Unit 1 HBS
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Epithelial Locations
Outer layer of skin, lining of intestines
Nervous Locations
Brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Muscle Locations
Throughout the body
Connective Locations
All free body surfaces (in between other tissues in the body)
Epithelial Functions
Absorption, filtration, and protection
Nervous Functions
Responsible for controlling many body activities (send electro-chemical signals throughout body)
Muscle Functions
Contract to produce movement
Connective Functions
Give structure to other tissues and organs in the body and binds them.
Canaliculi
Connects osteocytes
Hormone that increases calcium in blood
Parathyroid hormone
Shaft of bone is also known as
Diaphysis
Calcitonin stimulates
Osteoblasts
Spongy bone is found in
Epiphysis
Compact bone is made out of
osteons
Periosteum
Connective tissue that covers surface of bone
Osteocyte lives in
lacunae
Lucunae
Cavities containing bone cells (Osteocytes)
Lamellae
Rings around central canal sites of lucanae
Osteons
functional units of the bone
Osteocyte lives in
Lacunae
Abduction
Movement away from body’s midline
Adduction
Movement toward body’s midline
Circumduction
Movement at synovial joint in which distal end moves in circle and proximal end remains in one place
Rotation
Moving bone around its own axis
Extension
Unbending movement around limb joint that increases angle between bones of limb at joint (anterior)
Flexion
Bending movement around joint in limb that decreases angle between bones of limb at joint (anterior)
Plantar Flexion
Pointing foot down (pointing toe)
Dorsiflexion
Bending foot upwards
Muscle Contraction
Calcium ions are released into the cell causing filaments in the muscle fiber to contract
Fibrous
Doesn’t move at all
Cartilaginous
Moves a little
Synovial
Can move in any direction
Muscle rule #1
Muscles must have 2 attachments and must cross at least one joint
Muscle rule #2
Muscles always “pull” and get shorter
Muscle rule #3
The attachment that moves is insertion and the one that stays still is the origin
Muscle rule #4
Muscles work in opposing pairs
Muscle rule #5
Striations show direction of the pull
Muscle fiber (Myocyte)
Muscle cell wrapped in Endomysium (connective tissue)
Sarcolemma
Membrane surrounding muscle fibers receives and conducts stimuli
Endomysium
Connective tissue surrounding a muscle fiber
Epimysium
Surrounds the entire muscle with a tough layer of connective tissue
3 types of muscular tissue
Smooth, Cardiac, and Skeletal
Perimysium
The connective tissue that surrounds the fascicles
Myofibril
Bundles of proteins in a muscle cell
Muscles are named by
Location, function, shape, size, direction of fibers, and number of heads
Fascicle
Bundle of muscle fibers
Muscle fiber
Individual muscle cell
Brachialis OIA
O:Distal half of anterior humerus
I: Coronoid process of the ulna
A: Flexes the elbow
Triceps medial head OIA
O: Posterior surface of the humerus
I: Olecranon of the ulna
A: Extends the elbow
Pectoralis Major OIA
O: Clavicle, sternum, and cartilage of the first ribs
I: Greater tubercle of the humerus
A: Adducts, medially rotates, and Flexes the shoulder
Pectoralis Minor OIA
O: Ribs 3-5
I: Coracoid process of the scapula
A: Stabilizes the scapula
External Intercostals
Elevates ribs during inhalation
Internal intercostals
Depresses ribs during exhalation
Ball and Socket joint
Hip and shoulders
Pivot Joint
Between C1 and C2 vertebrae
Hinge joint
Elbow (Movement in 1 direction)
Saddle joint
Between carpal bones (wrists) and metacarpal bone (thumb)
Plane joint
Tarsal bones (ankles)
Condyloid joint
Between radius and carpal bones of wrist
3 examples of a Hinge Joint
Knees, Elbows, and Phalanges
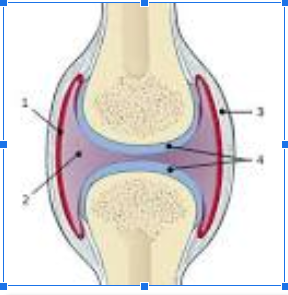
What is #1
Synovial Membrane
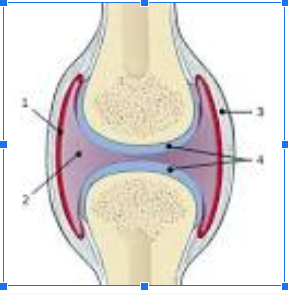
What is #2
Joint cavity
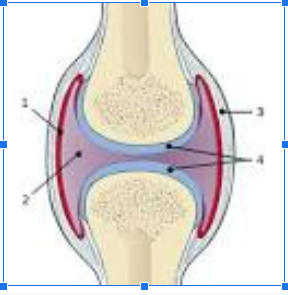
What is #3
Fibrous Capsule
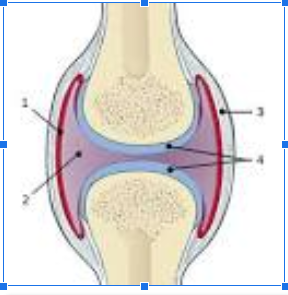
What is #4
Articular Cartilage
Gonimeter
Used to measure the range of motion
Range of Motion (ROM)
the extent or limit to which a part of the body can be moved around a joint or a fixed point
Tendon
band of tissue that connects muscle to bone
Ligament
elastic band of tissue that connects bone to bone and provides stability to the joint
Cartilage
Cartilage is soft, gel-like padding between bones that protects joints and facilitates movement
Valgus Test
Assess the integrity of the collateral ligament of the knee
Varus Test
Assess the integrity of the lateral collateral ligament
Axillary
Armpit
Calcaneal
Heel
Coxal
Tailbone
cephalic
head
inguinal
groin
lumbar
lower back
olecranal
elbow
popliteal
behind knee
sacral
hip bone
thoracic
chest cavity