MicroBio Lab Mediums
1/219
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For lab exam #3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
220 Terms

MR-VP Methyl Red Test — This medium tests for the fermentation of what sugar?
Glucose

MR-VP Methyl Red Test — What is the product of this fermentation?
Mixed Acid
MR-VP Methyl Red Test — What reagent is added to this medium?
Methyl Red

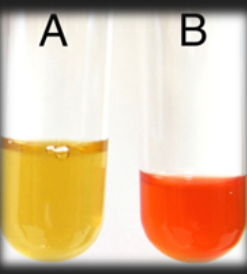
MR-VP Methyl Red Test —What is the result for organism A?
Negative; Organism does not ferment mixed acids from glucose

MR-VP Methyl Red Test —What is the result for organism B?
Positive; Organism does ferment mixed acids from glucose
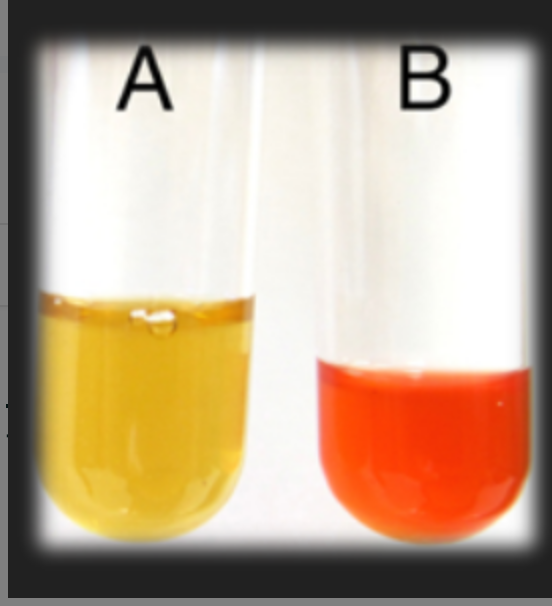
What test is this?
MR-VP; Methyl Red Test or Voges Proskaeur Test

Lysine Decarboxylase Medium — What reagent is added to this medium?
Mineral Oil

Lysine Decarboxylase Medium —When is the reagent for this medium added?
After inoculation, Before incubation

Lysine Decarboxylase Medium — A positive result results in a ___ of the pH
increase/raising (basic environment)

Lysine Decarboxylase Medium — What is the result for organism A?
Negative; Organism does not decarboxylate from lysine; pH was not raised

Lysine Decarboxylase Medium — What is the result for organism B?
Positive; Organism does decarboxylate from lysine; pH was raised
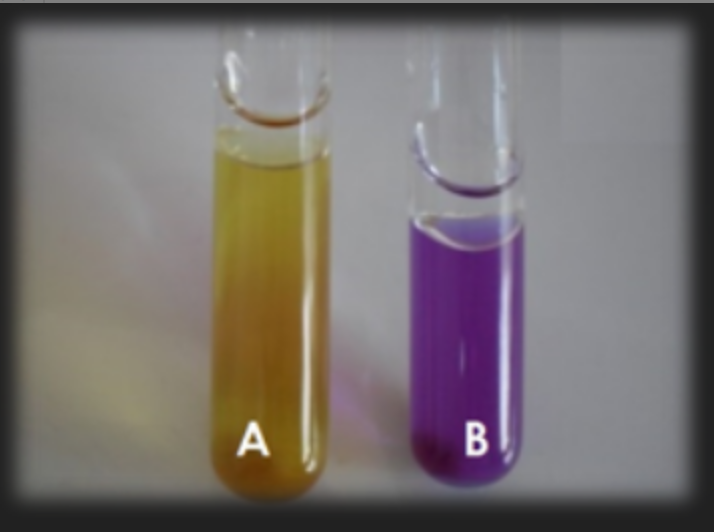

What test is this?
Lysine or Ornithine Decarboxylase Medium
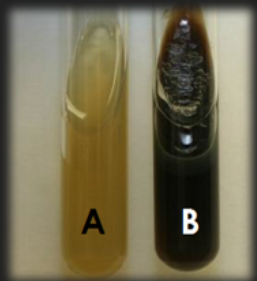
Bile Esculin Agar — What characteristic is tested for in this medium?
Hydrolysis of esculin to esculetin by esculinase
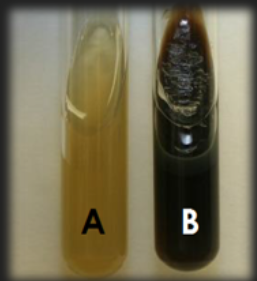
Bile Esculin Agar — Is this medium differential? Selective? Both?
Selective against non-strep organisms
Differential for esculinase production
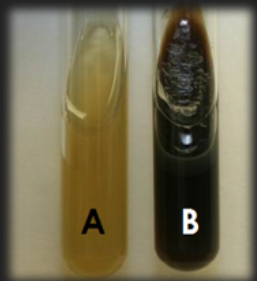
Bile Esculin Agar — With which genus is this medium used?
Streptococcus / Enterococcus
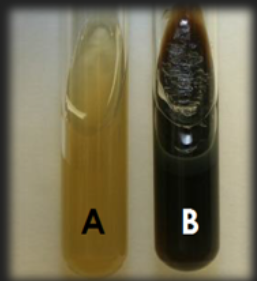
Bile Esculin Agar — What is the result for organism A?
Negative; Organism does not hydrolyze esculin to esculetin; Enzyme esculinase is not present
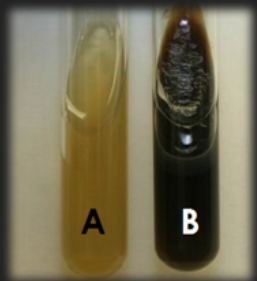
Bile Esculin Agar — What is the result for organism B?
Positive; Organism does hydrolyze esculin to esculetin; Enzyme esculinase is present
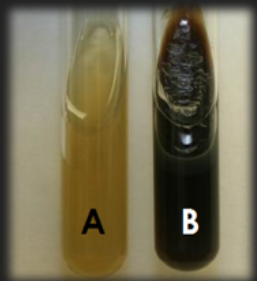
What test is this?
Bile Esculin Agar
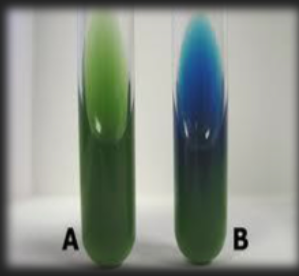
Simmon’s Citrate — What enzyme is tested for in this medium?
Citrase (citrate permease)
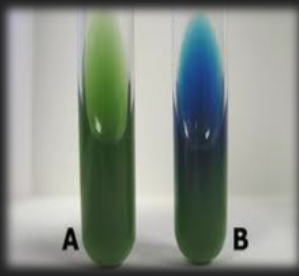
Simmon’s Citrate — What reagent is in the medium?
Bromothymol Blue
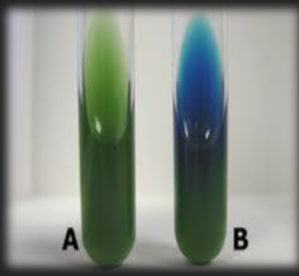
Simmon’s Citrate — What is the result for organism A?
Negative; Organism does not use citrate; Citrate permease is not present in the organism
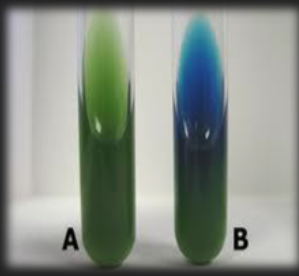
Simmon’s Citrate — What is the result for organism B?
Positive; Organism does use citrate; Citrate permease is present in the organism

Nitrate Broth: A & B added — What enzyme is tested for in this medium?
Nitrate Reductase

Nitrate Broth: A & B added — What is the result for organism A?
Positive; Organism reduces NO3 to NO2

Nitrate Broth: A & B added — What are the TWO possible results for organism B?
1) Negative for nitrate reductase and denitrification
2) Negative for nitrate reductase; Positive for denitrification (NO3 to N2)

Nitrate Broth: A & B added — What is added to differentiate the results for organism B?
Reagent C - Zinc Dust
Nitrate Broth — reagent A + reagent B = RED
Positive for NO3 reduced to NO2 (Nitrate Reductase present)
Denitrification not present
(+NO2, -N2)
Nitrate Broth — reagent A + reagent B = COLORLESS
Negative for NO3 reduced to NO2 (Nitrate Reductase not present)
Denitrification not present
(-NO2, -N2)
Nitrate Broth — reagent A + reagent B + reagent C = RED
Negative for NO3 reduced to NO2 (Nitrate Reductase not present; NO3 not reduced)
(-NO2)
Nitrate Broth — reagent A + reagent B + reagent C = COLORLESS
Positive for Denitrification of NO3 to N2
(NO3 not present)
(-NO2, +N2)
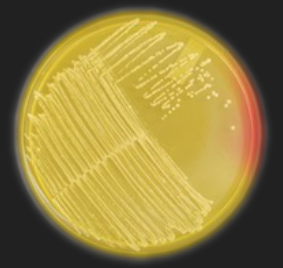
MSA — With which genus is this medium used?
Staphylococcus
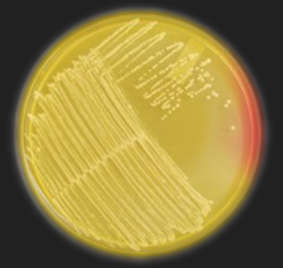
MSA — What is the selective ingredient in this medium?
7.5% NaCl / Salt
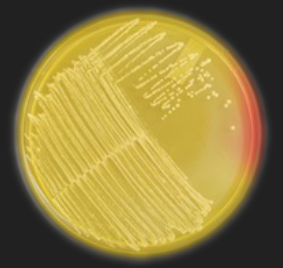
MSA — What is the differential ingredient in this medium?
Phenol Red
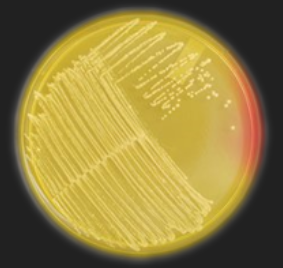
MSA — What are the results for this organism?
Staphylococcus organism
Salt tolerant (halotolerant)
Mannitol Fermenter
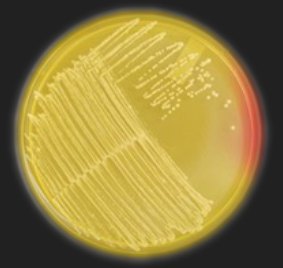
MSA — Which species of Staphylococcus could this be?
S. aureus or S. saprophyticus
What does phenol red do in MSA and CDT?
Causes a pH sensitive color change of red to yellow for differentiation of mannitol fermentation / acid production
Differential characteristics of S. aureus
Mannitol Fermentation = Positive (+)
Novobiocin Susceptibility = Sensitive (S)
Coagulase Production = Positive (+)
alpha-toxin Production = Positive (+)
Pigment on Solid Media = Negative (-)
Differential characteristics of S. epidermis
Mannitol Fermentation = Negative (-)
Novobiocin Susceptibility = Sensitive (S)
Coagulase Production = Negative (-)
alpha-toxin Production = Weak Positive (+)
Pigment on Solid Media = Negative (-)
Differential characteristics of S.saprophyticus
Mannitol Fermentation = Variable (±)
Novobiocin Susceptibility = Resistant (R)
Coagulase Production = Negative (-)
alpha-toxin Production = Negative (-)
Pigment on Solid Media = Negative (-)
Differential characteristics of S.xylosus
Mannitol Fermentation = Positive (+)
Novobiocin Susceptibility = Resistant (R)
Coagulase Production = Negative (-)
alpha-toxin Production = Weak Positive (+)
Pigment on Solid Media = Positive (+)

Rabbit Plasma — With which genus is this medium used?
Staphylococcus

Rabbit Plasma — For what enzyme does this medium test?
Coagulase

Rabbit Plasma — What are the results for this organism?
Positive for coagulation of blood plasma proteins; Coagulase is produced and present in organism

Rabbit Plasma — Which species of Staphylococcus could this be?
S. aureus
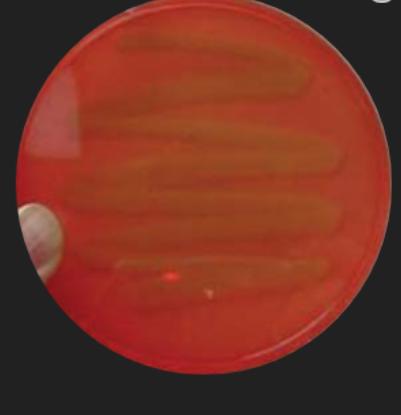

Blood Agar: Staphylococcus Identification — For which staphylococcal capability does this inoculation test?
Alpha toxin production
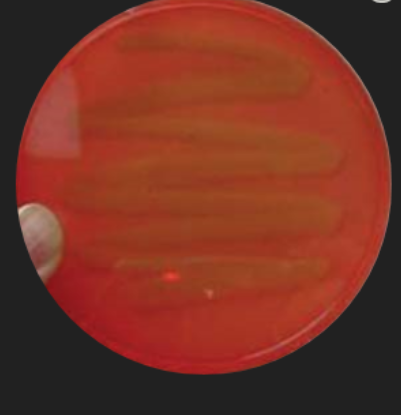

Blood Agar: Staphylococcus Identification — What type of hemolysis does this toxin produce?
Beta hemolysis of red blood cells
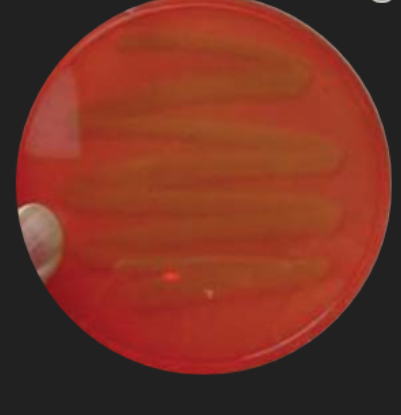

Blood Agar: Staphylococcus Identification — What are the results for this organism?
Negative; Organism does not produce alpha toxins to hemolyze beta red blood cells
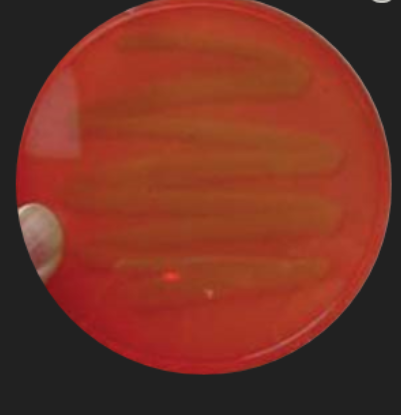

Blood Agar: Staphylococcus Identification — Which species of Staphylococcus could this be?
S. epidermis, S. saprophyticus, or S. xylosus
What does a positive result on Blood Agar look like and indicate?
Look: Prominent yellow halo surrounding the cells
Indicates: Alpha toxin production was present to hemolyze beta red blood cells
What does a negative result on Blood Agar look like and indicate?
Look: No yellow halo surrounding cells
Indicates: Alpha toxin production is not present to hemolyze beta red blood cells
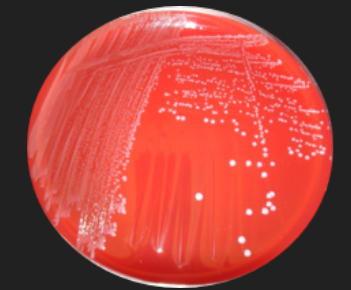
Blood Agar: Streptococcus Identification — For which capability does this inoculation test?
Hemolysis of red blood cells
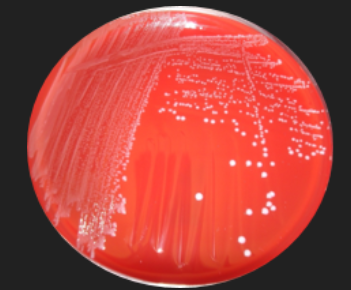
Blood Agar: Streptococcus Identification — What is the differential ingredient in this medium?
Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
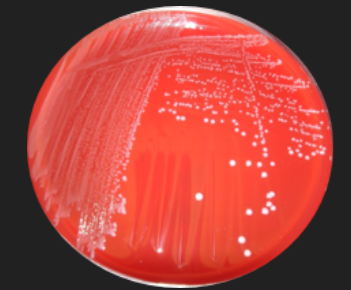
Blood Agar: Streptococcus Identification — Which hemolysis results from the production of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)?
Alpha Hemolysis
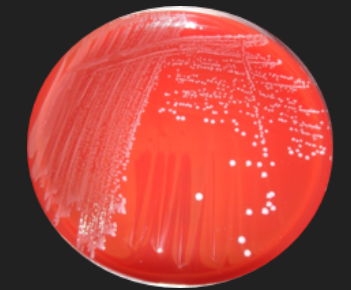
Blood Agar: Streptococcus Identification — Which hemolysis results from teh production of streptolysin S or O?
Beta Hemolysis
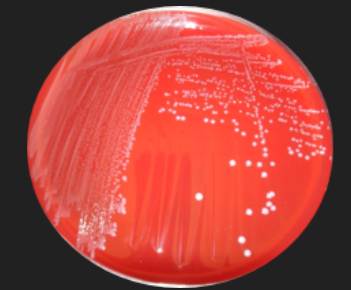
Blood Agar: Streptococcus Identification — What result is pictured here?
Gamma Hemolysis
In Streptococcal Blood Agar testing, what does hemolysis refer to in the medium?
Hemolysis refers to the color of the red blood cells in the medium adjacent to the bacterial growth, not the colonies themselves
Is Streptococcal Blood Agar differential or selective?
Differential
How is Streptococcal Blood Agar Differential?
Differentiates bacteria based on their ability to damage RBCs
What does a dark halo on Streptococcal Blood Agar represent
Alpha — Oxidation of RBCs
What does a light/yellow halo on Streptococcal Blood Agar represent
Beta — Hemolysis of RBCs
What does no halo on Streptococcal Blood Agar represent?
Gamma — RBCs are unaffected
Blood Agar: CAMP Factor Production — For which genus is CAMP capability important?
Streptococcus/Enterococcus
Blood Agar: CAMP Factor Production — Which organisms are CAMP positive?
Weakly beta hemolytic streptococci
Blood Agar: CAMP Factor Production — Which organism is used to test for CAMP production?
Staphylococcus aureus
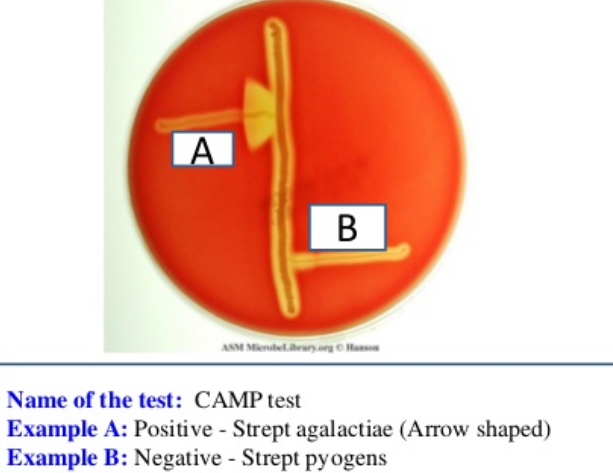
Blood Agar: CAMP Factor Production — What result is pictured here?
Positive; Organism produces CAMP factor by increased beta hemolysis of red blood cells
Stain used to determine cell shape
Gram Staining
Stain used to determine cell arrangement
Gram Staining
Stain used to determine Gram Reaction
Gram Staining
Medium used to determine motility
Motility Medium & SIM
Medium used to determine Oxygen Requirement
FTM - Fluid Thioglycollate Medium
Redox Indicator in FTM
Resazurin
Reducing Agent in FTM
Thioglycollate
O2 Stabilizer in FTM
Agar
What tests determine Respiration-Related Characteristics
Cytochrome Oxidase
Hydrogen Peroxide Test
Nitrate Broth
Positive Result of Cytochrome Oxidase/Oxidase Test
Purple/blue color change of oxistrip
Negative Result of Cytochrome Oxidase/Oxidase Test
No color change of oxistrip
Cytochrome Oxidase test determines what?
Oxidase Production
Production of membrane bound electron carrier of ETC cytochrome oxidase
Medium used in Oxidase Production
Agar
Reagent(s) used in Oxidase Production
Oxistrips
Enzyme used in Oxidase Production
Cytochrome Oxidase
Negative Result of Hydrogen Peroxide/Catalase Test
no bubbles
Positive Result of Hydrogen Peroxide/Catalase Test
bubbles
Hydrogen Peroxide Test determines what?
Catalase Production
conversion of H2O2 to O2 & H2O by catalase
Medium used in Catalase Production
Agar
Reagent(s) used in Catalase Production
Hydrogen Peroxide
Enzyme used in Catalase Production
Catalase
Nitrate Broth Test determines what
Nitrate Reduction & Denitrification
Conversion of NO3 to NO2 by nitrate reductase
What medium is used in Nitrate Reduction?
Nitrate Broth
What substrate is used in Nitrate Reduction
Nitrate
What Reagent(s) is used in Nitrate Reduction
reagent A and reagent B
What enzyme is used in Nitrate Reduction
Nitrate Reductase
What medium is used in Denitrification
Nitrate Broth
What substrate is used in Denitrification
Nitrate
What reagent is used in Denitrification
reagent C - Zinc Dust
What tests determine Protein Catabolism-Related Characteristics
SIM
Hydrogen Peroxide
Indole Production
Motility
Gelatin Deep
Urea Broth
Tryptone Broth
Skim Milk Agar
Phenylalanine Afar Slant
Decarboxylase Media
Lysine
Ornithine
Positive Result of SIM-H2S Test
Black precipitate
Negative Result of SIM-H2S Test
No black precipitate
SIM— H2S Test determines what
H2S production
Hydrogen Sulfide Production: Removal of sulfur group from amino acids (cysteine) by various amino acids desulfurases
What medium is used to determine H2S Production
SIM
What substrate is used to determine H2S Production
Sulfur-containing amino acids