Plant Phys Final
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Cell shape or direction of a cell expansion mainly depends on _________.
A. Orientation of cellulosic fibril
B. Direction of turgor
C. Cell wall synthesis
D. Direction of light
A. Orientation of cellulosic fibril
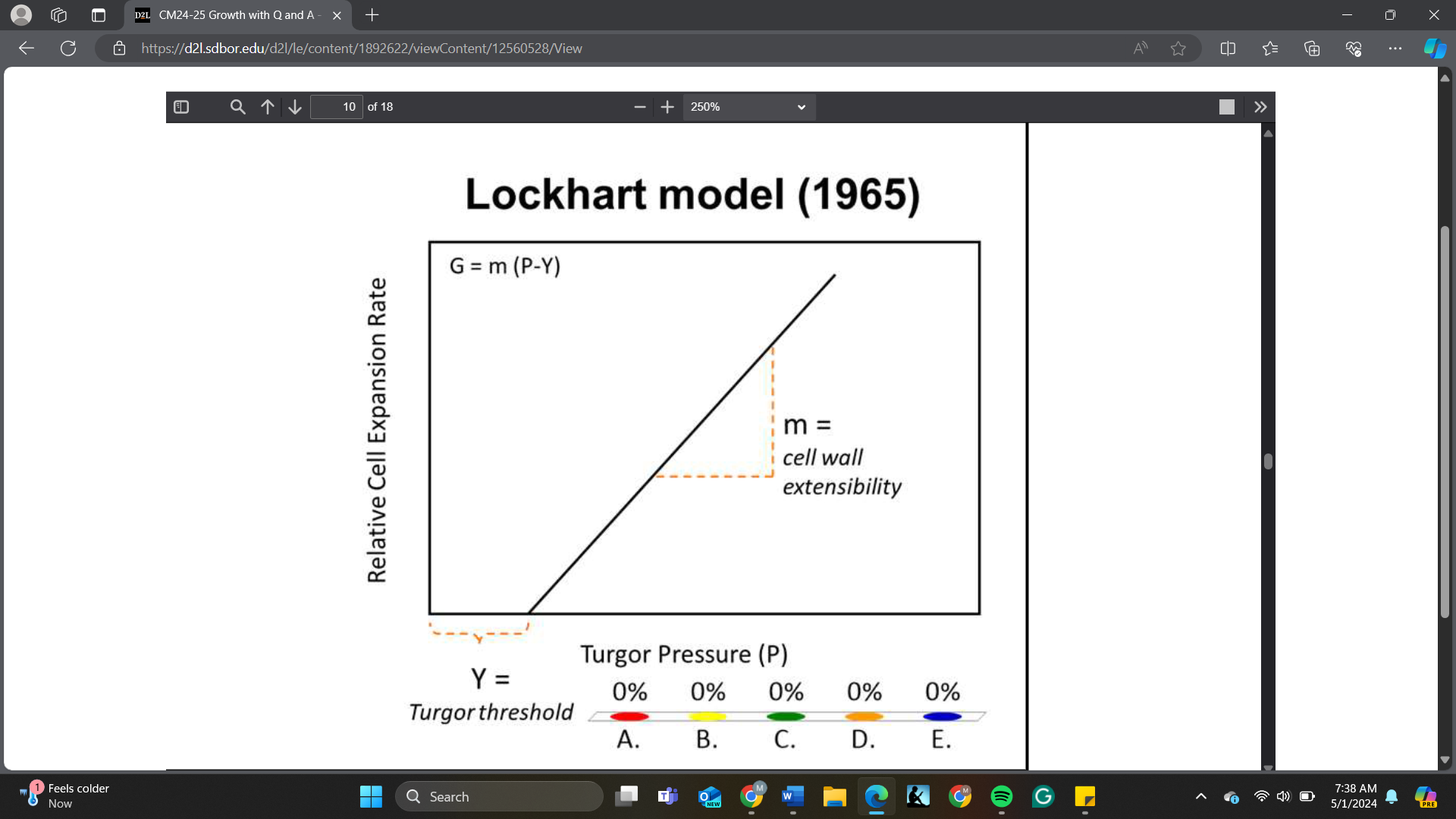
To initiate cell expansion, P must be greater than ______ based on the Lockhart model
A. Y
B. m
C. P
D. All of the above
A. Y
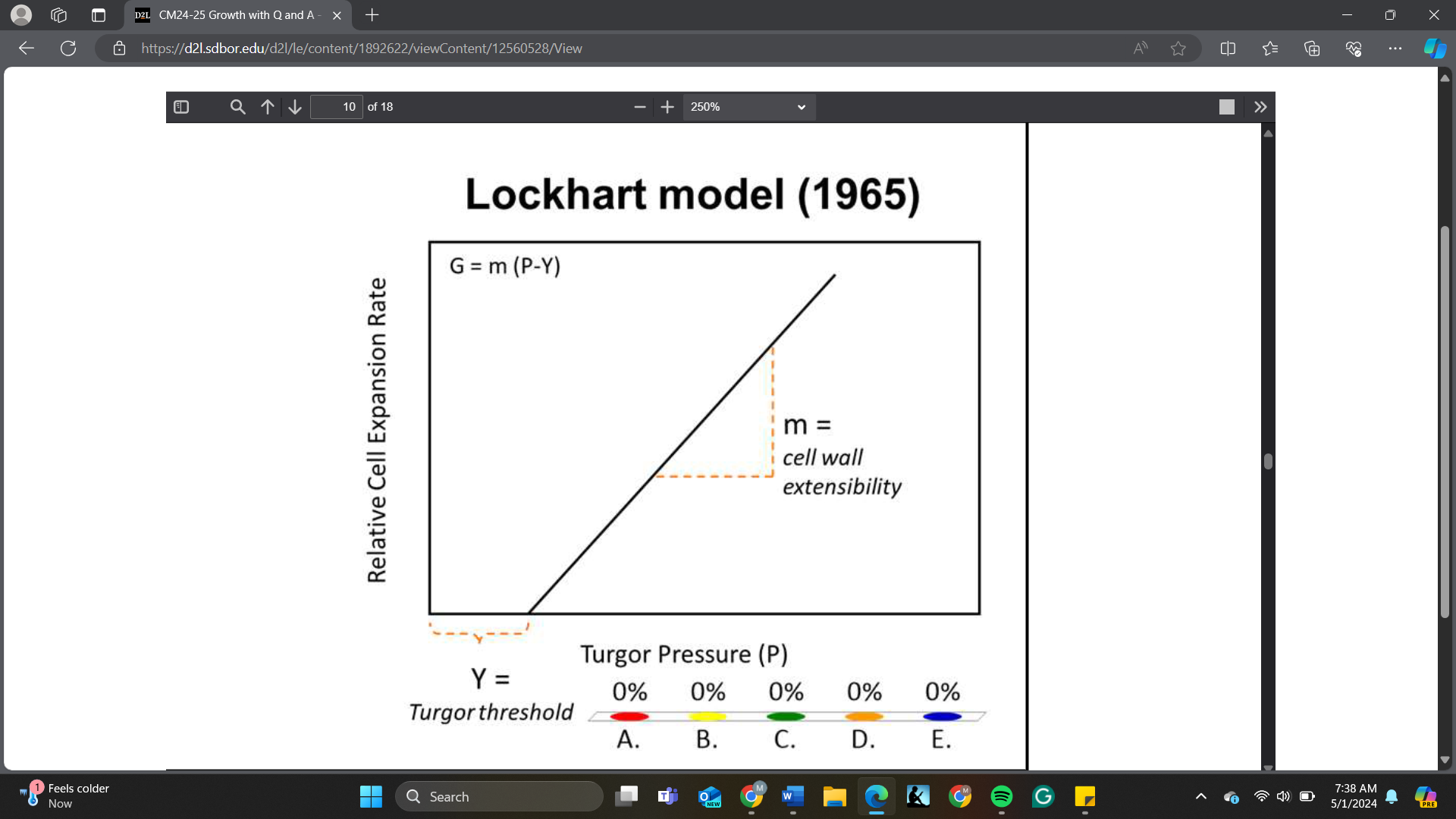
The relative rate of cell expansion mostly depends on ____ based on the Lockhart model when turgor pressure is greater than the threshold
A. Y
B. m
C. P
D. Y and m
E. P and m
E. P and m
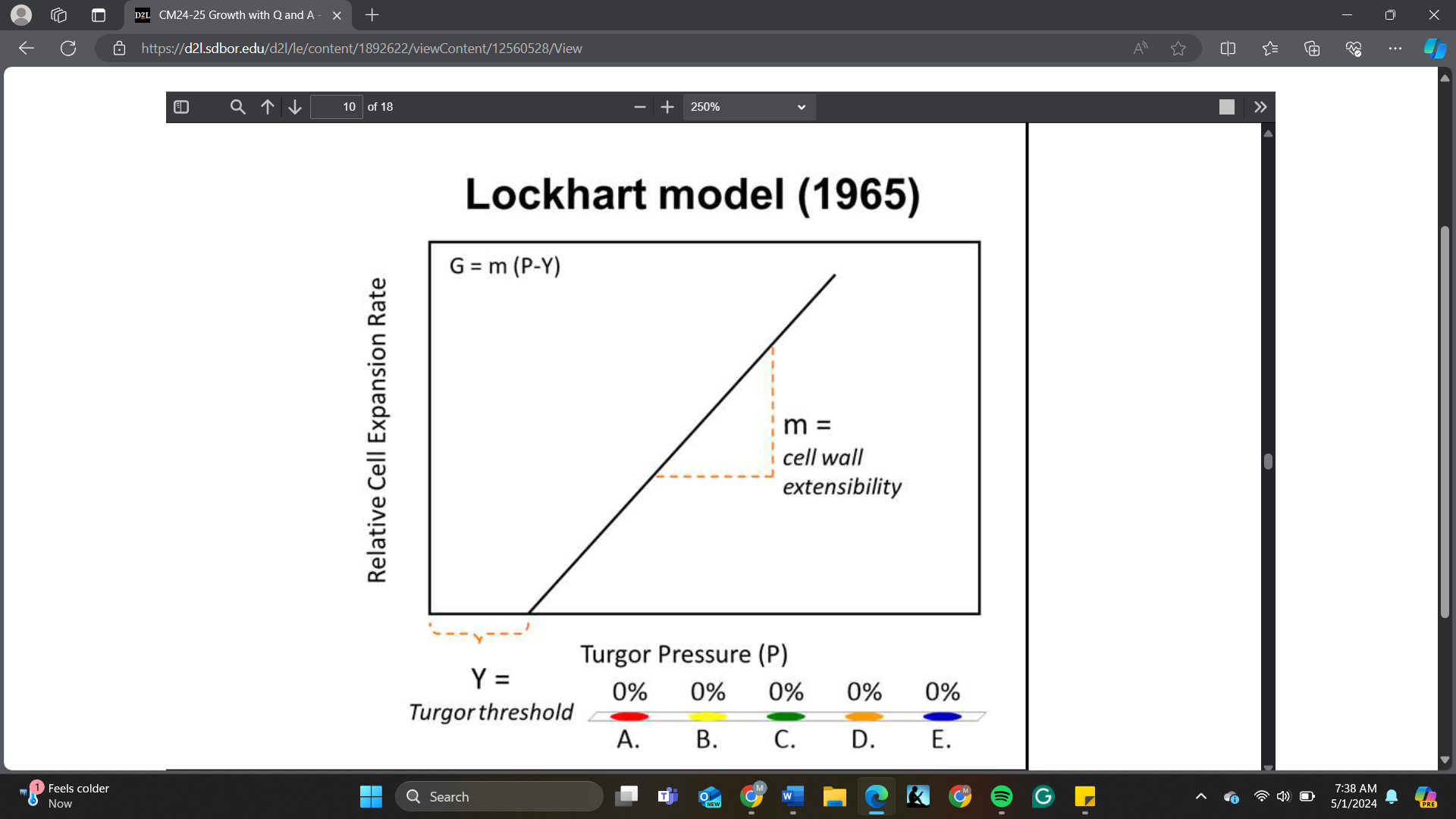
The relative rate of cell expansion of an expanding cell mostly depends on ____ at a given turgor pressure based on the Lockhart model
A. Y
B. m
C. P
D. Y and m
E. P and m
B. m
IAA treatment causes a _______
A. A decrease in pH
B. An increase in pH
C. No change in pH
D. Fluctuation in pH
A. A decrease in pH
IAA treatment causes _______
A. A decrease in coleoptile cell elongation
B. An increase in coleoptile cell elongation
C. No change in cell elongation
D. A decrease followed by an increase
B. An increase in coleoptile cell elongation
Cells elongate faster at more acidic conditions is possibly due to __________
A. an enhanced turgor pressure
B. degradation of cell walls
C. greater activity of expansin
D. All of the above
C. greater activity of expansin
In phototropism, auxin promotes ___.
A. Cell division in the shaded side
B. Cell elongation in the shaded side
C. Cell division in the light side
D. Cell elongation in the light side
B. Cell elongation in the shaded side
Polar transport of auxin in stem include the following, except ___ ?
A. Directional movement
B. Movement from apical to basal
C. Requirement of transporters
D. Movement from basal to apical
D. Movement from basal to apical
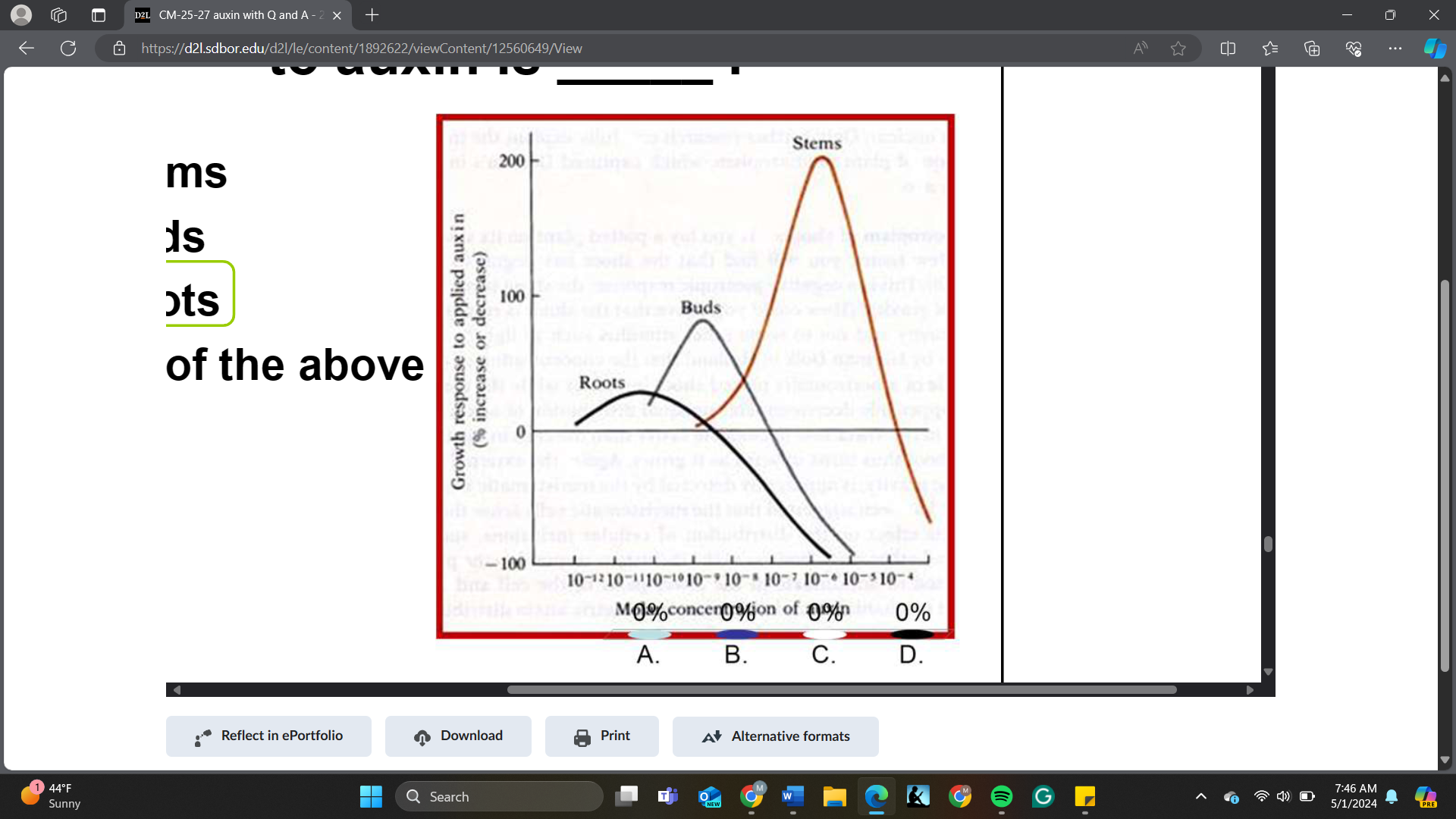
The organ that is the most sensitive to auxin is _____
A. Stems
B. Buds
C. Roots
D. All of the above
C. Roots
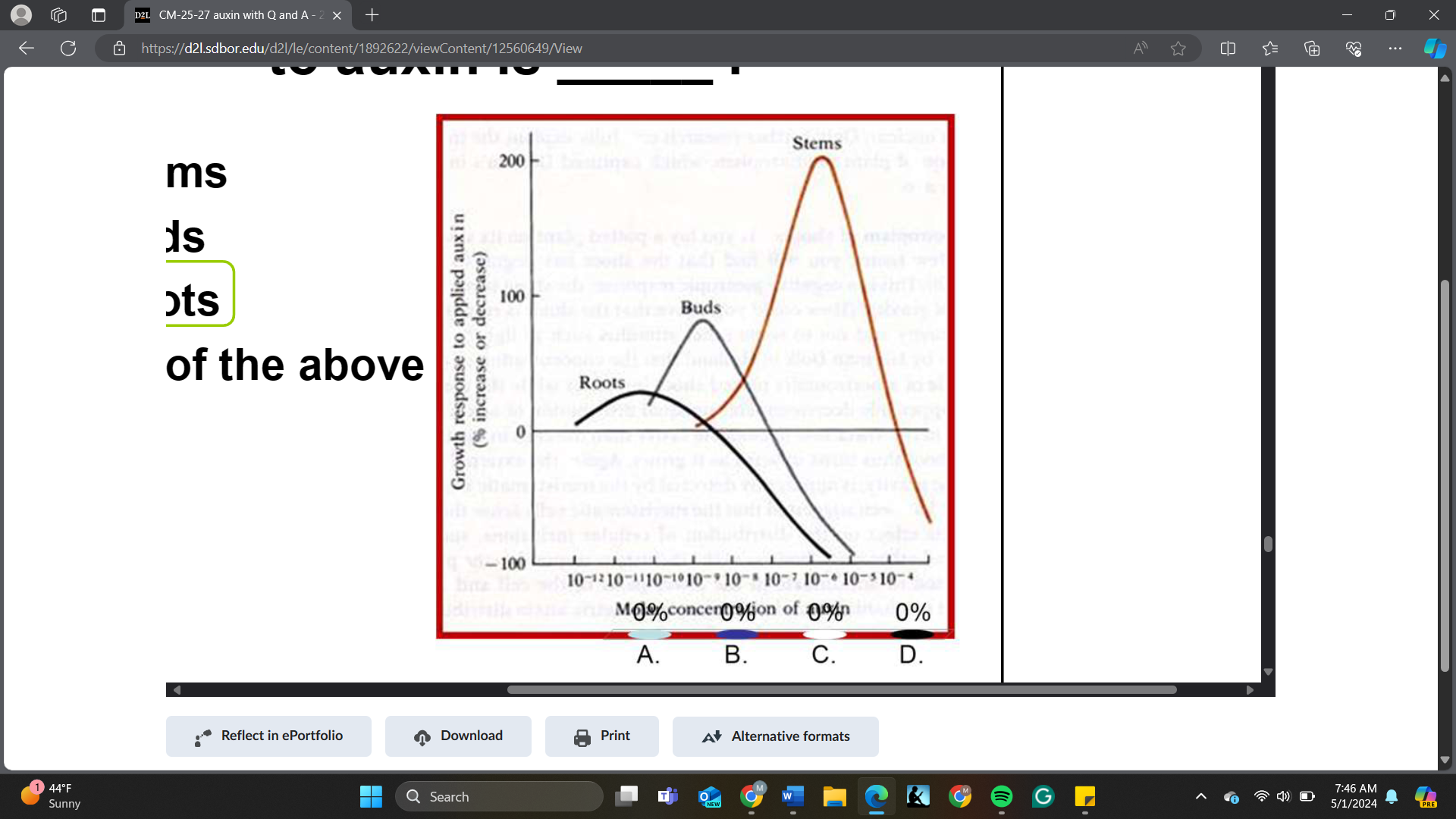
The organ that shows the greatest growth promotion to auxin is _____
A. Stems
B. Buds
C. Roots
D. All of the above
B. Buds
Identify the one that is not a major function of auxin
A. Promote cell division
B. Enhance cell expansion
C. Phototropism
D. Gravitropism
E. Fruit softening
F. Apical dominance
G. Root initiation
E. Fruit softening
Which of following is NOT a function of cytokinin?
A. Cell elongation
B. Senescence
C. Cell division
D. Apical dominance
D. Apical dominance
In tissue culture, a high ratio of Cytokinin and IAA enhances ___
A. Fruit formation
B. Root formation
C. Shoot formation
D. Flower formation
C. Shoot formation
Which of the following is not a function of cytokinin?
A. Enhance cell division
B. Promote shoot formation in tissue culture
C. Promoting flower senescence
D. Delay leaf yellowing
C. Promoting flower senescence
For auxin and cytokinin long distance transport through the plant, ______ .
A. Both hormones going through cells
B. Both going through xylem
C. Cytokinin through xylem and auxin through cells
D. Auxin through xylem, and cytokinin through cells
C. Cytokinin through xylem and auxin through cells
In order to induce the root formation in tissue culture, one usually uses ______.
A. A high ratio of IAA to cytokinin
B. A high ratio of cytokinin to IAA
C. Equal amount of IAA and cytokinin
D. No IAA and only cytokinin
A. A high ratio of IAA to cytokinin
GAs play roles in _______
A. Seed germination
B. Stem elongation
C. Increasing fruit size
D. Forming seedless grapes
E. All of the above
F. Only A, B
G. Only A, B and C
E. All of the above
In a generalized signaling pathway, GA can be considered as a ligand. It needs to bind to the _____ first to trigger the signaling cascade
A. Cytokinin
B. membrane
C. Transcription factor
D. DNA
E. Receptor
E. Receptor
Both GA and IAA stimulate ______
A. Cytokinin production
B. Stem elongation
C. Fruit ripening
D. Early flowering
B. Stem elongation
Among the phytohormones studied, which of the following hormones is also important for seed germination, besides ABA?
A. Cytokinin
B. IAA
C. GA
C. GA
Considering their function in seed germination, GA and ABA act ____
A. Additively
B. Synergistically
C. Antagonistically
D. Cooperatively
C. Antagonistically
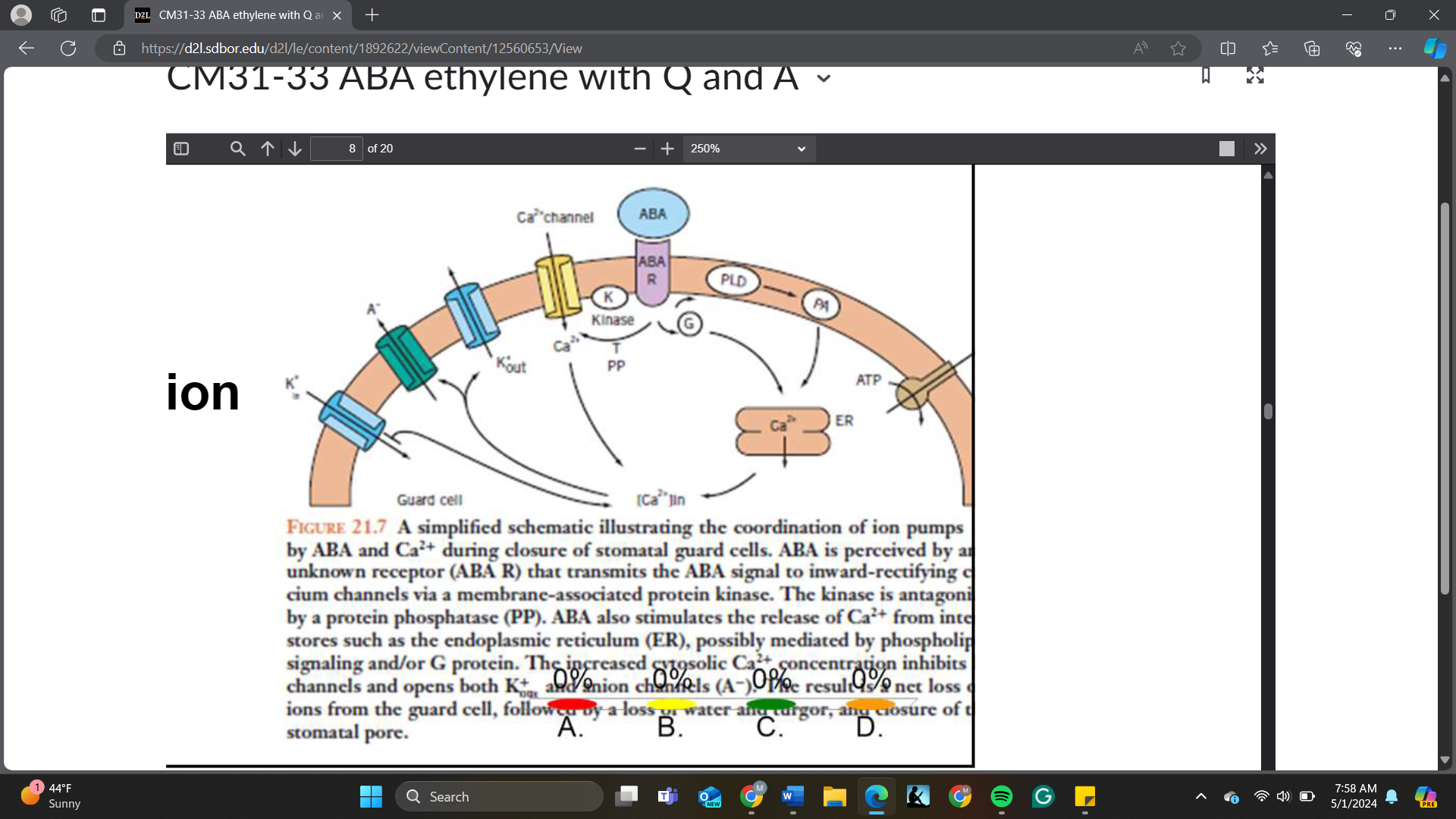
In a generalized signaling pathway, K channels in this figure are _____.
A. ligands
B. receptors
C. transcription factors
D. effectors
D. effectors
Which of the following is not a function of ABA?
A. Inhibition of seed germination
B. Abscission of leaves
C. Maintaining winter bud dormancy
D. Closing stomata
D. Closing stomata
Which of the following is not a function of ABA under drought stress?
A. Closing stomata
B. Inducing stress-response gene
C. Inhibit root elongation
D. Inhibit leaf cell expansion
C. Inhibit root elongation
What is the triple response of an Arabidopsis seedling to ethylene?
A. Inhibits stem cell elongation, enhances radial cell expansion, and delaying hook opening
B. Inhibits radial cell elongation, enhances abscission, and delaying hook opening
C. Inhibits stem cell elongation, enhances radial cell expansion, and stimulating hook opening
D. Inhibits stem cell elongation, enhances radial cell expansion, and delaying leaf abscission
Inhibits stem cell elongation, enhances radial cell expansion, and delaying hook opening
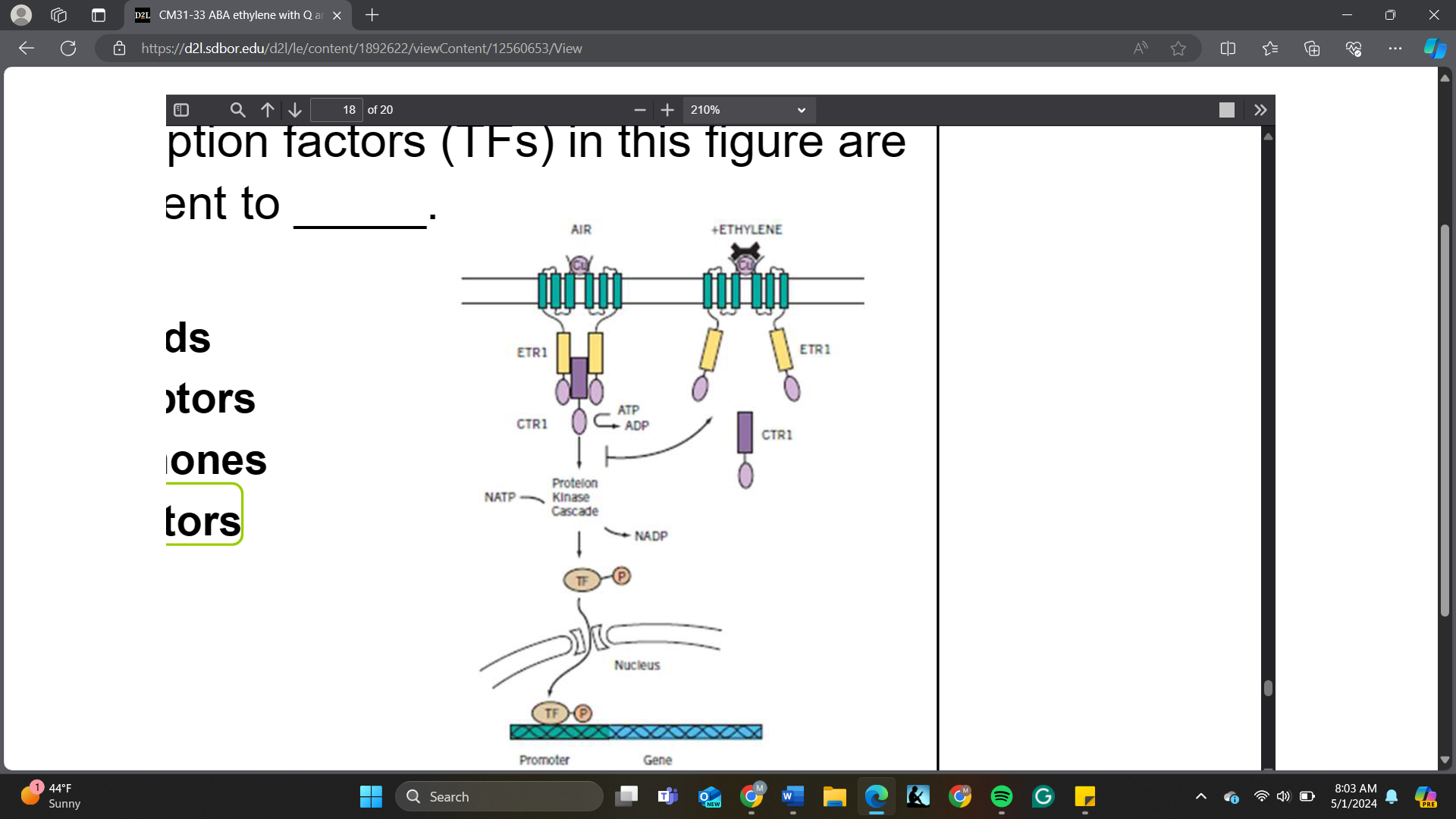
In a generalized signaling pathway, transcription factors (TFs) in this figure are equivalent to _____
A. ligands
B. receptors
C. hormones
D. effectors
D. effectors
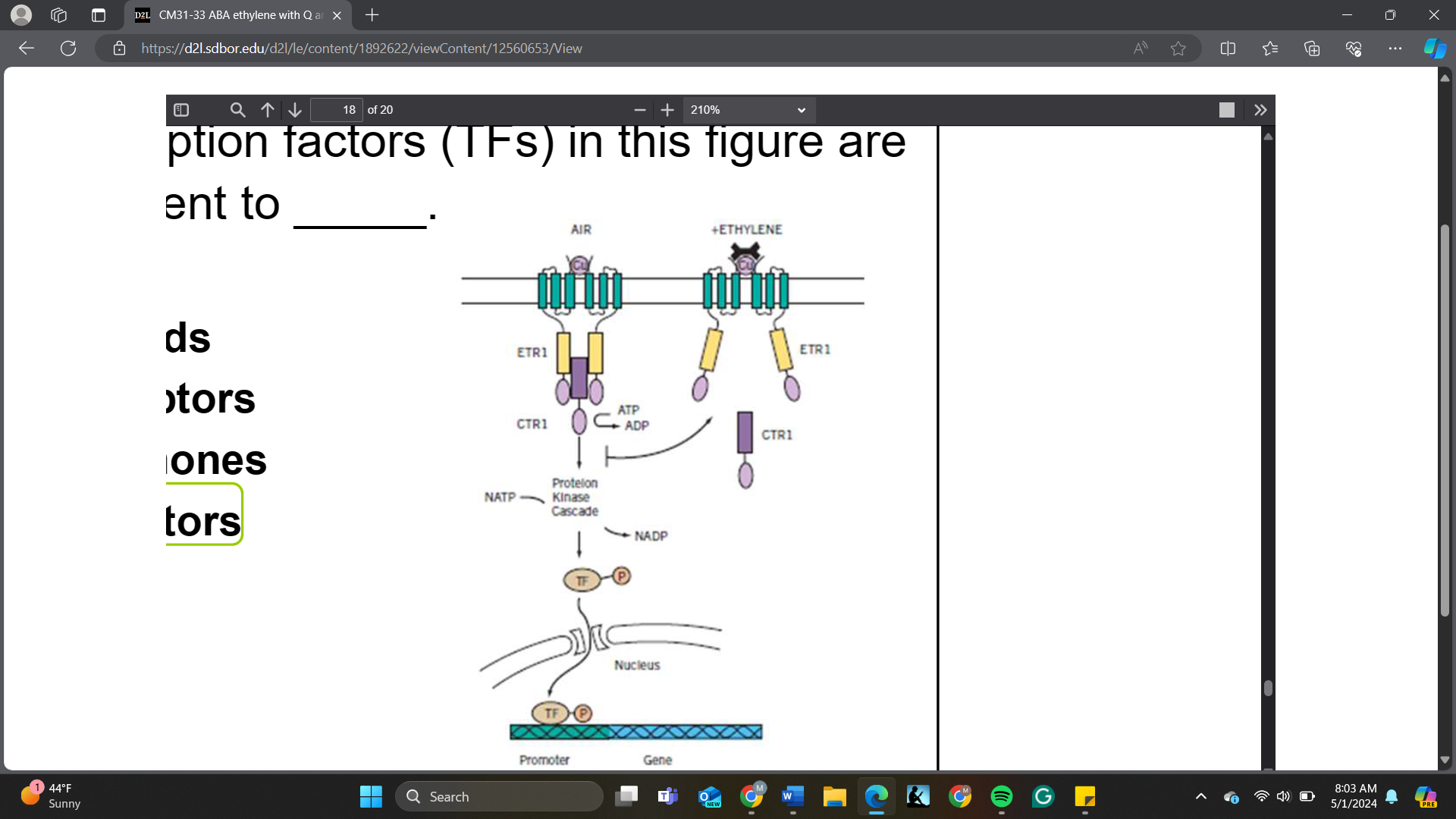
Based on the ethylene response signaling pathway, a null mutation of CTR will result in _____ in Arabidopsis seedlings
A. A triple response
B. Normal plants
C. Non-functional ethylene receptor
D. No ethylene production
A. A triple response
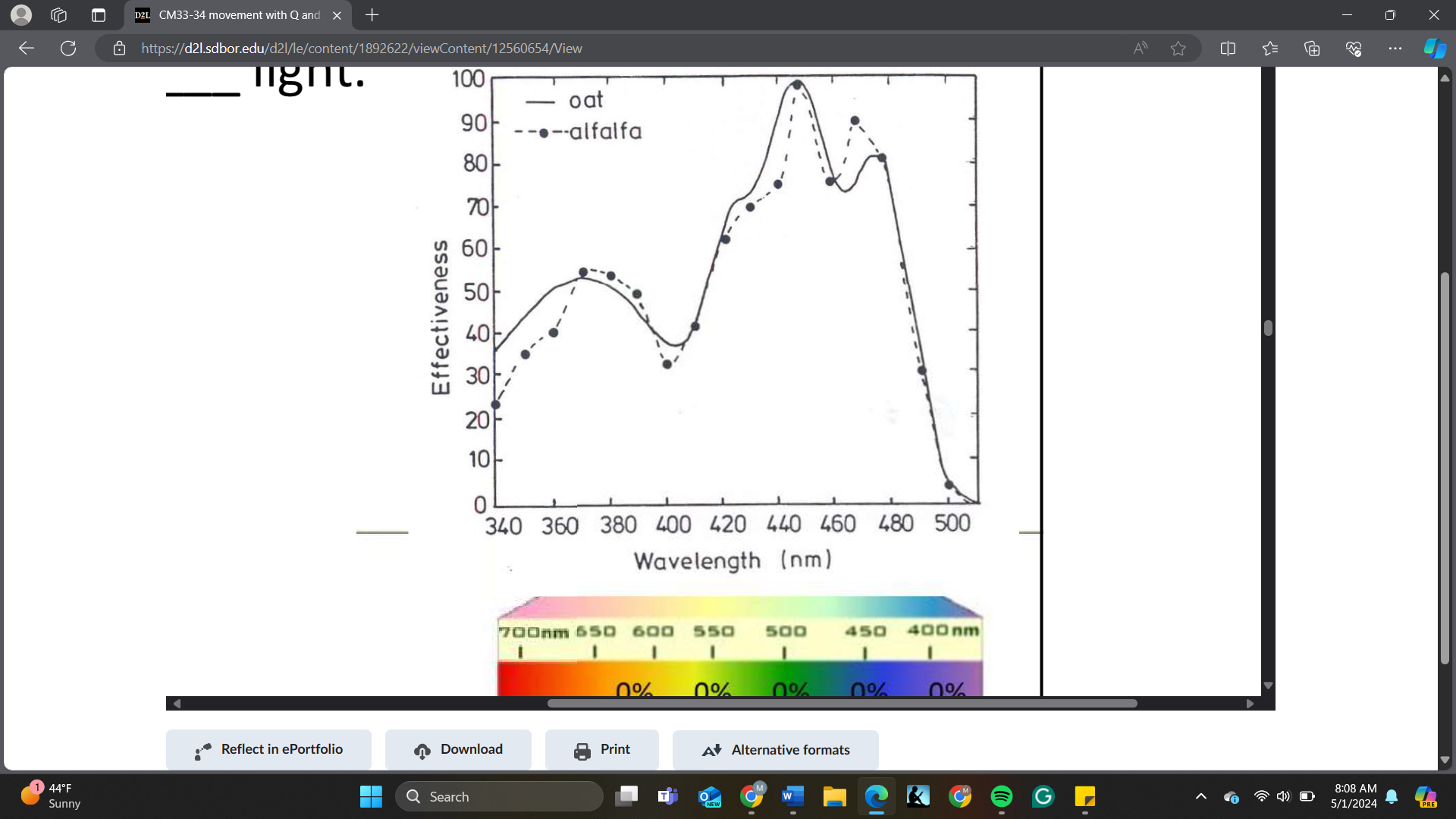
The most effective light inducing phototropism is _________ light
A. uv
B. red
C. yellow
D. green
E. blue
E. blue
An accumulation of more IAA at the lower side of the horizontally-placed root ____ cell elongation.
A. Stimulates
B. Inhibits
B. Inhibits
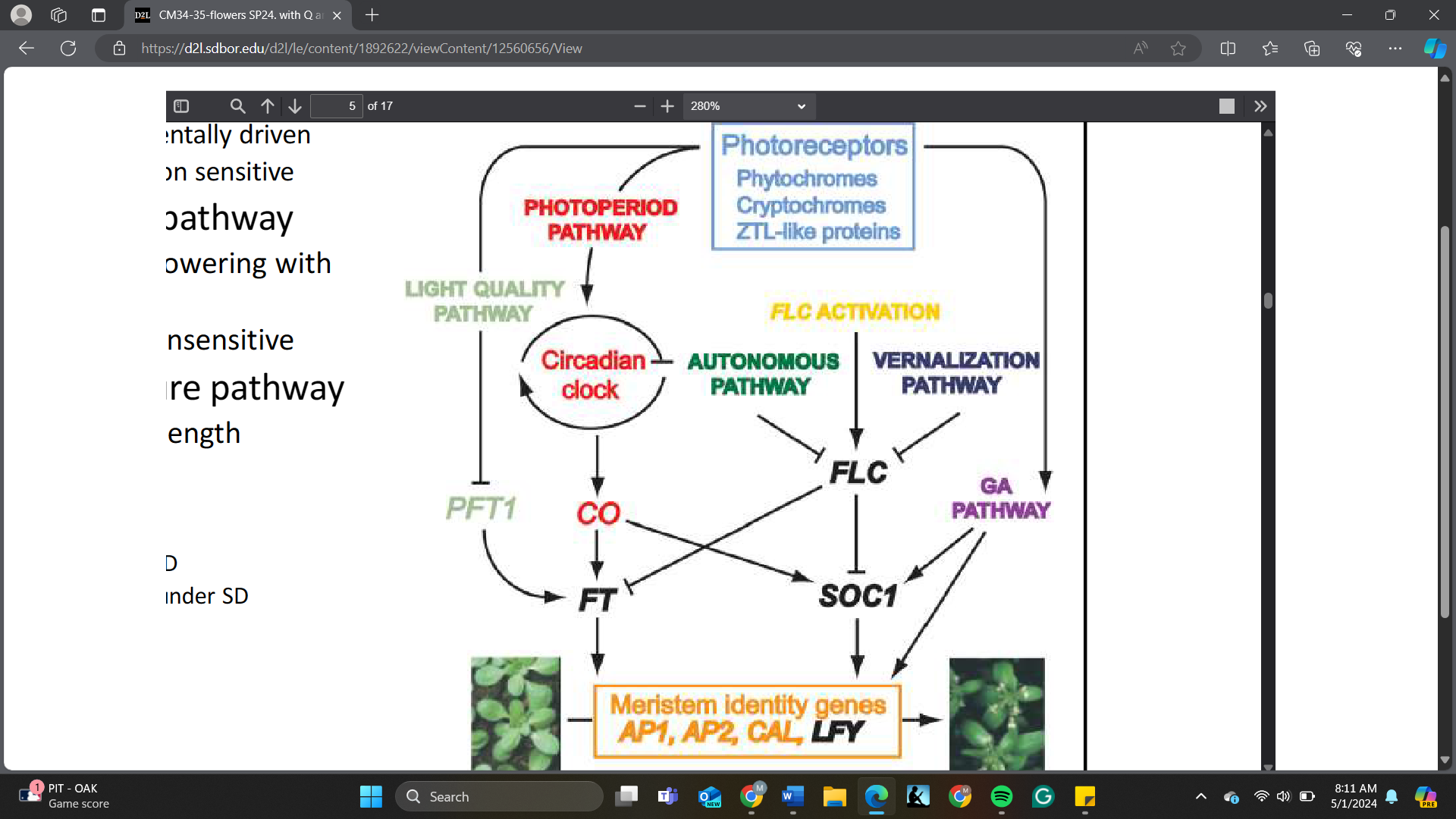
The integrators of flowering pathways are _______
A. SOC1, FT
B. CO, FT
C. FLC, SOC1
D. AP1, AP2
A. SOC1, FT
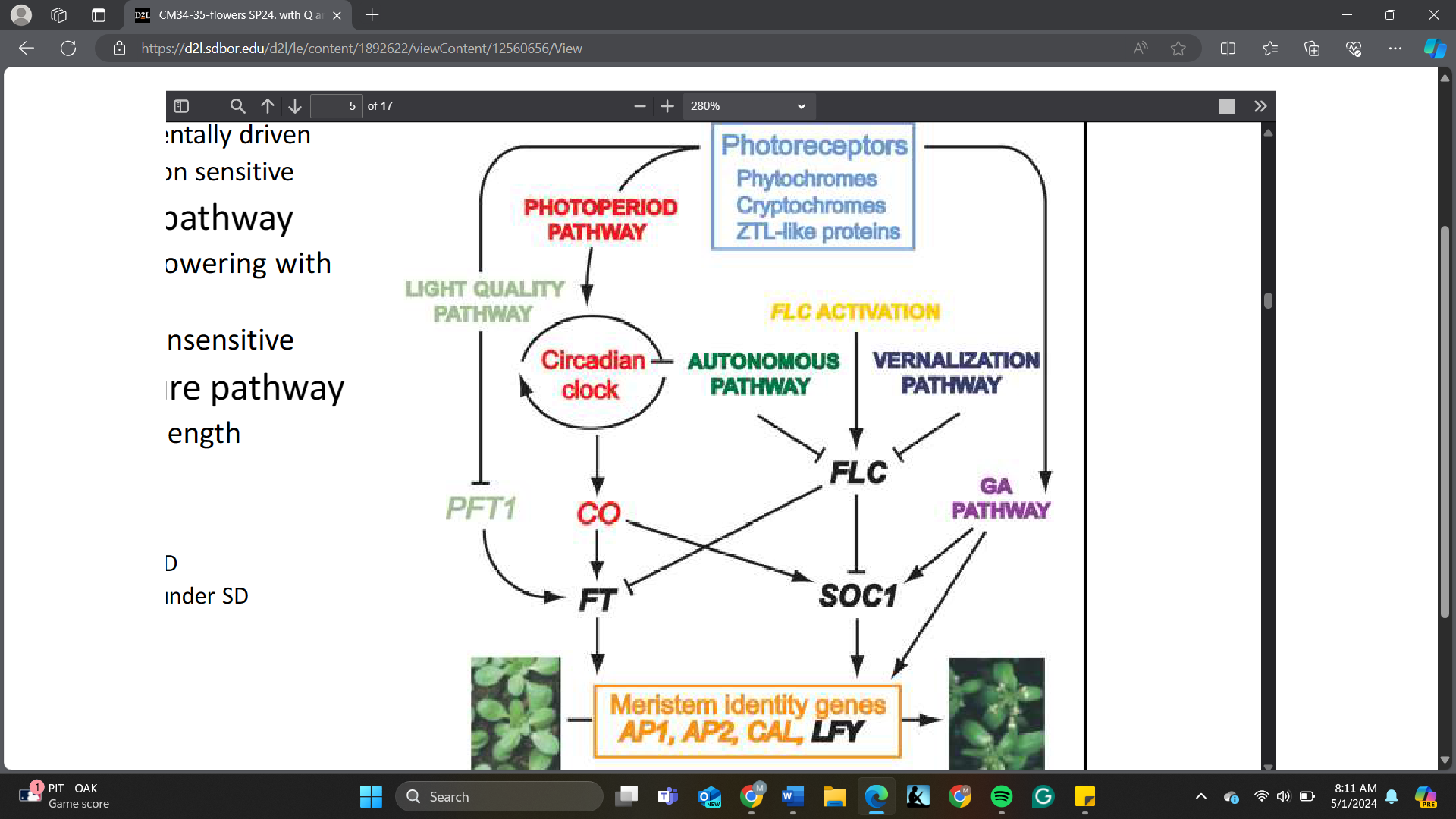
What is the consequence of FLC activation or having more FLC protein?
A. Promote flowering
B. Delay flowering
C. No effect on flowering
D. Activate SOC1
B. Delay flowering
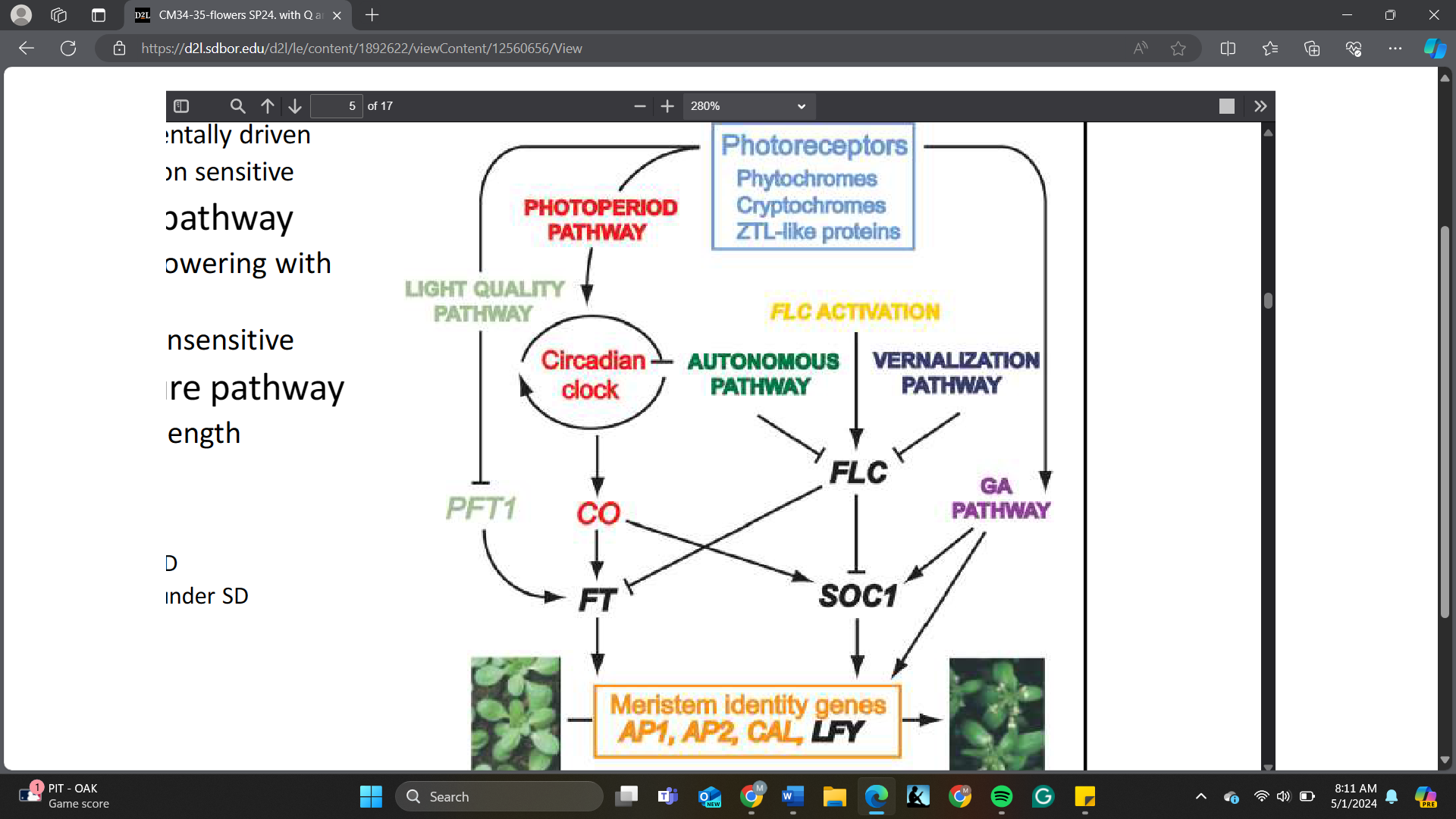
After vernalization, the expression level of FLC will ______
A. increase
B. decrease
C. remain the same
B. decrease
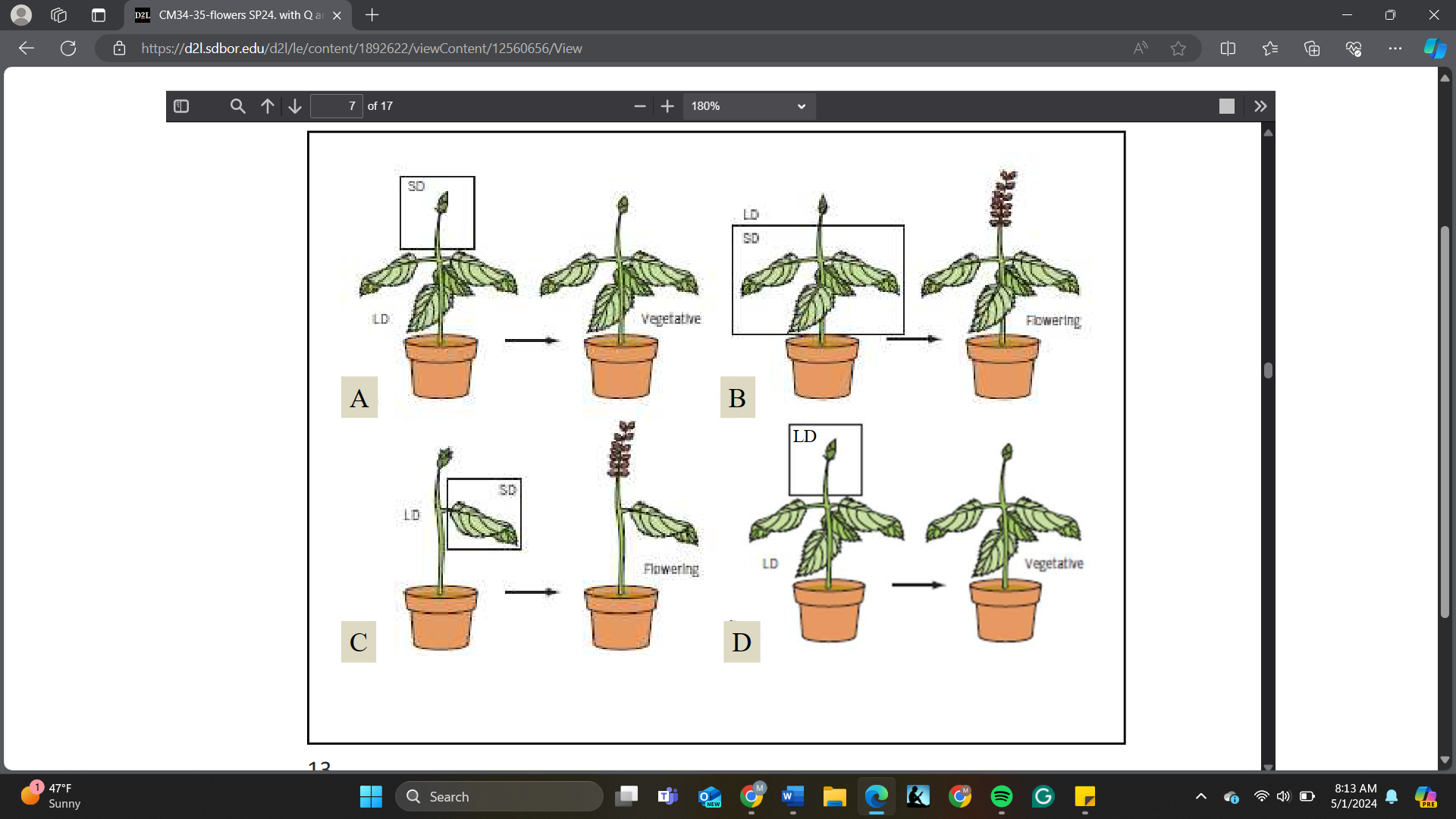
This is a ______ flowering plant.
A. Short day
B. Long day
C. Both long and short day
D. Not sensitive to day length
A. Short day
Which organ is sensing the day length for flowering?
A. stem
B. leaf
C. leaf and stem
D. bud
B. leaf
Short day plants will flower as long as the day length is shorter than 12h?
A. True
B. False
B. False
Florigen is a _______
A. hormone
B. GA
C. protein
D. gene
C. protein
FT (Florigen) is transported through _______
A. Air
B. Bundle sheath
C. Xylem
D. Phloem
E. Stomates
D. Phloem

In ABC model, a mutation in _____ gene leads to this phenotype showing below
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
A. A
In ABC model, a mutation in _____ gene leads to this phenotype showing below (only sepals)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. A and B
F. A and C
G. A and D
H. B and C
I. B and D
H. B and C
Many desert plants close stomates during the day and open stomates in the evening. This is an
example _____
A. Acclimation
B. Adaptation
B. Adaptation
Under drought stress conditions, the root/shoot ratio is greatly increased. This is an example _____
A. Acclimation
B. Adaptation
A. Acclimation
Some marsh plants are salt tolerant and have glands on leaf surface to excrete salt. This is an example _____
A. Acclimation
B. Adaptation
B. Adaptation

Based on the figure, _____ is most sensitive to drought stress
A. Cell expansion
B. Proline accumulation
C. Stomatal opening
D. CO2 assimilation
A. Cell expansion
Auxin stimulated cell expansion or elongation by _____.
Question options:
synthesizing more cellulosic fibrils. |
acidification of vacuoles |
activating expansins |
synthesizing more ATPs |
activating expansins
The elongating cells have _______.
Question options:
primary cell walls |
secondary cell walls |
tertiary cell walls |
quaternary cell walls |
primary cell walls
Xyloglucan is a ______ polymer.
Question options:
cellulosic |
pectin |
peptide |
hemicellulosic |
hemicellulosic
Orientation of microfibrils in the cell wall is often controlled by ____.
Question options:
Microtubules inside the cell. |
Microtubules inside the wall. |
Xyloglucan inside the wall. |
Pectin inside the wall. |
Cellulose synthase inside the cell |
Microtubules inside the cell.
_____is the driving force for cell expansion.
Question options:
Hydrolase activity |
Cell wall synthesis |
Turgor pressure |
Cell wall extensibility |
Expansin protein |
Turgor pressure
Expansin proteins loosen up cell walls by ________.
Question options:
Increasing wall acidity and removing the tethers. |
Acidifying cell walls. |
Hydrolyzing crosslinks or tethers in the wall. |
Removing hydrogen bonds between microfibrils and the tethers. |
Removing hydrogen bonds between microfibrils and the tethers.
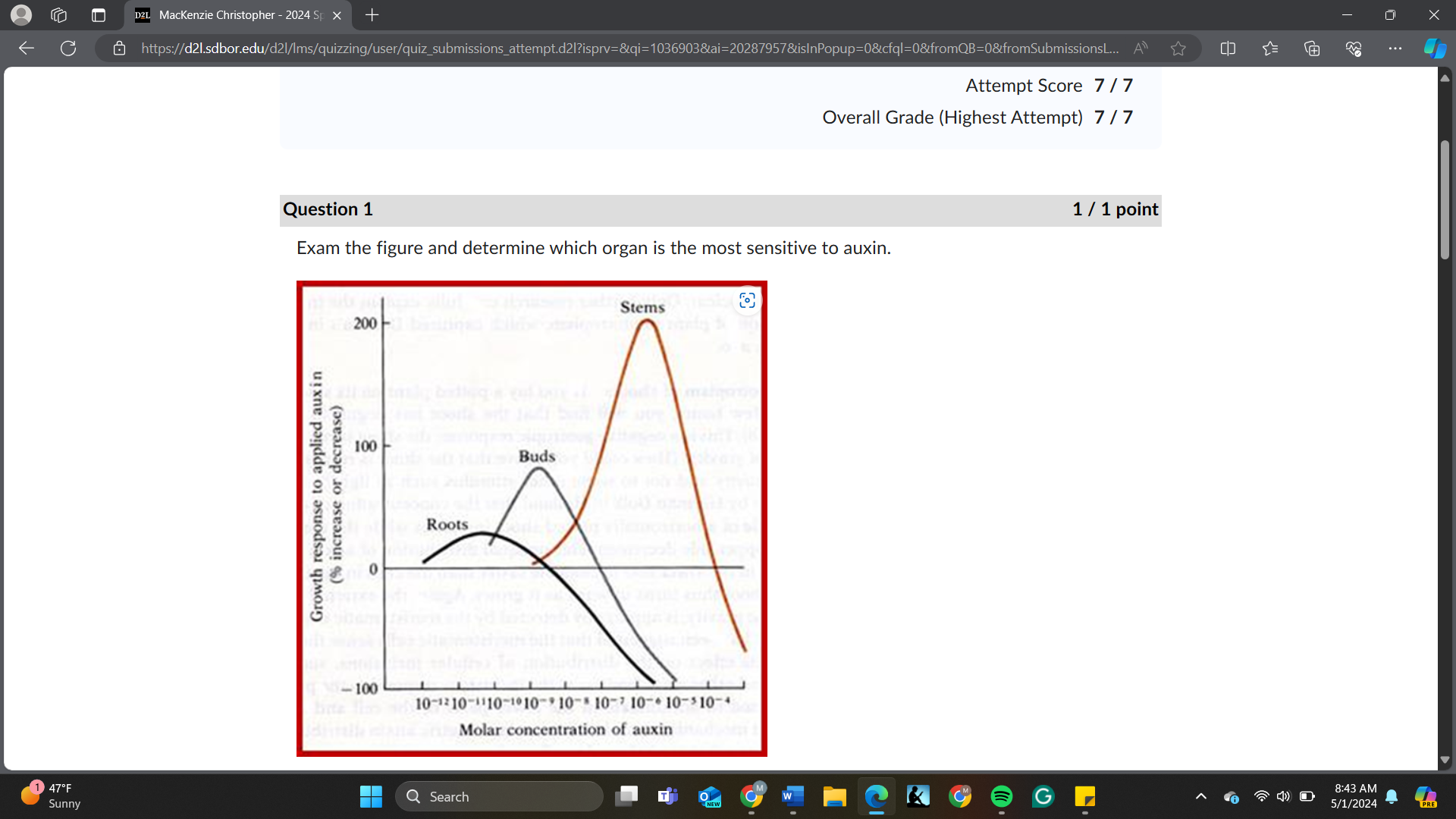
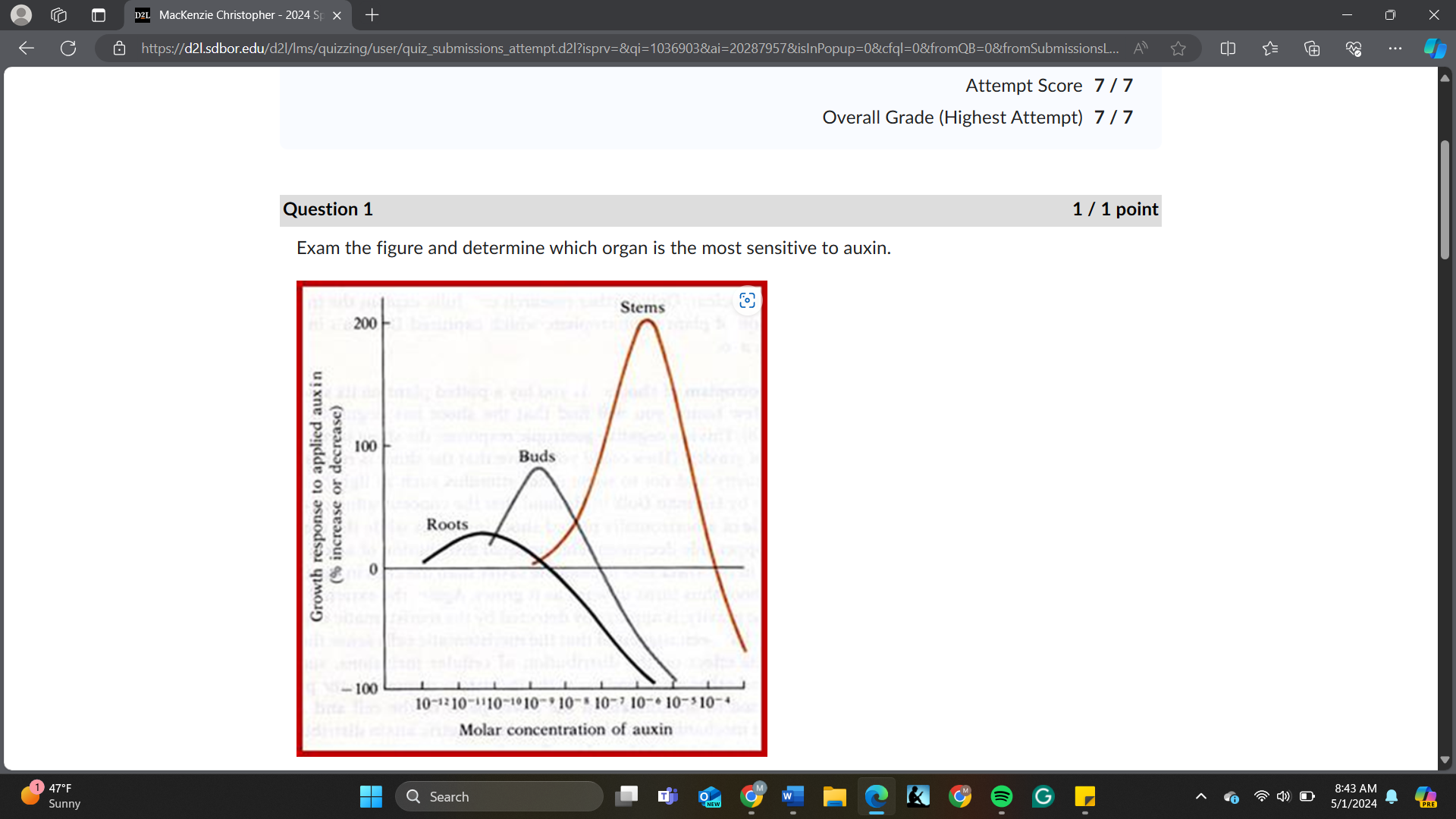
Exam the figure and determine which organ is the most sensitive to auxin.
roots
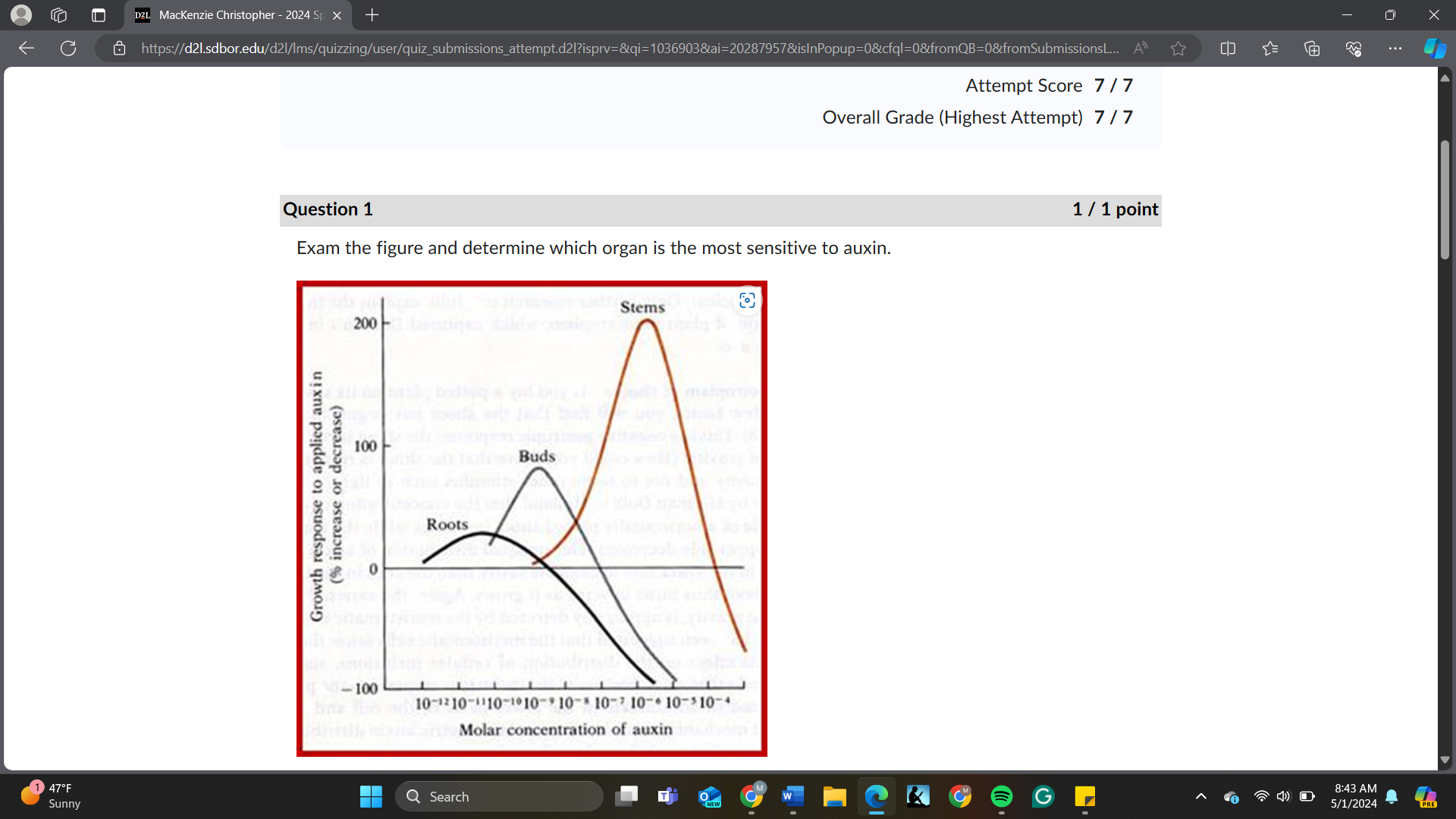
Based on the information in the figure, the organ that shows the greatest growth promotion to auxin is _____.
stems
Based on the information in the figure, predict the impact on corn grain production if you apply 10 micromolar (uM) to the young plants.
increase |
decrease |
no effect |
zero grain yield |
zero grain yield
Based on the generalized model of hormone-induced signalling transduction pathway, auxin is a _______ .
Question options:
final response |
receptor |
repressor |
ligand |
ligand
Which of the following statements is better describing the acid-growth hypothesis?
Question options:
An acid treatment enhances expansin activity which activates IAA and cell elongation. |
An acid treatment increases the content of IAA in coleoptiles, facilitating cell elongation. |
Auxin treatment activates expansin proteins, resulting in acidification of cell walls. |
Auxin treatment causes acidification of cell walls which activates expansin activity. As a result, cell wall extensibility increases, and cell elongation accelerates. |
Auxin treatment causes acidification of cell walls which activates expansin activity. As a result, cell wall extensibility increases, and cell elongation accelerates.
In a generalized signaling pathway, IAA is considered as a ligand. It needs to bind _______ first to trigger the signal transduction.
Question options:
Transcription factor |
DNA |
Membrane |
Receptor |
Receptor
Which of the following are the characteristics of a plant hormone?
Question options:
It is synthesized at one location in a plant and can either act at the same location or be transported to another location for action. |
It is synthesized in very low amounts. |
It can have a profound impact on plant growth and development. |
All of the above. |
All of the above.
Which of the following is NOT a function of cytokninin?
Question options:
enhancing cell division |
promoting shoot formation in tissue culture |
promoting flower senescence |
delaying leaf yellowing |
promoting flower senescence
In order to induce shoot formation in tissue culture, one usually uses _____ .
Question options:
a high ratio of IAA to cytokinin |
equal amount of IAA and cytokinin |
only IAA and no cytokinin |
a high ratio of cytokinin to IAA |
a high ratio of cytokinin to IAA
GAs play a role overlapping with IAA, promoting cell elongation in stems.
Question options:
True |
False |
True
GA is a phytohormone and is solely produced by plants.
Question options:
True |
False |
False
Which of the following is NOT a function of GAs?
Question options:
promoting flowering in many dicots |
enhancing cell elongation |
promoting seed germination |
acting in apical dominance |
producing seedless grapes |
acting in apical dominance
In a generalized signaling pathway, GA can be considered as a ligand. It needs to bind to the _____ first to trigger the signaling
Question options:
Transcription factor |
Receptor |
DNA |
Auxin |
Membrane |
Receptor
CRE1 in the plasmamembrane binds to cytokinin and then activates down stream components. CRE1 is called a ____ in the generalized signalling transduction pathway.
Question options:
ligand |
receptor |
repressor |
transcription factor |
receptor
Abscisic acid plays a major role in leaf abscission - plants drop leaves in late autumn.
True |
False |
False
Seeds of some corn mutants precociously germinate on the ear in the field. It is mostly due to ____.
Too little GA accumulated in the seeds |
Too much ABA accumulated in the seeds |
Too much ABA and too little GA |
Too little ABA accumulated in the seeds |
Too little ABA accumulated in the seeds
Which of the following is incorrect in ABA induced stomatal closure?
Less potassium in the cell results in a decease in water potential in the guard cells. |
ABA signalling also inhibits uptake of potassium. |
ABA has to bind to the receptor to activate the process. |
ABA signalling activate Kout channels, and potassium leaves the cell. |
Less potassium in the cell results in a decease in water potential in the guard cells.
ABA synthesized in the root under drought was transported through ______ to leaves.
phloem |
xylem |
cell to cell |
none of the above |
xylem
Which of the following is not a purpose of partial root drying (PRD) in agriculture practice?
Enhancing stomatal closure. |
Reducing irrigation water use. |
Stimulating ABA synthesis in the root. |
Killing about half of the root system to reduce water consumption. |
Killing about half of the root system to reduce water consumption.
The triple response in dark-grown dicot seedlings triggered by ethylene does not include _____ .
suppressing hook opening |
inhibiting stem elongation |
enhancing the diameter of seedling stem |
stimulating cell division |
stimulating cell division
Which of the following is not a function of ethylene?
inhibiting stem cell elongation |
closing stomata |
stimulating abscission of leaves |
hastening fruit ripening |
closing stomata