CHEM2313 Lecture 5: Molecular Orbital Theory; Functional Groups
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary from CHEM2313 Lecture 5, focusing on Molecular Orbital Theory and Functional Groups.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Node
A region in a wave function where ² = 0, meaning there is zero probability of finding an electron, and the phase of the wavefunction always changes across it.
Constructive Interference
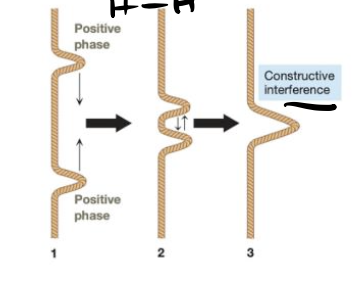
Combination of in-phase waves (atomic orbitals), leading to an increase in electron density between the nuclei and resulting in a bonding molecular orbital.
Deconstructive Interference
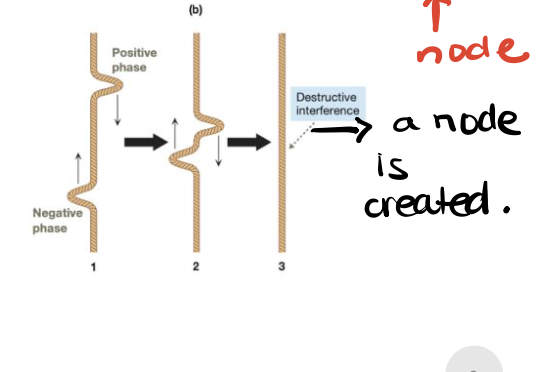
Combination of out-of-phase waves (atomic orbitals), creating a node (region of zero electron density) between the nuclei and resulting in an antibonding molecular orbital.
Bonding Molecular Orbital
A molecular orbital that is lower in energy than the contributing atomic/hybridized orbitals, has no new nodes along the bonding axis, and has high electron density between the nuclei.
Antibonding Molecular Orbital
A molecular orbital that is higher in energy than the contributing atomic/hybridized orbitals, has a new node along the bonding axis, and has low electron density between the nuclei.
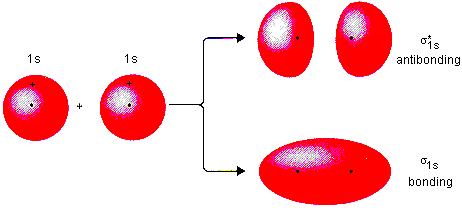
Sigma (σ) Bonding Molecular Orbital
A bonding molecular orbital formed by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals, resulting in electron density along the internuclear axis, and lower in energy than its antibonding counterpart.
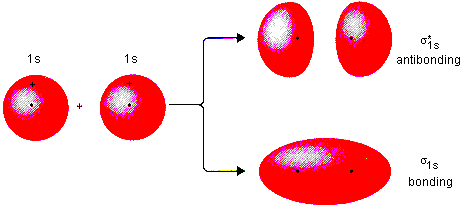
Sigma (σ*) Antibonding Molecular Orbital
An antibonding molecular orbital formed from sigma overlap, which is higher in energy than the atomic orbitals and has a node along the bonding axis.
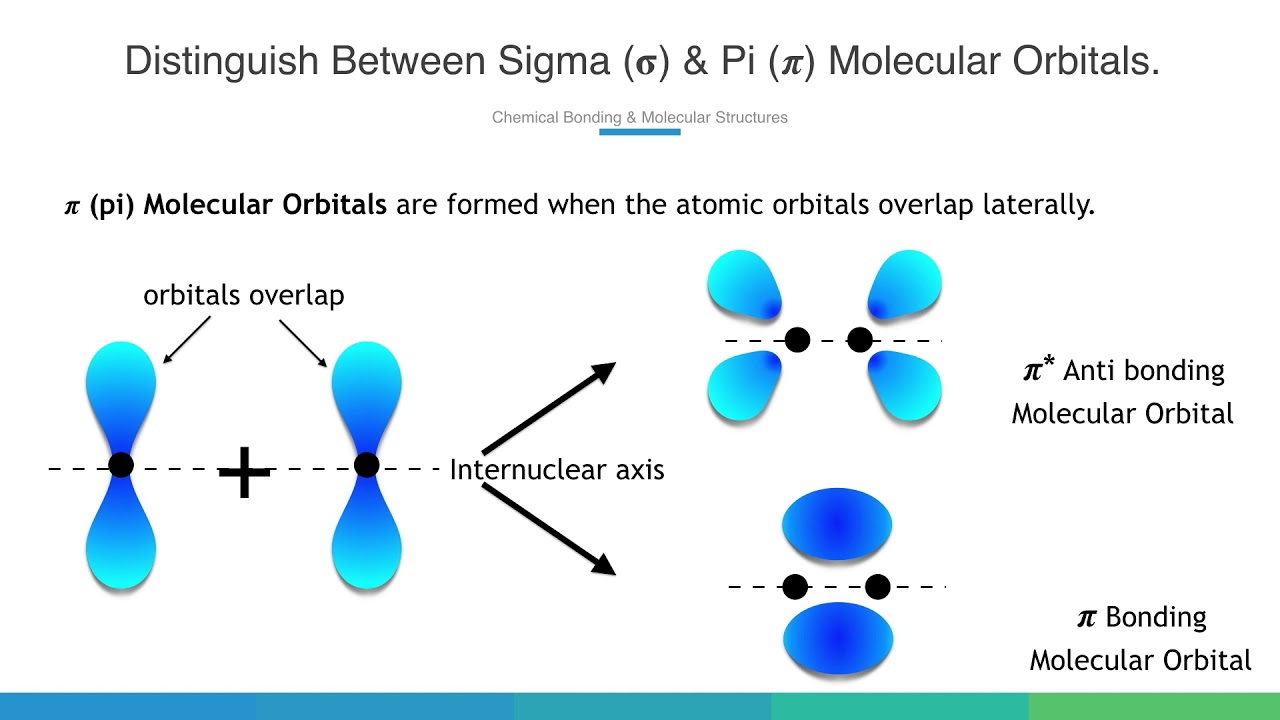
Pi (π) Bonding Molecular Orbital
A bonding molecular orbital formed by the side-to-side overlap of p-orbitals, with electron density above and below the internuclear axis, and generally less stable (higher energy) than sigma bonding MOs.
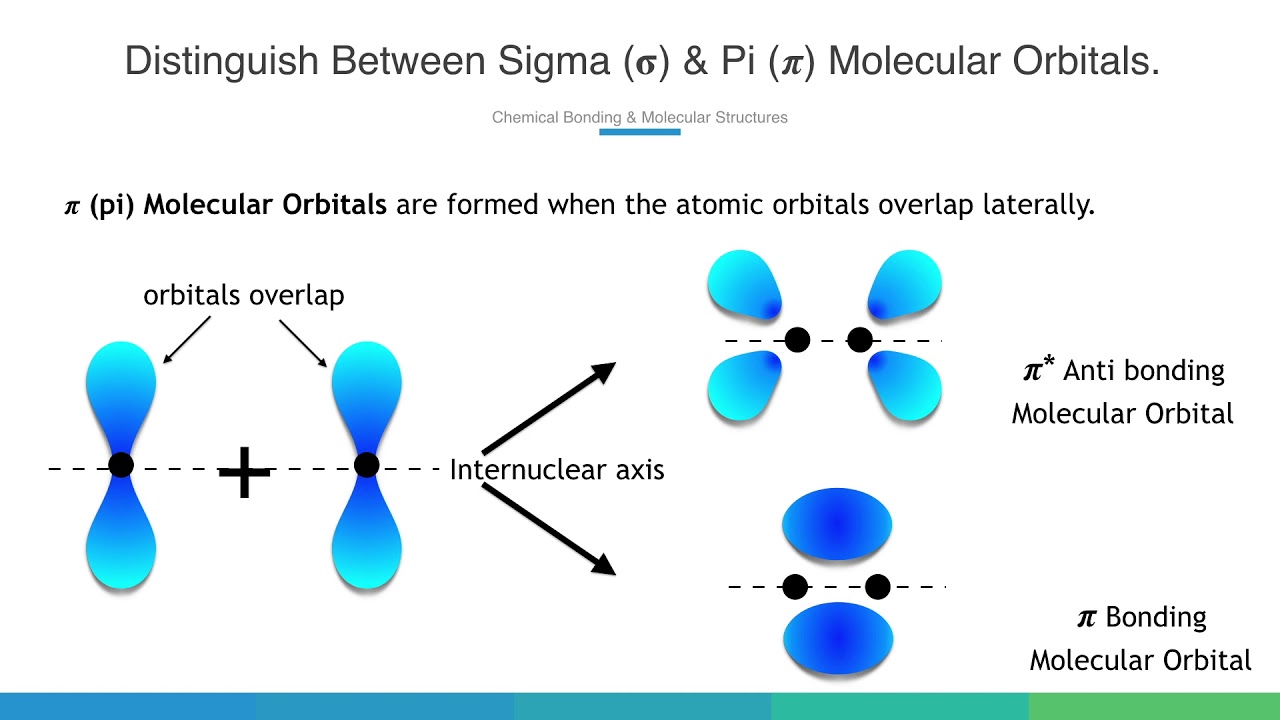
Pi (π*) Antibonding Molecular Orbital
An antibonding molecular orbital formed from pi overlap, which is higher in energy than the atomic orbitals and has a new node perpendicular to the bonding axis in addition to the original nodal plane.
Non-bonding (nb) Hybridized Orbitals
Hybridized orbitals that hold lone pairs and whose energy does not change when considered in a molecular orbital diagram.
HOMO
Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital; the molecular orbital with the highest energy that contains electrons.
LUMO
Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital; the molecular orbital with the lowest energy that does not contain electrons.
Functional Group
Common groupings of atoms within a molecule that have predictable chemical and physical properties.
Alkenes
Unsaturated hydrocarbon functional groups containing a carbon-carbon double bond, with each pi bond representing one degree of unsaturation.
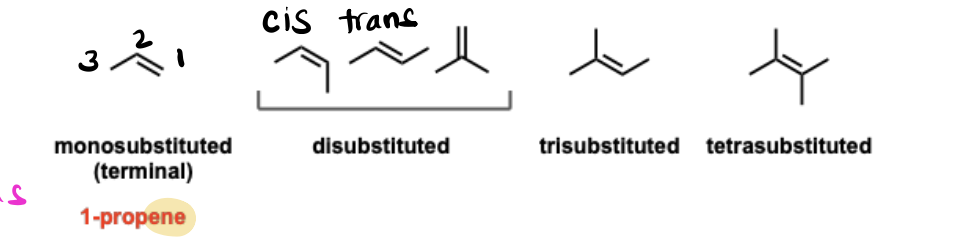
Alkenes (Cis/Trans Isomers)
Geometric isomers of alkenes that cannot be interconverted by rotation of the pi bond due to its restricted rotation, making them different molecules.
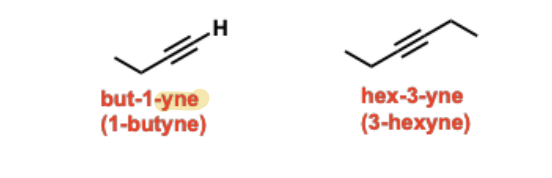
Alkynes
Unsaturated hydrocarbon functional groups containing a carbon-carbon triple bond, which are linear in geometry and have two degrees of unsaturation.
Arenes
Unsaturated hydrocarbon functional groups containing a ring of alternating single and double bonds (fully conjugated), often with 6 pi electrons, exhibiting special stability due to resonance and proportionality.
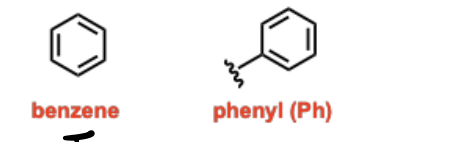
Alkyl Halides
Alkanes substituted with a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I), named using a halo prefix (e.g., fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo) in IUPAC nomenclature.
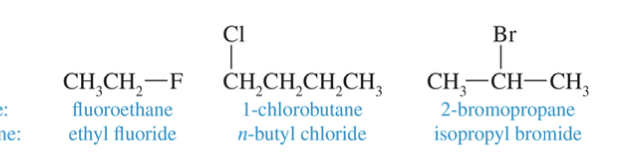
Primary (1º) Alkyl Halide
An alkyl halide where the carbon bearing the halogen is bonded to only one other carbon atom.

Secondary (2º) Alkyl Halide
An alkyl halide where the carbon bearing the halogen is bonded to two other carbon atoms.

Tertiary (3º) Alkyl Halide
An alkyl halide where the carbon bearing the halogen is bonded to three other carbon atoms.

WAVEFUNCTION (ψ)
A mathematical description of an orbital, representing the shape of the wave as it vibrates, often depicted with different shading for its two phases (+ or -).
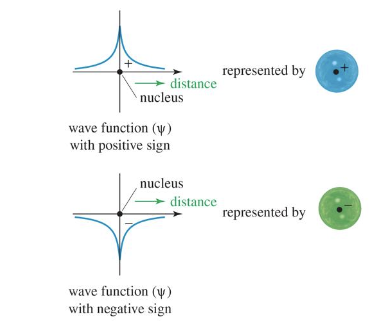
WAVEFUNCTION SQUARED (ψ²)
Represents the electron density at any given point in an orbital.