Biology 1406 Lecture Exam 3
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What is the purpose of photosynthesis
make sugar for cellular respiration
How does cellular respiration compare to photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the flip opposite of cellular respiration
Photoautotroph
self-feeding organism that uses light energy from the sun
some are prokaryotes
plants
some are protists
what do SOME protists and plant cells have when they are photoautotrophs?
Chloroplasts
what makes chloroplasts green?
chlorophyll
what is chlorophyll?
green pigment that captures light energy
What type of energy is light energy?
kinetic energy
what is light described and measured in?
wavelength
What is the main pigment for photosynthesis?
chlorophyll a
what are some "accessory" also present in many cells?
chlorophyll b
carotenoids
what are some functions of accessory pigments?
they absorb the same kinds of light as chlorophyll a to power photosynthesis
they are also a sunscreen to protect against damaging light.
What does light energy do to the pigment molecules?
IT EXCITES THEM!
what do excited electrons have more of when light energy excites them?
Chemical energy
so, excited electron =
POWER
6CO2 + 12H2O --> C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H20
change in G= 686 kilograms
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
highly endergonic
oxidation reduction reaction
Where does photosynthesis take place
Chloroplasts
light reaction part of photosynthesis
occurs in thylakoids
produces chemical energy from the to power the calvin cycle
has an electron carrier NADP+ which turns into NADPH when it has excited electrons
calvin cycle
occurs in stroma and is light dependent
produces sugar
powered by electrons and ATP from light reactions
what is the sugar that is produced by the clavin cycle
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Light reactions
1.) Linear electron flow
2.) 1st ETC
3.) Chemiosmosis
4.) ATP synthase
what is converted in the light reactions
H20---> O2
kinetic energy to chemical energy
-electrons and ATP come from H2O
H2O GETS OXIDIZED
what captures the light in the thylakoid membrane and what for?
photosystems and to excite electrons.
What are the two complexes in a photosystem
light-harvesting complex
reaction center complex
what does a light-harvesting complex have
chlorophyll a and accessory pigments
what does the reaction center complex have
chlorophyll a and a primary electron acceptor
The light reactions
two photosystems:
-photosystem I
-photosystem II
and they have the exact same structure and do the same thing at the same time.
electrons move through photosystem through
linear electron flow
electrons flow from H2O--> O2
linear electron flow
one way path of electrons in both photosystems and ETCs
The first electron transport chain powers
ATP synthesis
The second electron transport chain
reduces NADP+
How light reactions work
light hits the light harvesting system and pigment gets excited and energy transfers to other pigments which eventually transfers energy to chlorophyll a in reaction center. electrons are released from the pair of cholorphyll a pigments when they are excited.
What is NOT made in the light reactions
SUGAR IS NOT MADE
Electron flow from electron transport chains pump out what and power what
pump out H+ ions from stroma into thylakoid space to create concentration gradient which powers ATP synthesis- which is chemiosmosis
how do some photoautotrophs make extra ATP
cyclic electron flow- diverting e- back to first ETC so the repeat it and make more ATP
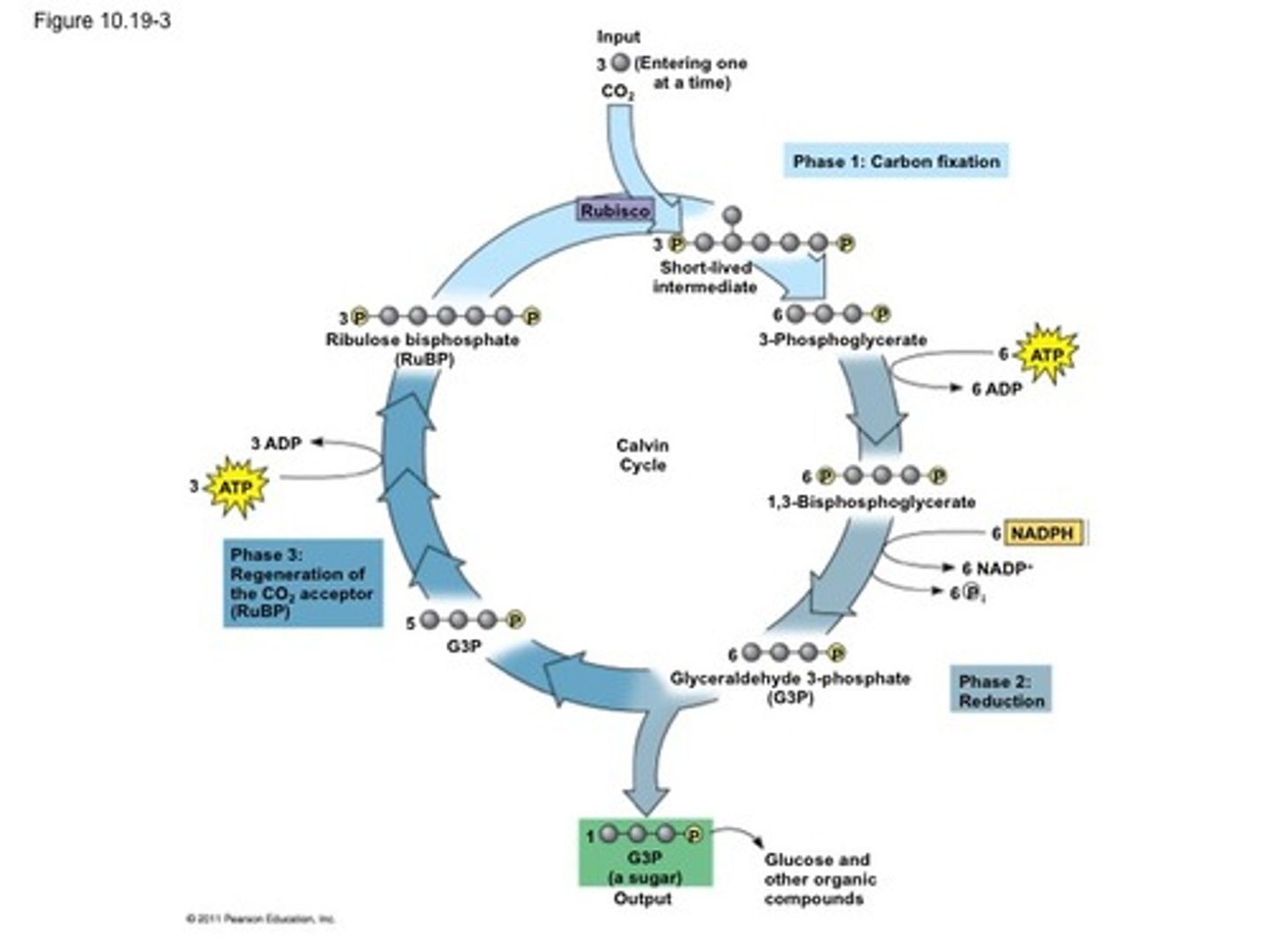
point of calvin cycle
make sugar- glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Calvin cycle reactants and products
CO2----> Sugar
what is calvin cycle powered by
NADPH and ATP from light reactions
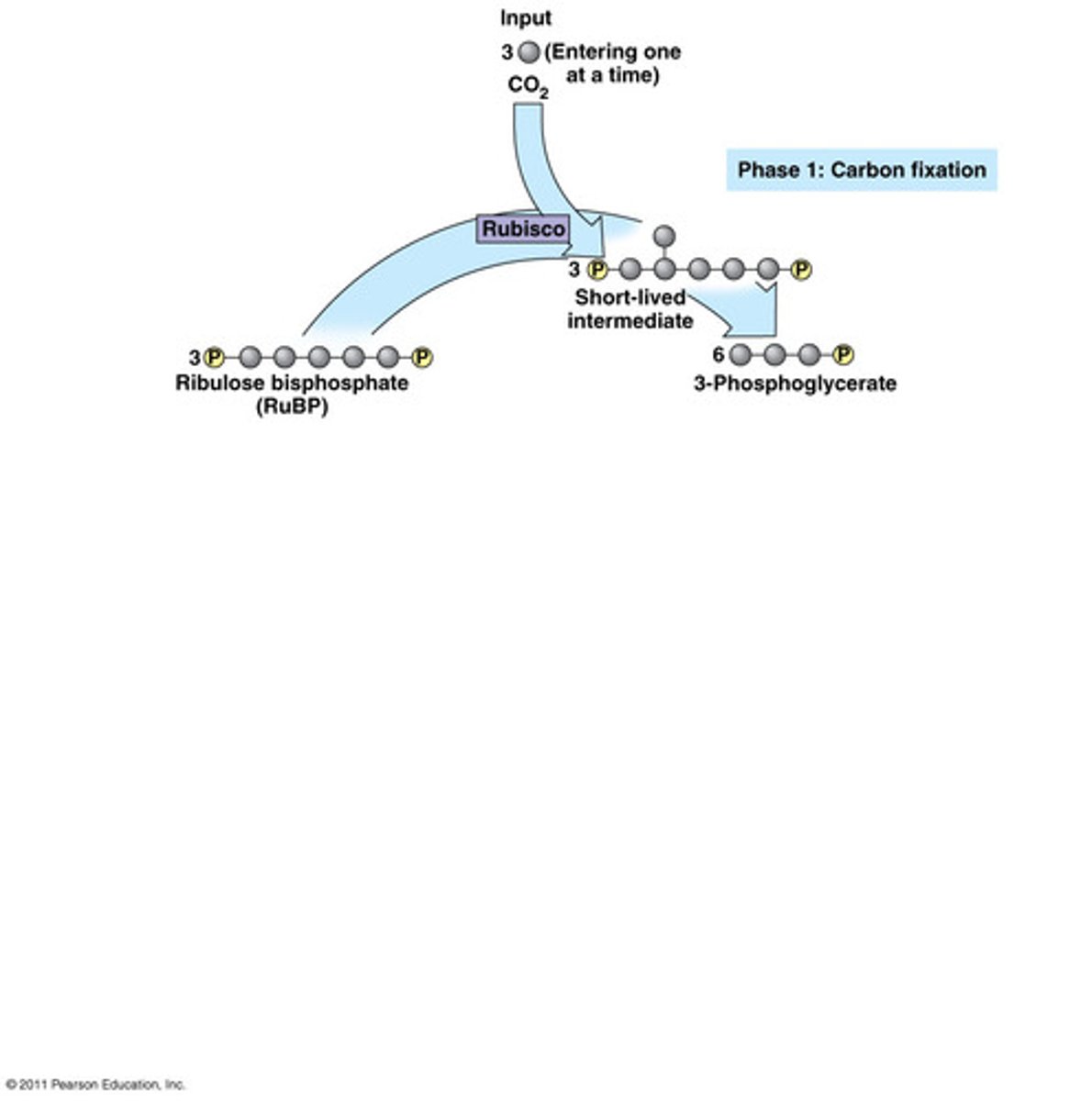
first phase of calvin cycle
carbon fixation phase- traps carbon dioxide molecules
carbon fixation phase
CO2 gets into cell through simple diffusion through stomata pores on leaves
most plants are
C3 plants
C3 plants
not succulents or grass
how many CO2 captured per calvin cycle
3
what is carbon fixation is catalyzed by
the rubisco enzym= Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/ oxygenase
phase 2 of calvin cycle
reduction phase- gaining of electrons
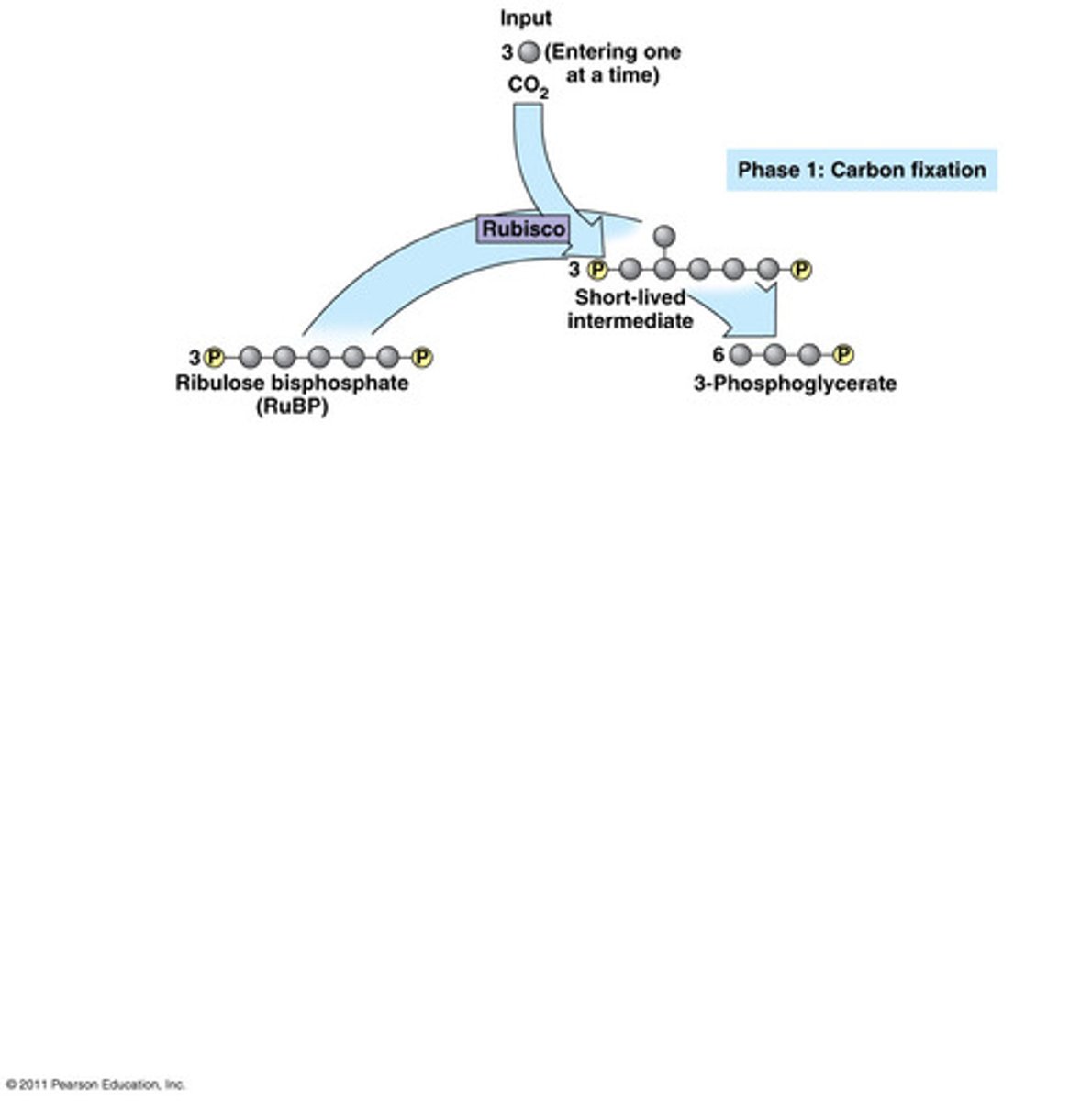
reduction phase
uses ATP and NADPH from the light reactions to power the phase
makes 6 glyceraldehydes 3-phosphate but only one of those leaves the cycle.
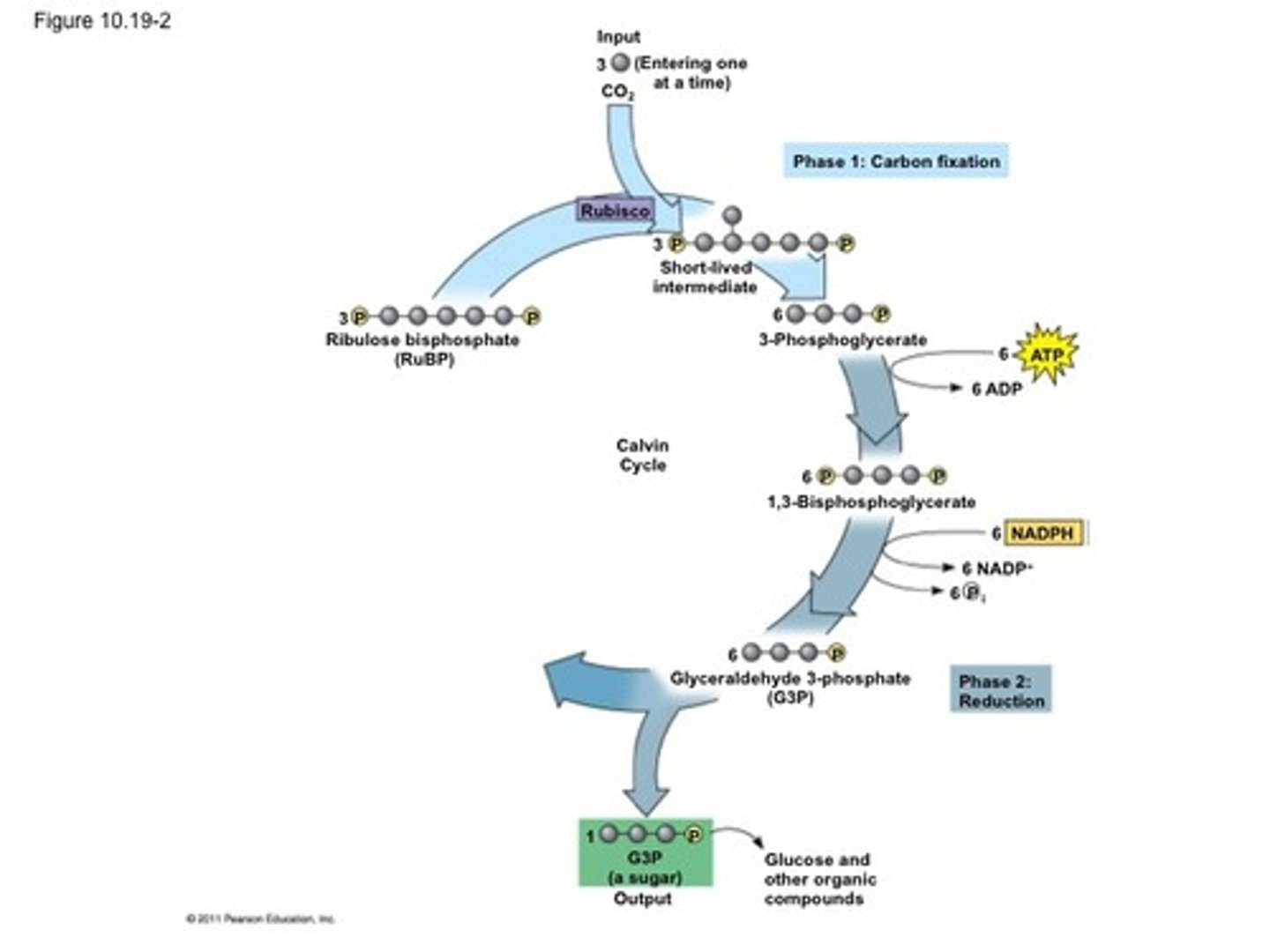
where can glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate be used
glycolysis phase of cellular respiration- in the energy payoff phase.
can also be used to build larger carbohydrates
-glucose--> cellulose, starch
-sucrose--> cellular respiration in other plants
phase three of the calvin cycle
regeneration phase- which uses the 5 other glyceraldehyde 3-phosphates
regeneration phase
uses ATP from the light reactions
makes 3 ribulose bisphosphate to restart calvin cycle.
all cells must be able to...
communicate
cell to cell communication
cell signaling
cell signaling helps bacteria form structures of biofilms
which helps bacteria survive
cell signaling help with apoptosis
programmed cell death
what helps with cell signaling
biomolecules on the surface of the cell
how does cell signaling occur
direct contact
without direct contact
direct contact
cell junctions
cell-cell recognition
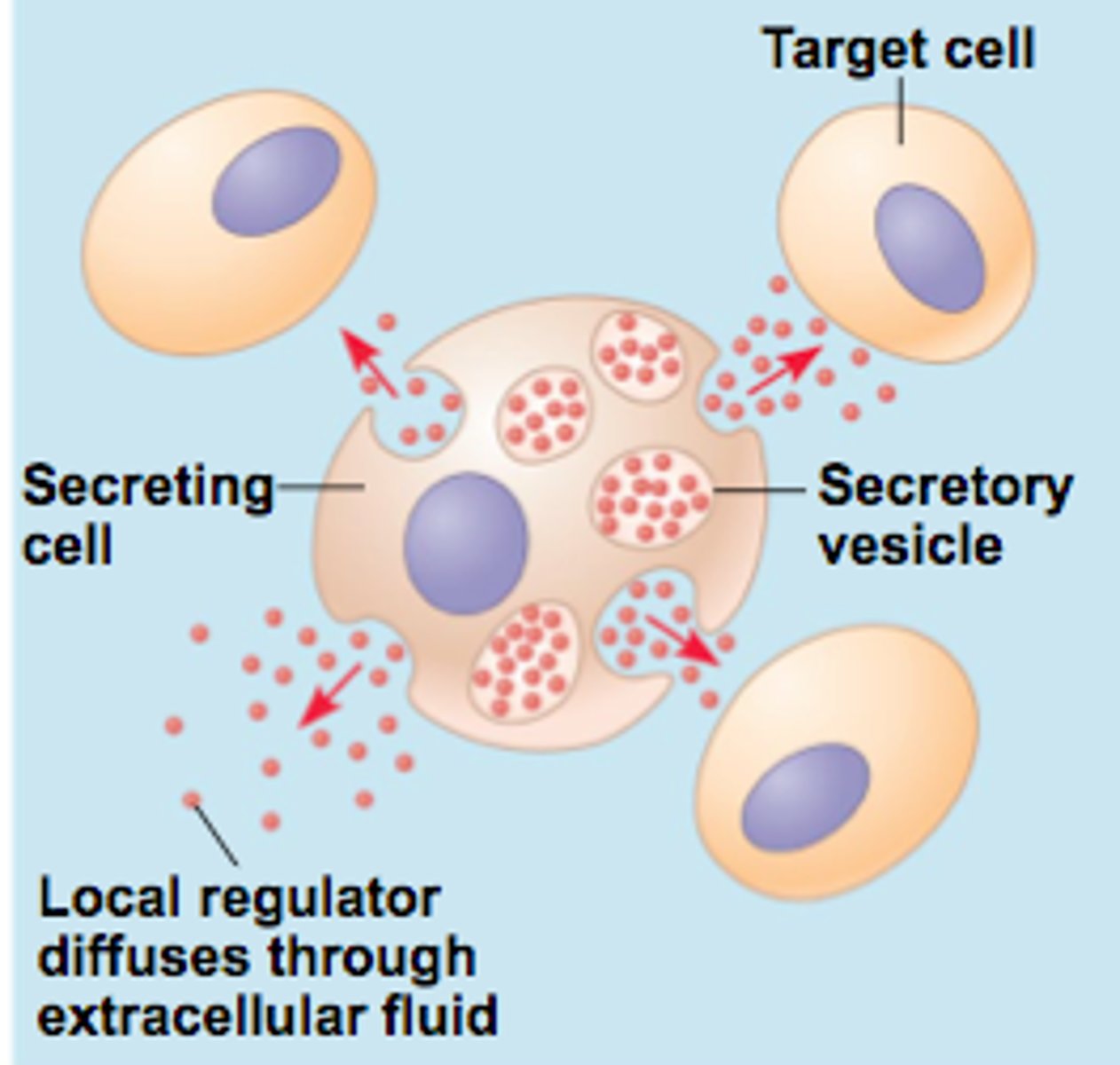
without physical contact
paracrine signaling
synaptic signaling
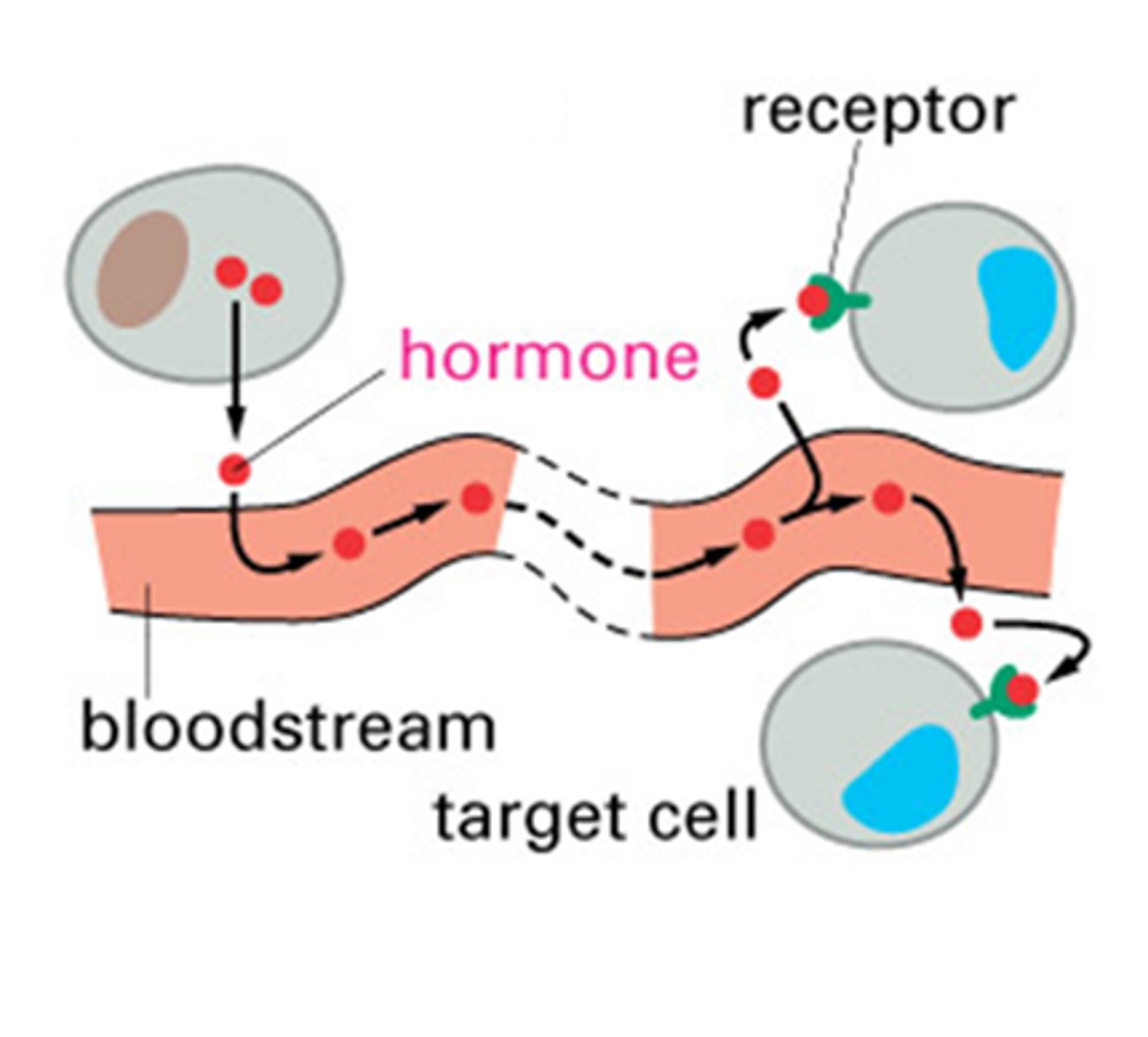
Endocrine hormonal signaling
cell junctions or plasmodesmata
permanent tunnels that allow diffusion of molecules and communication
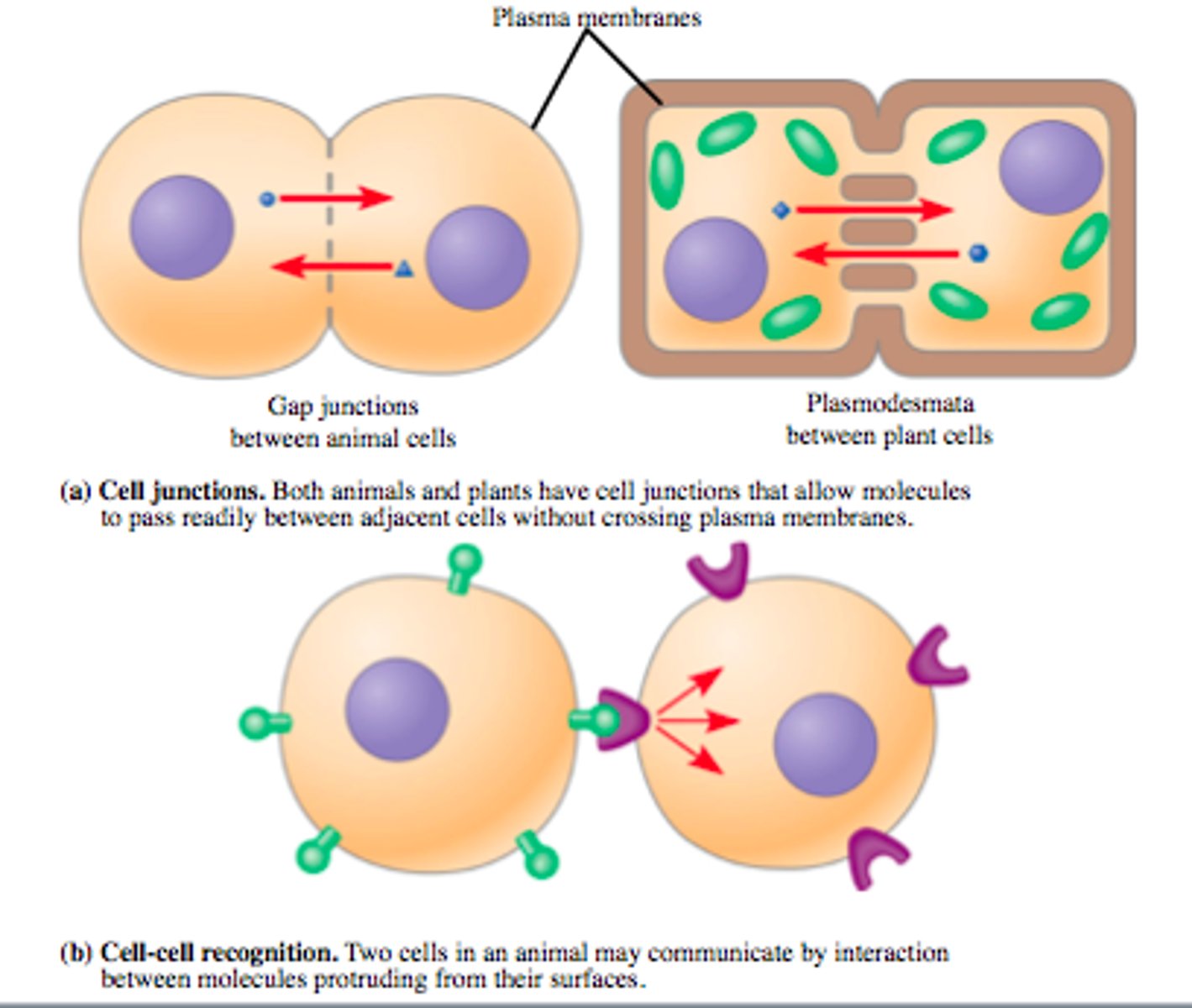
cell to cell recognition
temporary
-neutrophils
-macrophages
paracrine signaling
synaptic signaling
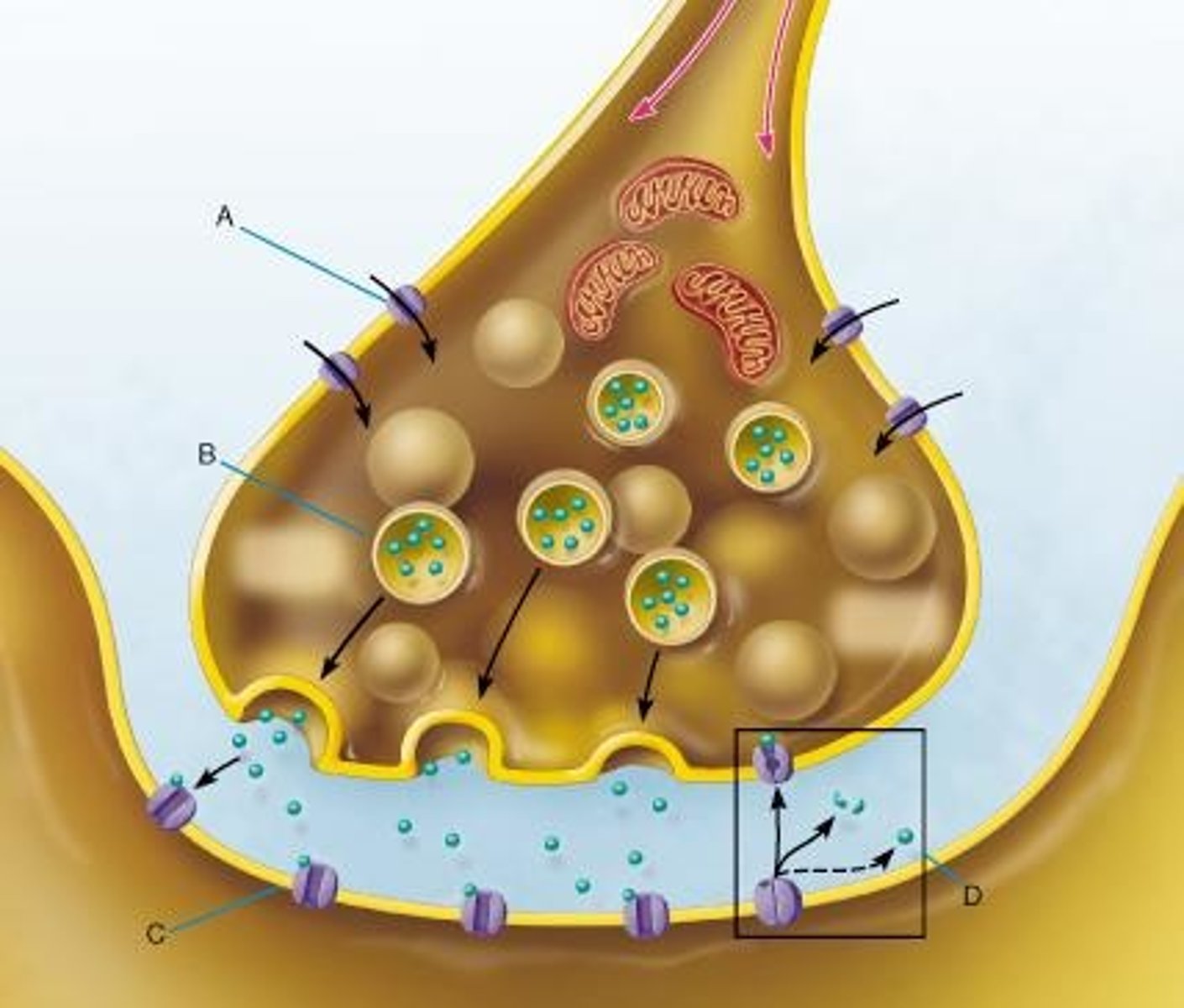
endocrine signaling
insulin acts as a hormone
what does a target do during cell signaling
1.) Reception
2.) Transduction
3.) Response
Reception
signaling molecule binds to the receptor at the active site
like a substrate fits into the active site of an enzyme
signaling molecule
ligand
what is a receptor
most of the time they are proteins
all receptors have a very specific shape at the ligand binding site
can be intracellular or cell surface transmembrane
examples of cell-surface transmembrane receptors
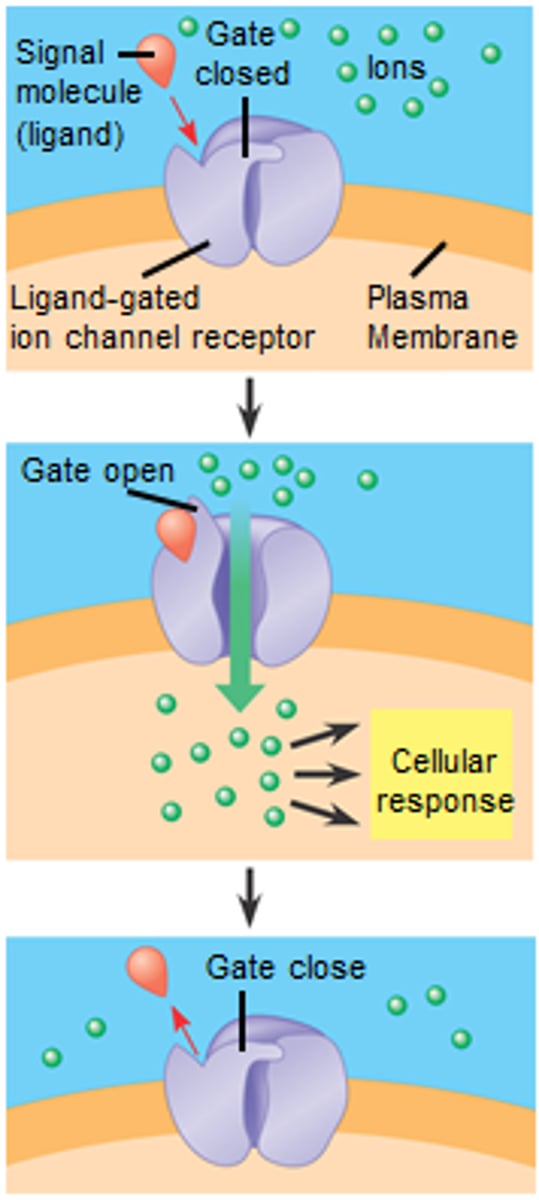
ion channel receptors
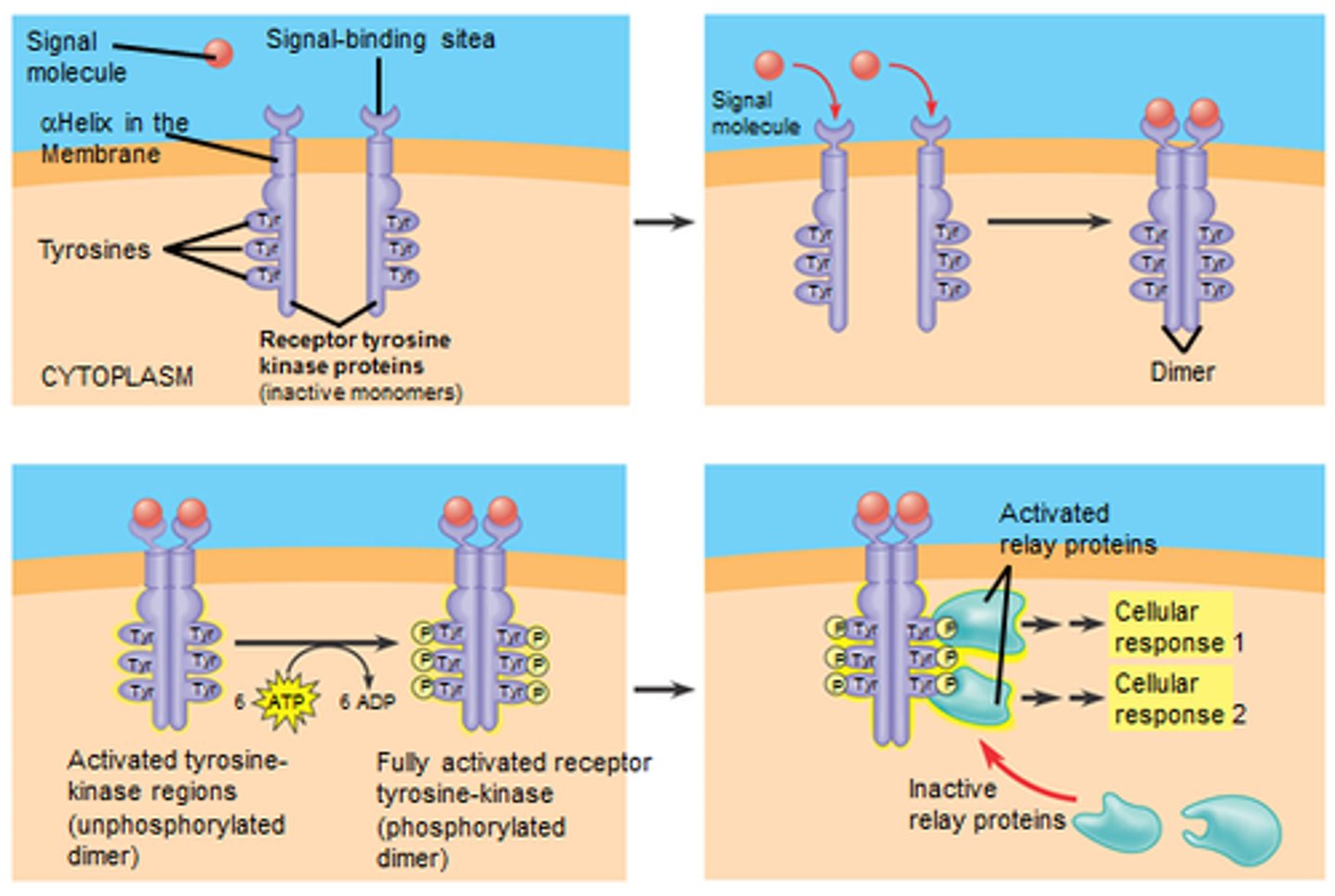
receptor tyrosine kinase
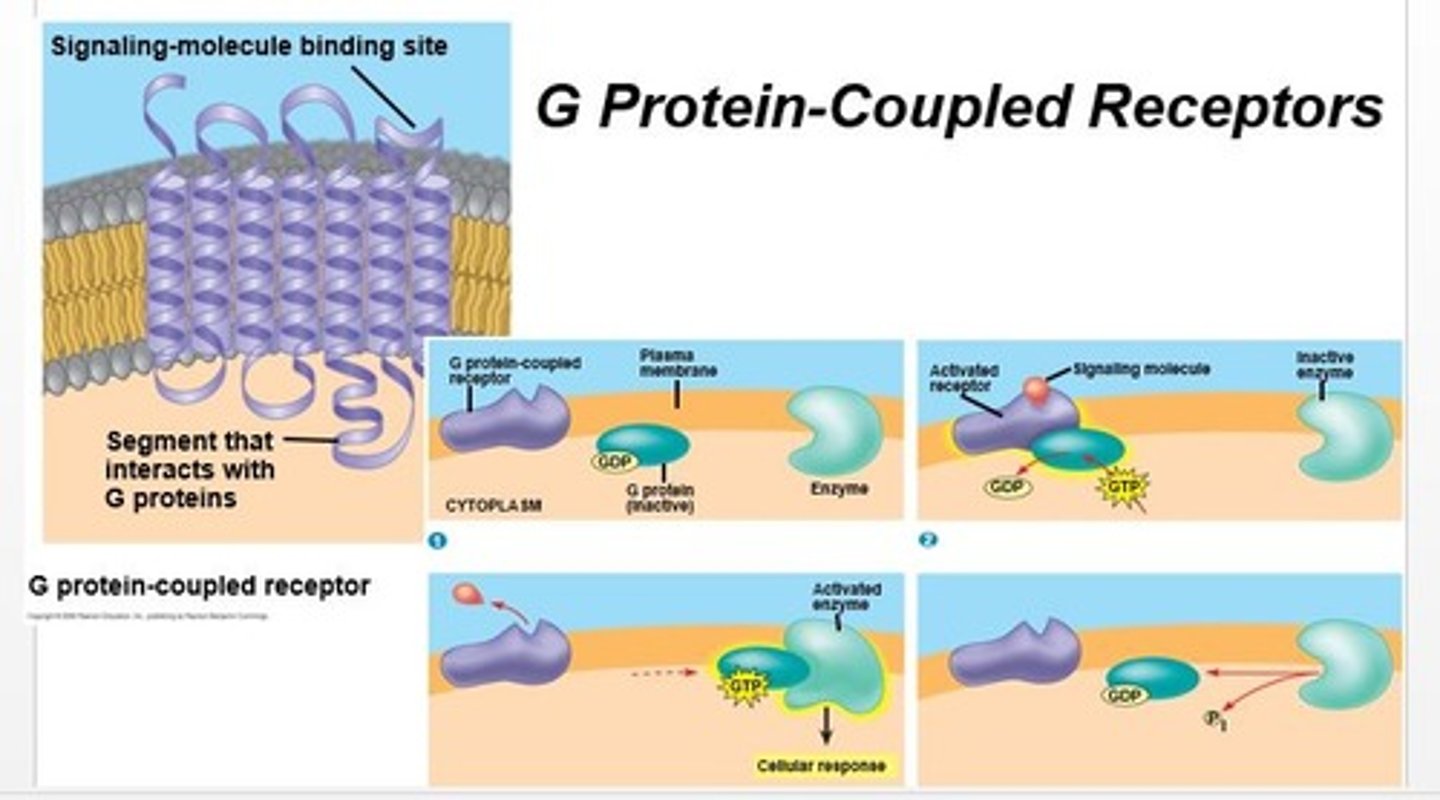
g-protein coupled receptors
ion channel receptors
critical for muscles and neurons
part receptor and part channel
receptor tyrosine kinase
part receptor and part enzyme
tells cell when to start and stop properly dividing
two bars are dimers and they need to work in pairs
powered by a phosphate group from ATP
Transfers phosphate group to other proteins until ready to divide
g protein-coupled receptor
helps with seeing, smelling, and tasting
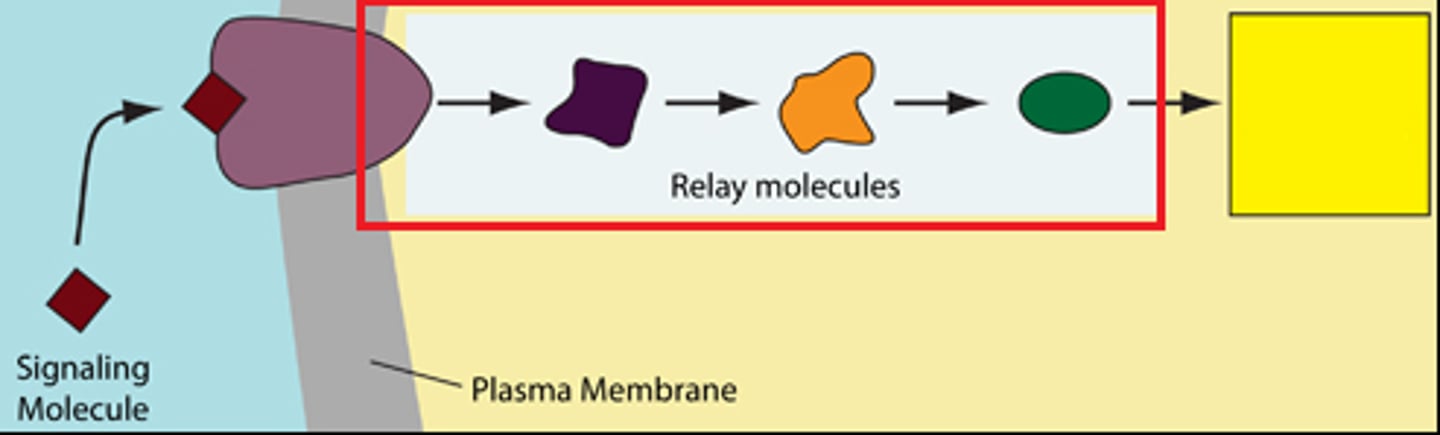
transduction
mobile intracellular receptors do it all by themselves but cell-surface transmembrane receptors use relay molecules
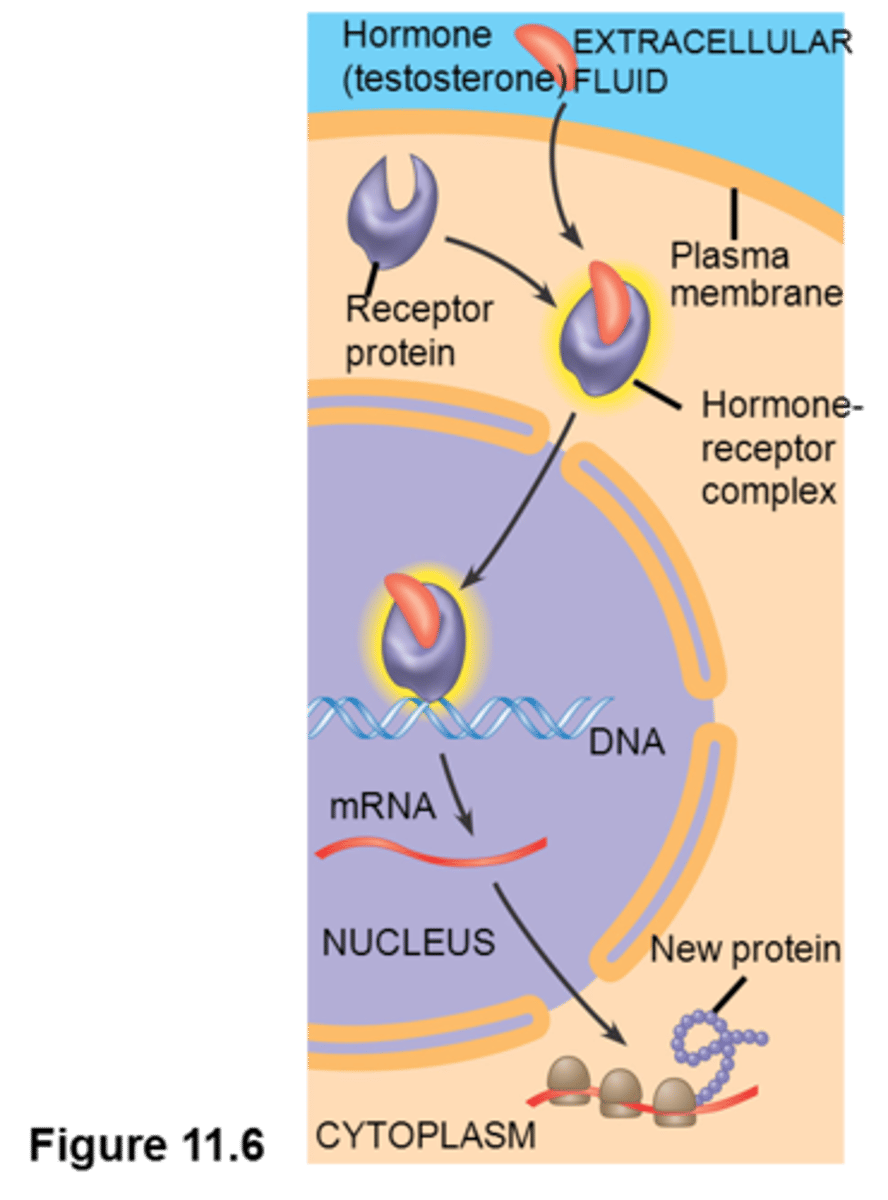
example of intracellular receptor
steroid-hormone receptors
aldosterone-
the ligand aldosterone has to go through membrane through simple diffusion then bind to receptor and change shape. Then receptor produces the response
cell-surface transduction
most boring game of telephone
what can relay signals in signal transduction?
ions
proteins
organcic molecules other than proteins lie cyclic AMP
What usually happens to signal transduction proteins to pass on the signal?
they proteins are phophorylated
Response
can be just about anything that that target cell is supposed to do or not supposed to do.
where could response occur
nuclear DNA
OR any other part of the target cell
- and response controls various cell functions.
multiple cell signaling pathways and their responses
one response
two responses
two pathways lead to one response- cross-talk
different receptor leads to a different response
cell signaling in the end
not straightforward
all designed to trigger apoptosis
cell division
binary fission
mitosis
meiosis
why is cell division important?
unicellular organisms- reproduction
multicellular organisms- reproduction
-growth and development
-tissue renewal
BEFORE A CELL DIVIDES IT MUST DO WHAT?
REPLICATE ITS DNA
Prokaryotic cell division
binary fission
Eukaryotic cell division
mitosis
meiosis
Binary Fission
faster than Eukaryotes
Replication of DNA happens at the same time as the division
-the cell elongates and needs more cell wall
-cell's chromosomes are replicated as the cell elongates
Results- daughter cells that are identical to the parent cell
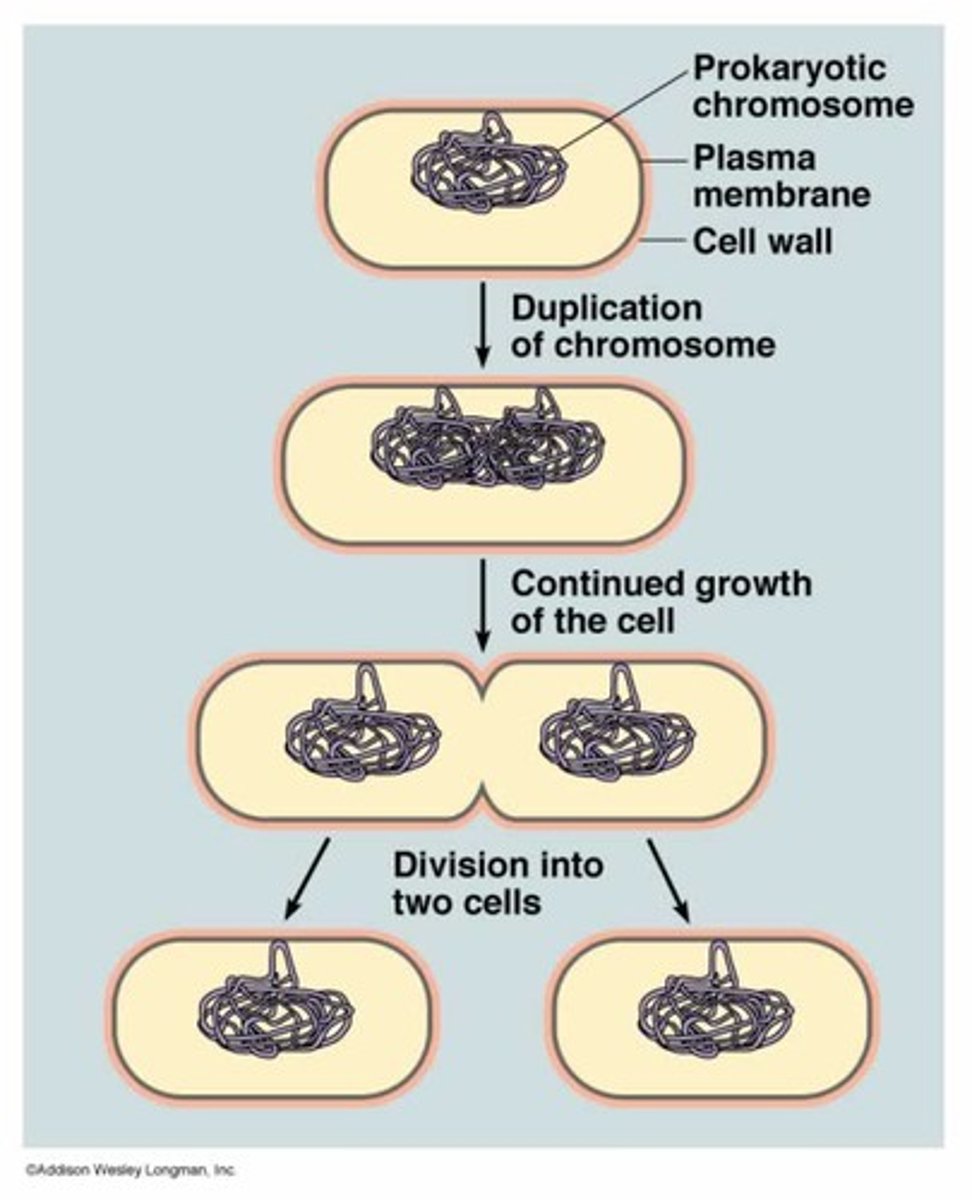
goal of binary fission
to make more of original cell
what prevents cell from elongating
penicillin
Eukaryotic cell division is
much more complicated- more complex and way more DNA
multiple chromosomes
organized as chromatin
chromatin
protein spools with DNA wrapped around them
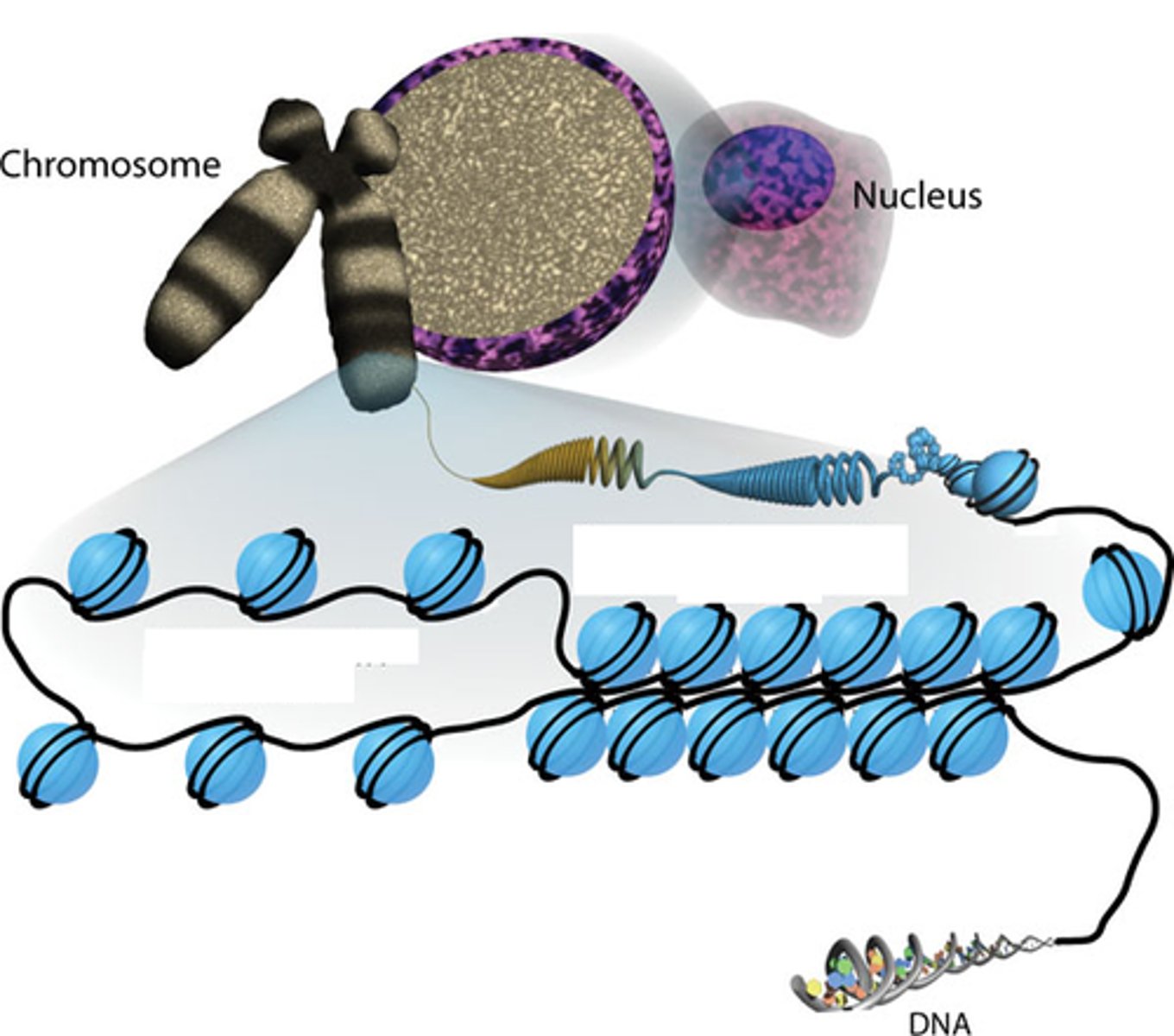
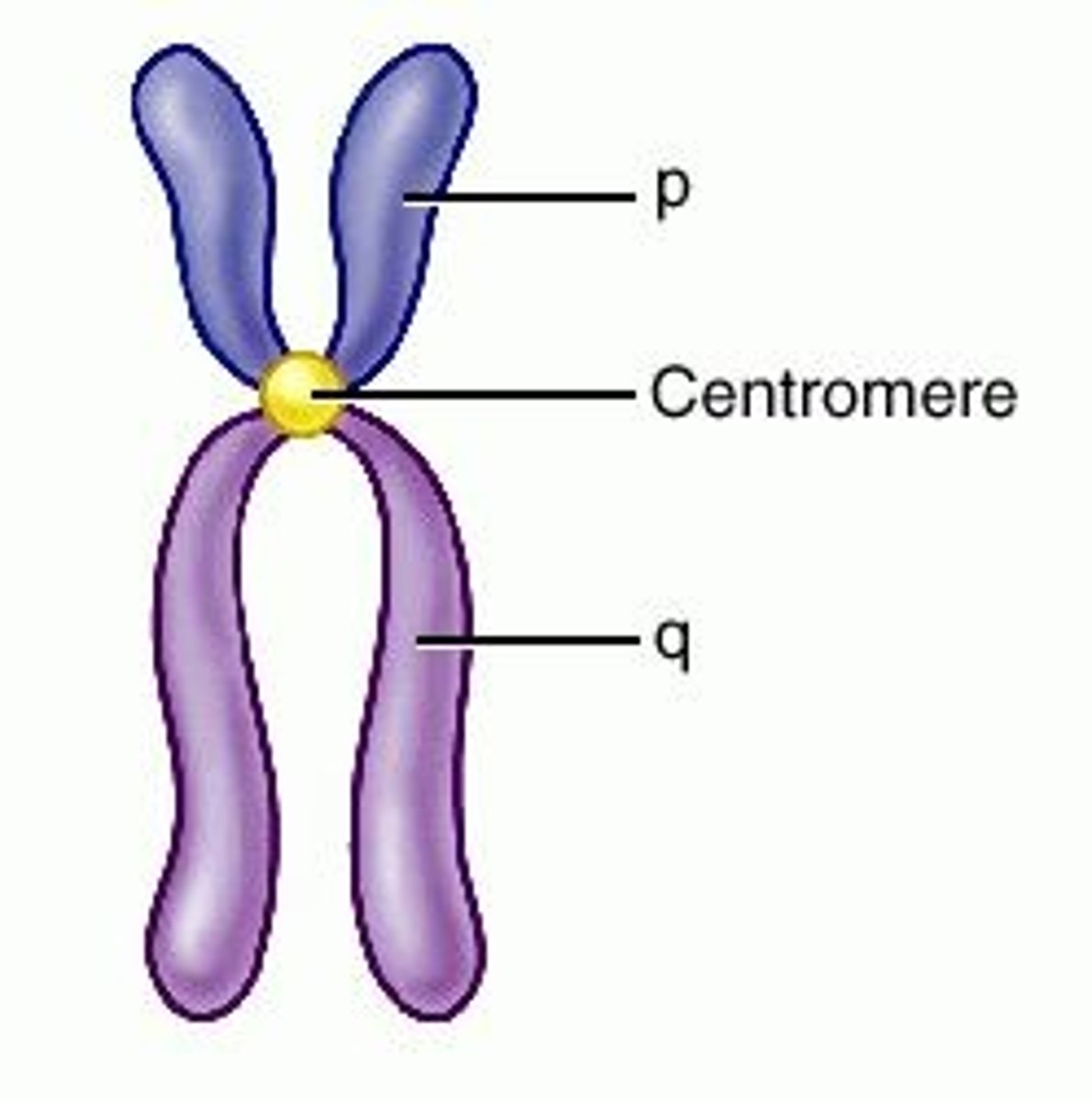
centromere
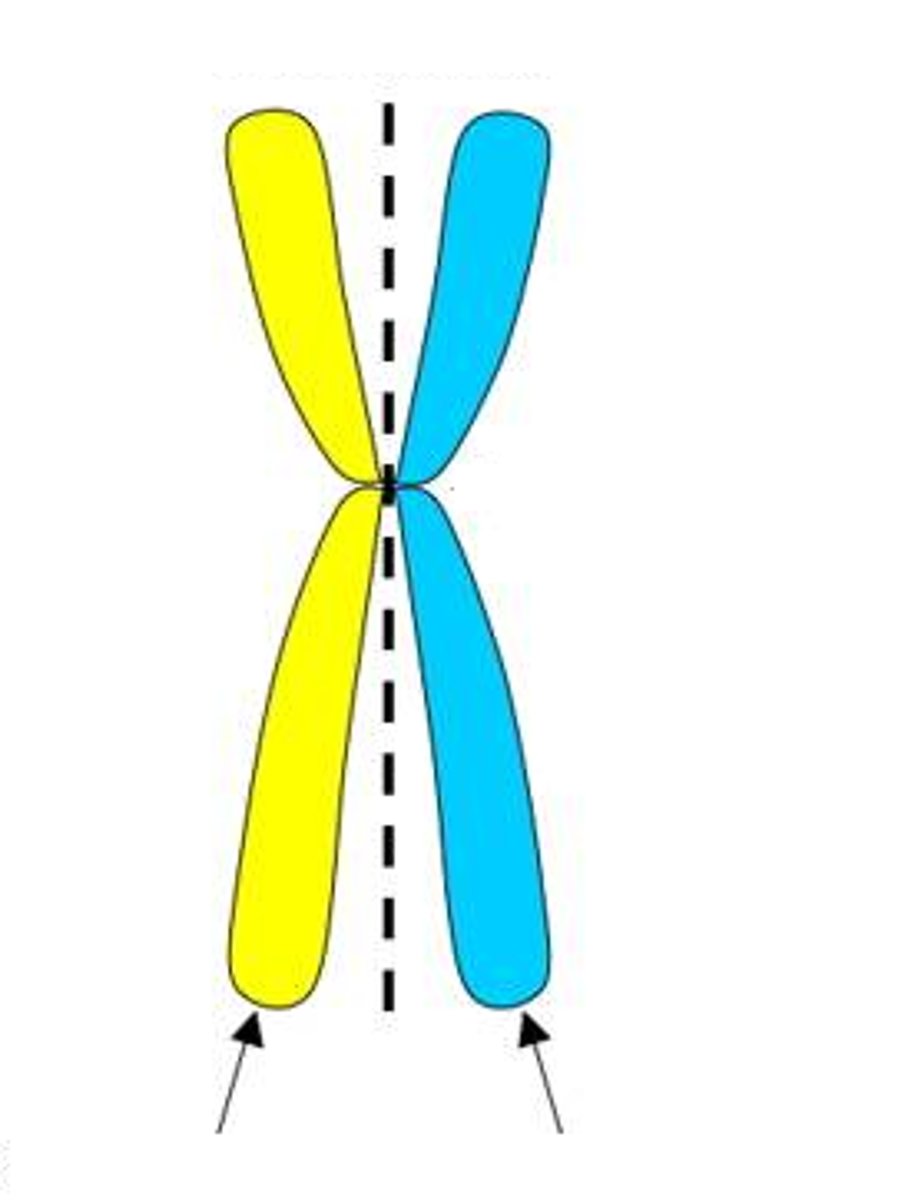
sister chromatids
mitosis daughter cells
are identical to parent cells
from somatic cells
meiosis daughter cells
are different from the parent cells
from sex cells
cell division is part of a timed cell cycle
dividing eukaryotic cells follow a cell cycle
cell cycle
interphase: G1, S, G2
M phase- mitosis or meiosis
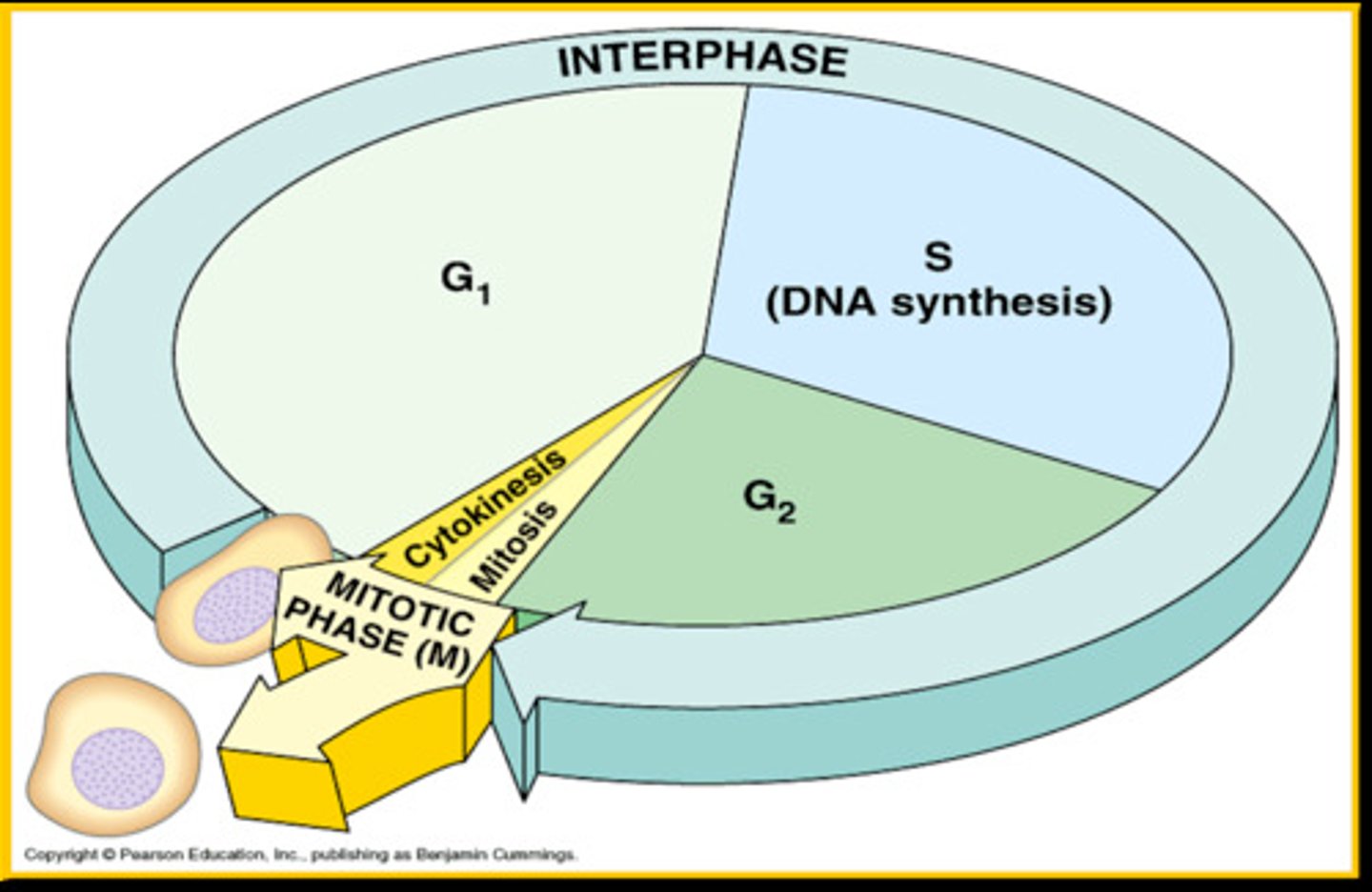
G-
gap--> preparation time
S-
synthesis- 10 to 12 hours
DNA Replication
takes longer than prokaryote
happens BEFORE cell division
Go
healthy non-dividing cells like muscle cells are in this phase
they are not getting ready to or actively dividing
what controls cell cycle
cyclins- proteins
with help from cyclin-dependent kinase
cyclins tell cells
when to move on
if not ready, it will not continue past cell cycle checkpoint
if process is messed up, cyclin tells cell when to do apoptosis
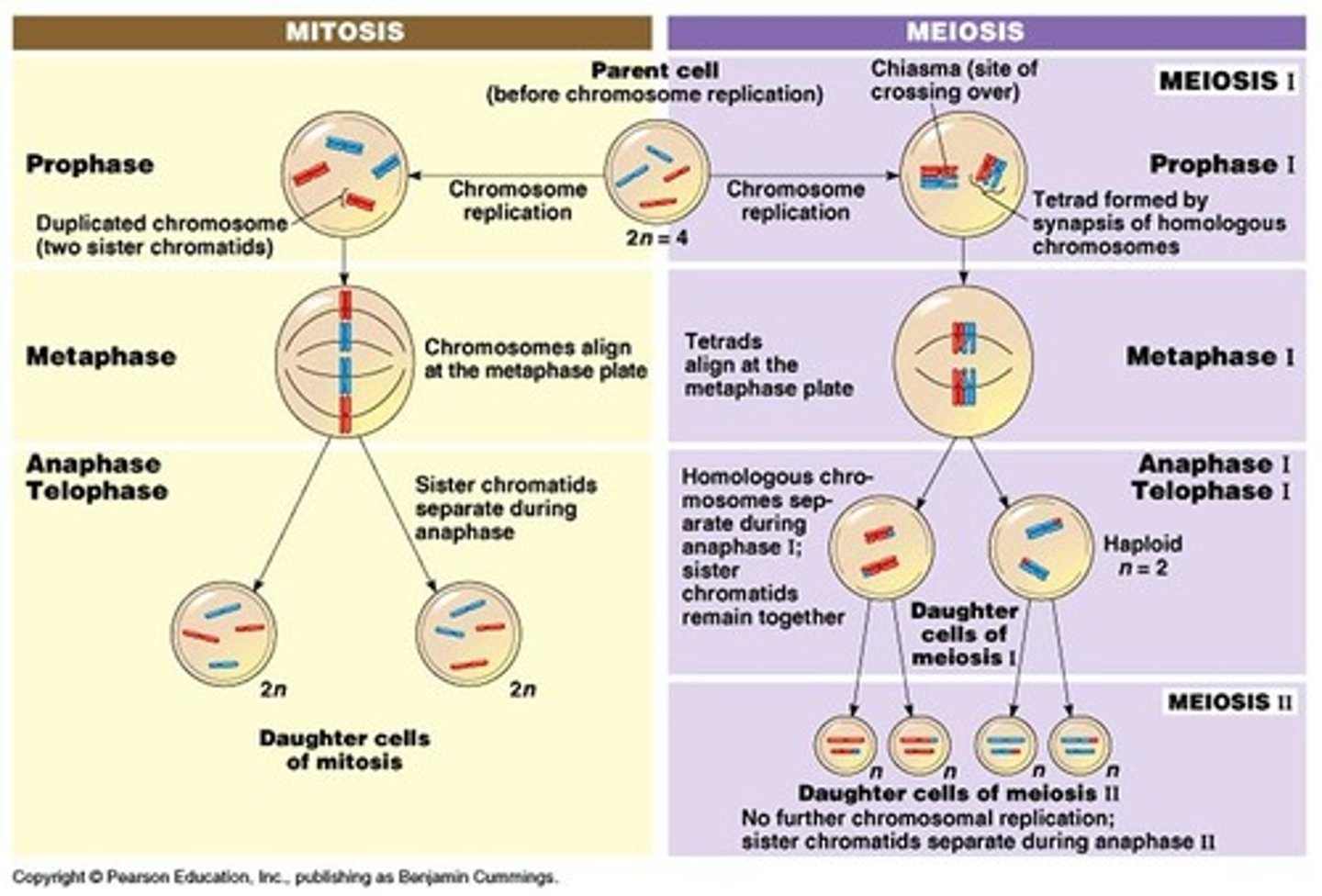
Mitosis
2 daughter cells are divided from identical parent cell
animal somatic cells have 2 sets of chromosomes--> are diploid--> 2n