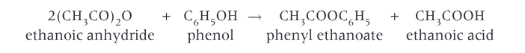Acyl chlorides
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are acyl chlorides also known as?
Acid chlorides
How are acyl chlorides prepared?
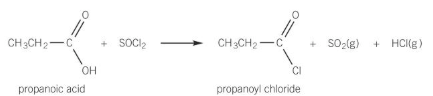
Carboxylic acids area chlorinated with SOCl2 (thionyl chloride / sulfur dichloride oxide)
Give the general reaction for the production of acyl chlorides
Carboxylic acid + SOCl2 → Acyl chloride + SO2 (g) + HCl(g)
What should be remembered about the preparation of acyl chlorides regarding safety?
The reaction should be carried out in a fume cupboard as the products are harmful
Show the preparation of propanoyl chloride from propanoic acid
Give the conditions for reacting acyl chlorides with alcohols
Cold and anhydrous
How should acyl chlorides be named?
Remove ‘-ic acid’ from carboxylic acid and replace with ‘-yl’
Follow with halogen with -ide ending
Name the structure

Butanoyl bromide
Name the structure
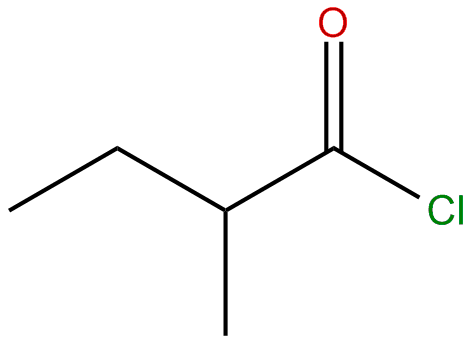
2-methyl butanoyl chloride
What are the 4 physical properties of acyl chlorides
Form colourless liquids
Have a pungent odour
Creates fumes in moist air
Are readily hydrolysed to form a carboxylic acid and halogen acid
An acyl chloride like ethanoyl chloride is a colourless fuming liquid. Explain its properties
The strong smell is a mixture of vinegar (ethanoic acid) and acrid smell of HCl gas
Smell and fumes due to reactions with water vapour in the air
What is the reactivity of acyl chlorides like and why are they very useful in organic synthesis?
Acyl chlorides are extremely reactive and are more acidic than carboxylic acids
They are useful because they can easily be converted into carboxylic acid derivatives such as esters and amides, with good yields
Describe the reaction of acyl chlorides with nucleophiles
Acyl chlorides lose their chloride ion whilst retaining the C=O double bond
Summarise the overall reaction of acyl chlorides
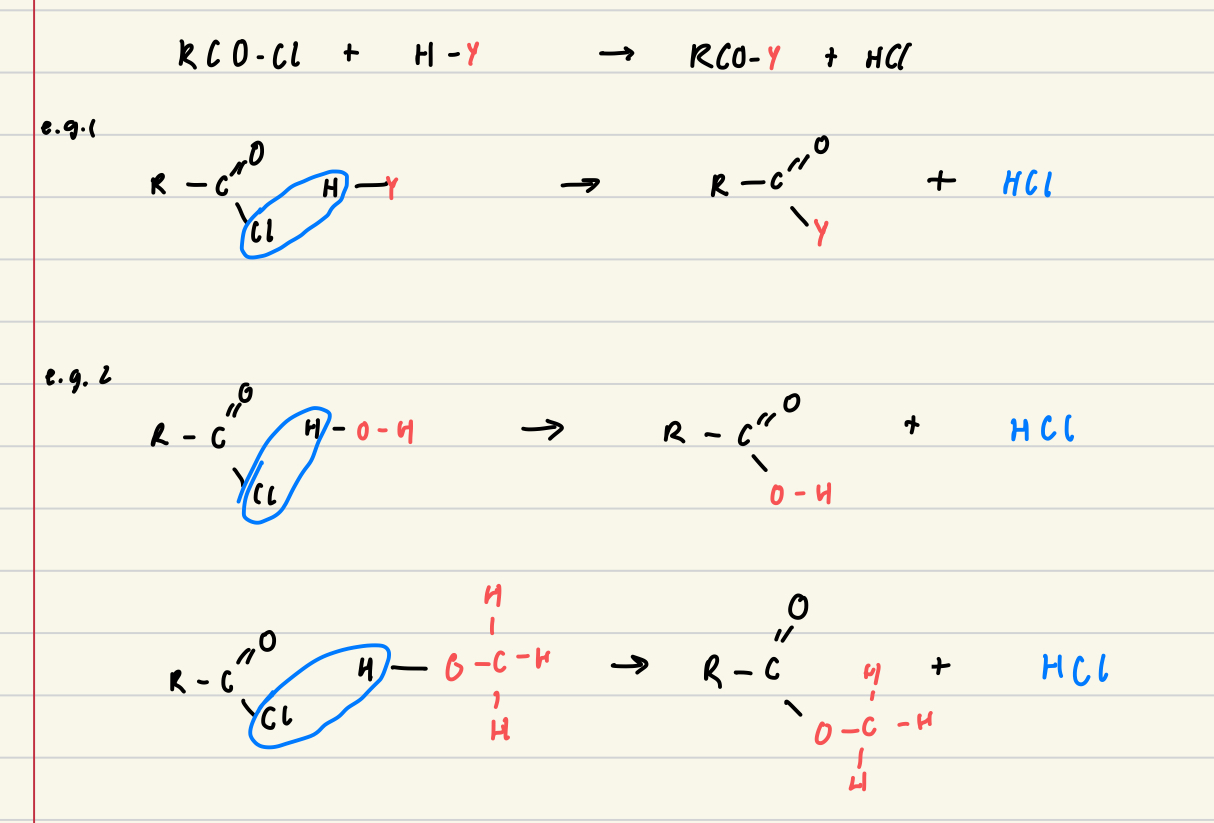
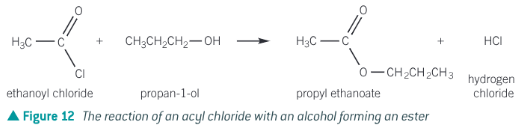
Acyl chloride + alcohol
Acyl chloride + alcohol → ester + HCl
Show the formation of propyl ethanoate from ethanoyl chloride
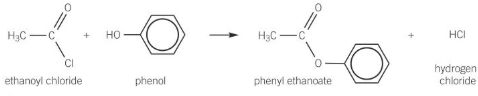
Acyl chlorides + phenols
Acyl chlorides + phenols → esters + HCl
Why are acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides better than carboxylic acids when reacting with phenols?
Carboxylic acids are not reactive enough to form esters with phenols
Acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides are more reactive and don’t need acid catalysts
Give the advantage of making esters with acyl chlorides and alcohol rather than carboxylic acid and alcohol
Esterification through an alcohol and carboxylic acid is reversible and has a low yield
Alcohols will readily react with acyl chlorides to produce esters
The yield is much higher and the reaction is not reversible
Show the formation of phenyl ethanoate
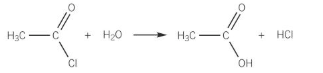
Acyl chloride + water
Acyl chloride + water → carboxylic acid + HCl
Explain the reaction of acyl chlorides with water
When water is added to an acyl chloride, a violent reaction takes place and dense steamy hydrogen chloride fumes are formed
A carboxylic acid is formed
Show the reaction of acyl chlorides with water
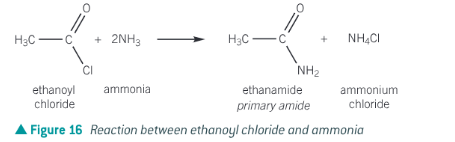
Acyl chlorides + ammonia
Acyl chlorides + ammonia → primary amide + ammonium salt
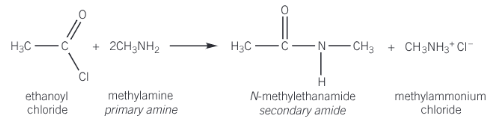
Acyl chloride + amine
Acyl chloride + amine → secondary amide + ammonium salt
What happens when ammonia and amines react with acyl chlorides?
Ammonia and amines act as nucleophiles by donating the lone pair of electrons on the N atom to an electron deficient species
Show the reaction of ethanoyl chloride and ammonia
Show the reaction of ethanoyl chloride and methylamine
When do acid anhydrides become useful?
Acid anhydrides are less reactive than acyl chlorides and are useful for some laboratory preparations where acyl chlorides may be too reactive
Give the equation for formation of phenyl ethanoate from ethanoic anhydride