ecology
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
1
New cards
species
group of genetically similar living organisms able to interbreed and produce fertile offspring
2
New cards
fertile offspring
offspring that can reproduce
3
New cards
ecosystem
all biotic and abiotic factors in an area
4
New cards
population
group of same species that live in the same area
5
New cards
community
All the different populations that live together in an area
6
New cards
Abiotic factors
Non-living factors, such as pH, salinity, wind speed, type of soil, etc.
7
New cards
Biotic factors
Living factors in an ecosystem, such as the plants and animals.
8
New cards
Ecology
study of relationships between living organism and interactions with environment
9
New cards
mutualism
both organisms benefit
10
New cards
commensalism
one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
11
New cards
parasitism
one benefits and the other is harmed
12
New cards
symbiotic relationship
the relationship between two species in close physical association
13
New cards
Symbiosis
means 'living together' - refers to the following outcomes of interactions between populations.
14
New cards
Autotrophic
organism - organic molecules made using abiotic environment
15
New cards
Heterotrophic
organism - obtain organic molecules from other organisms
16
New cards
Mixotroph
uses both autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition
17
New cards
reservoir (aka sink)
place where certain element (carbon) has pooled/accumulated
18
New cards
flux
when carbon moves from one sink to another
19
New cards
example of flux
photosynthesis: inorganic carbon -\> organic biomass (atmospheric CO2 to glucose and compounds by autotrophs) -\> carbon is locked in organism
20
New cards
lithosphere
crust and upper mantle (biggest carbon sink)
21
New cards
hydrosphere
water areas on earth (ocean, lake, pond, river)
22
New cards
biota
living organisms
23
New cards
atmosphere
layer of gases surrounding earth
24
New cards
carbon cycle
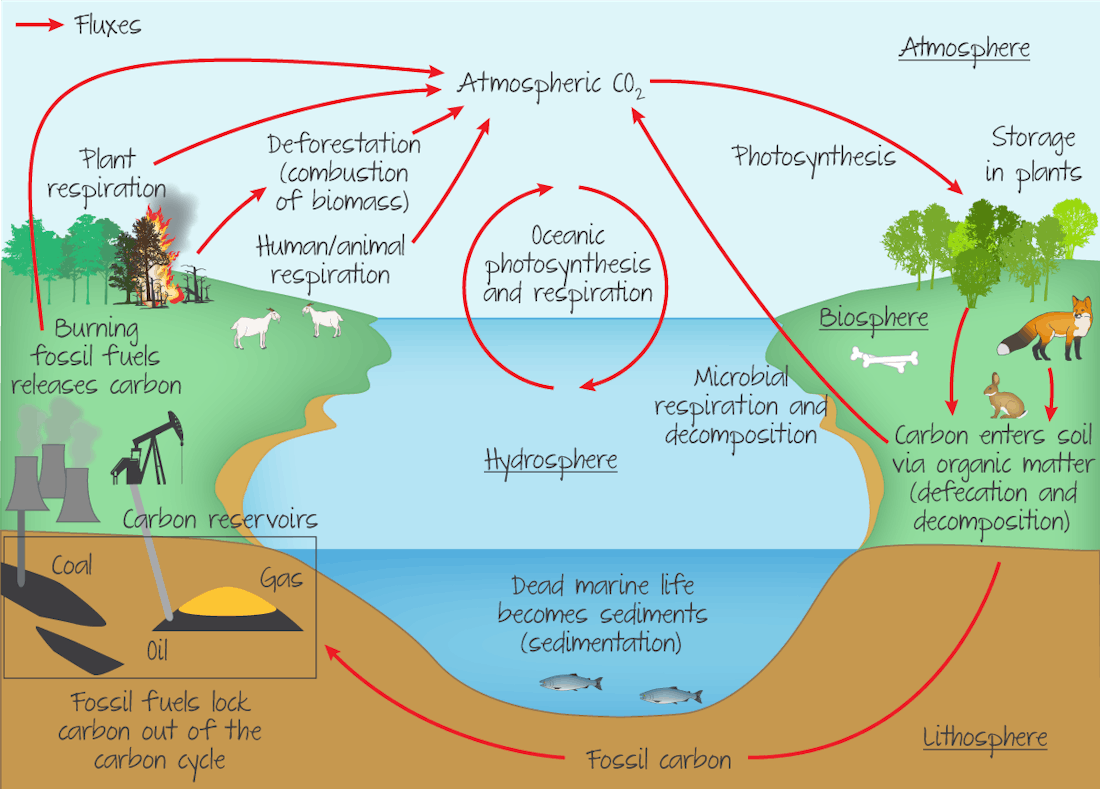
25
New cards
carbon flux
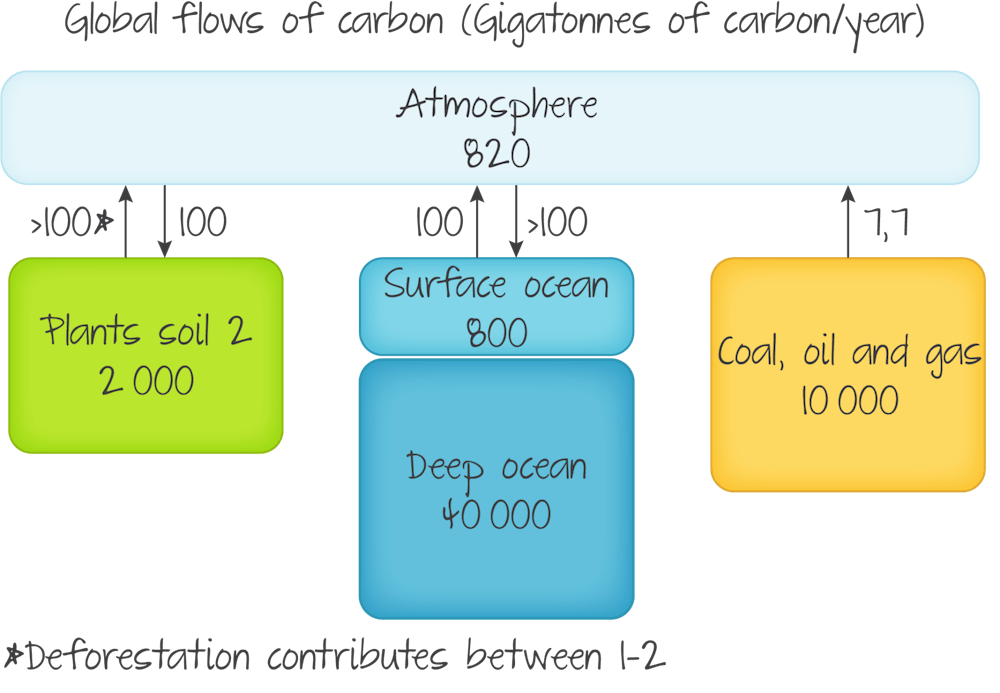
26
New cards
habitat
environment a species normally lives
27
New cards
food chain
steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten
28
New cards
food web
a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains.
29
New cards
cellular respiration
oxygen and glucose -\> CO2, H2O and ATP
30
New cards
photosynthesis
light CO2 and H20 -\> O2 and glucose
31
New cards
nutrient cycling
movement of organic and inorganic material
32
New cards
detritivore
eats dead organic matter (vulture, dung beetle)
33
New cards
saprotroph
secretes enzyme to externally digest dead organic matter (fungus, bacteria)
34
New cards
niche
An organism's particular role in an ecosystem, or how it makes its living.
35
New cards
biomass
total mass of a group of organisms
36
New cards
CO2
main greenhouse gas -\> from cellular respiration and combustion of fossil fuels
37
New cards
water vapour
water found in the atmosphere, most abundant greenhouse gas part of water cycle
38
New cards
greenhouse gases
gases found in the atmosphere such as water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides, that contribute to the greenhouse effect.
39
New cards
greenhouse effect
warming that results when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere
40
New cards
radiation
energy that may be a subatomic particle
41
New cards
solar radiation
energy from sun in electromagnetic waves
42
New cards
ozone layer
protects earth from UV radiation
43
New cards
UV radiation
short wave from sun
44
New cards
infrared light
long wavelength emitted from earth and atmospher
45
New cards
ecology
study of how living things interact with each other and their environment
46
New cards
carbonic acid (H2CO3)
when CO2 and water combine -\> unstable and H ions are released into ocean water
47
New cards
ocean acidification
pH becoming more acidic from increased CO2
48
New cards
peat
waterlogged decaying organic materials
49
New cards
coal
compressed peat over long time
50
New cards
oil
coal compressed even longer
51
New cards
limestone
calcium carbonate from dead marine animals fossilized in sea beds
52
New cards
Ruminants
mammals that have mutalistic relationship with methanogenic archaens -\> digest cellulose from plants ( in the walls) -\> methane produced as gas
53
New cards
methanogenic achaeans
bacteria found in anoxic environment -\> produce methane
54
New cards
anoxic environment
lacks oxygen
55
New cards
hydrolysis
breaking down a polymer (plants)
56
New cards
acidogenesis
organic matter -\> acids/alcohols from bacteria
57
New cards
acetogenesis
bacteria take alcohol/acids -\> acetate
58
New cards
methanogenesis
methane made from CO2 + H2 in bacteria or acetate breakdown
59
New cards
precautionary principle
if human change -\> severe harm -\> must prove will not do harm
60
New cards
albedo effect
ability of earths surface to reflect light
61
New cards
(bright \= high albedo because less light absorbed)
62
New cards
climate
Overall weather in an area over a long period of time
63
New cards
Coral reefs
ridge in the ocean where living coral polyps attach and secrete calcium carbonate -\> in warm shallow water
64
New cards
Calcification
process used by molluscs, crustaceans, and corals to build their shells and exoskeletons using calcium carbonate
65
New cards
methane
main natural gas + fossil fuel emitted from marshes, water logged places and landfills but has lowest concentration in atmosphere
66
New cards
anaerobic
form of respiration that happens when there is no oxygen