Chapter 3- The Cell
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Organelle
specialized structure that performs important cellular functions within a eukaryotic cell
Diploid
An organism or cell having 2 complete sets of chromosomes
Haploid
An organism or cell having only one complete set of chromosomes.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Hydrophobic
Having an aversion to water; tending to coalesce and form droplets in water.
Hydrophilic
Having an affinity for water.
Hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution.
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
Isotonic
Having the same solute concentration as another solution.
Lyse
Cell bursting.
Plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
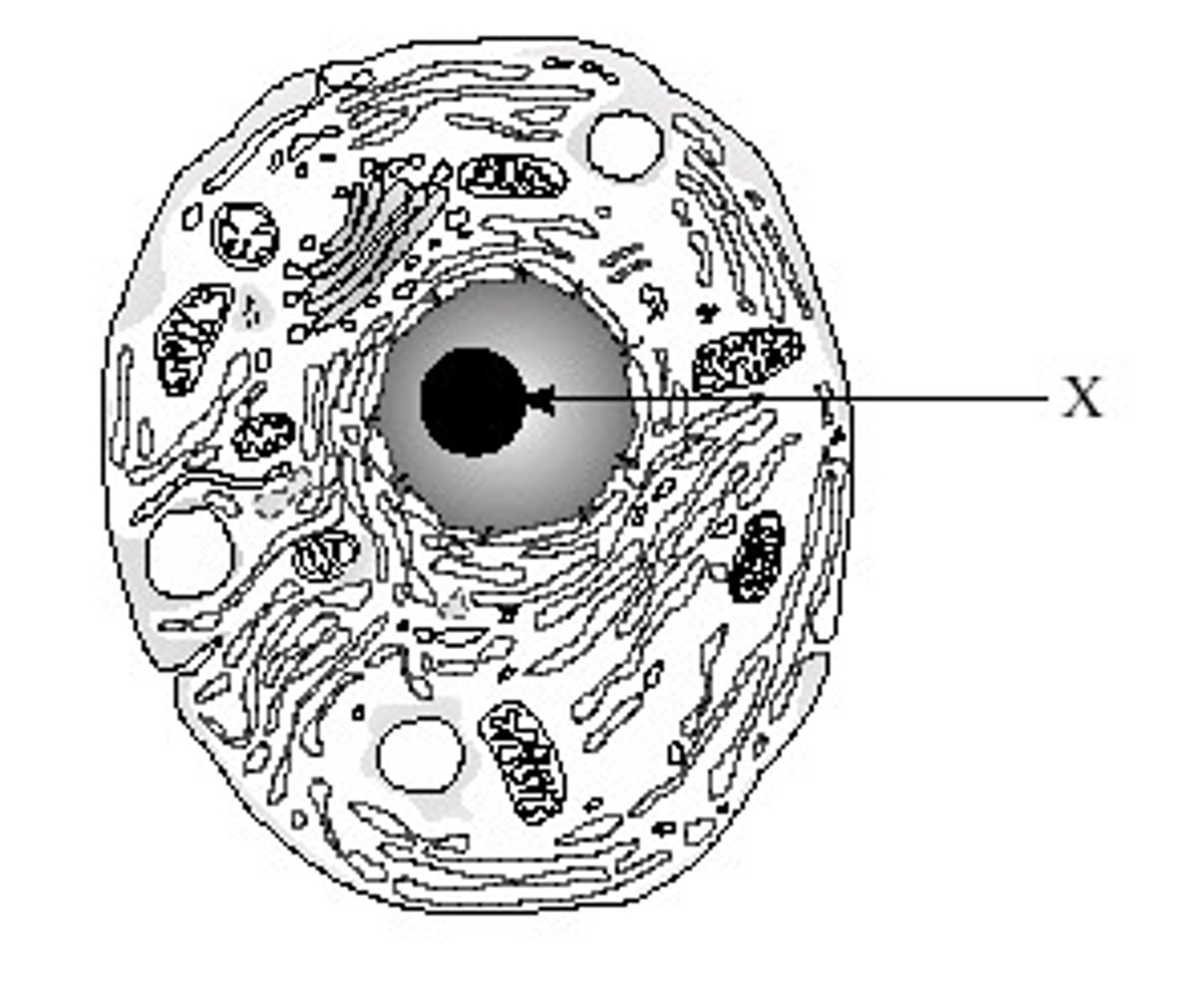
Nucleus
Control center of the cell; contains DNA; two membranes
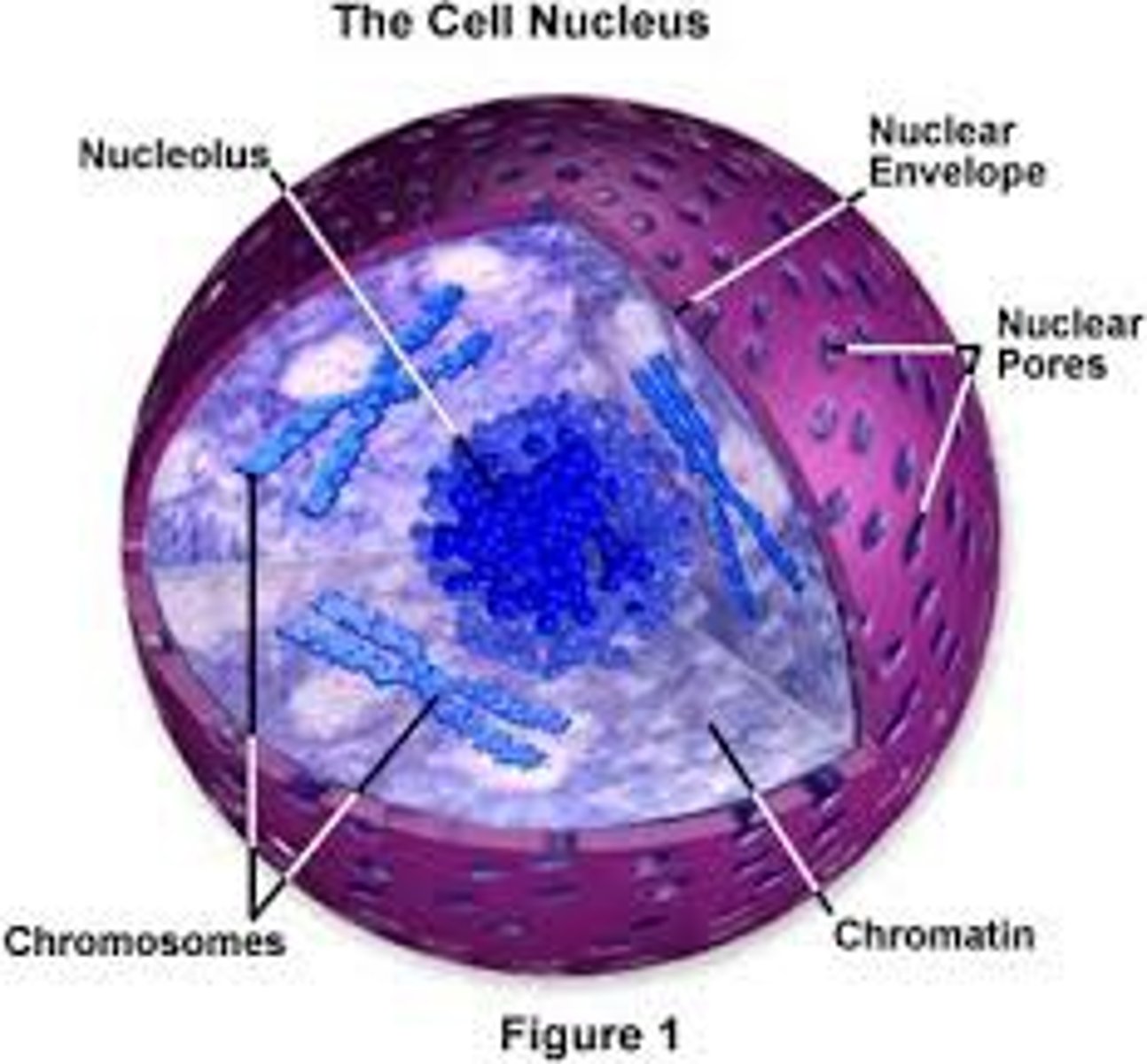
Chromatin
Clusters of DNA, RNA, and proteins in the nucleus of a cell
Euchromatin
The less condensed form of eukaryotic chromatin that is available for transcription.
Heterochromatin
Eukaryotic chromatin that remains highly compacted during interphase and is generally not transcribed.
Nucleoli
dense masses of RNA and protein that manufacture ribosomes, several of these are located in the nucleus.
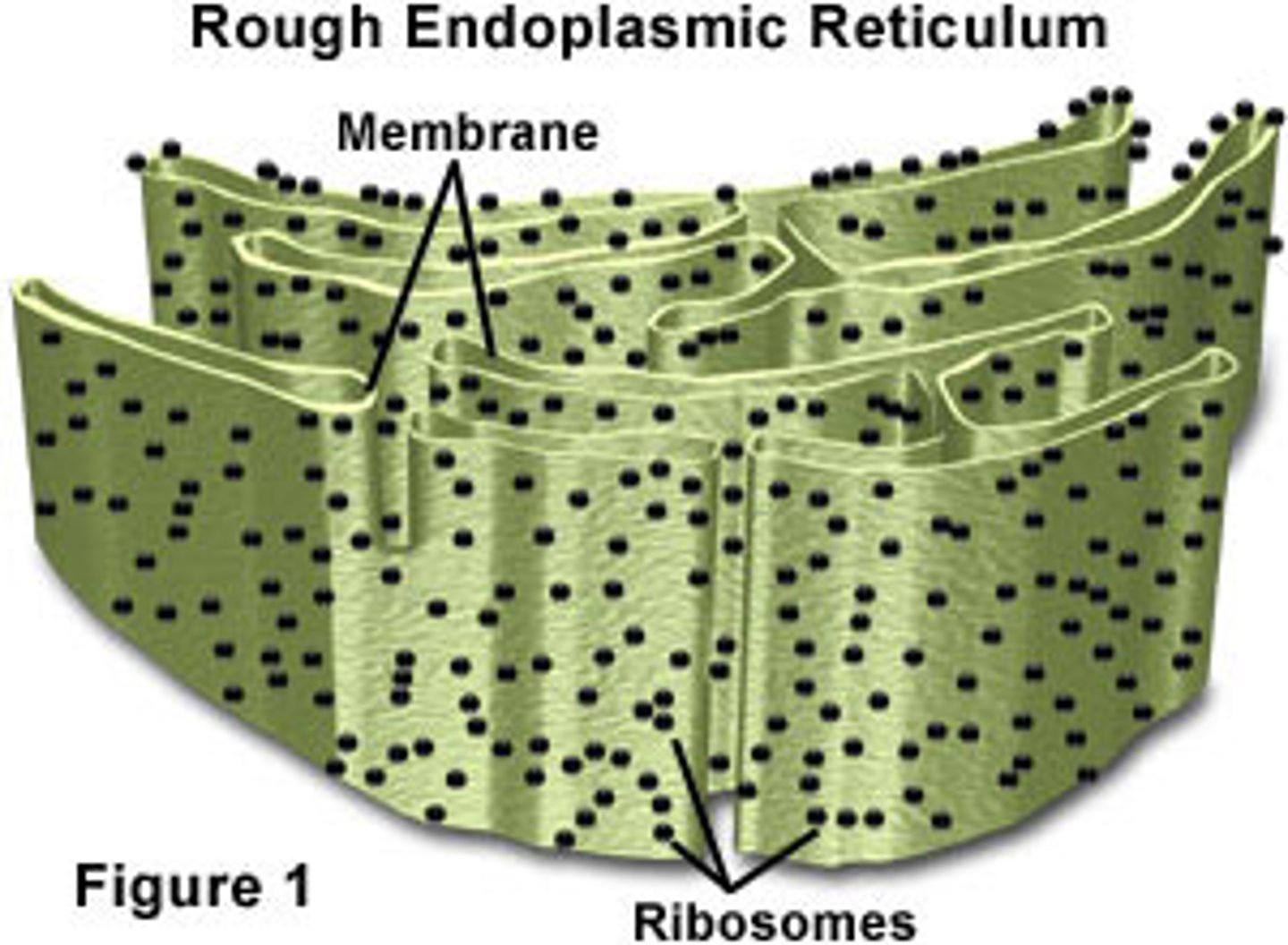
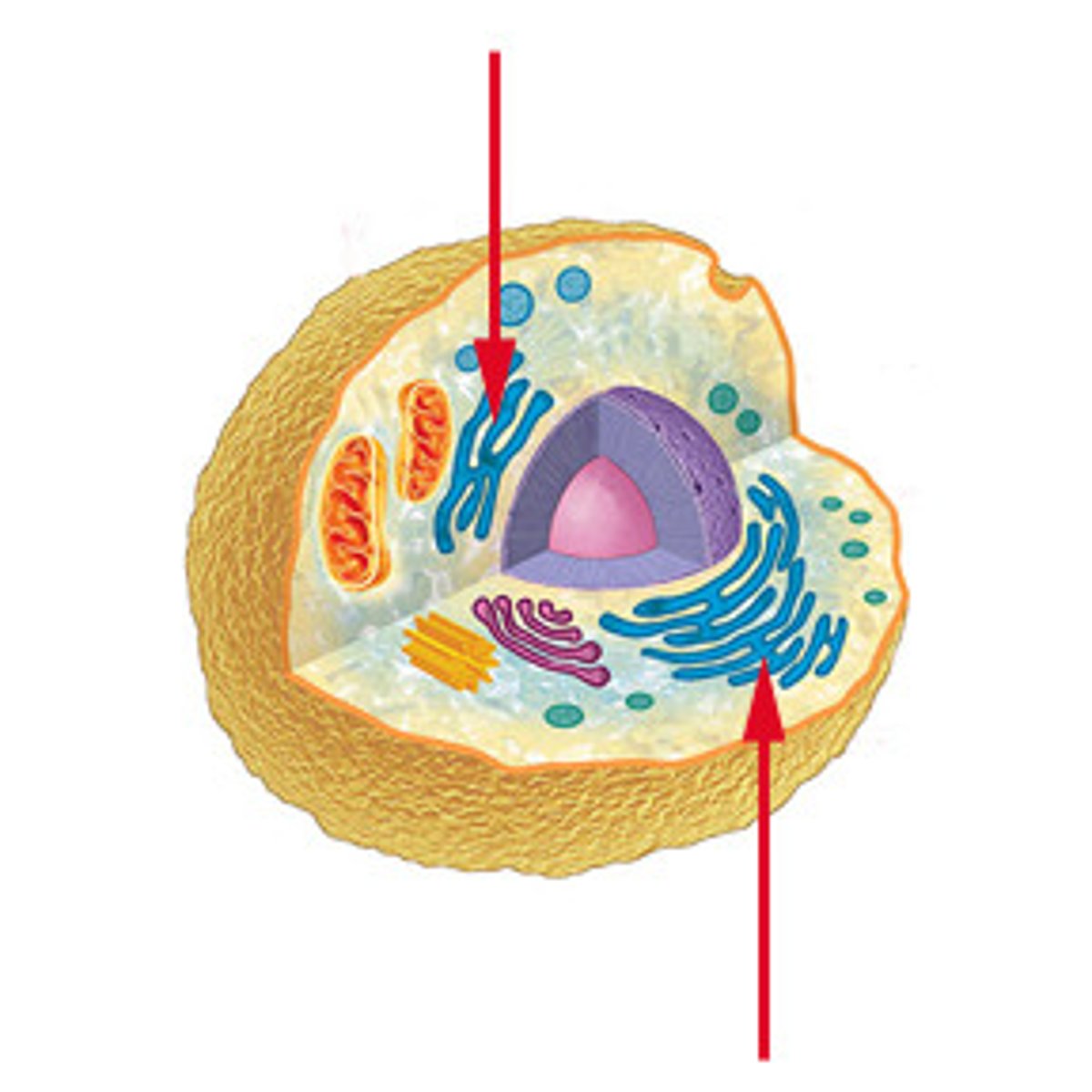
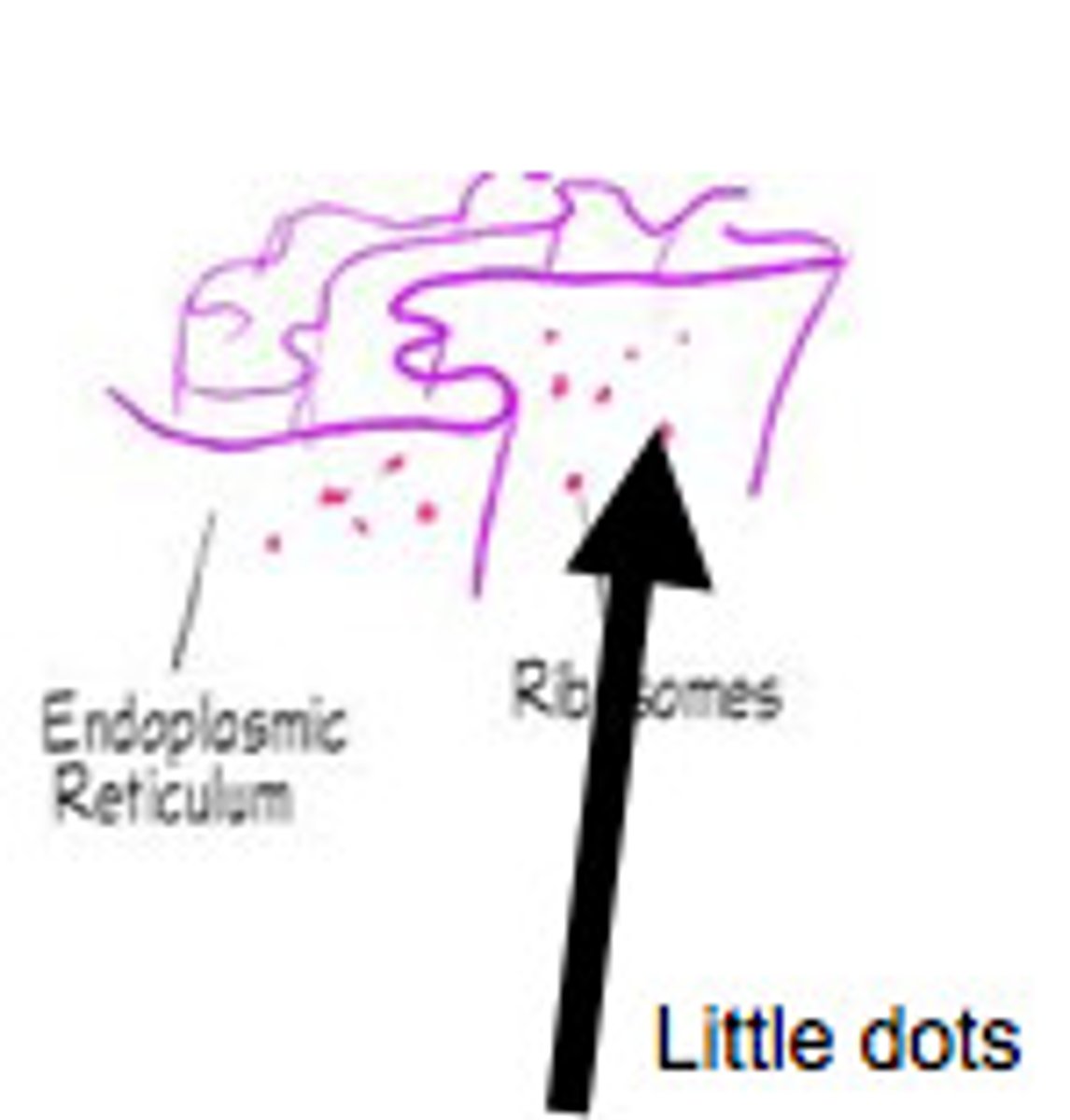
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
System of internal membranes within the cytoplasm. Membranes are rough due to the presence of ribosomes. functions in transport of substances such as proteins within the cytoplasm
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
An endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down.
Golgi apparatus (complex)
Packages and sends proteins; Assists in the transport, but is not the actual transport network
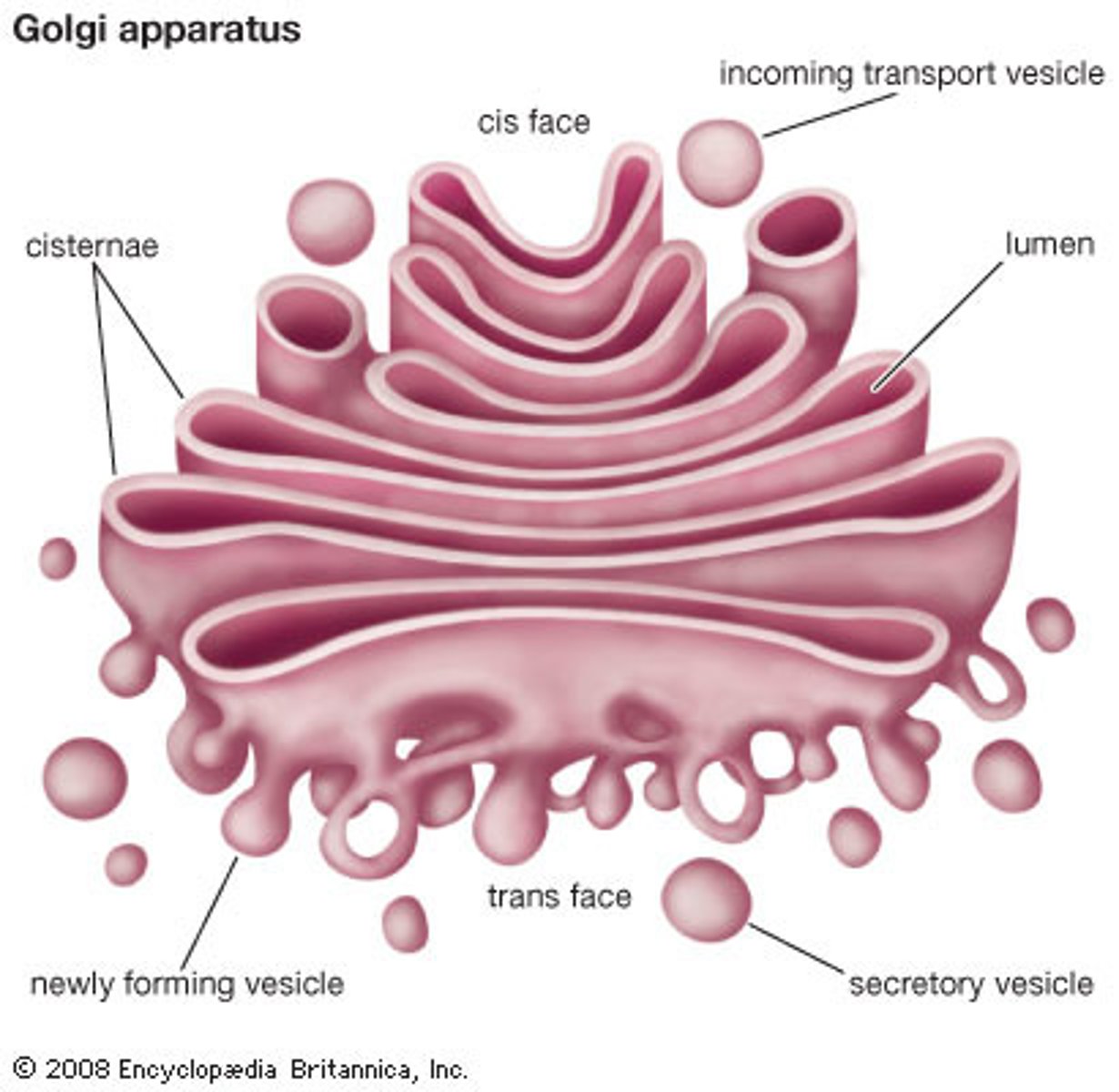
Exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material
Centrioles
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells only
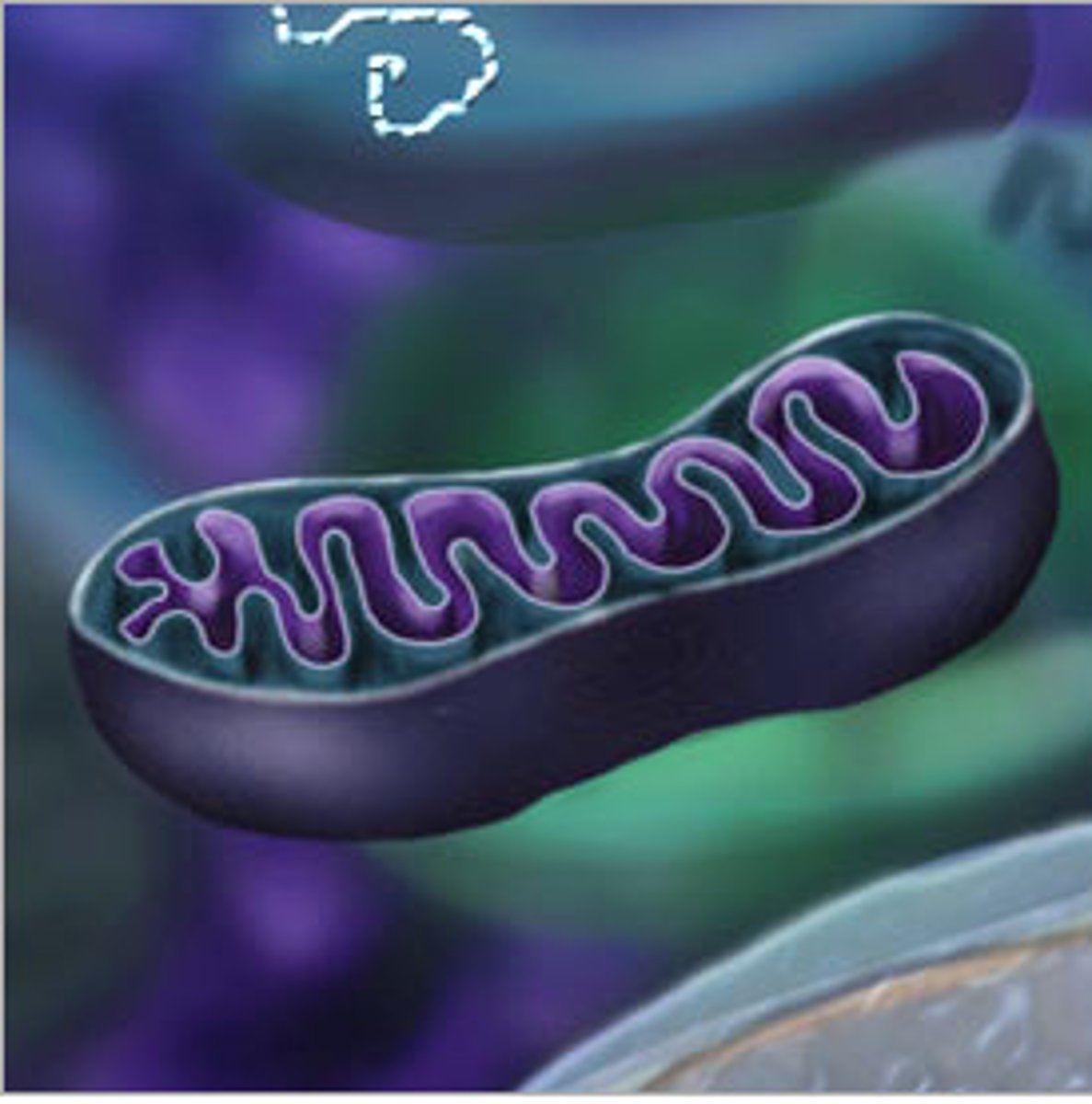
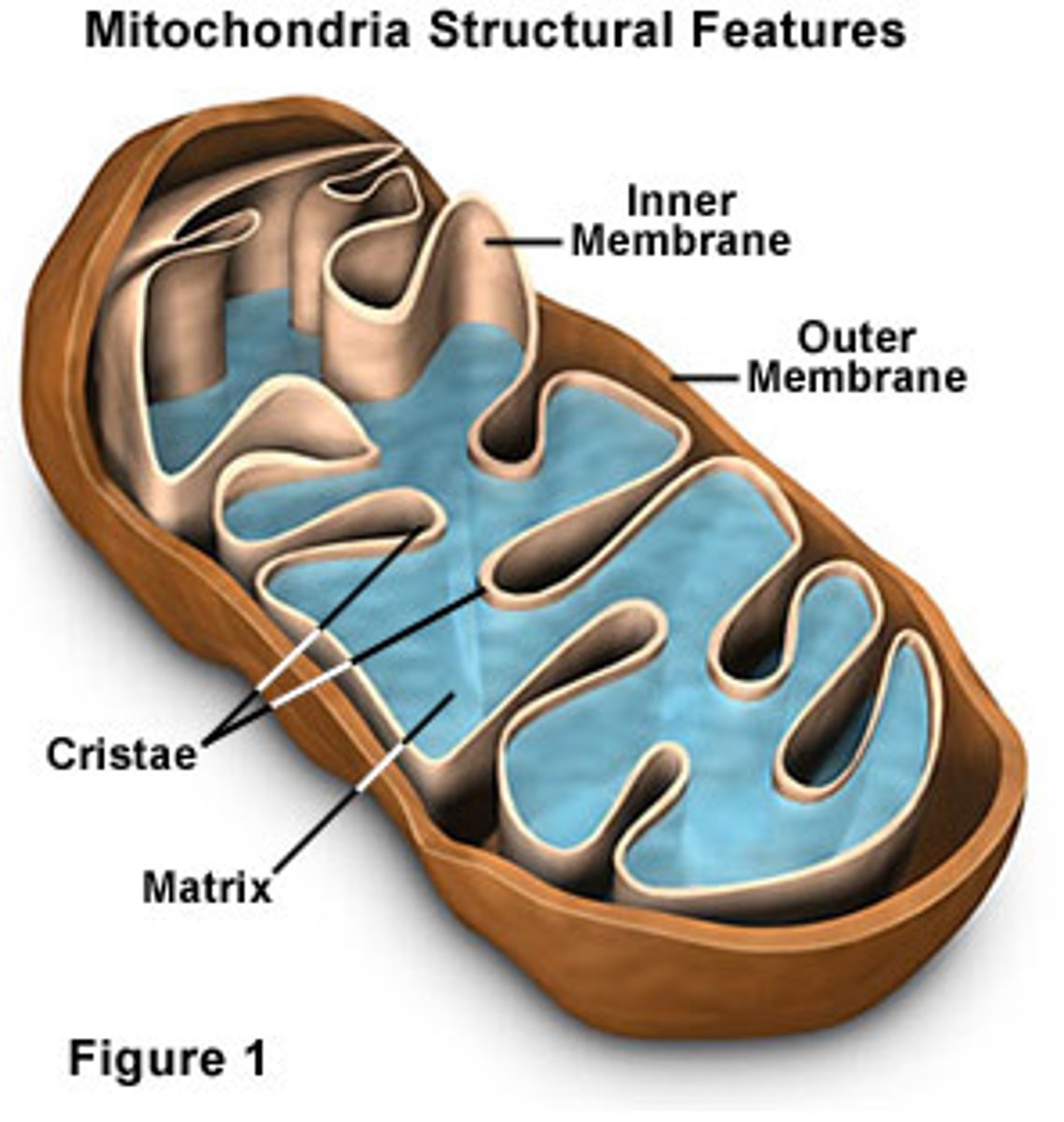
Mitochondria
An organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur.
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
Vesicles
small membrane sacs that specialize in moving products into, out of, and within a cell
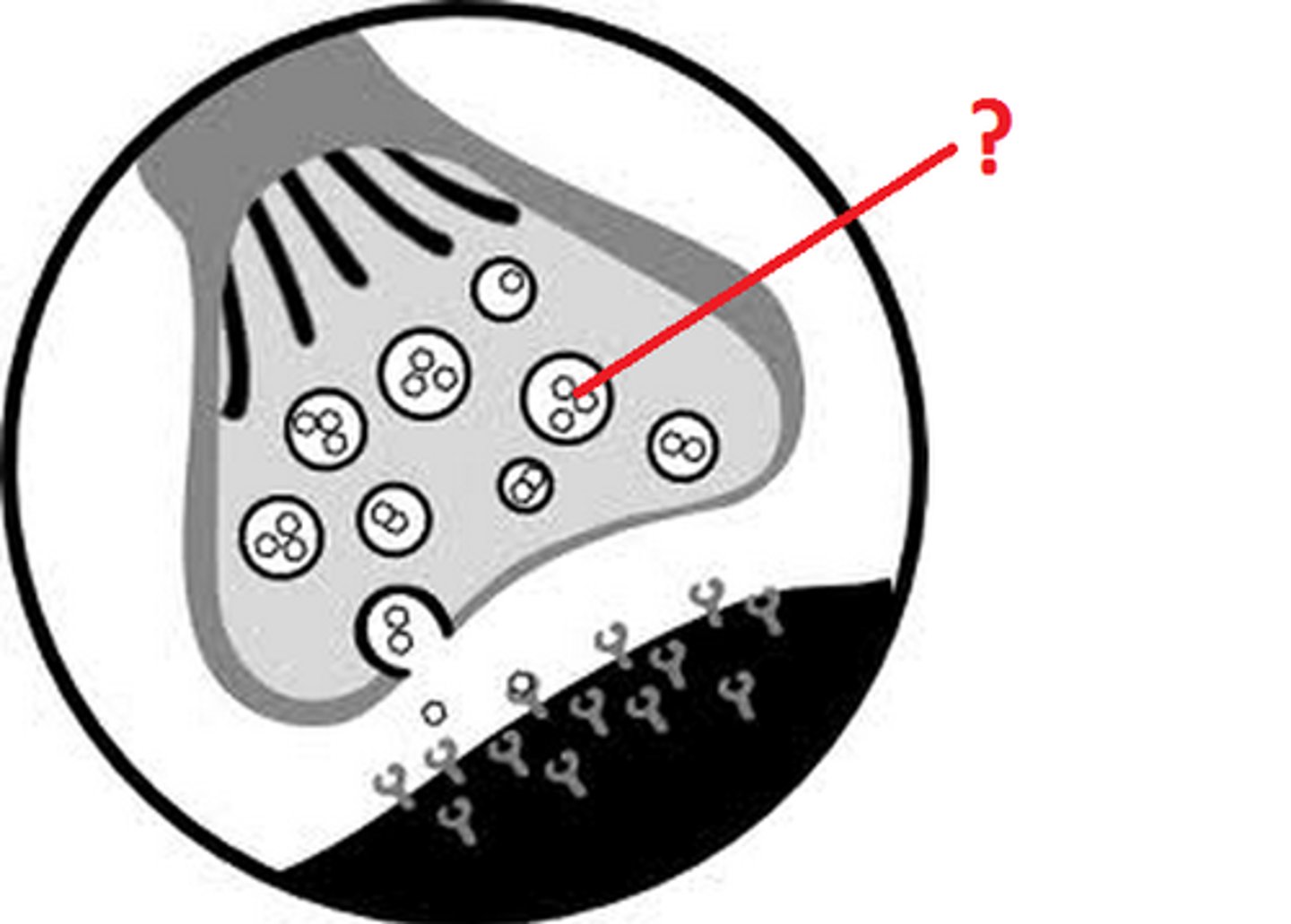
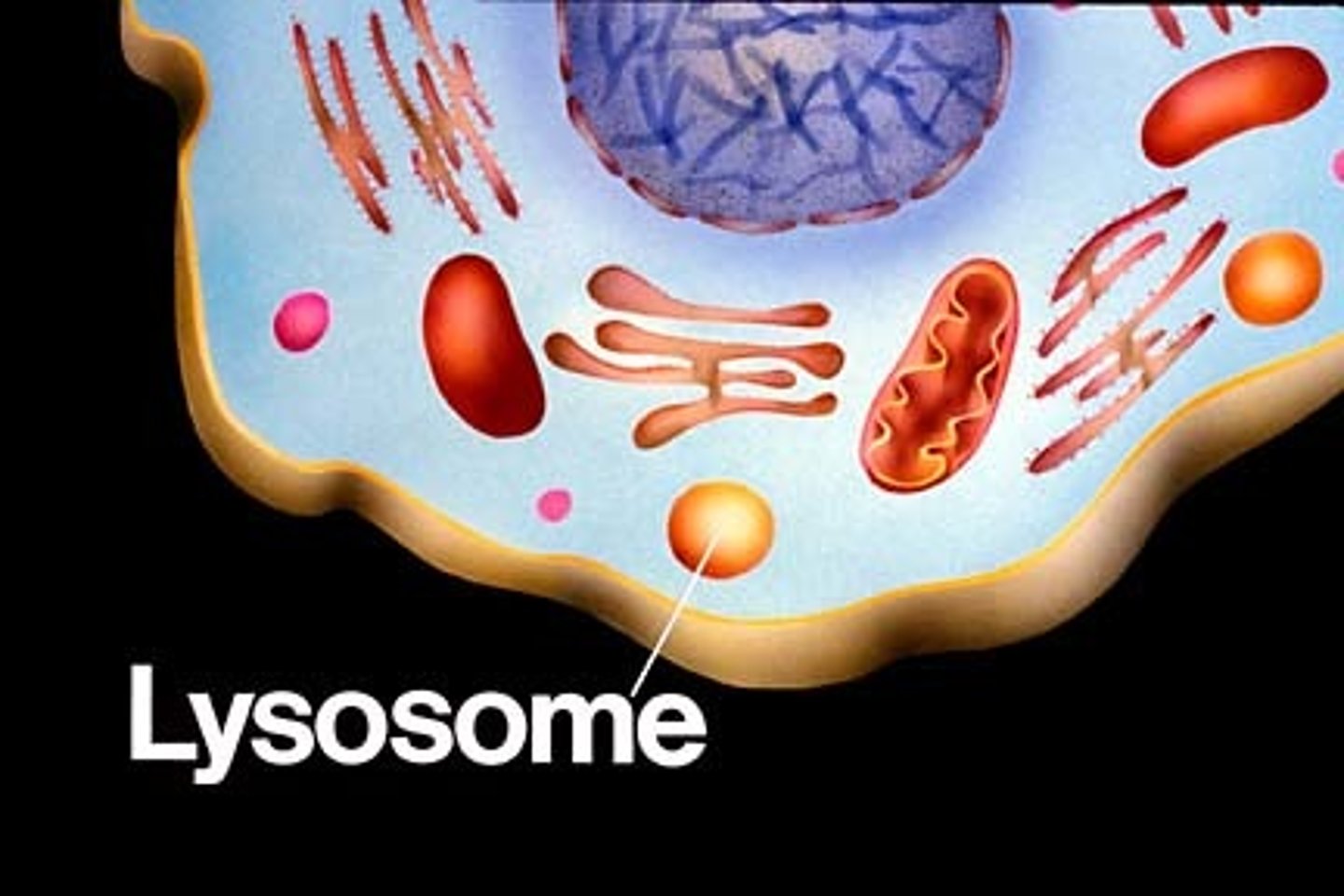
Lysosomes
A vesicle containing digestive enzymes
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Matrix
Innermost compartment of the mitochondrion
Kreb's cycle
second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions
Where does the Kreb's cycle occur?
matrix of mitochondria
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP.
Where does the ETC occur?
inner membrane of mitochondria
Chemiosmosis
A process for synthesizing ATP using the energy of an electrochemical gradient and the ATP synthase enzyme.
Interphase
period of the cell cycle between cell divisions; cell grows and carries on with normal business
G1 phase
The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins.
S1 phase
phase of chromosomal replication and DNA synthesis during interphase
G2 phase
The second growth phase of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs.
G0 phase
A nondividing state occupied by cells that have left the cell cycle, sometimes reversibly.
Apoptosis
process of programmed cell death
Mitosis
part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides
Prophase
Chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms
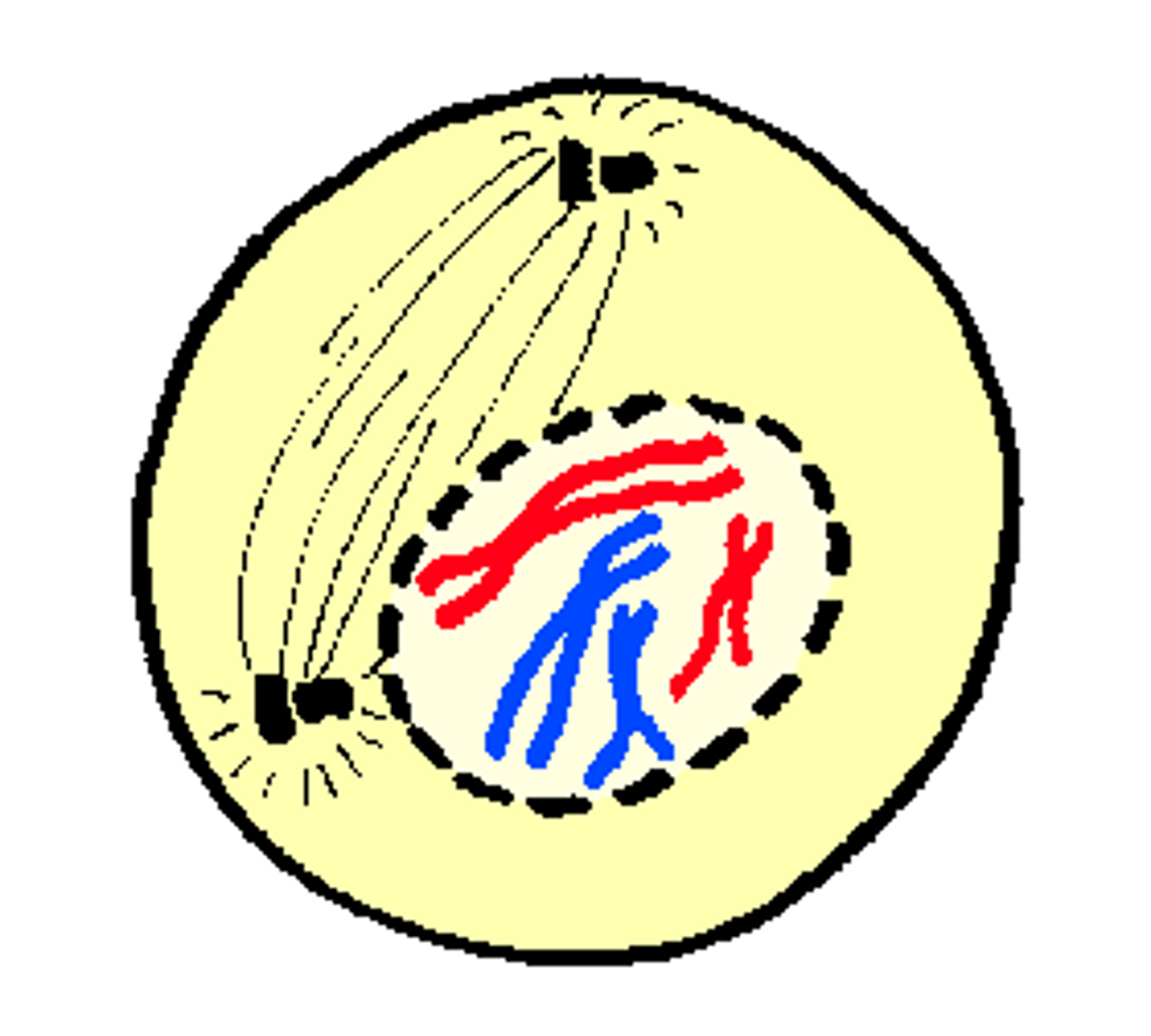
Metaphase
second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
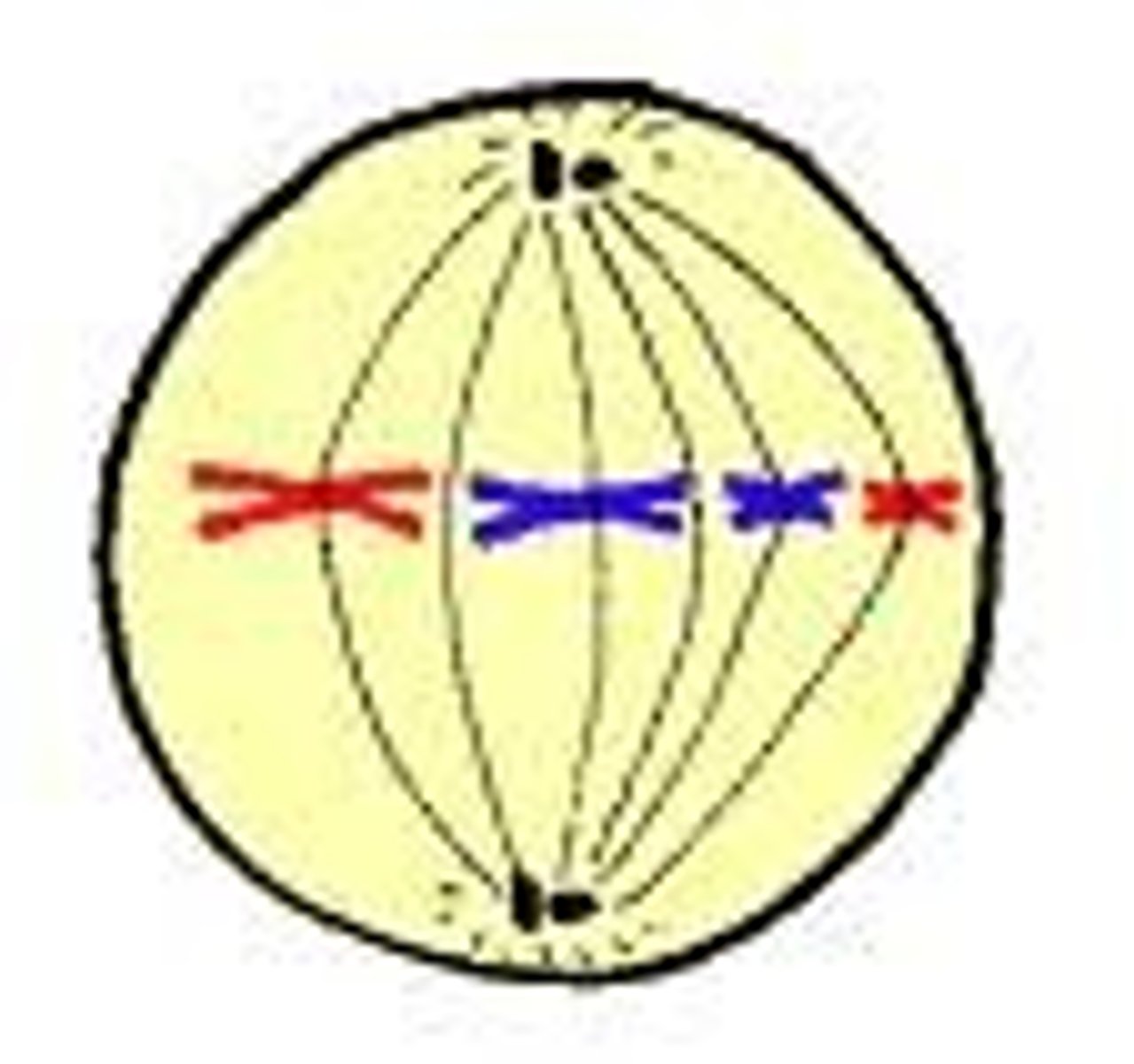
Anaphase
the third phase of mitosis, during which the chromosome pairs separate and move toward opposite poles
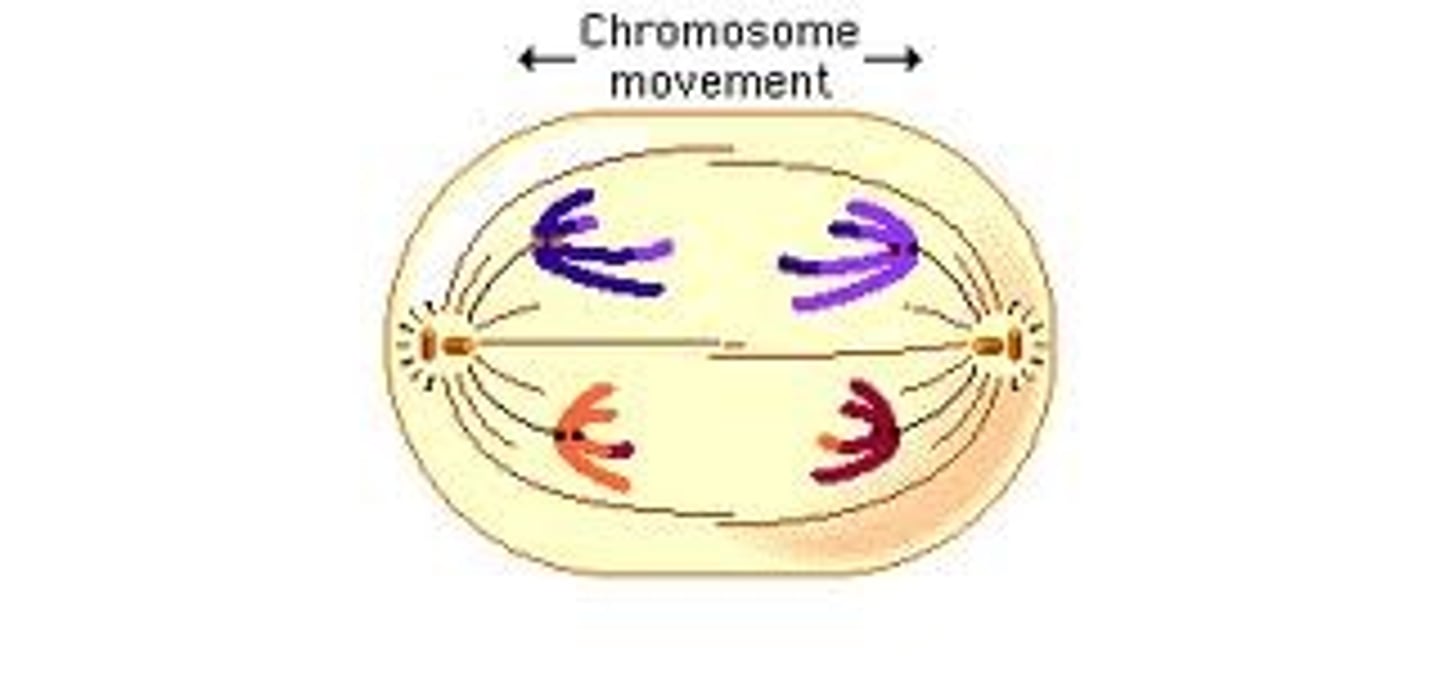
Telophase
the final phase of cell division, between anaphase and interphase, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed.
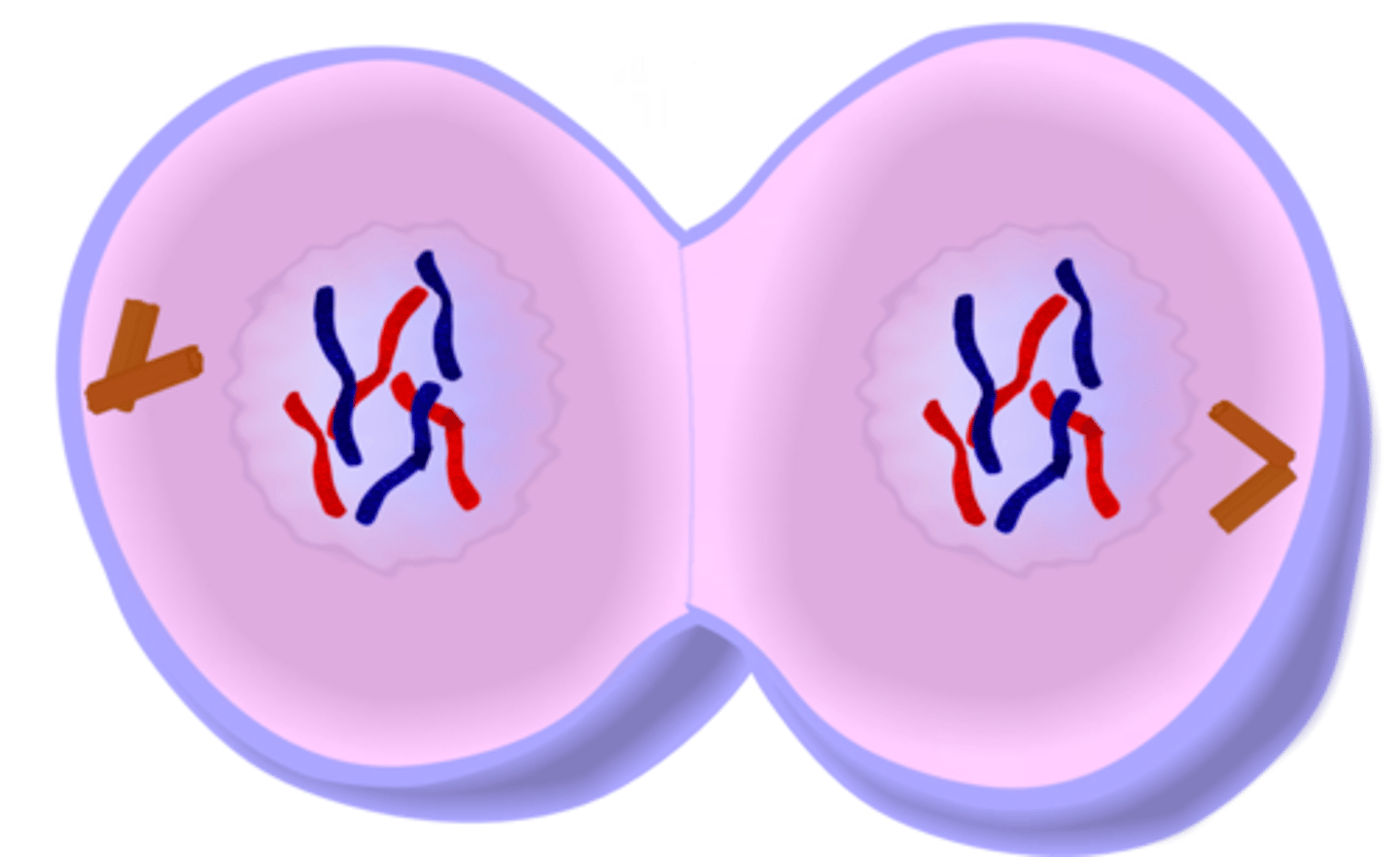
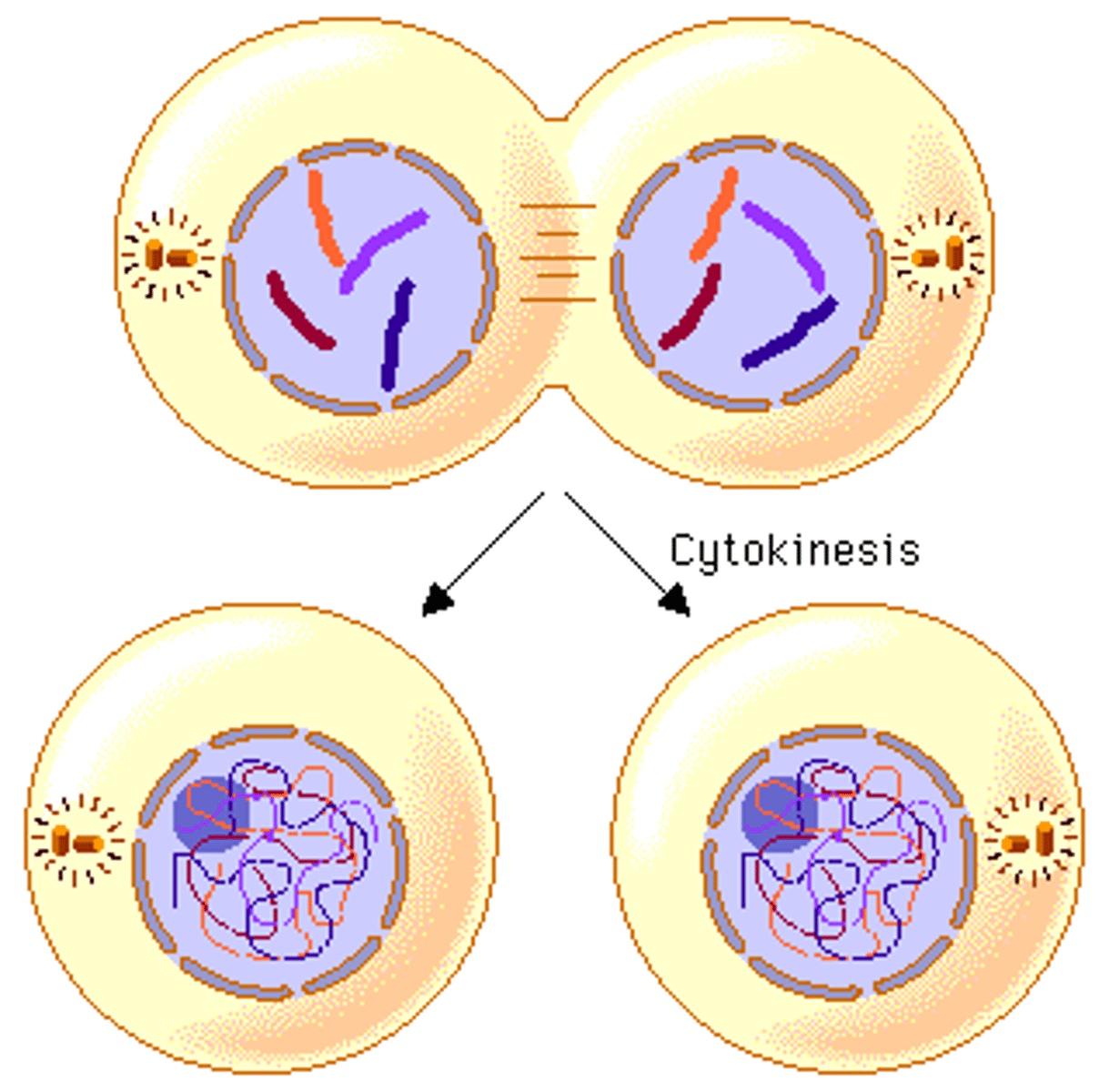
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division
Chromosome
A threadlike, gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus. Each chromosome consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins.
Chromatid
one of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome
Homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that have the same sequence of genes and the same structure