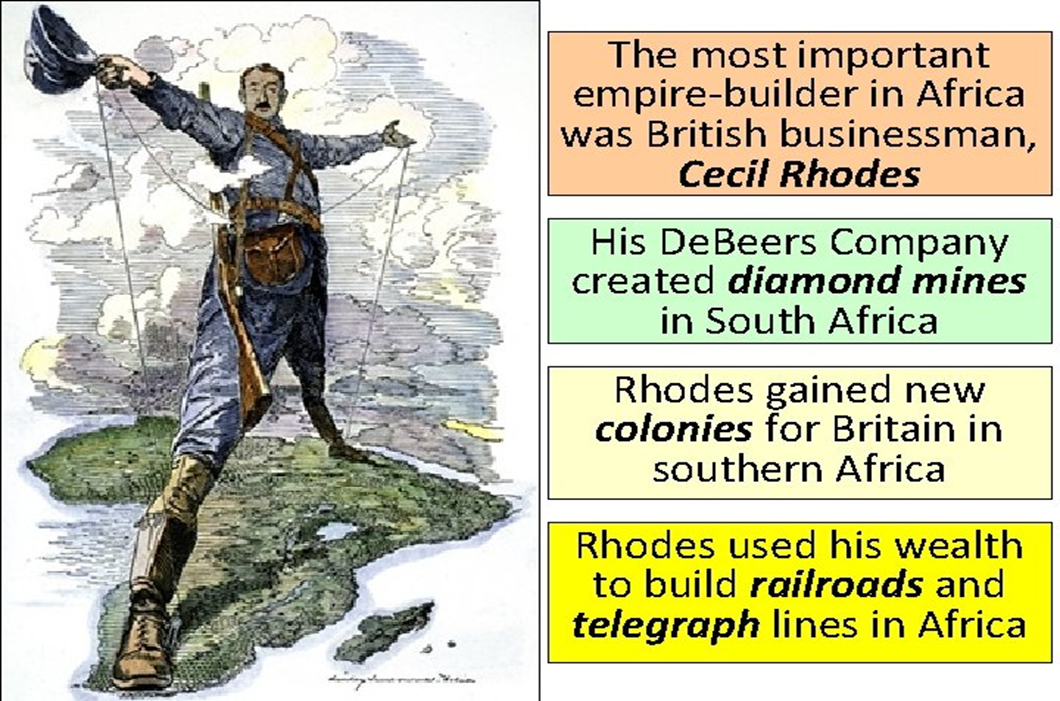
Cecil Rhodes
____ feet are on Cape town, South Africa and Cairo, Egypt because he wanted to build a railroad between north and south Africa. Though unsuccessful, he was able to build lines of communication between the two (The ______ Colossus)
The Industrial Revolution
With its technological advancements, Europe had a large advantage over the Native Africans when it came to claiming the land through violence
The British East India Company
A corrupt, private British company that was unable to handle military affairs, which forced the British government to get involved to assume control of the colonized territories of India, Australia, and New Zealand.
India became the “center” of the British Empire because it had an abundance of cotton for them to exploit, and early British Industrialization depended upon it
Britain created a civil service (puppet) government to run India, making it the “jewel in the crown” of the British Empire
Sepoy Mutiny
Rumors of the Indian troops having to bite paper gunpowder cartridges had spread. The cartridges were speculated to have been greased with cow or pig fat, which is against the Hindu and Muslim Faiths
This caused the Indian Soldiers to rebel. Violence on both sides:
Mass casualties and atrocities
Mass hanging and indiscriminate shootings
Australia and New Zealand
Britain shipped 50,000 convicts to Australia, the empire’s prison colony
Mining generated gold and silver rushes which brought immigrants to Australia.
Mohandas K. Gandhi
Gained independence for India with the use of non-cooperation and nonviolence with Britain
MLK studied under him to employ nonviolent civil disobedience
Concert of Europe
1815-1914: The International political system that promoted a balance of power among European powers