1. Milkmaids and Vaccines
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Vaccine
Substance that builds preventative immune protection against a specific infection
Types:
Inactivated (killed)
Attenuated (weakened)
How long does vaccine development usually take?
10–15 years from concept to federal approval
Why are vaccines important?
Extremely effective at preventing disease
Have saved millions of lives
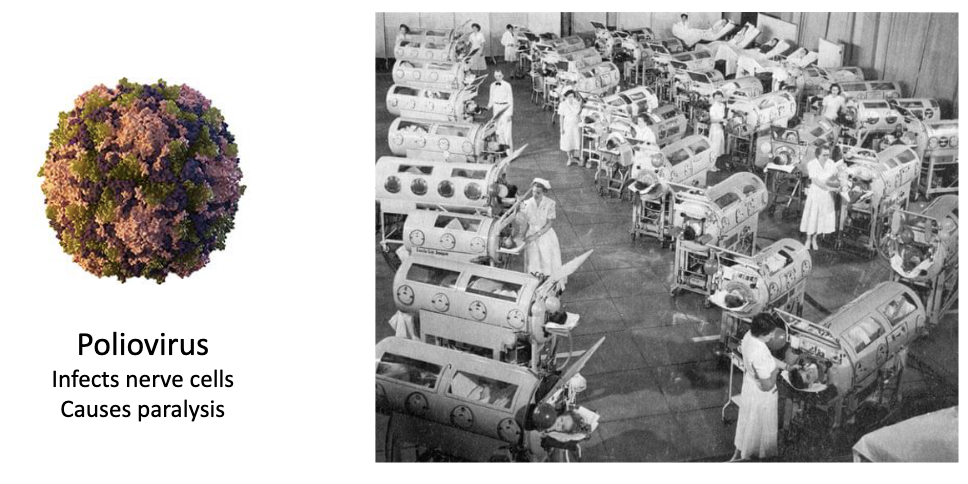
Example of vaccine success: Poliovirus
Poliovirus infects nerve cells → causes paralysis
Early solution: Iron lungs
Jonas Salk developed the polio vaccine → became very popular
What were plagues like before vaccines and antibiotics?
Infectious diseases killed huge numbers of people
Plagues shaped history (wars, populations)
What happened during the Plague of Athens (430 BC)?
Athens vs. Sparta (war)
Spartans = good warriors, Athenians = big walls
Plague hit Athens → 25–33% of population died
Spartans didn’t avoid Athens → later conquered the weakened city
Who gave the earliest written description of immunity?
Thucydides, physician during Plague of Athens
Observed that people who recovered did not get sick again
Quote: “the sick and the dying were tended by the pitying care of
those who had recovered, because they knew the course of
the disease and were themselves free from apprehensions.
For no one was ever attacked a second time, or not with a
fatal result"

Did Athenians understand germs?
No → germ theory not known until 1860s (2300 years later)
Instead, people believed in “miasma” (bad air theory)
What did John Snow discover in 1854?
Investigated London cholera outbreak
Found cause was contaminated water (not air)
Removed pump handle → outbreak ended
Suggested boiling water → led to modern water safety practices
Couldn’t yet prove microbes caused it

What did Louis Pasteur discover between 1860–1864?
Studied why wine & beer spoiled
Discovered microorganisms caused spoilage
Heating liquids (then cooling) killed microbes → prevented spoilage
This process = Pasteurization

Why is pasteurization important?
Greatly prolongs shelf life of milk
What was the main problem with early disease research?
No definitive proof that microorganisms caused disease
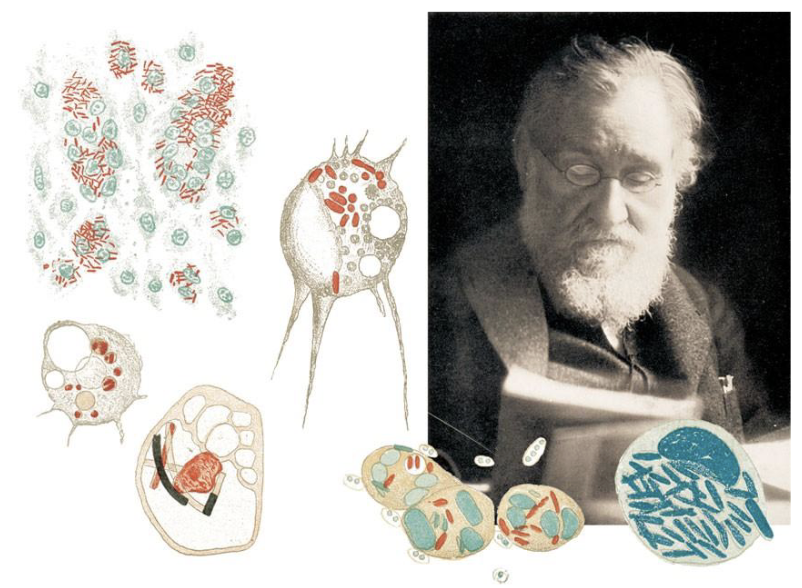
What did Robert Koch discover in 1876?
Built microscope to look at bacteria
Used microscopy + culture techniques → generated pure cultures of bacteria
Published the first picture of bacteria (Anthrax)
Showed anthrax bacteria caused disease in animals → Germ Theory proven

What are Koch’s Postulates?
A specific microorganism is always associated with a given disease
Microorganism can be isolated from diseased animal & grown in pure culture in lab
Cultured microbe causes disease when transferred to a healthy animal
Same microorganism can be re-isolated from newly infected animal
But… viruses can’t be re-isolated
How did Louis Pasteur accidentally discover immunity with chickens?
Studied chicken cholera bacteria
Assistant forgot to use fresh culture, injected old (weakened) bacteria → chickens survived
Later, fresh bacteria injected → chickens immune and survived again
Led to inactivated vaccines → basis for Salk’s polio vaccine
What was the relationship between Koch and Pasteur?
Knew each other, rival scientists
Teased each other’s work (pure cultures vs. pasteurization)
Both made foundational discoveries in microbiology and immunity

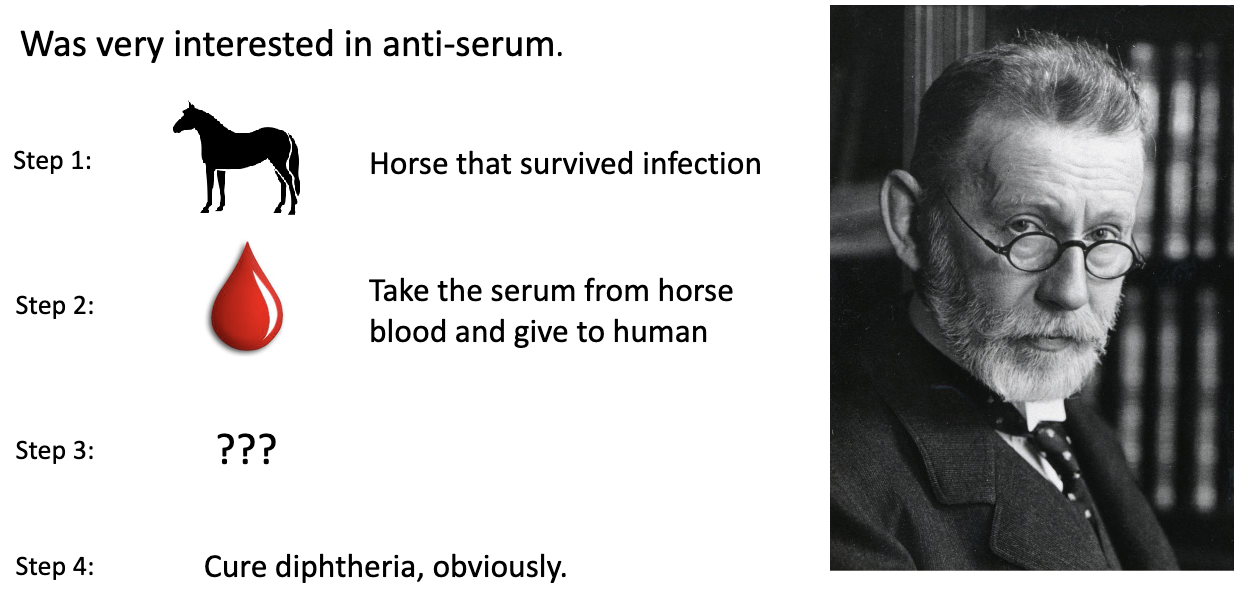
Who was Paul Ehrlich and what did he discover around 1900?
Studied anti-serum therapy (horse → human transfer) to cure diphtheria
Proposed Side Chain Theory of Immunity → blood proteins protect against pathogens
Thought immunity is: Adaptive (responds to infection) + Humoral (in blood)
He was right → talking about antibodies (structure defined in 1959)
Won Nobel Prize in 1908
Who was Eli Metchnikoff and what did he discover in 1883?
Used microscopes to study starfish cells
Found cells eating foreign material → called them “phagocytes” (later macrophages = big eaters)
Proposed immunity is: Innate (pre-programmed and simple) + Cellular (cell-based protection)
He was also correct
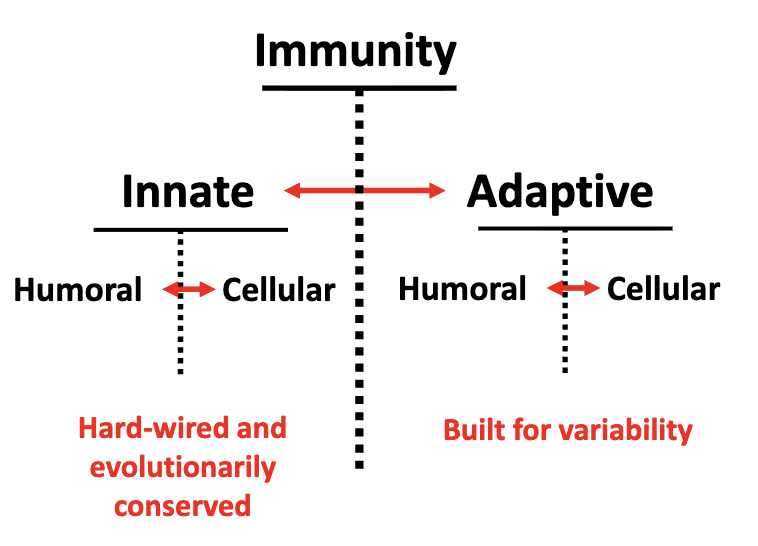
What are the two major arms of immunity?
Innate immunity: hard-wired, evolutionarily conserved
Humoral (proteins in fluids)
Cellular (phagocytes, natural killer cells)
Adaptive immunity: built for variability
Humoral (antibodies)
Cellular (T cells, B cells)
What disease was first eradicated by vaccines, and when?
Smallpox → first vaccine in 1796, widespread immunization by 1800 (60 years before Pasteur’s work)
WHO global vaccination campaign → eradicated in 1980
No cases since
There is only one eradicated virus = smallpox
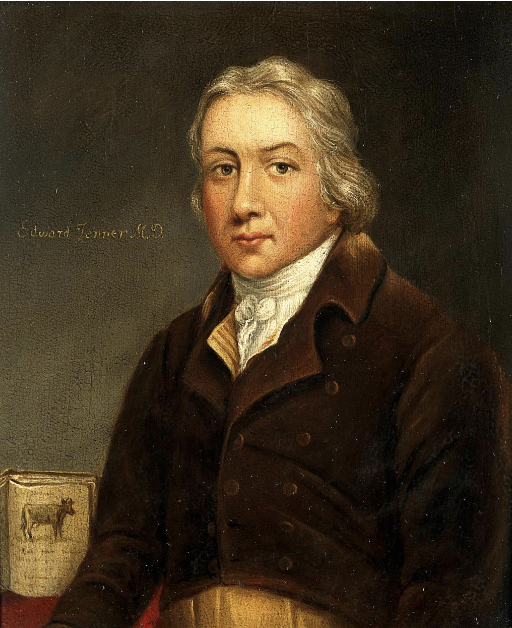
What did Edward Jenner do in 1796 with milkmaids and cowpox?
Observed milkmaids who got cowpox were protected from smallpox
Collected cowpox material from milkmaid Sarah Nelms → injected 8-year-old James Phipps
James got mildly sick but recovered
Later injected James with smallpox → fully protected, even on repeat exposure
Jenner called it vaccination (from “vacca” = cow)

Was Jenner the only one who thought of vaccination?
Others had noticed cowpox-smallpox link
Jenner knew about variolation (giving smallpox to induce mild infection) and was variolated himself
Risky → many died
Variolation practiced in China, India (16th century) and brought to England by Lady Mary Wortley Montagu (after seeing it in the Ottoman Empire - Turkey)

What’s the “clickbait” version of vaccination history?
“Did England steal credit for vaccination from China?”
Because variolation and early protective practices existed long before Jenner