9 - Capnography
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
capnography
continuous measurement and display of CO2 concentration over time
capnometry
numerical value of ETCO2 without waveform
types of capnography
mainstream
sensor placed directly in the airway
sidestream
sample continuously drawn from airway into external sensor
physiology of CO2
metabolism → transportation via bloodstream → elimination through lungs
factors affecting ETCO2
ventilation
hypoventilation (↑__)
hyperventilation (↓__)
perfusion
shock
pulmonary embolism
C.O. changes
metabolism
fever
sepsis
metabolic acidosis
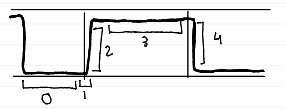
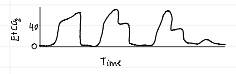
phases of capnogram
phase 0 (baseline)
no CO2 during inhalation
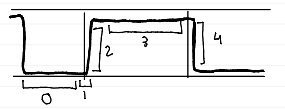
phases of capnogram
phase 1 (dead space ventilation)
CO2-free air from VDanat
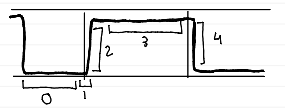
phases of capnogram
phase 2 (ascending)
rapid rise as alveolar gas mixes with dead space gas
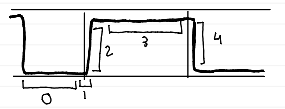
phases of capnogram
phase 3 (alveolar plateau)
CO2-rich alveolar gas exhaled; indicates effective ventilation
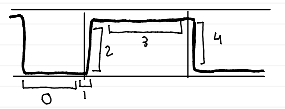
phases of capnogram
phase 4 (ETCO2)
highest CO2 concentration at end of exhalation (normal: 35-45 mmHg)
clinical application of capnography
ET intubation verification (gold standard)
no waveform = tube in esophagus
MV monitoring
titrating ventilator settings (PCV vs VCV)
detecting hypo-/hyperventilation and auto-PEEP
sedation and procedural monitoring
conscious endoscopy
early detection of respiratory depression
cardiac arrest and CPR
low ETCO2 (<10 mmHg) = poor compressions or no perfusion
sudden increase in ETCO2 = ROSC
PE detection
sudden ETCO2 drop with maintained oxygenation
assessment of readiness for extubation
capnography waveforms
normal
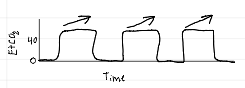
capnography waveforms
hyperventilation
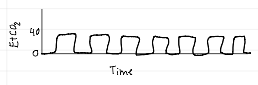
capnography waveforms
hypoventilation
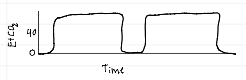
capnography waveforms
emphysema
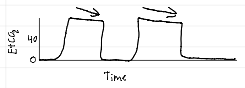
capnography waveforms
curare (spontaneous breathing during mechanical ventilation)
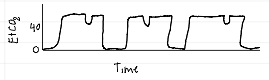
capnography waveforms
hyperventilation / decreased pulmonary blood flow
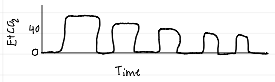
capnography waveforms
rebreathing CO2
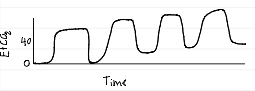
capnography waveforms
obstruction

capnography waveforms
pneumothorax
capnography waveforms
poor compliance
