Euro Topic 7
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
romantic idealism
Looking back as the past as a nobler and more perfect time, emphasizing folk traditions, music, and legends of one's past.
3 multiple choice options
racialism
the belief that some races of people are better than others. Used very much to promote nationalism in the 19th c.
3 multiple choice options
Pan-Slavism
nationalist movement in which Slavic peoples of Eastern and East-Central Europe strove to unite as one to further their mutual cultural and political hopes.
3 multiple choice options
anti-Semitism
hostility to or prejudice against Jews.
3 multiple choice options
Napoleon III
president of the Second Republic of France in 1848 and engineered a coup d'etat, ultimately making himself head of the Second Empire. Promoted reforms in France to modernize it.
3 multiple choice options
Risorgiamento
Resurgence of Italian nationalism, begun under Giuseppe Mazzini (the <3 of Italian Unification).
3 multiple choice options
Otto von Bismarck
Iron Chancellor of Prussia who was the primary figure in using nationalism to create the unification of Germany.
3 multiple choice options
Christian Social Party
German political group who used anti-Semitism and the fears of the German working class to draw its power.
3 multiple choice options
Dreyfus Affair
A divisive case in which a Jewish captain in the French army, was falsely accused and convicted of treason. He was later found innocent. Exemplary of anti-Semitism in France.
3 multiple choice options
Zionism
A movement founded in the 1890s to promote the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine.
3 multiple choice options
Giuseppe Garibaldi
The Sword of Italian Unification, he united Southern Italy and then gave power over to King Victor Emmanuel II so that Italy could be unified.
3 multiple choice options
Crimean War
a conflict, lasting from 1853 to 1856, in which the Ottoman Empire, with the aid of Britain and France, halted Russian expansion in the region of the Black Sea. Broke the Concert of Europe.
3 multiple choice options
Victor Emmanuel II
first king of a united Italy
3 multiple choice options
Realpolitik
the practice of acting for political power rather than for a religious, moral, or ideological goal.
3 multiple choice options
Giuseppe Garibaldi
The sword of Italian unification who unified southern Italy then gave up power to have a united Italy.
3 multiple choice options
Three Emperors' League
Agreement in 1870s between Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Russia designed to avoid conflict in the Balkans.
Congress of Berlin
Assembly of representatives from Germany, Russia, Hungary, Britain, France, Italy, and the Ottoman Empire. Meeting was to reorganize the countries of the Balkans and lessen tensions there.
3 multiple choice options
Entente Cordial
Agreement between France and Britain, stated that Britain would help France in the case that France was attacked by Germany
3 multiple choice options
Triple Entente
A military defensive alliance between Great Britain, France, and Russia in the years preceding World War I.
3 multiple choice options
Balkan Wars
two wars (1912-1913) that were fought over the last of the European territories of the Ottoman Empire. Rose nationalist tensions in the region.
3 multiple choice options
Charles Darwin
English natural scientist who formulated a theory of evolution by natural selection
3 multiple choice options
natural selection
A natural process resulting in the evolution of organisms best adapted to the environment and the weeding out of unfit species.
3 multiple choice options
Social Darwinism
The application of ideas about evolution and "survival of the fittest" to human societies - particularly as a justification for their imperialist expansion.
3 multiple choice options
Survival of the Fittest
Phrase used by Herbert Spencer that justified not imperialism and the bad treatment of the poor. They are too weak to survive.
3 multiple choice options
Victorian Era
the time frame spanning the reign of Queen Victoria of England (1837-1901)
3 multiple choice options
materialism
the philosophy that everything, including the human mind and consciousness is made of matter/substance, or influenced by it.
3 multiple choice options
physicalism
the theory that human beings can be explained completely and adequately in terms of their physical or material components
3 multiple choice options
positivism
the belief that knowledge should be derived from scientific observation only. Emphasizes rational and scientific analysis of nature and human affairs
3 multiple choice options
modernism
Philosophy rejecting traditional beliefs and morals as out-dated. Rationality, industry, and technology were cornerstones of progress and human achievement.
3 multiple choice options
irrationalism
Any explanation of human behavior stressing determinants that are not under rational control—for example, explanations that emphasize the importance of emotions or unconscious mechanisms.
3 multiple choice options
Georges Sorel
French political philosopher who argued social change required revolutionary action.
3 multiple choice options
Henri Bergson
A French philosopher who said that personal experiences and intuition were more important than rational thought and thinking. Rejected established values--embraced change.
3 multiple choice options
Sigmund Freud
Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, and the father of modern psychology.
3 multiple choice options
Albert Einstein
German physicist who developed the theory of relativity, which states that time, space, and mass are relative to each other and not fixed.
3 multiple choice options
Max Planck
German physicist who developed quantum theory which attempts to explain the physics of atomic and subatomic processes.
3 multiple choice options
balance of trade
the value of a countries exports is greater than value of imports
3 multiple choice options
"The White Man's Burden"
idea, put forth in a poem, that Europeans had an obligation to help less developed regions by colonizing them--even though it was a struggle for the Europeans to do so.
3 multiple choice options
minie ball
new type of bullet invented in 19th c. with greater accuracy and range increasing deaths in battle.
3 multiple choice options
Louis Pasteur
Formulated germ theory. Began a method of heating milk to kill bacteria
3 multiple choice options
Joseph Lister
discovered how antiseptics prevented infection in hospitals
3 multiple choice options
quinine
A drug, taken from the bark of a tree in South America, that prevented Malaria and enabled Europeans to go to the interior of Africa.
3 multiple choice options
exports
Goods and Services sold to other countries
3 multiple choice options
Imports
goods and services purchased from other countries
3 multiple choice options
Pasteurization
A process of heating food to a temperature that is high enough to kill most harmful bacteria without changing the taste of the food.
3 multiple choice options
Berlin Conference
Meeting at which Europeans agreed on rules for colonizing Africa in order to avoid conflict.
"Scramble for Africa"
Competition between European Nations for colonization of Africa
3 multiple choice options
Fashoda Crisis
Conflict between France and England in the Sudan over the establishment of railroads.
3 multiple choice options
Moroccan Crises
A series of conflicts between France and Germany where Germany tried (and failed) to support rebellions against France.
3 multiple choice options
Sphere of Influence
an area of control over a foreign territory, often for commercial purposes.
3 multiple choice options
Edmund D. Morel
launched first international human rights movement, because he saw the immoral situation in the Congo.
3 multiple choice options
Congo Reform Association (CRA)
A group formed to bring attention to and end the atrocities in the Belgian Congo and exposing the brutality of Leopold II there.
3 multiple choice options
Vladimir Lenin
Leader Russia's Bolshevik movement. His view of imperialism was that it was the "monopoly stage of capitalism" exploiting the colonized people.
3 multiple choice options
Zulu Resistance
When the indigenous people of modern South Africa rose up against the British.
3 multiple choice options
Sepoy Rebellion
Revolt of Indian soldiers, who were mostly Hindu and Muslims, who were upset over disrespect of their faith by British officers.
3 multiple choice options
Boxer Rebellion
An uprising in China aimed at ending all foreign influence in the country.
3 multiple choice options
Meiji Restoration
The overthrow of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan in 1868, returning power to the Emperor. Led to the rapid industrialization and militarization.
3 multiple choice options
Pan-German League
Organization whose goal was to raise German nationalism and promote German Expansion and "superiority of Aryan race".
3 multiple choice options
Romanticism
a movement in the arts and literature that originated in the late 18th century, emphasizing inspiration, subjectivity, and the primacy of the individual.
3 multiple choice options
John Constable
English landscape painter. Used natural color stippled with white to demonstrate shifting atmosphere and changing seasons. (The Hay Wain)
3 multiple choice options
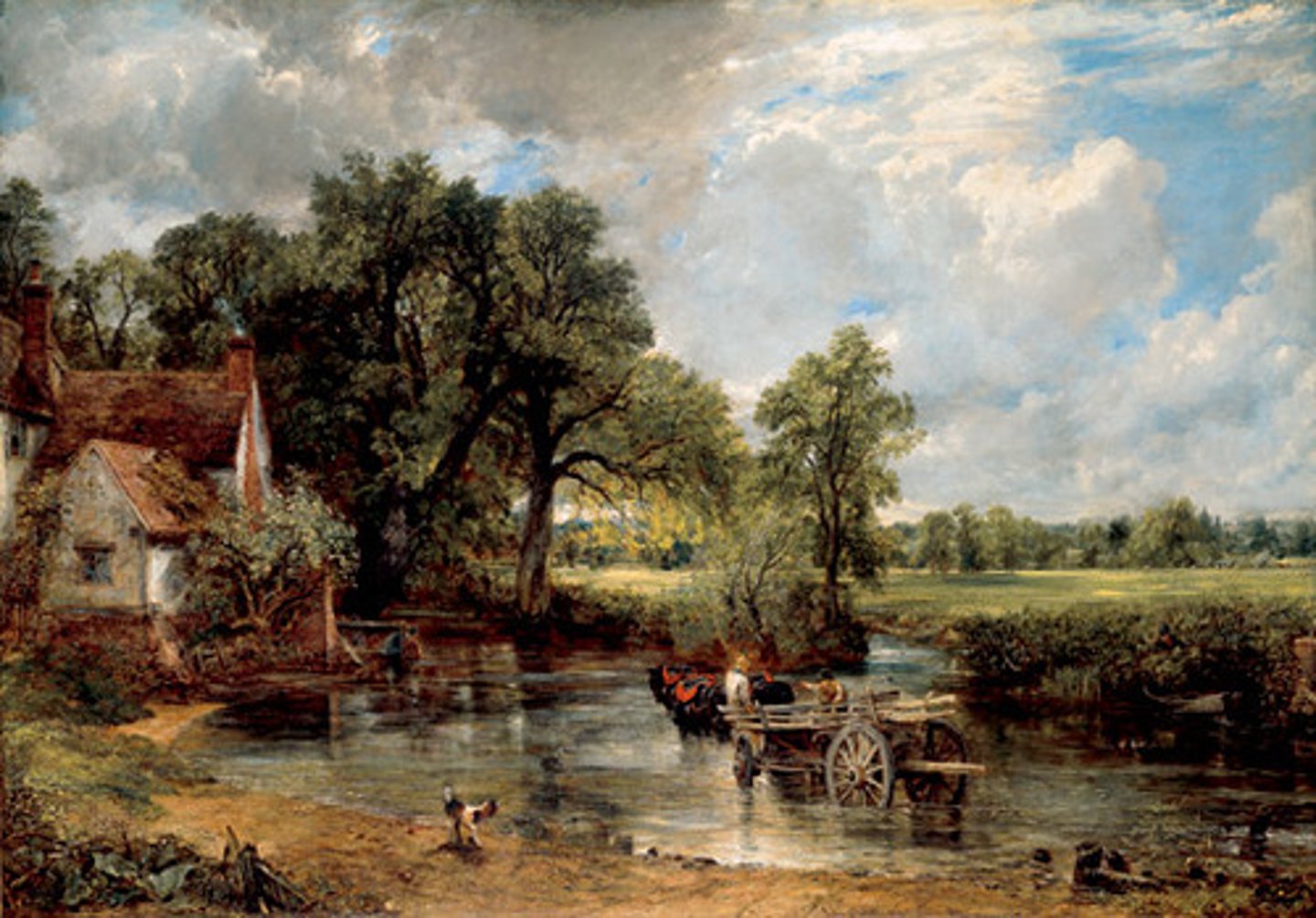
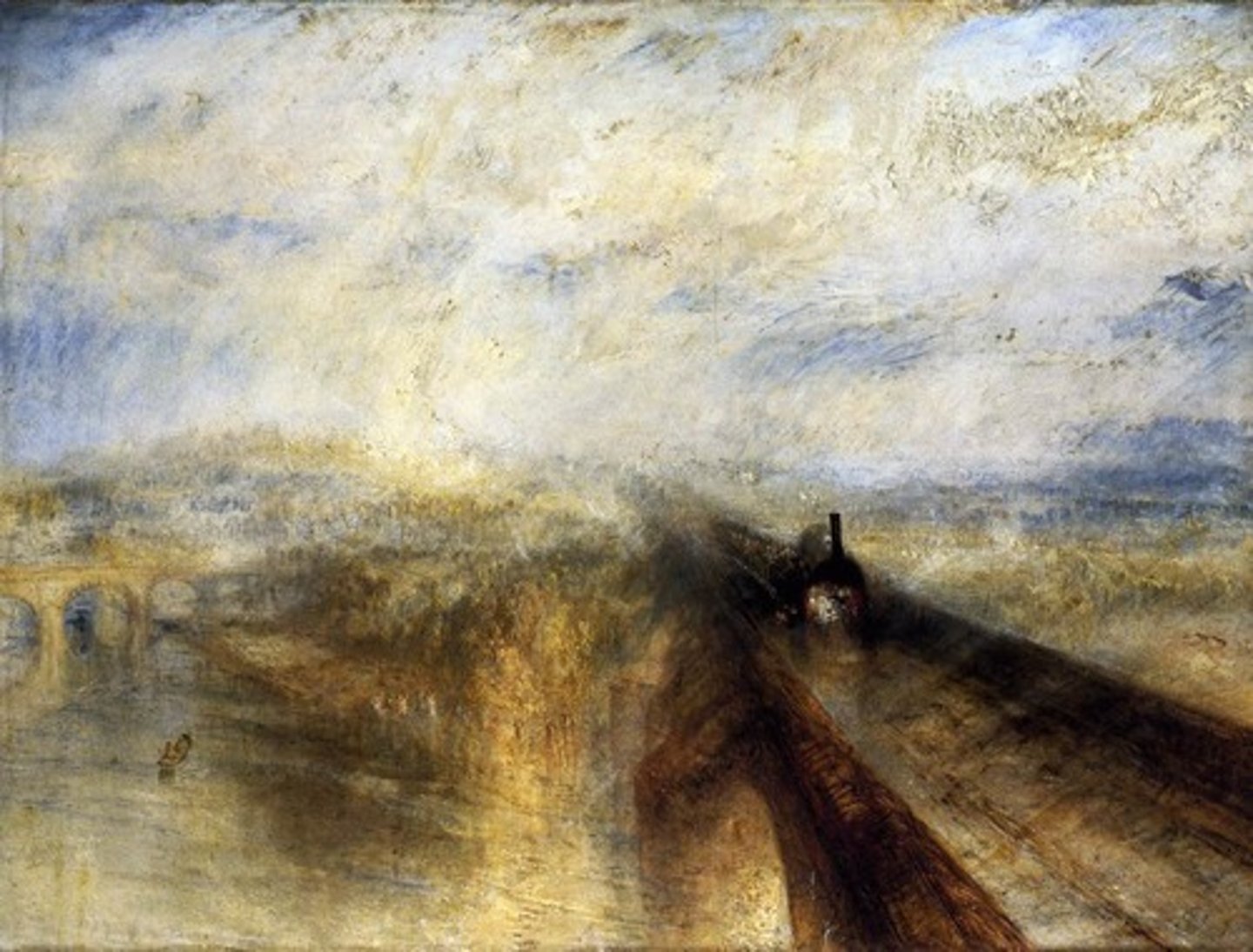
J.M.W. Turner
An English romantic painter of the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, known especially for his dramatic, lavishly colored landscapes and seascapes. (Rain Steam and Speed)
3 multiple choice options

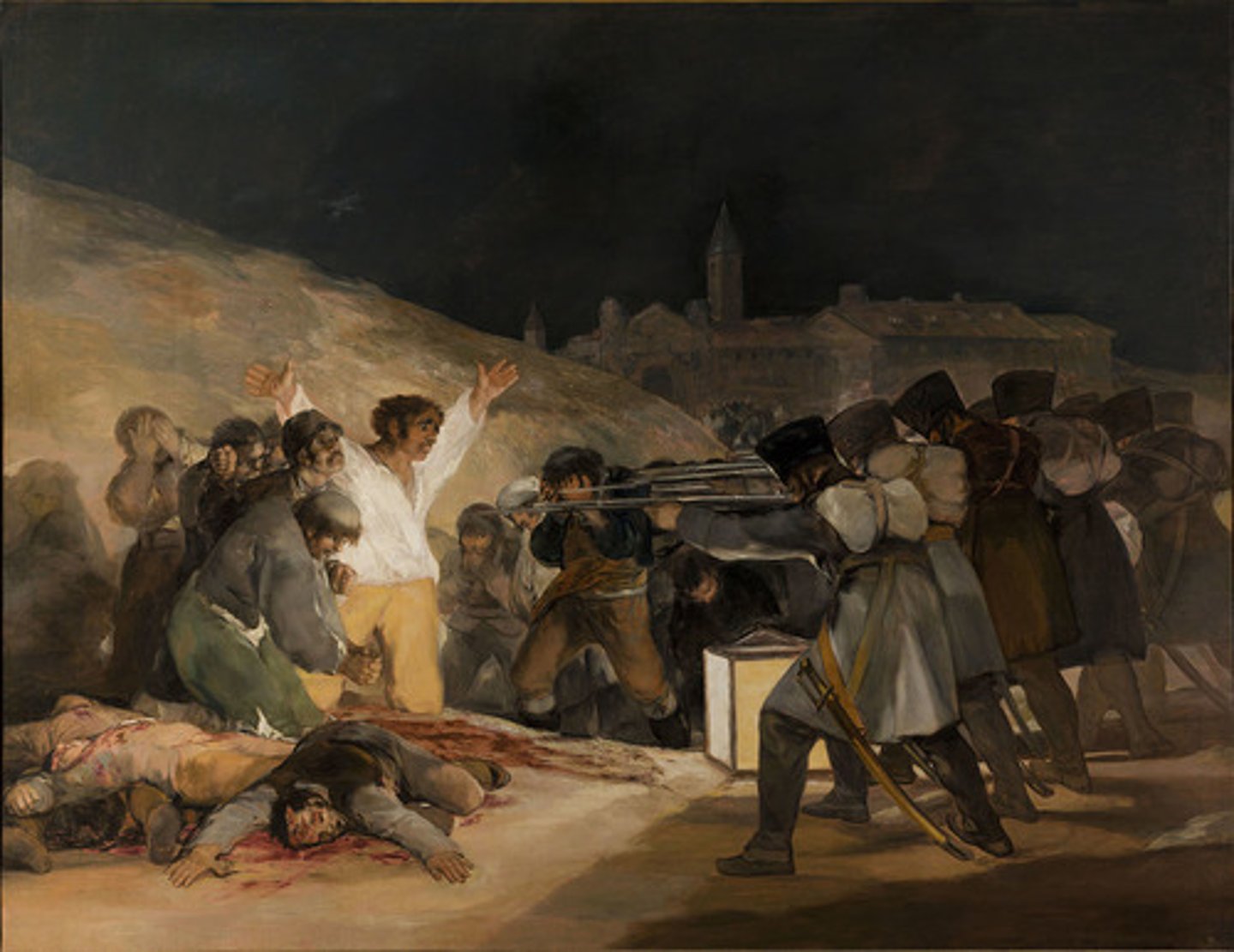
Francisco Goya
A Spanish painter of the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries. Among his works is a series of paintings and etchings that powerfully depict the horrors of war. (The Third of May)
3 multiple choice options

Ludwig van Beethoven
romantic composer who was the first to take full advantage of the broad range of instruments in the modern orchestra (5th Symphony, Egmont Overture)
3 multiple choice options
Lord Byron
English Romantic poet who embodied the idea of the "Romantic Hero" died on way to fight in the war for Greek independence
3 multiple choice options

Percy Bysshe Shelley
English Romantic poet; Ode to the West Wind, To a Sky-Lark, Ozymandias
3 multiple choice options
John Keats
English Romantic poet who wrote "Ode to a Nightingale"
3 multiple choice options
Realism
A 19th century artistic movement in which writers and painters sought to show life as it is rather than life as it should be
3 multiple choice options

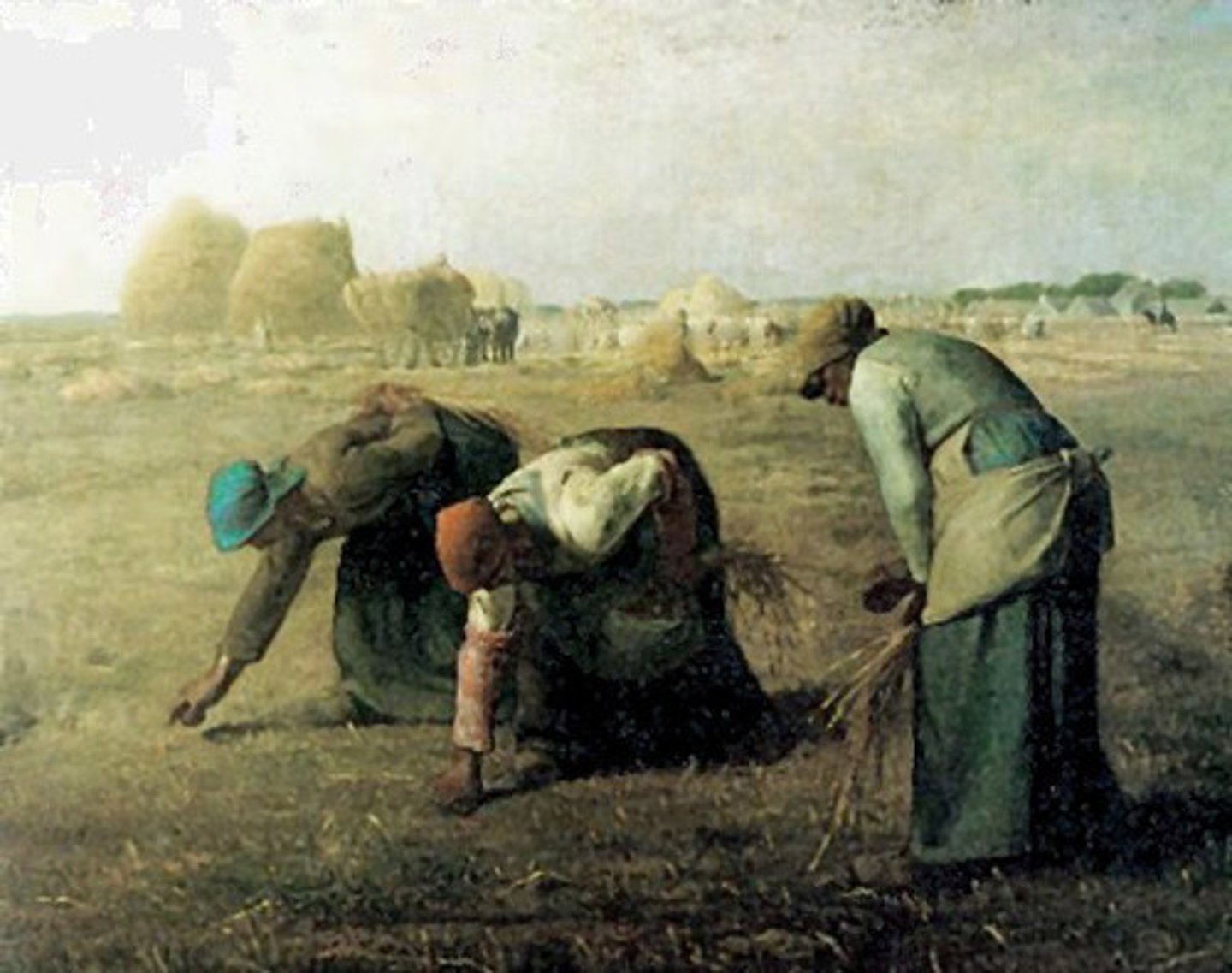
Jean-Francois Millet
French Realist Painter (The Gleaners)
3 multiple choice options

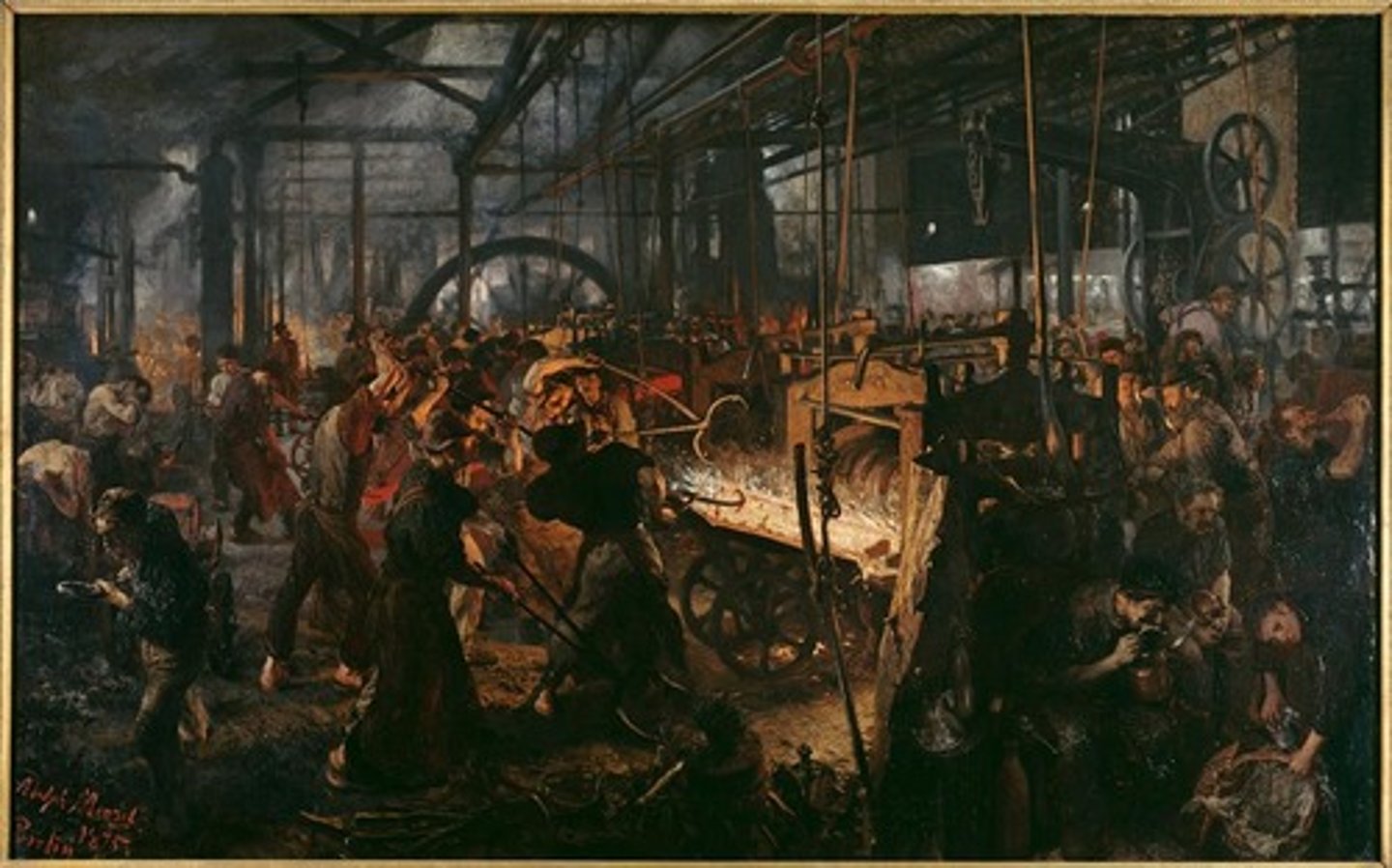
Adolph von Menzel
German Realist Artist (The Iron Rolling Mill: Modern Cyclopes)
3 multiple choice options

Honore Daumier
French Realist artist who often portray the brutality of industrialization and urbanization for the poor (The Third Class Carriage).
3 multiple choice options
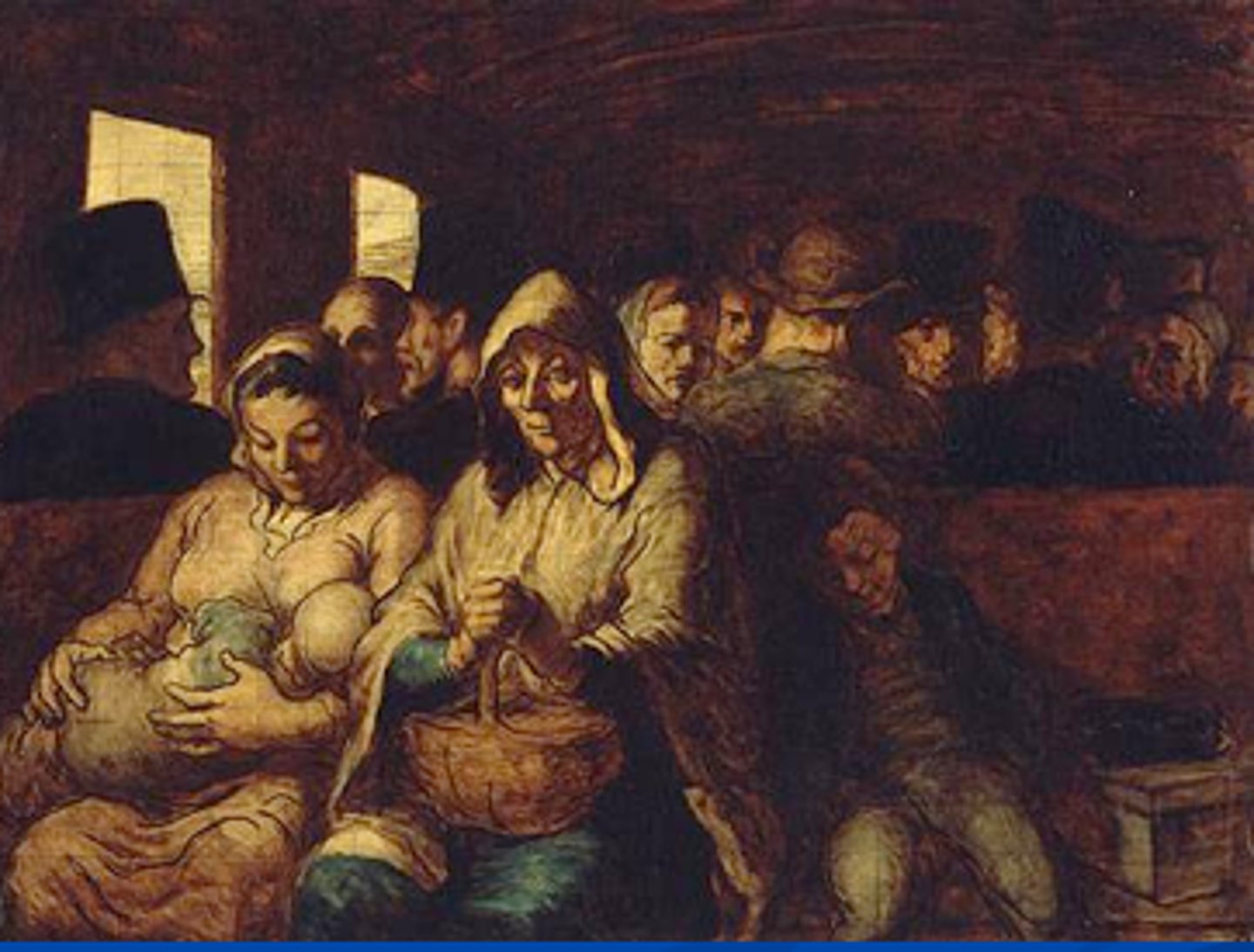

naturalism
A nineteenth-century literary movement that was an extension of realism and that claimed to portray life exactly as it was.
3 multiple choice options
scientific determinism
the belief that all natural events and social changes are exclusively the results of the events that preceded them.
3 multiple choice options
Charles Dickens
English realist writer whose novels depicted and criticized social injustice (Tale of Two Cities, A Christmas Carol)
3 multiple choice options
modern art
Describes several art movements that occurred in a shift from realism after the invention of photography, where artists felt less obligated to show the world exactly as it was. More subjective and abstract.
3 multiple choice options
Impressionism
artistic movement emphasizing light and color as the true subjects of their work (influenced by Japanese art).
3 multiple choice options
Post-Impressionism
used symbolic motifs, unnatural colors, and visible brush strokes to show emotion.
3 multiple choice options
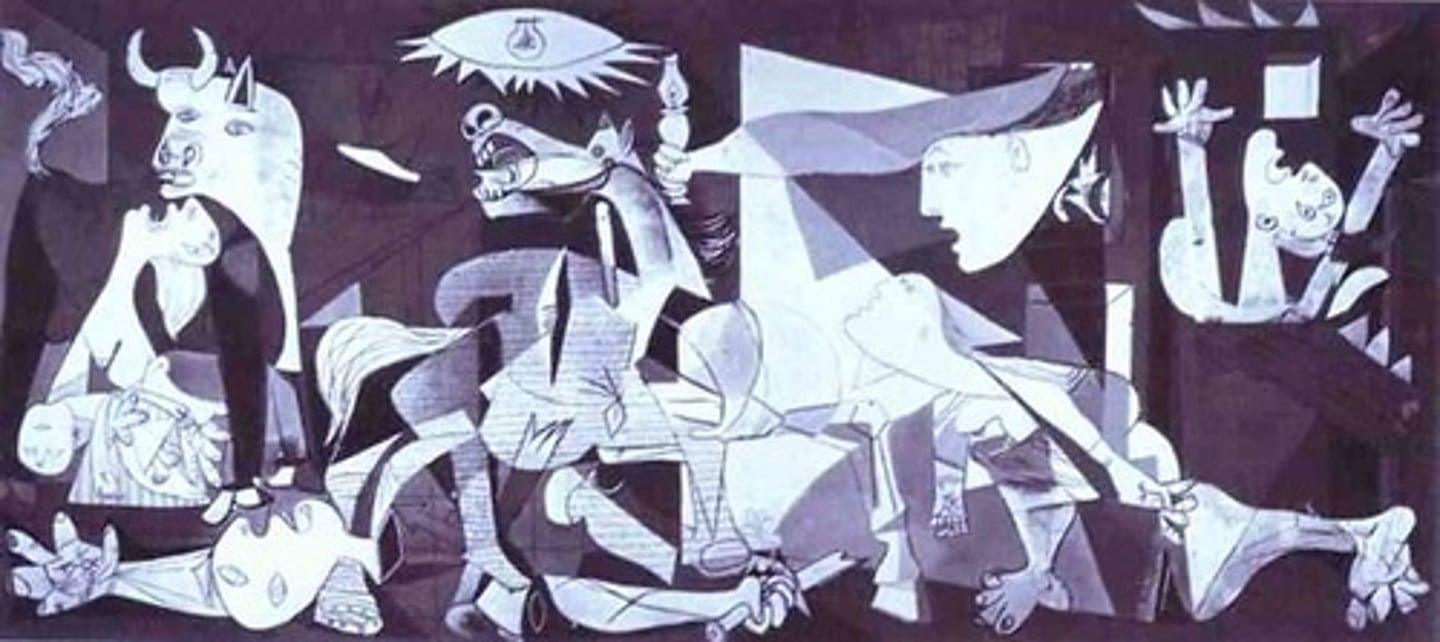
Cubism
A style of art in which the subject matter is portrayed by geometric forms, especially cubes to create a 3D subject on a 2D plane.
3 multiple choice options

Henri Matisse
Fauvism artist. Used brilliant color to get strong reactions (Woman with a Hat).
3 multiple choice options

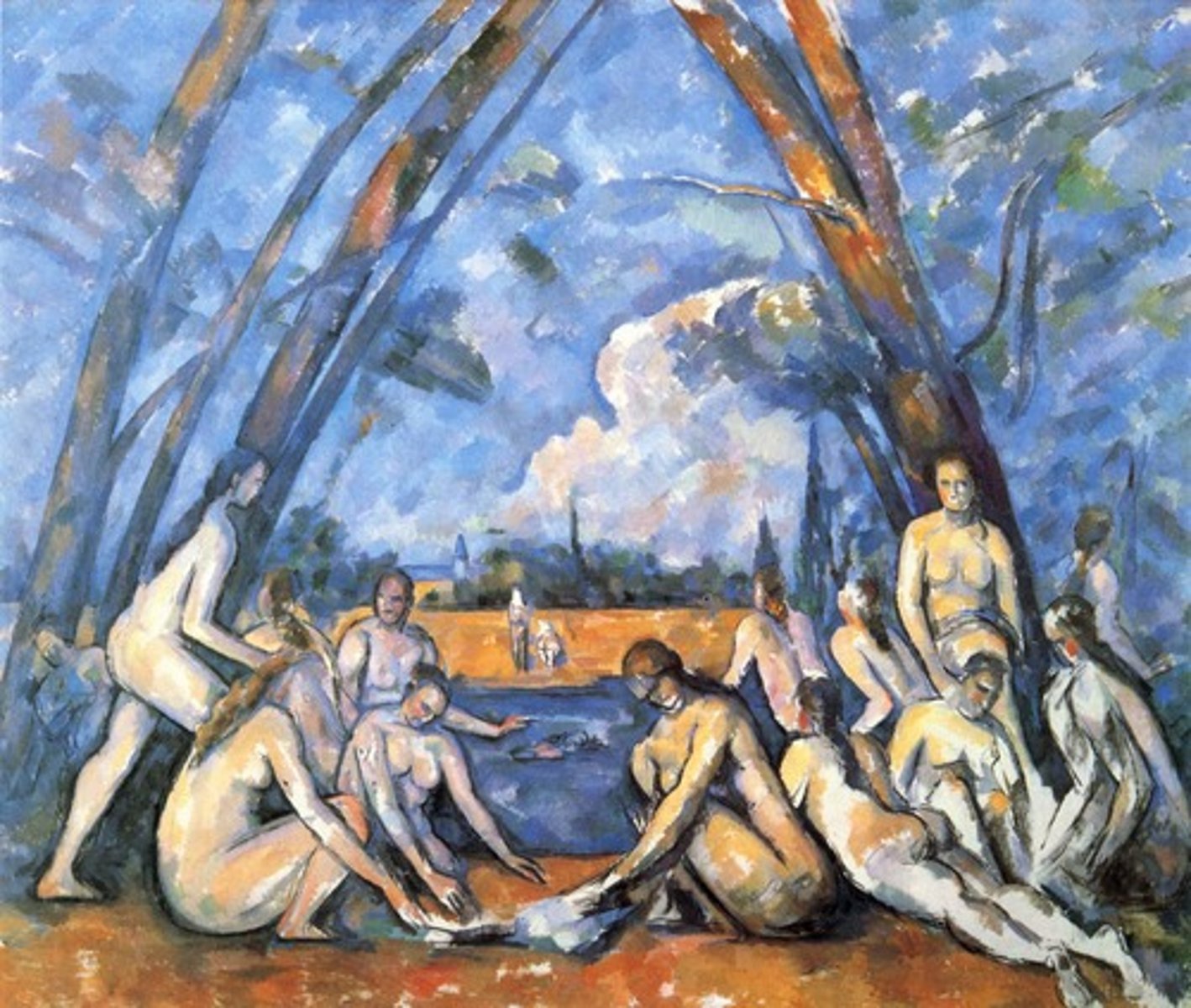
Paul Cezanne
French postimpressionist painter who influenced modern art (especially cubism) by stressing the structural components hidden in nature (The Bathers)
3 multiple choice options
