134 — Chapter 3: Improving the User Experience
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
User Experience Issue (UX)
_____ with health IT products are a worldwide concern
Expansion of technology has resulted in complex interactions among users, products, and environments
Can result in patient safety problem and errors.
Stem from the human-computer interface, workflow inefficiencies, and communication breakdowns
Lack of interoperability impact patient care can cause difficulties in extracting relevant data, leading to omissions and errors in care continuity mechanisms such as handoffs
User experience (UX)
Human factors
Human - computer interaction (HCI)
Usability
Basic Consepets
User Experience (UX)
A person’s perceptions and responses that result from the use or anticipated use of a product, system or service.
Human Factors
It is the scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of interactions among humans and other elements of a system.
In healthcare, _____ might concern the design of a new operating room to better support workflow, teamwork, and patient flow, or identifying obstacles to intensive care nurses in their task performance.
Human - Computer Interaction (HCI)
It is the study of how people design, implement, and evaluate interactive computer systems in the context of users’ tasks and work.
Usability
Extent to which a product can be used by specific users in a specific context to achieve specific goals with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction.
Effectiveness
Efficiency
Satisfaction
Goals of Usability
Effectiveness
The accuracy and completeness with which specified users achieve specified goals in particular environments, including worker and consumer or patient safety
Efficiency
Includes the resources expended in relation to the accuracy and completeness of goals achieved
Satisfaction
The level of comfort and acceptability that users and other people associate with the product or work system and deals with users’ perceptions
User - Centered Designs
This kind of design allows us to integrate health data, information, and knowledge into health IT products.
Early and central focus on users in design & development
Interactive design
Systematic measures of the interactions between users and products
UX experts employ a process of user-centered design composed of three axioms:
Why is understanding users important in health IT design?
Understanding users' characteristics, environment, and tasks ensures the design meets their needs and improves efficiency in the care process.
Direct Contact
_____ _____ with actual users is needed early and often throughout a design or redesign process.
Why is a single design iteration not enough?
At least three rounds of design are typically needed to refine effectiveness and efficiency in health decisions.
Designers or Informaticians
Once a design is available, _____ or _____ work with users to determine any issues by having them systematically interact with and respond to the design. Major usability issues are identified and corrected early in the process. Design and evaluation then occur in a cycle until major usability issues are corrected.
Increased individual effectiveness
Increased organization efficiencies
Benefits of improved UX
Increased user productivity and efficiency
Decreased user errors and increased safety
Improved cognitive support
Increased individual effectiveness
Decreased maintenance costs
Decreased customer and individual training and support costs
Decreased development time and costs
Increased organizational efficiences
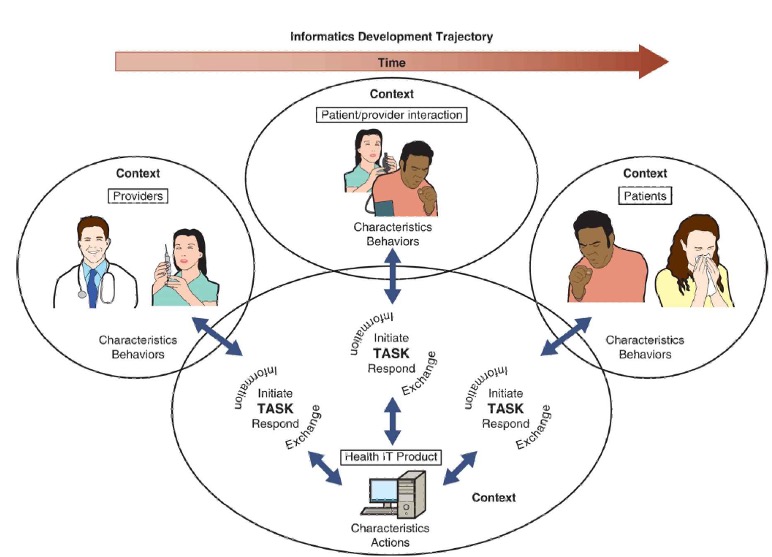
Human - Computer Interaction (HCI) Framework
Study of how people design, implement, and evaluate interactive computer systems in the context of users’ tasks and work.
Information
Interactions
Context
Developmental timeline
Humans or products
Recipient
Elements of Health HCI Framework
Information
E.g., patient care, administrative, or educational information
This is the exchange mechanism.
Interactions
These occur in a system of mutual influences where elements (e.g., individuals, health IT) act and respond based on specific characteristics.
Context
This means that any outcomes of interactions are distinct, as they are defined by a context.
Developmental timeline
Indicates that interactions change over time. Thus, the outcomes of interactions are different based on when an interaction occurs in time.
Human or Products
Initiate interactions. The information is processed through either the product or the humans, according to characteristics.
Recipient
Reacts to the information
Health HCI Framework
The framework builds on early works describing health care worker-computer interaction.
It was expanded to include groups of healthcare providers and interactions with patients. It further adapted to acknowledge that IT is only one example of an available health IT product.
Discount usability methods
Heuristic evaluations
Traditional usability methods
Think-aloud protocol
Task analysis
Methods to improve UX
Heuristic Evaluations
Compare products against accepted usability guidelines to reveal issues
At least 3 to 5 experts complete independent evaluations and then combine issues into a master list after discussion and consolidation.
HE violations of guidelines are made and severity scores are then assigned to the identified issues

Consistency and standards
Visibility of system state
Match between system and world
Minimalist
Informative feedback
Flexibility and efficiency
Good error messages
Prevent errors
Clear closure
Reversible actions
Use the users’ language
Users in control
Help and documentation
Categories for Heuristic Evaluations
Consistency and standards
Consistency across all aspects of the product: methods of navigation, messages and actions, meaning of buttons, and terms and icons.
Visibility of system state
Users understand what the system is doing and what they can do with it from the system messages, information, and displays.
Match between system and world
The technology matches the way users think and do work, uses appropriate information flow, has typical options that users need, and includes expected actions by the system
Minimalist
No superfluous information. System and screen design targeted to primary information users’ needs. Use of progressive disclosure to display details of a category of information only when needed.
Informative feedback
The technology provides prompt and useful feedback about users’ interactions and actions
Flexibility and efficiency
The ability to tailor and customize to suit individuals’ needs. Includes novice and expert capabilities
Good error messages
Tell users what error occurred and how users can recover from the error. Precise and polite and does not blame the user.
Prevent errors
Catastrophic errors must be prevented
Clear closure
Users should know when a task is completed or accepted
Reversible actions
Whenever possible, actions and interactions should be able to be undone within legal limits. If actions cannot be reversed, there is a consistent procedure for documenting the correction.
Use the users’ language
The technology uses language and terms the targeted users can comprehend and expect. Health terms are used appropriately.
Users in control
Users initiate actions versus having the perception that the technology is in control.
Help and documentation
Provide help for users within the context the actions occur (context sensitive). Embed help functions throughout the application.
Think - aloud protocol
Traditional method where users talk aloud while they interact with a product and complete the tasks. As users voice what they are trying to do, they indicate where interactions are confusing and provide other thoughts about the product
Task Analysis
Traditional method where systematic methods used to understand what users are doing or required to do with a health IT product. They focus on tasks and behavioral actions of the users interacting with products.
Patient Safety
It is the freedom from accidental injury due to medical care, or medical errors.
It is also the reduction of risk of unnecessary harm associated with healthcare to an acceptable minimum.
Inconsistent use of language and variations in definitions are barriers to understanding the concepts of quality care and patient safety, as well as to benchmarking beyond the organizational level.
Safe
Effective
Patient - centered
Timely
Efficient
Equitable
Quality of Care - the degree to which health services increase the likelihood of desired health outcomes:
Safe
Prevents injury or other adverse outcomes
Effective
Ensures that evidence-based interventions are used, with patients always receiving the treatments most likely to be beneficial
Patient-centered
Ensures that patient preferences, needs, and values are front and center in the process of clinical decision making
Timely
Delivered when needed and without harmful delays
Efficient
Prevents the waste of valuable human and material resources
Equitable
Provided to all individuals without regard for ethnic, racial, socioeconomic, or other personal characteristics
Why improve HIT?
HIT is playing an ever-larger role in health care
Poor design adds complexity, while good design enhances safety and minimizes harm. In a HIT-enabled environment, safety expectations are higher, and software-related issues go beyond coding or human error.
Easy retrieval of accurate, timely, and reliable native and imported data
A system the user wants to interact with
Simple and intuitive data displays
Easy navigation
Evidence at the point of care to aid decision making
Enhancements to workflow, automating mundane tasks, and streamlining work, never increasing physical or cognitive workload
Easy transfer of information to and from other organizations and providers
No unanticipated downtime
Features of a safe HIT
Poor user-interface design
Poor workflow
Complex data interfaces
Lack of system interoperability
Features of an unsafe HIT