Quotas Non-tariff Barriers
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Import Quota
government-imposed limits on the quantity or value of goods traded between countries.
Quotas are viewed as being more _____ than tariffs:
restrictive
international trade rules of WTO have long ______ quotas on most manufactured products
prohibited
Ex. Quotas on agricultural goods
Japan and Korea have imposed quotas on rice imports,
engaged in embargo but had not completely banned rice imports, but rather limited them through quotas
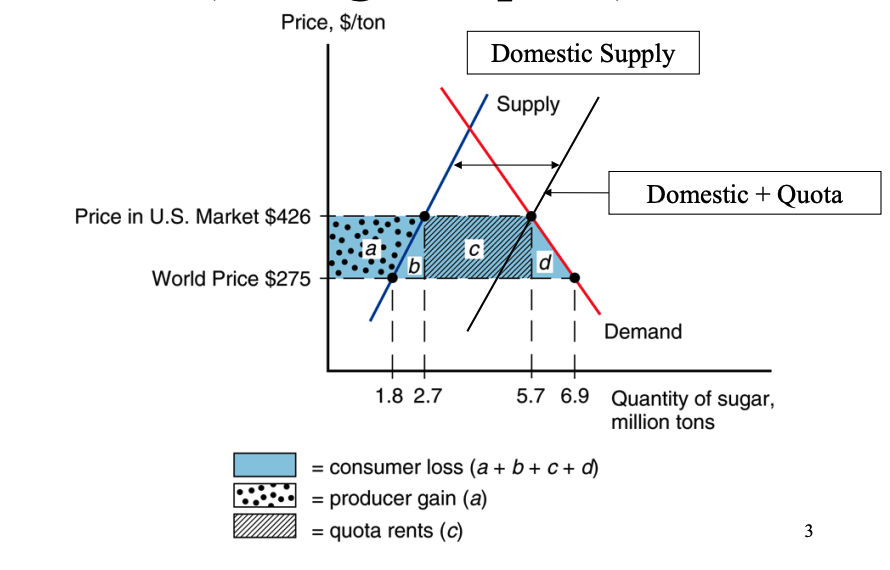
US Sugar Quota: Price Increase
By limiting the supply of imported sugar, the quota artificially reduces the overall supply in the domestic market.
This reduced supply leads to a higher equilibrium price for sugar.
In the case of the US sugar quota, the price increased from $275 to $426 per ton.
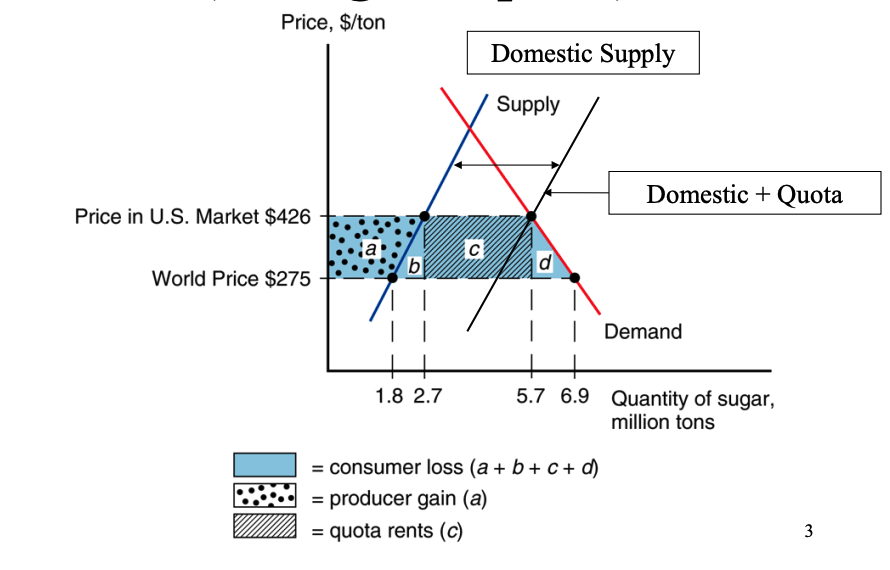
US Sugar Quota: Producer Surplus
Domestic sugar producers benefit from higher price.
They can produce and sell more sugar at a higher price, increasing their producer surplus.
This is represented by the area 'a' in the diagram.
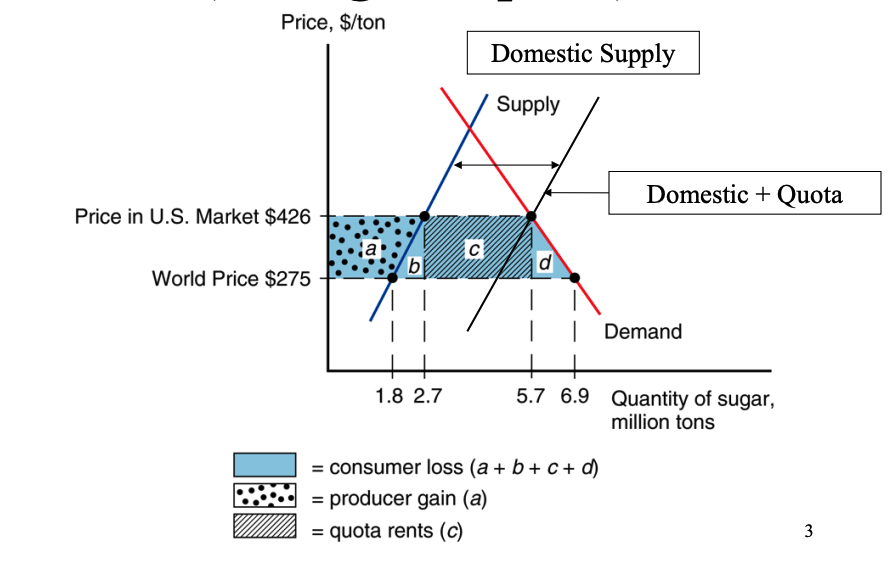
US Sugar Quota: Consumer Surplus
Consumers are worse off due to the higher price.
They consume less sugar and pay a higher price for each unit, reducing their consumer surplus.
This is represented by the areas 'a', 'b', 'c', and 'd' in the diagram.
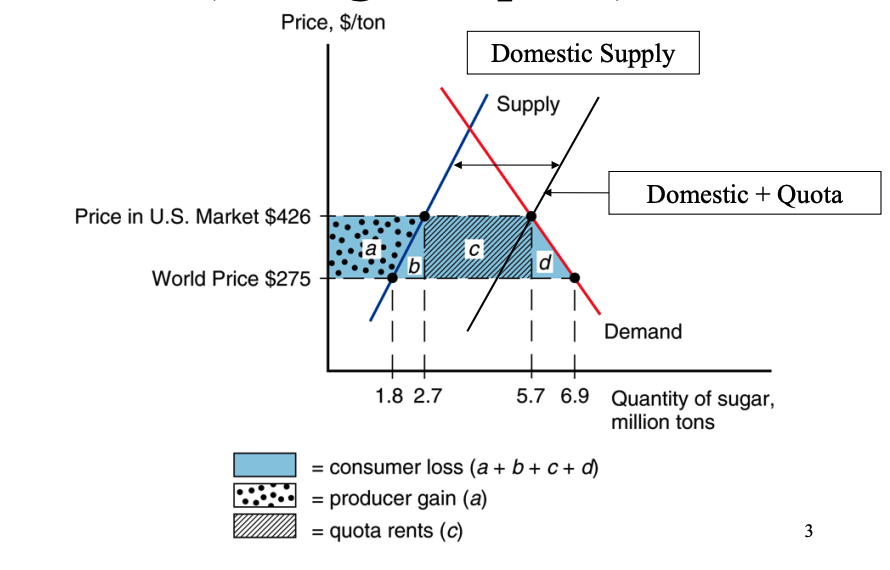
Quota Rent:
licenses are bought and sold, and difference between the world price and the domestic price is known as the quota rent.
This is represented by area 'c' in the diagram.
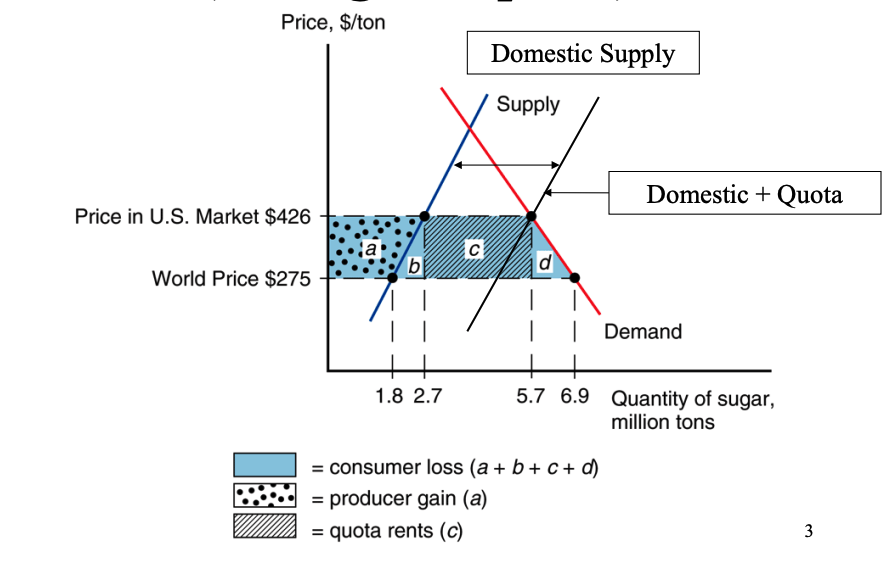
Deadweight Loss:
Quota leads to a loss of overall economic efficiency.
Areas 'b' and 'd' represent the deadweight loss, which is the net loss to society due to the quota.
Who gets Quota Rent:
Government, domestic producers, foreign exporters
Quota Rent: Government
government can competitively sell “import licenses” to companies
import license must be the difference between the free trade price and the price under the quota
Quota Rent: Domestic producers
US government imposed the quota on oil and quota rent was given to US oil producers in the 1960s
Quota Rent: Foreign exporters
Voluntary Export Restraint (VER). –Quota rent is additional profits for foreign exporters.
US-Japan Trade War
US pushes for Voluntary export restraint (VER) allowed Japan to maintain control over its exports and capture a significant portion of the quota rents.
Phased out under WTO
US-Japan Trade War (major consequences)
HIgher prices for japense cars for US consumers
higher prices reduced consumer surplus
Japanese car manufacturers benefited from the VER sell their limited number of cars at a higher price, increasing their profits.
US lost billions of dollars due to the VER, primarily in the form of higher consumer prices and lost economic efficiency.
Key Similarities in Quotas and tariffs
increase in the domestic price of the good
consumers reduce their consumption of the good
Domestic producers benefit from the higher price and increase their production.
differences in quotes versus tarriffs
Tariff: The government collects revenue from the tariff
Quota: quota rent, which is the difference between the world price and the domestic price, can accrue to various groups, including importers, government officials, or foreign producers.
Welfare Effects of tariff and quota
Both policies result in a deadweight loss to society, as the reduction in consumer surplus exceeds the increase in producer surplus - welfare changes are the same
Why quotas more restrictive than tariffs - domestic market expands
Tariff - raises imports, and the domestic price is constant
Quota - quantity of imports does not change, and the domestic price increases.
Why quotas more restrictive than tariffs - When the domestic market is monopolized
tariff - domestic firm can charge no more than the world price plus the tariff because the firm faces potential competition with foreign firm
quota - domestic firm can exploit its monopoly power because the firm knows that the competition is limited to a specific quantity of imports.