BIOL 325 GENE MUTATIONS STUDY GUIDE
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
what is the typical way to write genes? what would be in front of it?
3 lowercase letters, italicized
in front = proteins in a capitalized letter
ex. leuA
what does a + mean in mutant nomenclature? what about a - ? what if none are used?
+ symbol after gene = wild type
- symbol after gene = mutant
none used = mutant
what do the ts, cs, and R subscripts mean?
ts = temperature sensitive
cs = cold sensitive
R = resistance (RisR)
has resistance to it
what does Δ, - or :, ::, Ω mean?
Δ = deletion in a gene and occurs before the gene
- or : = fusion between two genes (leuA-lacZ or leuA:lacZ)
:: = insertion (leuA::Tn10)
Ω = genetic constructure introduced by a two-point crossover (ΩleuA)
what is Δdeleted gene::replacing gene?
deletion w replacement —> gene has been deleted and replaced by another gene
what can detect big chromosomal differences and what are those differences?
FISH can detect BIG chromosomal differences
deletions, translocation, duplication, inversions
what is sickle cell anemia?
hemoglobin beta subunit has sickle cell (Hgb5)
is due to a single DNA mutation that results in a single amino acid substitution
cannot be picked up by a chromosomal assay because it is too small
most common single nucleotide polymorphism (A to T) of the beta-globin gene, results in glutamic acid (E/Glu) being substituted by valine (V/Val) at position 6
allele’s locus is 11p15.5
what is cystic fibrosis?
a small scale deletion where three nucleotides are deleted to remove one amino acid, F (phenylalanine) at 508/1480 aa in CF transmembrane conductance regulator protein
CFTR ΔF508
1500 alleles
7q31.2
hard to cure because you can fix one mutation but another one can pop-up
what is the frequency and mutation of the 5 deletions and substitutions?
mutation = ΔF508
frequency = 66%-70%
mutation = G542X
frequency = 2.4%
mutation = G551D
frequency = 1.6%
mutation = N1303K, W1282X
frequency = 1.3% each
all others = 27.5%
what are point mutations?
gene mutations involving one or few base pairs and cannot be detected by cytogenetic (FISH or G-bands) methods
detected at the DNA sequence level
what is the SNP nomenclature for DNA?
base sequence at front then the original base after with an arrow to the replacement base
5162 (base sequence) G (original) —> A (replacement)
5162G→A
deletion = 197delAG
insertion = 2552insT
what is the SNP nomenclature for amino acids?
original amino acid in front then amino acid position then the replacement amino acid
R (original AA) 197 (amino acid position) G (replacement)
R197G
what do you have to look at for amino acid mutations?
look at R group to predict severity of mutations
mutate non polar R group with non polar = no effect
mutate + charge R group to polar R group = CAN affect protein function
mutate NP + P = absolutely will affect protein function
list the various types of point mutations and their effects on the DNA sequence and phenotypes (written response question)
silent = point mutation that codes for the same protein and is in the third position/third base of codon. the silent mutation does not affect the phenotype of an individual.
nonsense = introduces early stop codon and is in the first position/first base of the codon. since the nonsense mutation terminates a sequence early with the stop codon, the protein becomes shorter and potentially lose its function.
missense = misplaces one amino acid and always codes for a different protein and has two categories
conservative = places a new amino acid that has the same chemistry and does not affect the folding of a protein, resulting in little to no changes in phenotype.
non-conservative = places a new amino acid that has a completely different chemistry and affects the folding of a protein. non-conservative mutations can lead to diseases like sickle cell anemia
how common are polymorphisms? how do they affect phenotypes? (written response question)
polymorphism are quite common with SNP’s being the most common. there are millions of SNPs and a majority of them do not affect phenotypes but some SNPs can cause a change in protein function and gene expression. some SNPs also cause disease like sickle cell anemia and cystic fibrosis.
what is in genetics?
the balance between neutral mutations, purifying selection, and beneficial mutation can help uncover a protein-coding gene
if an area has more synonymous mutations than nonsynonymous, it suggests the area encodes a protein and nonsynonymous deleterious mutations have been removed by purifying selection
what is antigen retrieval?
epitope is hidden (not to the antibody but to the researcher) so it is when an epitope is exposed so the antibody of interest can bind to it
name and describe an immunoassay that can be used to detect aberrant proteins (written response question)
One immunoassay that can detect aberrant proteins is immunohistochemistry. Immunohistochemistry can detect aberrant proteins by utilizing a primary and secondary antibody conjugated with an enzyme which will indicate the target proteins’ presence. Immunohistochemistry can detect the aberrant protein estrogen receptor for breast cancer, TP53, and BRCA1 in tumors.
what is HPLC? what is liquid chromatography?
high performance liquid chromatography
separate molecules based on polarity, charge, and size
separates and identifies molecules based on their migration through various solvents and matrices
is an expensive piece of equipment that can be easily messed up because it is tedious
liquid chromatography = sample/analyte is in liquid from and is moved through a column using a liquid
how do you read the chart in HPLC?
time of retention is on the x axis in minutes and the peaks in the chart/area under the peak is how much of the protein there is
what is denaturing HPLC used for and how does it separate molecules? (written response question)
Denaturing HPLC is used for finding polymorphisms in DNA. It separates molecules through their heteroduplexes. Denaturing HPLC isolates DNA from a polymorphic sample and PCR amplifies it. The DNA is denatured to single-stranded stranded and since it is polymorphic, some of the fragments will adhere to the same one, and some will adhere to a polymorphic sequence that is different, creating a heteroduplex. The denatured sample will be injected into an HPLC, and the heteroduplexes will come off the chromatography complex first since it is less stable.
what is gas chromatography?
automated and is coupled with MS to detect disease biomarkers
analytes have to be converted into a vapor/gas
what is mass spectrometry?
converts molecules to ions and separates based off mass to charge ratio (how big to how - charge or + charge)
analyzes and separates a big mixture like liquid chromatography however it is a bit more sensitive because another parameter is used to separate protein mixture
often coupled with HPLC or GC
what can mass spec analyze? (6 things)
drug testing and discovery
food contamination detection
pesticide residue analysis
isotope ratio determination
protein ID
carbon dating
what is the application of pre-analytical analysis for mass spec in clinical diagnostics?
barcode printing
phlebotomy
transportation
forensics
drug of abuse
blood and urine analysis
biopharmaceuticals
antibody drugs
protein and glycan analysis
what is the application of analytical in mass spec for clinical diagnostics?
barcode scanning
sample prep
analysis
environment
water and soil analysis
persistent organic pollutants
pharmaceuticals
phospholipid profiling
chiral drugs analysis
bioanalysis
what is the application of post-analysis for mass spec in clinical diagnostics?
results to HIS
verification
action
food and beverage
pesticide residues
food additives and sweetners
veterinary drugs
industrial
textile testing
industrial discharge
what is matrix assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI)?
powerful tool for analysis of peptides and proteins
soft ionization technique that utilizes an energy absorbing matrix to aid in analyte detection
ionization is triggered by a laser beam (normally nitrogen laser)
what is the process for MALDI?
a sample is added to the matrix (column with a bunch of beads), a laser will hit it and desorption (to come off) will happen
sample gets desorbed because of the laser and the matrix will surround the sample as it gets desorbed
matrix will then break down the desorbed product into ionized forms and will be ran through a mass analyzer
ionized form is ran through a column and will come off at different times (retention time) and researcher will count the peaks to see what the initial analyte is and how much of it there was
why do MALDI?
do it when analyte is big because if the analyte is hit with something harsh, it will be fragmented unpredictably
what is MALDI-TOF (time of flight)?
determines when it flies off the matrix (like retention time)
in MALDI-TOF-MS, the ion source is matrix assisted laser desorption ionization and the mass analyzer is the TOF analyzer
why is MALDI-TOF used with MS?
analyzes large bio/organic molecules, which tend to be fragile and fragment when ionized by conventional methods
how are mass spec and MALDI used diagnostically? (written response question)
Mass spectrometry is used diagnostically to analyze any class of molecule. Mass spectrometry can detect food contamination, determine isotope ratio, analyze pesticide residue, identify protein and carbon date, and be used for drug testing and discovery.
MALDI is used diagnostically for the early identification of bacteria in clinical specimens such as blood culture, UTIs, cerebrospinal fluids, respiratory tract infections, and stool samples.
what is “classical” mutation analysis?
inherited mutations found in buccal cells or blood
somatic mutations (cancer) are more difficult
what are the interpretation problems for nucleic acid analyses?
is mutation silent, conservative, or nonconservative?
is mutation found responsible for phenotype?
is phenotype due to previously uncharacterized mutant in known gene?
what is single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP)?
hybridization based assay
scans for several hundred base pairs
looks for unknown or unexpected mutations in a large region
based on intrastrand folding
strands will fold based on sequence and a single mutation will affect the folding of it
folded single strands (conformers) can be resolved by size and shape
what is the process to detect SSCP?
start with separating DNA from whatever specimen and let it denature and cool to allow the long strand to fold into a secondary structure
long strand with a single nucleotide difference between two strands will fold slightly different
folded strands with a wild type or mutation can be resolved through capillary gel electrophoresis or PAGE
PAGE bands are detected through silver staining
must have a control
what does a wild type, mutant, and heterozygous mutant look in CGE with SSCP?
wild type has sharp peaks
homozygous mutant has peaks in different locations than the wild type locations
heterozygous mutants have peaks in the wild type locations and the mutant locations
what does a wild type, mutant, and heterozygous mutant look in PAGE with SSCP?
wild type bands will be at a specific position(s) in the gel
mutant bands will be at different positions in the gel than the wild type bands
heterozygous mutant bands will be at the wild type bands and the mutant bands locations
what is the real world application for SSCP?
took lots of specimens from 5 different chinese ethnic population and looked for their SNPs
the stem in the ssDNA is what the SNP was
results suggested that microhaplotype could be more useful as personal ID than SNPS
could be ancestry identifying marker and applied to kinship ID
what is allele-specific oligonucleotide hybridization (ASO)?
a reverse dot blot method
specimen in solution is spotted on nitrocellulose
labeled oligonucleotide probe is hybridized to immobilized specimen
relies on binding effects of nucleotide mismatches
the probe can be tagged with enzymes or colorimetric
cheap and excellent
has been applied to HLA typing which is often replaced by microarray and next gen sequencing
what is the process of allele-specific oligonucleotide hybridization (ASO)
three specimens are spotted on duplicate membranes
one membrane is exposed to probe complementary to normal (+ probe) and other membrane is exposed to a complementary probe to mutant (- probe)
+ probe = will be positive in heterozygous (+/-) and positive in wild type (+/+) and negative in homozygous mutant (-/-)
- probe = will be positive in heterozygous (+/-) and positive in homozygous mutant (-/-) but negative in wild type (+/+)
how was sickle cell tested in allele specific oligonucleotide (ASO)?
commonly done in Africa and is done quickly
6 patients were tested for sickle cell (A for wild type and S for sickle)
the dots in 2 and 6 have sickle cell dises
3 and 5 are sickle cell carriers
sickle cell is caused by recessive allele so individual needs to inherit both allele to have sickle cell disease
the sickle cell carriers have a survival advantage by being protected against malaria and sickle cell disease
what is heteroduplex analysis? what are the ways to resolve heteroduplex?
method of detecting sequence differences between normal DNA and the DNA to be tested
common screening method to detect potential mutations in a gene
can be resolved through:
gel electrophoresis (HIV and hematological typing)
denaturing HPLC
melt curve analysis
array technology
what is the process for heteroduplex analysis?
in a tissue, some will be wild type and some will be mutant
in this analysis, one should be able to guess where the WT and mutant are because PCR is used to create a product/amplicon where the mutation is right in the middle
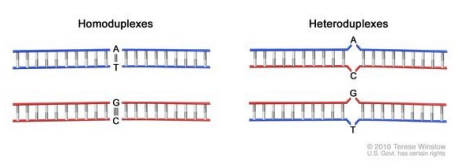
what is melt curve analysis?
post amplification step of real time PCR
based on sequence effect of melting temperature (Tm)
one base in a sequence would change the melting temperature
uses/requires double-stranded DNA-specific dyes which are intercalating agents
SybrGreen
Ethidium Bromide
also performed with FRET probes
can detect epigenetic changes
what would the graph look like in a melt curve analysis with heterozygous, wild type, and homozygous mutant?
when the DS-DNA specific dyes intercalate with the DNA it will be at 100% fluorescence but as it denatures, there will be a loss in florescence since it is going to single stranded
in a homozygous mutant = curve will start to lose its fluorescence and turn into single stranded DNA at a cooler Tm
in a wild type/normal = curve will start to lose its fluorescence and turn into ssDNA at a hotter Tm
in a heterozygous mutant = curve will mimic both the wild type and homozygous mutant
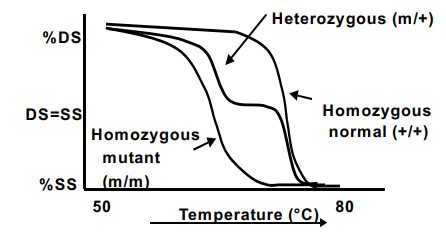
what does the melt curve for normal and heterozygous mutant look like when detected by an instrument software?
detection instrument software can convert the melt curve to a derivative of fluorescence (speed of drop vs. temperature)
all the sample is heated all the way to observe peaks
wild type has big peak at a warmer Tm because it is homozygous
heterozygous mutant = early peak at a cooler temp and the same peak at wild type peak
what is array technology?
reverse dot blot methods
used to investigate multiple genomic sites simultaneously
unlabeled probes are immobilized on substrate
specimen DNA is labeled and hybridized to immobilized probes
what is macroarray? what is the substrate for macroarray and how is it detected?
not common because not a lot of target is probed on it
substrate = nitrocellulose
detection = radioactive, chemiluminescence, chromogenic
what is the substrate for microarray/high-density oligonucleotide array and how is it detected?
substrate = glass, nitrocellulose
detection = fluorescent
what is the substrate for microelectric arrays and how is it detected?
substrate = electrode grid (newer technology and is kind of like computer chip)
detection = fluorescent
what is the array for comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) and what is its application?
array = micro, macroarray
application = detection of genomic amplification/deletions
what is the array for expression array and what is its application?
array = micro, macroarray
application = detection of changes in gene expression
what is the array for SNP detection, mutation analysis, and sequencing and what is its application?
array = high density oligonucleotide
application = detection of single-base differences in DNA
what is high-density oligonucleotide array?
examines thousands of genes simultaneously
take one persons tissues and analyze thousands of genes simultaneously
done on something the size of a glass slide and robot makes the array
unlabeled probes are synthesized on the substrate
every dot is a different probe to a different gene
what is the process for high-density oligonucleotide array?
isolate the gDNA or transcriptome from sample and fragment into manageable sizes
take all the isolated DNA and hybridize on the slide and let the targets hybridize with the probes
test DNA is fragmented before hybridization
needs a new array for each sample
fragments bind specifically to complementary sequences on the array
what is tiling for high-density oligonucleotide arrays? what is affymetrix human SNP 5.0 GeneChip?
overlapping probe sequences
is used to blanket detection of nucleotide changes in the sample
genome-wide assay that can genotype over 500,000 human SNPs
since high-density oligonucleotide arrays do not scan entire genome, what scans the contiguous sequences? what does the IP mean?
uses overlapping probes
ChIP-chip = discovers DNA protein interactions
MeDIP-chip = uncovers methylation
DNase Chip = DNAse sensitivity
Maps transcripts to genome
IP = immuno precipitate (ppt)
how is high density oligonucleotide arrays detected? what happens if trying to detect an SNP through this array?
detected through fluorescence where the fluorescent signal indicates which sample hybridized DNA to probe
detected, normalized, and averaged by array readers and software
nucleotides will be fluorescently tagged with different colors since the DNA is tagged
if trying to detect SNP
waste 5 spots for 5 labelled probes for the 5 test samples on the chip
graph will represent each probe from sample, each carrying the indicated base of deletion at the same position
5 probes only differ at that SNP and must be in different colors
what is a DNA microarray? what is the process for DNA microarray?
can analyze 100-1000 of DNA fragments
similar to CGH
process:
isolate healthy cells and cancerous cells
looks at gene expression
convert the isolated mRNA into cDNA then have microarray with probes already on it
cDNA from cancerous/diseased cell = tagged with red
cDNA from normal/wild type = tagged with green
what do the red, green, yellow, and grey dots mean in DNA microarray?
red = overexpressed
green = overexpressed in normal but underexpressed in diseased/cancer cell
yellow = both wild type DNA and cancerous DNA expressed in that gene
NOT GOOD
grey = not present in both cells (nothing bound to it)
what is DNase chip? why is it done? what are the sites?
identifies DNA that is readily cleaved by DNase1
DNase 1 cuts exposed DNA (euchromatin)
done because we do not know everything about our genome/don’t know what DNA is readily avaliable
if it is accessible = possible a coding sequence
sites are often promoters, enhancer, or silencer (control) regions
what is DNase1 cleavage a sign of?
a sign that it is an important region that will eventually turn into a protein
if patient sample does not cut at that site their DNA structure has changed → changed structure of protein that is necessary in that patient
what is a MeDIP-chip (methyl DNA immunoppt)?
looks for methylated DNA changes and is done more frequently
5-methyl-cytosine is where our DNA gets methylated
5th position of cytosine is where some of the cytosine bases get methylated (silenced)
mapping the methylated sequences in the genome called the “methylome”
necessary to describe epigenetic effects
what is the process for MeDIP-chip? why should unmethylated and methylated DNA be tested on an array?
there is an antibody to 5-methyl-cytosine so when DNA is fragmented and there is methylated DNA, it will put out of the sample
separates methylated DNA from unmethylated DNA with the antibody
use methylated DNA on the microarray and make all probes to different sequences to know if they are methylated or not
know methylated DNA is added to the chip then it is picking up methylated targets
better to do the experiment in reverse to see if unmethylated DNA binds to the assay
do both if you have negative on one and positive on the other to confirm if you have a methylated target
what is a transcriptome and its meaning? what is transcriptome mapping?
transcriptome = the sum of the mRNA expressed in a gene in an organism
meaning = working with mRNA and converting it to cDNA into a microarray
compare normal tissue to adjacent cancerous tissue and both get cDNA
normal tissue gets tagged with green and cancerous tissue gets tagged with red and both are spotted on the arrays
what do the red and green spots mean in transcriptome mapping? why isn’t there a yellow spot?
green = high in control DNA and low in experimental DNA
red = high in experimental DNA than control
doesn’t have yellow because it isn’t comparative on the same assay
separate array for red and green then overlapped
what is microarray barcoding?
only have two colors and is not a quantitative assay
yes or no assay
output is binary denoting which genes are estimated to be expressed (one) and not expressed (zero)
gene expression barcode
what is the cancer genome atlas (TCGA)?
landmark genomics program that molecularly characterized over 20,000 primary cancer and matched normal samples spanning 33 cancer types
was a joint effort between NCI and NHGR beginning in 2006
by 2018, 2.5 petabytes of genomic, epigenomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic data was generated
looked at aneuploidy, DNA hypermethylation, mRNA, microRNA, and protein
still going through TCGA information and individual research labs are mining the data and looking at it
what is sequence-specific primer PCR (SSP-PCR)?
polymerization based method for mutations
only works with SNPS or small mutations like sickle cell or BRCA1
can aid in distinguishing known alleles
generation of PCR product indicates the presence of mutation or polymorphism in the template
not expensive and not usually ran on agarose gels —> usually ran on qPCR or capillary gels
what is the primer design for SSP-PCR? what is the important part of the primer design?
end of primer are designed at the spot of the mutation
want something that just amplifies around the whole mutation
want to have good quality DNA so there are control parameters
important part = the 3’ position of the primer must be AT the location of the mutation due to the 3’ clamp
the 3’ clamp must be bound to keep the primer anneal because if it is not 100% homologous to its complementary sequence, it will come off
how did SSP-PCR detect BRCA1’s deletion?
mutation in Exon 3 inactivates the BRCA1 DNA repair enzyme
looked at it on a gel and the 180 bp band indicated the presence of the BRCA1 mutation
what is allele specific qPCR?
looks to see if an individual has wild type or a mutation through qPCR
use plasmid with one copy of wild type, one copy of mutant, and include standards (number of copies)
if a threshold cycle isn’t seen until 40 cycles, it is a bad primer set and needs to be designed better
when doing two charts, the wild type and mutant must be at the same location and threshold cycle
detects more accurately than sequencing mutant allele frequency of <10%
what is BRAF and how was allele specific qPCR used for it? what does a low threshold mean?
BRAF = gene that causes cells to grow
BRAF is a common mutation that causes a lot of different cancers like colorectal, lung, leukemia, thyroid, and melanoma
there are a lot of therapies that target BRAF so it is a quick test that is always done
a plasmid was used with one copy of wild type, one mutant BRAF as standards
the wild type was at a threshold of 25 and mutant at a threshold of 30
lower the threshold cycle = more target and as it gets higher = less target
what is allelic discrimination?
discriminates against two alleles
best but expensive
uses fluorescently labeled probes and is similar to taqman
generates color signal for mutant or normal sequence
performed on real time PCR instruments
how does allelic discrimination work?
primers that amplify sequence of interest and between those is a probe that anneals to the same sequence of interest
probe is green for normal and red for mutant and has a fluorophore on one end and a quencher on the other end
as polymerase synthesizes, it has exonuclease activity to chew off the fluorophore to release it to produce a color signal
if the probe did not bind to the sequence, there is not way to separate the fluorophore from the quencher
what dye is labeled to the probe for the normal sequence in allelic discrimination? what about the mutant sequence?
normal = FAM fluorescent dye
mutant = VIC fluroescent dye
what is the use of molecular probes for allelic discrimination?
molecular beacon has a stem loop formation where the fluorophore is silenced by the quencher since they are sat close together
molecular beacon binds to normal or mutant = fluorophore will produce different color sequences because it is far enough from the quencher to fluoresce
if both of the molecular beacon probes bind = heterozygous mutant
signals are detected and analyzed by the instrument software and multiple samples are analyzed simultaneously
what is restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) for cleavage based methods?
restriction enzyme site recognition detects sequence changes
if there is a restriction enzyme site at the site of the mutation, the mutation destroys the restriction enzyme site and it won’t cut
can be resolved on an agarose gel
normal sequence = it will have one band for cut and uncut because it does not have the same sequence as the mutant
mutant sequence = it will have two bands in the cut section because it cut and one band in the uncut section
heterozygous sequence = one allele doesn’t cut and the other allele does —> looks like a fusion between mutant and wild type
what is heteroduplex analysis with single strand specific nucleases?
cleavage based assay
uses nucleases that cut ss bubbles in heteroduplexes
observed by gel electrophoresis or electron microscope
widely used for rapid screening of the 3 bp deletion in cystic fibrosis
what is the process for heteroduplex analysis with single-strand specific nucleases?
PCR amplify region of interest
PCR products denatured and renatured with or without added normal PCR product
some strands will reanneal with themselves but some strands will reanneal with a different sequence (wt + mut) to make a heteroduplex with one nucleotide difference in the middle
the bubble in the duplex is recognizable by S1 nuclease and will cut at the single strand disturbance
what is cleavage (invader) assay?
uses two oligonucleotide probes that hybridize to the single-stranded target and form an overlapping invader structure at the SNP site
tests for only one SNP
mutation is detected with a proprietary cleavase enzyme
enzyme cleavage of probe-test sample hybrids yield fluorescent signal
signal will only occur if probe/test sequence are complementary
what is the process for cleavage (invader) assay?
invader oligo binds to the target and does not come off and the other probe that is more complementary to the target has an overhang that is not complementary
if probe that was designed is complementary to the target it will anneal and so will the invader oligonucleotide (triplex)
due to cleavage of the arm, it is released and will fluoresce because it is far enough away from the quencher on the probe
if one of the two oligo’s anneal but not the third, it means that it is not complementary and will not fluoresce because there is not cleavage of the arm
what is not done in CNV (copy number variants)? what is occasionally done?
does not do sequencing, only does FISH and CGH
sometimes next gen is used but FISH and CGH is most common
list and understand the philosophy behind the mutations detection assays discussed in class. this includes hybridization based, sequence, and cleavage based methods (written response question; part A)
a) hybridization based
Single-strand conformation polymorphism is a hybridization based method that detects unknown or unexpected mutations in a large region. This method is based on intra-strand folding, where a strand with an SNP will affect the folding of its original sequence and can be resolved through gel electrophoresis or capillary gel electrophoresis
Allele-specific oligonucleotide hybridization is a reverse assay where probes are on the dot blot first, and then the sample is added. In this method, the presence of wild-type, mutant, or heterozygous mutant is detected through different membranes and will present a color indicating a positive presence depending on the probe.
High-resolution melt is when a melt curve is used to detect the presence of wild type, mutant, or a heterozygous mutation through their different melting temperatures through qPCR. The different curves are detected through fluorescence and will lose fluorescence as the double-stranded DNA are denatured to single-stranded DNA.
list and understand the philosophy behind the mutations detection assays discussed in class. this includes hybridization based, sequence, and cleavage based methods (written response question; part B)
b) sequence
Whole genome sequencing is when a whole genome is sequenced by shearing the whole genome and using a computer to realign and overlap the sequenced fragments. Whole genome sequencing has two ways: shotgun and hierarchical sequencing.
Whole exome sequencing is when a whole exome is sequenced by targeting the coding regions of the genome.
Sequence Specific Primer PCR (SSP-PCR) is a polymerization-based method for mutations and only works for SNPs or small mutations. In this PCR, the 3’ ends of the primers are designed to be at the site of the mutation to be analyzed.
list and understand the philosophy behind the mutations detection assays discussed in class. this includes hybridization based, sequence, and cleavage based methods (written response question; part C)
c) cleavage based methods
Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) is a cleavage based method that uses restriction enzymes to identify different fragment patterns in mutated and normal/wild type DNA. The restriction enzymes will cut at specific sequences and can be resolved on a gel.
Nuclease cleavage assay that was discussed in class was heteroduplex analysis using single-stranded specific nucleases. In this cleveage based assay, PCR amplifies and denatures a sample and S1 nuclease cuts the one nucleotide difference in heteroduplexs or the “bubble”.
Another nuclease cleavage assay would be the cleavage (invader) assay. In this cleavage-based assay, two oligonucleotide probes will hybridize to a denatured target and form a triplex at the site of the SNP. A probe that is designed to be complementary to a target and the invader oligo will anneal and cause cleavage of the arm, allowing it to fluoresce.