Ch. 1.1.a - International History: Why was imperialism a significant force for late 19th century Europe?
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Review of the first question in the AICE IH book.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What was the Scramble for Africa?
European powers took control of areas not formally controlled before. This rapid colonization occurred from the 1880s to the early 1900s, driven by economic interests, national prestige, and competition among European nations.
What is Imperialism?
A policy or ideology where a country extends its power and influence through colonization, military force, or other means, often exploiting resources and peoples of other nations.
What are some economic motives for imperialism?
European powers sought new markets, raw materials, and investment opportunities to fuel industrial growth. Businessmen and investors thought that it would be profitable to invest in the new trading companies that were being formed to trade in Africa and China.
What are tariffs?
Tariffs are taxes imposed on imported goods, designed to protect domestic industries by making foreign products more expensive. They can also generate revenue for governments and influence trade balances.
What was a result of more and more countries introducing tariffs?
More and more countries introduced them, and because of this, the possession of colonies was seen as the only way to guarantee access to vital raw materials needed by modern industrial companies.
What is an example of tariffs influencing the creation of colonies?
Businessmen in Marseilles, Liverpool, and Hamburg were constantly pushing their governments into annexing areas where they had important trading interests.
What is a political motive for imperialism?
A political motive for imperialism includes the desire for national prestige and power, as countries sought to expand their influence and assert dominance over rival nations through colonization and control of territories.
What is New Imperialism?
New Imperialism refers to the late 19th and early 20th century wave of colonial expansion by European powers, characterized by the rapid acquisition of territories in Africa and Asia, driven by economic, political, and social motivations. This helps support the political side/motive for imperialism.
What is an example of a political motive for Imperialism?
Britain’s occupation of Egypt in 1882, carried out to safeguard the Suez Canal as the main route to India, and the draft Anglo-Portuguese Treaty of 1884 concerning the Congo, both which led up to the partition of Africa.
What happened mid 19th century?
Interest in colonies had declined in Europe. Because of the era of free trade it seemed that political control of overseas markets was unnecessary. However, within just 20 years the political climate had dramatically changed, and the European governments and their large populations were fiercely competing for colonies in Africa, and by 1900 wanted to carve up China.
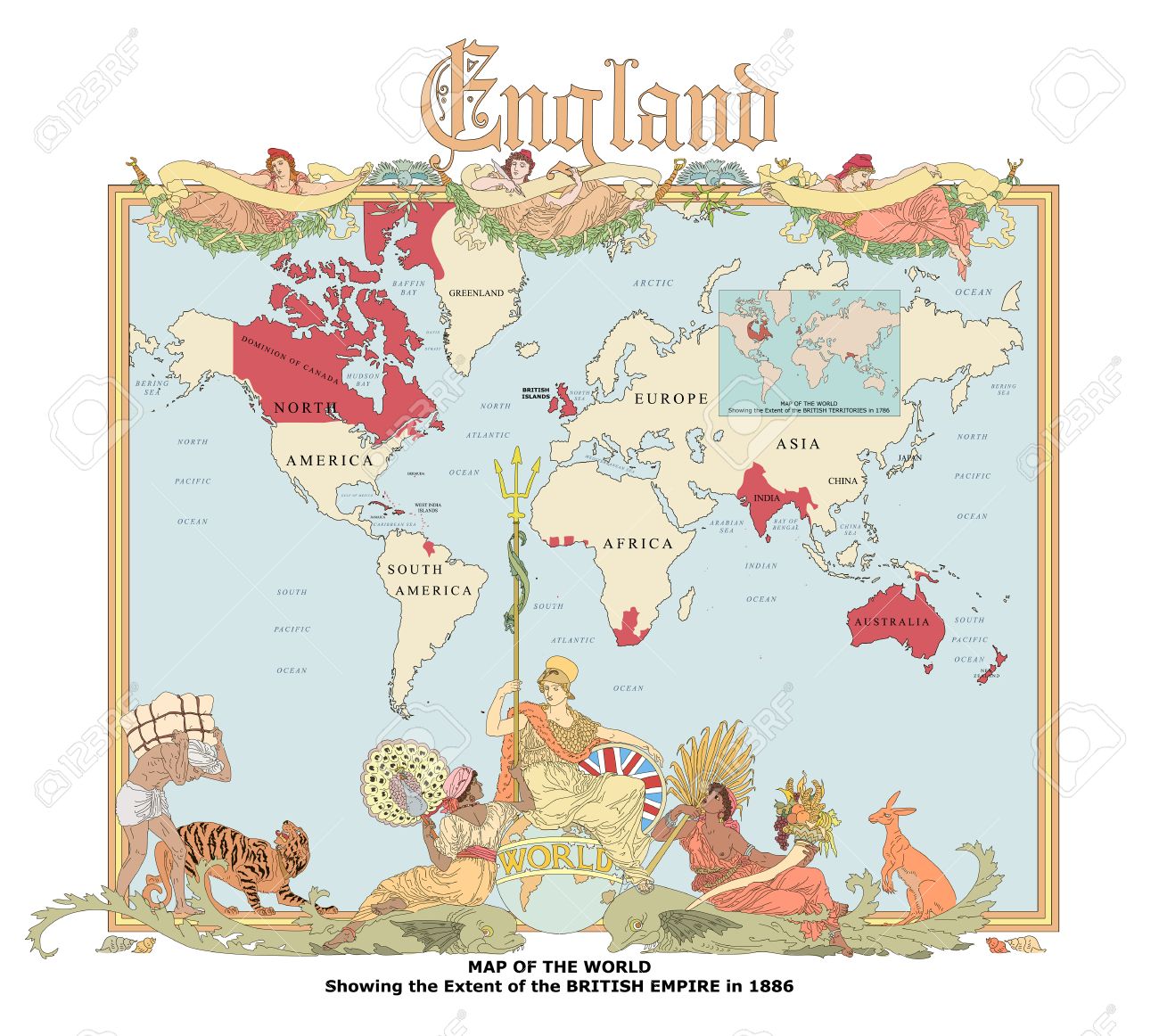
What happened to European empires after the political climate around imperialism grew around mid 19th century?
The British Empire and French Empire had greatly increased in size. This would be between 1870 and 1900. This dramatic expansion of land and territory is also know as New Imperialism.
How was New Imperialism made possible?
European powers had the technological lead over Africa, China, and much of the rest of Asia.
What were the technological developments Europe had over Asia and Africa in the late 1800s?
The maxim gun (machine gun), and quinine (anti-malaria drug).
In 1870, what was the status of European control, as compared to 1900?
1870: 10% in total.
1900: Only Ethiopia and Liberia were not colonized.
What development helped merchants sell to Africa and how?
The steamboat; It had enabled merchants to sell goods and textiles in exchange for groundnuts and other tropical products.
What kind of societies and communities were eager with communicating with Africa, and what view did they have on the slave trade?
Missionaries and churches; They had believed that they should remove the slave trade, and were hastily doing so with determination despite it still existing after the prohibition in 1807.
What kind of societies were gaining interest with the explorers that had went into Africa and their dramatic journeys?
The press and the newly founded geographical societies (people interested in the facts having to do with new geography such as the land in Africa).
What was the governments’ reactions to the discoveries of the explorers?
They welcomed them; They hoped that they would help open up Africa to their countries’ exports.
Who was David Livingstone, and he was the first to do what?
A Scottish missionary and explorer in Africa; He had been the first to cross the African continent (1854-56), and hoped to incorporate steamboats into the Lakes he had found (Nyasa and Zambezi).
What was Livingstone’s book ‘Missionary Travels and Researches in the South” aim to do?
Persuade public opinion and the government to support his plans for a British colony in the Zambian Highlands.
Who was Henry Morton Stanley?
A Welsh-American explorer famous for his explorations of CENTRAL Africa.
Who was King Leopold?
Ruled over Belgium; 1865-1909, founded the Free Congo State.
King Leopold setup what organization?
The International African Association (IAA).
What was the aim of the International African Association?
Publicly: to suppress the slave trade and open Central Africa to new international commerce.
Actual: ‘To get a piece of this African pie’ said by the association’s creator.
What happened to Pierre Brazza?
Brazza, unknown to the King of Belgium, had secret instructions to annex the territory of the lower Congo for FRANCE. His name sounds kinda french if that helps.
What is a Khedive?
Title for the governor and ruler of Egypt and the Sudan.
In the 1870s, what was Britain’s most expensive and important possession?
Suez Canal; It had been built by a French company and had helped become a key link of communications between Britain and India, which gave them money (sweet bread yay).
What happened in 1876 between Egypt and the European Investors?
They (the country not other group) became bankrupt and could not pay the interest on the money lent by Europe. As a result, Britain and France chose to take control of Egypt’s finances, as they were major shareholders of the Suez Canal Company.
What happened as a result of the uprising in Egypt? (1881)
France did not want to dispatch officers. Britain had to take care of it, and when they did they had become the major rulers of Egypt and the Suez Canal, despite saying they would leave multiple times.
What happened as a result of Britain staying in Egypt?
The French were infuriated; They wanted to thwart Brtish ambitions in both Egypt and in West Africa.
In May 1884, Britain had signed what treaty, and why?
Congo Treaty with Portugal; They were alarmed by the prospect of a French advance into the Congo.
What did the Congo Treaty do?
Acknowledged Portugal’s claims to the lower Congo, while allowing Britain to trade freely there and to have a monopoly of navigation rights on the Congo River.
What did France do in protest of the Congo Treaty?
They had appealed to Otto Von Bismarck; They had done this to force Portugal to renounce the Congo Treaty.
What did Otto Von Bismarck do in response of the Britain and Portugal taking the lower Congo?
Summoned a conference in Berlin; Despite British objections, 15 other countries other than Germany had attended, and had decided that all countries and powers can trade freely there.
Both France and King Leopold’s IAC suspected that the treaty between Britain and Portugal (Anglo-Portuguese Treaty) was an attempt by who to do what?
Britain; Expolit Portugal’s weakness to increase its own influence in the Congo.
Who is Otto Von Bismarck?
German Chancellor; German statesman and diplomat who oversaw the unification of Germany and served as its first Chancellor.
What’s a Reich?
Empire; Such as the German Empire.
What does it mean to be counter-revolutionary?
Person who opposes a revolution and wants to reverse its results.
What surprised Otto Von Bismarck’s own ministers and other imperial powers (what did he do)?
Annexing African territory; South West Africa (country), the Cameroon and east Africa.
What persuaded Bismarck to annex territory in Africa? I’m going to infodump, so say everything you know aloud and then check, as it will obviously be the large paragraph lol.
Main motive: Place himself in a position where he could collab with France and go against the British in order to distract the French from acting on their revenge on Germany. (that’s sum silly stuff)
He was also influenced by the cries of help from notrh German colonial traders. Mercantile cities feared being shut out of African markets.
German public opinion, influenced by the newly founded German Colonial Union and newspapers was convinced that Africa was an El Dorado of enormous wealth.
He also grasped how imperialism could unite the German people and discourage badmouthing of the government.
What is Social Imperialism?
A policy aimed at uniting all social classes behind plans for creating and expanding an empire.
What happened as a result of the Berlin Conference?
Scramble for Africa sped up; Rules were drawn up for defining how imperial powers could legitimately claim African territory.