B1 - Food Chain Marketing
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Basic characteristics of a market economy
Limited intervention from the government
The motive of self-interest - the “invisible hand”
The producer gets to decide what to produce, how much to produce, what to charge customers for those goods, and what to pay their employees.
These decisions in a free-market economy are influenced by the pressures of competition, supply and demand
Specialization
An organization concentrates its productive efforts on producing a limited variety of goods
Not only the first form of exchange, but also the first step in the formation of a food chain
The basis of an “aggregate marketing system”
Makes markets much more specific
Aggregate marketing system
Refers to a coordinated, large-scale framework through which goods and services are marketed from producers to consumers.
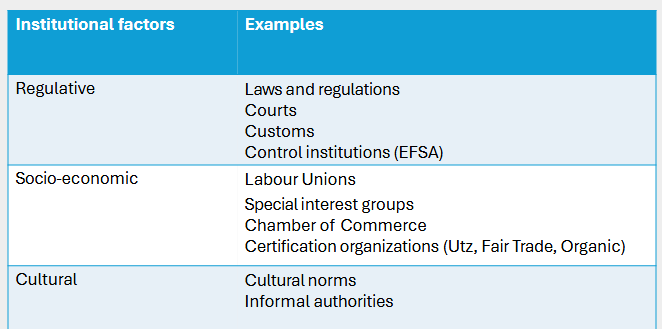
Definition institutions
The set of rules and organization that surround the chain and determine “the rules of the game”
e.g. the government
by laws and regulations, courts and control institutions
Examples institutions
Certification organizations
NGOs, interest groups
Summary of institutional factors
Why the chain is important
For managers it is important to know
Where the inputs come from (to assess risks, uniqueness, continuity of supply…)
How their products reach consumers
Understanding the chain
Select the most important service providers that add value
Different people draw chains differently
The underlying logic.
Mapping a chain: A chain is a mental model to simplify the messy network that an economy actually is.
Steps in analyzing the structure of chains
First, determine the “focal company” (e.g. Friesland Campina)
Determine the unit of analysis: the “business” (so a smaller part of a company, e.g. Optimel).
Assess the relevance (how do they contribute to the core benefits of the product, physical product or augmented producet)
Perspective of the focal business (upstream or downstream)